Causes
Separately, it is necessary to consider the causes of this disease. This disease occurs as a result of infection with streptococcus, which belongs to group A. The disease is mainly transmitted from the carrier of the virus. There are several options:
- You can get infected from a patient not only with scarlet fever, but also with streptococcal pharyngitis or tonsillitis. The patient is especially dangerous in the first days of illness.
- You can also become infected from an apparently healthy person who had scarlet fever some time ago. For some time (most often for three weeks) he still remains a carrier of streptococcus.
- A healthy person can also be dangerous. This happens if streptococci live on its mucous membranes. Such people, by the way, make up 15% of all those living on the planet.
The causative agent of scarlet fever in adults is streptococcus. The patient becomes contagious almost immediately after the pathogen appears in the body. Since scarlet fever is transmitted by airborne droplets, it is enough to inhale the bacteria after a sick person sneezes or coughs.
Can an adult get scarlet fever after using personal items? Yes, streptococcus is transmitted by sharing towels, bedding or clothing. Infection is also possible through a handshake. But the likelihood of infection through contact is lower than through the air.
Another route of infection transmission is nutritional. In these cases, streptococcus enters the body through contaminated food, especially raw milk.
Rarely, the disease occurs after an infectious disease caused by a bacterium, for example, acute pharyngitis or impetigo.
Clinical manifestations
When a child becomes ill, parents often ask whether an adult can get scarlet fever or catch this infection from the baby. Any source of streptococcus - an adult or a child, a sick person or a healthy carrier - is dangerous for a person who does not have immunity to this microbe.
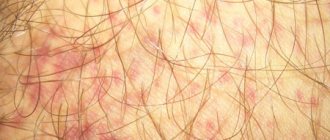
The main manifestations of scarlet fever are damage to the skin and pharynx. Skin lesions consist of the appearance of specific rashes. The rash begins to appear from the first day of illness on the face and neck, upper chest and back. By the end of the second day it covers the entire body.
Good to know: How many days is a child with scarlet fever contagious?
The pharynx mucosa almost immediately becomes inflamed. The tonsils, palatine arches and uvula are clearly hyperemic and may become covered with plaque. As a response, the cervical lymph nodes become enlarged. This is how scarlet fever manifests itself.
Can an adult get scarlet fever from a child?
In the group of infectious diseases is scarlet fever, a disease that affects children under 10 years of age. Thanks to maternal immunity, newborns and babies up to one year old who are breastfed suffer from pathology very rarely, like adults.
It is especially dangerous for women to get scarlet fever during pregnancy, since the consequences of the disease can be miscarriages or premature birth. The disease is characterized by pronounced symptoms. The spread of the infection can be either an adult or a child; animals do not suffer from this pathology.
To prevent infection of a healthy person, it is important to know what scarlet fever is, how the disease is transmitted, and the incubation period.
Scarlet fever occurs through damage to the body by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, which is also toxigenic. Simply put, this virus releases toxins against which the human body has no defense, which is why such a dangerous disease as scarlet fever occurs.
Basically, the disease is transmitted from an infected person. It is possible to become infected with the virus from a healthy person who has recently had scarlet fever. After the patient has fully recovered, the virus remains active in the body for 21 days.
Carefully! Among the inhabitants of the planet, there is a category of people who are constant carriers of the infection, but they do not show signs of scarlet fever.
Streptococci live and multiply on their mucous membranes, so when communicating with them, a person with reduced immunity or suffering from chronic diseases runs the risk of contracting a dangerous infection. One good thing is that the number of such people is very small.
Scarlet fever is a childhood disease, since their immune system does not yet have the same stability and protective mechanisms as in adults, fully formed people. It is very interesting how the infection is transmitted in children. There are basically two routes of infection:
- coughing, sneezing, communication - airborne droplets;
- the child’s toys, his personal belongings – household items.
From the moment the beta-hemolytic streptococcus virus enters the child’s body, he is considered its direct carrier and distributor. Children with scarlet fever must be isolated from others from the first day of illness. The virus can be transmitted from children to adults through toys, household appliances, and close contact.
Attention! An adult can become infected from a child only if he did not have scarlet fever in childhood and has a weakened immune system as a result of chronic diseases.
The opinion that scarlet fever is an exclusively childhood disease is erroneous; adults suffer from it, but in rare cases. According to statistics, among the adult population, people under 20 years of age are more likely to suffer from pathology, and less often people from 21 to 30 years of age. The risk of contracting the virus at the age of 31-40 decreases significantly, but cases of scarlet fever in old age are almost one in a million.
How the infection is transmitted to adults is a question that worries people who were “unlucky enough” to have scarlet fever in childhood. There is an opinion that children tolerate the disease more easily than adults, but this rather depends on the form of the pathology, its course, and the patient’s well-being.
If children mainly get scarlet fever due to communication with infected children with whom they are friends, play in kindergartens, schools, clubs, then adults, in most cases, become infected from their own children at home.
There is a risk of contracting a viral pathology:
- people who do not have strong immunity to group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, that is, who did not have scarlet fever in childhood;
- people with weakened immunity as a result of a previously suffered complex disease.
In adult life, a dangerous disease often awaits people living in dormitories and military barracks, whose work is related to social activities.
The routes of transmission of a viral disease can be as follows:
- airborne infection occurs when communicating with a patient;
- through the use of common household items;
- through food when it is being prepared. Dairy products are considered the optimal environment for the virus to multiply;
- through a third party, that is, a person in contact with the patient who touched him;
- infection can occur through wounds and other lesions on the skin.
Most often, an adult is affected by the erased or toxic-septic form. In the erased form, the symptoms are vague, similar to other diseases, the rashes are minor, redness of the throat, swelling, and pain when swallowing are noted.
A more severe case is when scarlet fever has a toxic-septic form; by the way, children do not get sick with this form at all. The disease is characterized by pronounced symptoms, rashes on the skin and mucous membranes, and damage to the cardiovascular system. Low blood pressure, general weakness, lightheadedness, and problems with heartbeat are often observed.
Carefully! If the symptoms of scarlet fever in adults are not recognized in time, complications in the form of pneumonia, arthritis, endocarditis, otitis media, myocarditis and other pathologies will not keep you waiting long.
To prevent infection of family members and others, it is important to know how long the infection period lasts. The information will help to isolate the patient in time and provide proper treatment.
The incubation period of scarlet fever begins from the first minutes of the virus entering the body, despite the absence of pronounced signs of the disease. Its duration is 1-10 days.
Important! The patient is considered contagious with the appearance of the first symptoms of scarlet fever.
The disease occurs in several periods:
- hidden or incubating;
- the first day when the disease just begins to develop;
- the peak of the disease lasts 2-4 days;
- recovery period up to 3 weeks.
As soon as you find out that your child has been in contact with another child who is sick, you must immediately isolate him from others and call a doctor home to examine the suspect. Your actions will help rule out the disease or, conversely, detect it in time and prevent further spread of the virus among others.
Scarlet fever is an insidious and very dangerous disease, which is characterized by a hidden course, so it is very important to detect it in time and begin proper treatment to prevent the development of complications or an epidemic among children.
Scarlet fever is a rather unpleasant disease. Unfortunately, it most often affects young children, but adults do not always have strong immunity to this disease. Therefore, you need to know everything about it - understand how scarlet fever is transmitted, and try to protect yourself and your child from possible infection.
Simply put, scarlet fever is an acute infectious disease, highly contagious and predominantly affecting children. That is, children aged two to ten years are most often affected.
The symptoms of this disease are very similar to sore throat, so it is extremely important to accurately diagnose and treat it.
The causative agent of the disease is the most common and numerous microorganism in the whole world - streptococcus, or more precisely, group A streptococcus.
By the way, this bacterium can also be found in the nasopharynx of healthy people. In about a quarter of them, streptococcus can provoke other serious diseases, such as kidney damage, sore throat or rheumatism. That is, you can catch scarlet fever if at the time of infection with streptococcus, there is no immunity to it.
Before talking about how scarlet fever is transmitted, you need to understand the signs of this disease. As noted above, in its symptoms this disease is very similar to a sore throat, but nevertheless has its own characteristics:
- It begins acutely and always with an increase in body temperature to high values (39ºC).
- From the very first minutes, the patient begins to experience headache, malaise, nausea, and discomfort when swallowing. That is why the first thing a doctor might suspect is a sore throat.
- But these symptoms are followed by a multiple and itchy rash that covers almost the entire body. It is most intensely localized on the cheeks, without affecting the nasolabial triangle, as well as in the area of skin folds, for example, in the armpits, elbows or groin areas.
- The skin in these places becomes very dry. This usually occurs at the end of the first or beginning of the second day after infection.
- Another important sign of scarlet fever is a crimson tongue. All these symptoms last, on average, three days, and then the disease subsides.
The incubation period is when the infectious microbe has already entered the human body, but has not yet shown any signs. Therefore, this period ends when the first symptoms appear.
But a person becomes contagious even before they appear. So, when figuring out how scarlet fever is transmitted, you need to know that the incubation period here lasts from 2 to 7 days.
This is followed by a day for the onset of the disease, about 5 days for the peak, and up to three weeks for complete recovery.
An interesting fact is that a recovered adult can be a carrier of a contagious infection for some time, while an ordinary child who has not yet recovered from the illness may not be contagious at all.
To understand how scarlet fever is transmitted, you need to know who is considered its carrier. It’s worth noting right away that you cannot become infected with group A streptococcus from an animal or other living creature. Only a person will be the distributor. But let’s figure out what kind of person he is. Conventionally, all carriers can be divided into three types:
- Sick people. Moreover, it does not matter whether they suffer from scarlet fever. It is important that they are carriers of group A streptococcus. That is, they may suffer from streptoderma or tonsillitis, but scarlet fever is transmitted to adults and children precisely from the carrier of this microorganism.
- People who have recently had this disease. Recovered people, even for several months after recovery, are quite capable of spreading the infection.
- As already mentioned, a healthy person can also be a carrier of streptococcus, who may not even be aware of it. Why don't these people get scarlet fever? This is because it is the immunity of this person that holds back the attack of the microbe.
Routes of infection
Treatment of the disease
The therapy is based on pharmaceutical drugs, folk remedies and physiotherapy. Correct analysis of symptoms and treatment of pathology will allow you to feel the first relief within 3-4 days.
Drug therapy
Antibacterial medications must be included in the treatment regimen. They are prescribed taking into account the severity of the pathological process:
- Mild degree. Medicines of the penicillin or macrolide group in tablet form are indicated. They should be taken no longer than 10 days.
- Average degree. The same drugs are used as for mild inflammation, but only in the form of an injection solution. The duration of the course is 10 days.
- Severe degree. Cephalosporins are prescribed for intravenous administration. The course lasts 2 weeks.
In addition to antibiotics, treatment of scarlet fever includes the following:
- Calcium gluconate. This remedy is indicated for cleansing the human body.
- Suprastin. This is an antihistamine that alleviates the patient's general condition.
- Paracetamol. This drug copes with elevated body temperature.
- Analgin, Ketanol. These are analgesics that relieve pain.
- Furacilin solution. Used to rinse the mouth. You need to carry out the manipulation 5-6 times a day, after mixing a glass of water with 2 tablets crushed into powder.
Additionally, the patient may be prescribed vitamins, which can strengthen the immune system and speed up the healing process.
Physiotherapy
This method of therapy can only be used in combination with drug treatment, because physiotherapy helps the body recover faster, cure scarlet fever and clear streptococcal plaque from the tonsils.
Effective procedures:
- The effect on the tonsils is from UV radiation, which has a destructive effect on the proteins of the bacterial microflora, as a result of which it dies.
- SVM therapy of tonsils.
- Magnetic laser therapy, which triggers the body's defenses.
- UHF therapy for rapid healing of ulcers and elimination of inflammation from soft tissues.
- FUF manipulations cleanse the tonsils from pathogenic microflora.
Traditional methods
To combat scarlet fever, the following methods of alternative medicine are effective:
- Lemon acid. Use a 30% citric acid solution to treat the oral cavity. It is necessary to rinse 5-6 times a day. You can replace the lemon with peeled lemon.
- Valerian root. To get an infusion of valerian, you need to pour 1 tbsp. finely chopped raw materials with a glass of boiling water. Wait 8 hours, filter with gauze, and then take 20 ml 3 times a day. The course lasts for 2 weeks.
- Cedar infusion. Pour 4 tbsp. chopped cedar branches with 2 cups boiling water. Keep the infusion in a thermos for 12 hours. Filter the composition and take it instead of water. Duration of the course is 4-5 months, and then rest for 2 weeks
Before use, you should consult your doctor.
Symptoms of scarlet fever in adults
Having figured out how scarlet fever is transmitted, you need to talk about the main symptoms that the child will have. However, first I would like to say that the incubation period of this disease ranges from 1 to 10 days. The first signs of the disease:
- Weakness.
- Chills.
- Temperature rises to 40°C.
- There may be nausea and vomiting (because during infection, severe intoxication of the patient’s body with streptococcal toxin occurs).
Other symptoms that most often appear after the first three days of the onset of the disease:
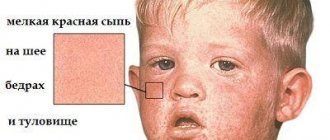
- A small red rash appears on the skin. Most often it is localized on the cheeks, on the sides of the body, in the groin and on the limbs.
- The rash may begin to peel off, often causing severe itching.
- The child's tongue becomes bright red.
- If a baby has scarlet fever, there will be a rash on the throat and roof of the mouth.
- Pain in the lymph nodes.
If childhood scarlet fever does not develop too quickly, then an adult feels the onset of the disease very acutely. In addition, at first, according to the symptoms, this problem can be easily confused with a sore throat. Main indicators of the disease:
- Severe pain in the throat, especially when swallowing.
- A pale yellow coating and ulcers may appear on the tonsils.
- The submandibular lymph nodes immediately become inflamed and enlarged.
Further, the symptoms increase along with the onset of intoxication of the body. The temperature rises (up to 40°C), chills, nausea, vomiting occur (in the first days of the illness), then headaches are possible.
Late complications
Late consequences of scarlet fever usually include those that are detected already in the second or third week after the complete disappearance of symptoms. Often the diseases are protracted and severe, some of them can lead to disability.
- Nephritis. Kidney damage also occurs in the early period, but, as a rule, these changes pass without consequences for health. Scarlet fever nephritis is detected approximately on the 20th day from the onset of the disease, sometimes kidney damage can occur a month later. This nephritis is defined as acute glomerulonephritis. The onset of the disease is acute, fever rises, swelling under the eyes and legs, fluid retention in the body, symptoms of intoxication. Acute glomerulonephritis requires immediate hospitalization in a hospital, where treatment is already being selected.
- Articular rheumatism mainly develops two weeks after the onset of scarlet fever. The child complains of pain in large and small joints of the extremities, initially it is usually the arms. The skin over the joint is hot, hyperemic, and painful on palpation. Timely treatment allows you to survive streptococcal rheumatism without consequences.
- Pathological damage to the heart valves is caused by the influence of the toxic-allergic factor streptococcus. This complication is irreversible with medications and can only be eliminated through surgery. When the valves are damaged, blood circulation is disrupted and signs of heart failure occur.
- Sydenham's chorea is one of the rarest consequences of scarlet fever. This disease affects the brain. Sydenham's chorea occurs three weeks after recovery. The child becomes distracted, forgetful, restless, laughs, or cries for no reason. Later, you may notice uncontrolled movements in the limbs, disturbances in speech and movement. In most cases, signs of chorea can be eliminated with appropriate treatment.
- At 3-4 weeks of the disease, a complication of scarlet fever may occur, such as a repeated relapse of the disease. The development of relapse is due to the repeated penetration of streptococcus into the body; at this time, the autoimmune complex has not yet formed and therefore weakened immunity cannot fight the microorganism. Recurrence of scarlet fever is characterized by a repetition of all signs of the disease.
We also recommend reading: Runny nose in a newborn
Late complications of scarlet fever in most cases are caused by incorrect or untimely treatment. Also, the number of secondary diseases depends on the general resistance of the body and the state of the immune system.
Some people believe that scarlet fever is more dangerous for boys than for girls. There are no differences in the number of complications and their severity in boys compared to girls. The only thing that doctors note is a large number of glomerulonephritis in males. Another infectious disease that poses a danger to boys is mumps or mumps; if it is not treated correctly, it can damage the genitals and, as a result, infertility.
Scarlet fever - transmission routes
Scarlet fever is transmitted to adults, not just children. This is a contagious disease that can affect different age groups of the population. If we talk about adults, the main routes of transmission may be as follows:
- Airborne path.
- Household, through a wide variety of household items.
- Alimentary or food. In this case, the infection gets on the food at the time of its preparation. It is especially well tolerated by dairy products that do not boil, as well as jellies.
- Through damage to the skin. Staphylococci can enter mucous membranes through various wounds. In this case, the closest lymph nodes will react first and they will begin to hurt. A rash will also appear around the site of infection.
So we come to the most important question: how is scarlet fever transmitted in children and adults. Despite the fact that this disease is considered a childhood disease, adults also suffer from it, but, of course, not with the same frequency as children. By the way, you can often hear the following question: is scarlet fever transmitted from children to adults? Of course, for example, if the parents of a sick child do not have immunity, then they too can quickly become infected with this disease.
So how is scarlet fever transmitted from children to adults or from an adult to a child? There are several ways of transmission of infection:
- The simplest and most common is airborne. If you are in close proximity to an infectious person, then when talking, coughing, sneezing or kissing, germs along with mucus can enter your nasopharynx.
- Contact path, that is, touch. There are several options here. For example, a person suffers from streptoderma, and there are infectious agents on the surface of his skin. They can get on a damaged area of skin or mucous membrane of a healthy person, and then infection occurs. Or, for example, a person with scarlet fever touched his mouth or nose with his hands, and then, with a handshake, transferred his germs to a healthy person.
- Household route of infection. Here, too, everything is banal: a sick person sneezed and bacteria simply fly away in different directions, settling on objects, which may include things for common use (dishes, towels, clothes, etc.).
- And one last thing. You can also become infected through breastfeeding, meaning the disease is passed from mother to child. Although this option is very, very rare, since infants have a special immunity to diseases.
Knowing how scarlet fever is transmitted will help protect yourself from the problem. The main way this infection spreads is through airborne droplets. Particles of pathogenic microorganisms are released when sneezing, coughing and even talking. From the air they fall onto furniture and household items - dishes, linen, clothes, toys - which also become potentially dangerous.
This disease is one of those that you only encounter once. That is, you need to suffer the disease once in your life, after which the body develops strong immunity, so the answer to the question of whether it is possible to get scarlet fever twice is most likely negative. However, there are also exceptions to the rules. Patients with weakened immune systems are at greater risk of encountering the disease again than others.
It is important to understand: scarlet fever is contagious. The main danger is the microorganisms that cause the disease. Since they feel great in human bodies, people automatically become carriers of infection and are an absolutely real threat to others.
A serious question, the answer to which is no. The fact is that sick children begin to release dangerous microparticles into the environment only after the infection manifests itself. That is, while scarlet fever passes the incubation period, you should not be afraid of it. The contagious period can last a different amount of time - from a couple of days to several weeks - it all depends on individual characteristics. On average, the danger disappears somewhere in 7-10 days after the start of proper treatment.
How is scarlet fever transmitted?
The pathogen enters the body mainly by aerosol (that is, by airborne droplets) through prolonged close contact with a carrier of streptococcus. You can also become infected through contact and nutrition (through food). The source of infection is always a person:
- Suffering from scarlet fever or other inflammation caused by streptococcus (tonsillopharyngitis), especially in the first days.
- A recovered adult or child (convalescent) releasing a pathogen into the environment. Such a person can remain potentially infectious for about 3 weeks.
- A healthy carrier whose microflora of the nasopharyngeal mucosa contains beta-hemolytic streptococcus, but he himself is not sick.
The resistance of the pathogen to external factors allows it to persist for a long time on clothes, toys, and various objects, which poses a danger to large crowds of people.
Can an adult get scarlet fever from a child?
Yes, it can, but in adulthood the disease more often occurs in the form of tonsillitis, erysipelas, pyoderma, etc. The risk of disease increases if a person’s immunity is weakened for any reason. In addition, constant contact with a sick child, even after his recovery, contributes to infection.
Symptoms of the disease
Signs of scarlet fever in adults are similar to symptoms of respiratory diseases:
- high temperature (40–41 ˚С);
- severe sore throat;
- redness of the pharynx, pharynx and tonsils, the appearance of a white-gray coating;
- skin rash;
- headache, dizziness;
- weakness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- tachycardia.
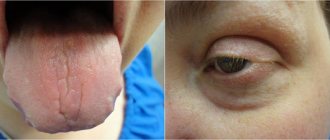
A distinctive symptom of scarlet fever is regional lymphadenitis, i.e. soreness and hardening of the anterior lymph nodes. It occurs against the background of hyperemia of the pharynx. On days 4–5, the coating on the tongue disappears, it acquires a bright crimson hue, and the papillae are enlarged.
The incubation period is 1–10 days. After this, the first symptoms begin to appear. Against the background of a general deterioration in health, skin rashes appear 1–2 days after incubation.
What does the rash look like? Exanthema appears as small, bright red dots. First, they can appear on the face and neck, then on the limbs (especially in the elbow and knee bends), and on the sides of the body. Over time, the rash spreads to the entire body. Blisters filled with fluid form in the groin area, armpits and folds.
On days 3–5, symptoms in adults weaken and become less pronounced, but pain in the throat persists. After a week, the skin at the site of the rash begins to peel and peel off in layers.
The manifestations of scarlet fever depend on its form. The following varieties are distinguished:
- Erased. The most common. Signs of intoxication are mild. The rash is pale and disappears quickly. Sometimes the rash may go away several hours after it appears.
- Extrabuccal (extrapharyngeal). Bacteria enter the body not through the mucous membrane of the oropharynx, but through wounds on the skin. There may be no incubation period. The rash is pronounced, and rashes appear after a short period of time near the place where the infection occurred. The peculiarity of this form is the absence of lymphadenitis and damage to the oropharyngeal mucosa.
- Septic. The most severe, often occurs in adults. Children rarely get sick. The likelihood of complications is high, especially from the heart. Symptoms are acute. The rash is small in the form of pinpoint hemorrhages.
How does the disease manifest itself?
The incubation period for adults with this disease ranges from one day to a week.
When the incubation period ends, pronounced signs of scarlet fever appear.
Symptoms of human intoxication come first:
- [high temperature] (sometimes there is a slight increase);
- chills;
- apathy;
- decreased appetite;
- nausea;
- general weakness;
- headache;
- tachycardia.
In general, scarlet fever manifests itself with a typical clinical picture and with an atypical clinical picture.
The typical clinical picture is characterized by the obligatory presence of signs of intoxication in scarlet fever.
Important to know: Signs and symptoms of scarlet fever
Then,
after 24 hours , the adult develops symptoms of characteristic skin manifestations:
- [small pinpoint rashes of bright color];
- Symptoms appear first on the face, then gradually they descend and reach the skin of the lower extremities;
- itching occurs;
- rashes merge in the natural folds of the skin;
- they can form areas of continuous hyperemia (redness).
Only the nasolabial triangle does not undergo skin changes; there are no clinical manifestations in its area. If you press on the skin, the skin rashes will temporarily disappear.
Skin manifestations last no more than seven days, they gradually disappear.
When skin manifestations disappear, the skin remains unchanged. Symptoms also occur in the oral cavity:
- swelling of the tonsils;
- redness of the tonsils;
- purulent plaques on the tonsils;
- crimson tongue.
When a patient gets streptococcus through the nasopharynx, all the symptoms characteristic of [purulent tonsillitis] occur.
But if streptococcus has penetrated the skin, then most often there are no signs of purulent tonsillitis. Also, the rashes spread differently, they come from the point of penetration.
After seven to fourteen days, a patient with scarlet fever begins to peel off the skin, the skin on the feet and palms comes off in layers.
Scarlet fever, in which the pathogen penetrates through damaged skin, is called atypical (extrabuccal).
Important to know: Incubation period for scarlet fever
The erased form of scarlet fever is characterized by the fact that all clinical manifestations are minimally expressed.
The rash may be pale and sporadic. With the erased form of scarlet fever, clinical manifestations disappear very quickly.
There may also be severe forms of the disease - toxic, with the development of complications. Complications may be as follows:
- spread of inflammation to kidney tissue;
- damage to the heart and its valve apparatus;
- inflammation of the periarticular bursae;
- purulent otitis;
- tonsil necrosis;
- toxic shock.
In most cases, adults get sick for about two to three weeks.
Diagnostics
Having figured out how scarlet fever is transmitted and whether it can affect adults, we will now talk about how this disease can be identified. So, it can be easily determined by the doctor during the first examination of the patient. If your child is sick, you need to go to the pediatrician. If an adult, see a therapist. In some cases, a blood test may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis.
Scarlet fever in adults is diagnosed based on clinical manifestations. At the initial stage, scarlet fever can be confused with ARVI, lacunar tonsillitis, rubella, measles, allergies, mononucleosis, dermatitis, adenoviral infection, toxicoderma, meningitis.
To exclude an incorrect diagnosis and get a general picture of the course of scarlet fever, laboratory tests are performed. These include throat swabs and skin scrapings. To prescribe effective therapy, a general blood test is performed.
What complications are possible?
It is very dangerous to get scarlet fever during pregnancy for up to 12 weeks; in most cases it ends in spontaneous miscarriage. If the family has children of preschool or primary school age, the pregnant mother needs to carefully monitor the epidemiological situation so as not to become infected from the child. An infection suffered in late pregnancy, with the exception of severe forms, does not affect the fetus.
Diseases of the ears and nasopharynx are the most common complications of scarlet fever in adults.
Most often, scarlet fever in adults can cause complications in the ears and nasopharynx (otitis and sinusitis), as well as in the heart (infectious-allergic myocarditis) and kidneys (nephritis). In the most severe cases, streptococcal sepsis, inflammation of the mastoid process of the temporal bone (mastoiditis) may develop, and adenophlegmon may form due to a festering lymph node.
Treatment
Since our article is not devoted to the treatment of scarlet fever, we will not dwell on this in detail, but will describe it superficially.
First of all, it is worth saying that scarlet fever is diagnosed quite easily by the characteristic rash and condition of the throat. Most often, treatment is carried out at home under conditions of complete quarantine. But, of course, if a child suffers a serious illness, he will be hospitalized.
For a week, the patient is prescribed bed rest, gargling with furatsilin, as well as vitamins and antiallergic drugs. And an important point in the treatment of scarlet fever is the use of antibiotics. Typically, they are taken for 10 days, even if symptoms disappear much earlier. This rule cannot be ignored; it is important to treat the disease and not cause complications.
Since scarlet fever is caused not by a virus, but by a bacterium, the use of antibiotics will be relevant. It is these drugs that actively fight streptococcus, stopping the spread of infection throughout the body within a day. What medications will help?
- If the patient has a mild form of the disease, then macrolides and penicillins will be relevant. These are drugs such as “Erythromycin”, “Azimed” (for adults - in tablets, for children - in the form of a suspension). The duration of treatment with these drugs is 10 days.
- If the patient has a moderate form, injections will be needed. In this case, a drug such as Oxacillin (course of treatment – 10 days) will be relevant for injection.
- In severe cases of the disease, first and second generation cephalosporins are prescribed. These may be drugs such as Vancomycin or Clindamycin. The course of treatment is from 10 to 14 days. These medications are administered intravenously.
Treatment of scarlet fever in adults is carried out at home. Patients with severe forms of the disease are subject to hospitalization.
First of all, antibacterial therapy is prescribed. These are penicillin drugs, cephalosporins or macrolides. The course is at least 10 days.
In addition to antibiotics, scarlet fever must be treated with detoxification solutions, for example, Ringer's solution or sodium chloride. These medications reduce the symptoms of intoxication. Antihistamines (Zyrtec or Cetrin) are also prescribed.
To reduce inflammation and hyperemia in the throat, Lizobact, Hexoral, Oralsept or Bioparox are used. In case of severe inflammation, physiotherapeutic procedures cannot be avoided.
Along with antibiotics, you need to take probiotics (Acipol and Hilak forte). To generally strengthen the immune system, vitamin complexes (Complivit) are prescribed. Herbal teas, rosehip infusion, tea with lemon are useful.
After recovery and the disappearance of scarlet fever symptoms, adult patients may remain infectious for several more weeks. Sometimes patients remain carriers of bacteria without showing signs of illness.
How is scarlet fever treated?
Today, treatment for scarlet fever is antibacterial. If you prescribe the appropriate medications in time, you can nip the disease in the bud. Treatment of scarlet fever became significantly easier with the invention of antibiotics. Scientists believe that this process was influenced by a general improvement in the quality of life and nutrition of people. Increasingly, the disease is so mild that it does not even require antibiotic therapy.
Scarlet fever - clinical recommendations
After diagnosing the disease, the patient is advised to stay at home.
Scarlet fever in adults clinical recommendations include the following:
- Hospitalization is carried out only in severe cases and when severe complications develop.
- In the initial period, when there is an increase in body temperature, scarlet fever requires bed rest.
You need to drink as much warm liquid as possible:
- tea;
- fruit drinks;
- juices;
- rosehip infusion.
Treatment of scarlet fever - drugs
In the treatment of this infection, penicillin antibiotics are used:
- Phenoxymethylpenicillin.
It inhibits the division of bacteria, accelerating their death. How to treat scarlet fever with its help? Take the tablets in the morning on an empty stomach before meals. The course of treatment is determined by the doctor. - Retarpen.
This natural antibiotic is obtained from a mold fungus. It inhibits the synthesis of microbial cell walls, especially gram-positive pathogens. - Amoxicillin.
Scarlet fever significantly worsens the patient's well-being; treatment with antibiotics includes this broad-spectrum drug. It also disrupts a component of bacterial cell walls and causes dissolution of the pathogen.
Scarlet fever - treatment with folk remedies
In adults, it often occurs in a mild form, but they can also use all kinds of traditional medicine to alleviate their condition.
People's advice:
- When it is hot, a warm drink is recommended, for which you can brew various herbs - raspberry leaves, sage grass, St. John's wort flowers, linden.
- Those interested in how to treat scarlet fever if their throat hurts can be recommended to gargle with cabbage juice. You can also take black radish juice with honey.
- To ease an allergic reaction, brew and drink valerian root.
Other medicines
Having understood whether scarlet fever is transmitted and how it can be infected, you should also learn about those drugs that, in addition to antibiotics, can be used for treatment. After all, it is complex treatment that will be most effective. What else can the doctor prescribe?
- Antiallergic drugs. These may be drugs such as Cetrin, Loratadine. They prevent the spread of an allergic reaction that may occur on the skin.
- Antipyretic drugs. Relevant in the first days of illness, when the temperature can rise to its maximum. In this case, you can take Ibuprofen or Paracetamol.
- Medications may also be prescribed to help relieve a sore throat. These are drugs such as “Chlorophyllipt”, “Furacilin”.
- If the patient's condition is very serious, he may be given intravenous glucose and saline solutions. This is important for maintaining water-salt balance in the body.
It is also worth saying that most often treatment for scarlet fever can be carried out at home. However, in some situations the patient needs to be hospitalized (in case of severe illness).
Causes of scarlet fever
Scarlet fever in adults develops under the influence of streptococcus that has entered the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx. Infection of adults mainly occurs through the air; less commonly, the pathogen is transmitted through personal objects. To become infected, it only takes a few minutes to interact with a sick child or use his utensils.
The main symptoms of scarlet fever in adults begin to appear mainly on the third day from the moment of infection. All symptoms appear almost in one day. All signs of the disease in adults increase within four to five days, the disease lasts from two to three weeks.
Adults suffer from three forms of scarlet fever. These include extrabuccal, erased and toxic-septic forms of the disease. In adults with good immunity, scarlet fever most often develops in an erased form. The toxic-septic form of the disease affects those people whose bodies are weakened by chronic diseases. The toxic-septic form is characteristic of adults; it does not occur in children.
Complications
Most often they occur due to untimely treatment or an erased form of scarlet fever. The following consequences are possible:
- purulent sore throat;
- otitis;
- sinusitis;
- pneumonia;
- foci of necrosis on the tonsils;
- glomerulonephritis, renal failure;
- hemorrhagic vasculitis;
- myocarditis, endocarditis, heart failure;
- toxic shock;
- joint damage, including arthritis;
- sepsis;
- hemorrhage in the adrenal cortex or brain.
In case of severe manifestations, you must immediately go to the hospital, otherwise death is possible.
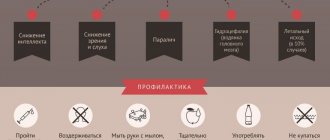
Prevention
Prevention is
- Isolation of the patient;
- Wearing protective equipment when in contact with a sick child (face mask);
- Increasing the functionality of the immune system with vitamin preparations and other means;
- Complete treatment of infectious pathologies of the oropharynx and other areas;
- Treating wound surfaces with an antiseptic and covering them with protective agents - bandages or plaster;
- Maintaining oral and skin hygiene;
- Normalization of lifestyle, nutrition, work and rest;
- Avoid contact with infected people.
Why scarlet fever is dangerous, watch in our video:
Forecast
The prognosis depends on the course and form of the disease, as well as on the speed of seeking treatment from a doctor. Severe forms without providing appropriate assistance in the first two days often end in complications at best, and death at worst.
For mild forms with adequate treatment, the prognosis is presumably good. Complications rarely develop. In case of pregnancy, positive prognosis is possible for the woman. For the fetus, the disease is not dangerous only if the period is more than 4 months. Early pregnancy usually ends in spontaneous abortion, which doctors are most often unable to prevent.
Source: gidmed.com