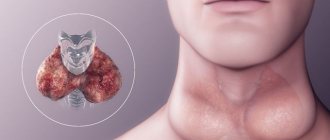
Thyroid tumors can be either benign or malignant. A benign tumor of an organ is called an adenoma, and a malignant one is divided into several types. These include: medullary, follicular, anaplastic and undifferentiated carcinomas.
Thyroid tumor compared to a healthy organ
Types of oncologies
In modern medicine, there are several types of cancer of the endocrine system. Below are the types of thyroid cancer and their manifestations ( to learn more about oncology, click on the name of the disease ):
Papillary
- Less aggressive than other diseases.
- About 4 times more women suffer from it.
- The occurrence of this type of oncology is often associated with the use of radiation therapy in the treatment of acne or adenoids.
- It is most often found between the ages of 32 and 55 years.
- When magnified, the cells look like human fingerprints.
- Acts within the neck.
- The most common form of thyroid cancer (65-80% of cases of thyroid cancer are due to this disease).
Follicular
- Men, compared to women, are much less susceptible to the disease.
- It most often occurs in people aged 38 to 63 years.
- Affected cells can enter the bloodstream and metastasize to the lungs or bone tissue.
- In older patients it becomes more aggressive.
- Diagnosed in 8-17% of cases of thyroid cancer.
- Follicular cells have a spherical shape.
Medullary. If you are diagnosed with this type of cancer, there is a possibility that you will be offered to participate in a clinical trial. Forms of the disease: multiple endocrine neoplasia - MEN 2A, MEN 2B (simultaneous damage to the thyroid gland and other parts of the endocrine system) and familial (genetic).
- Occurs mainly in people aged 42 to 53 years.
- Both men and women suffer from it.
- Accounts for 6-9% of all forms of thyroid cancer.
- The likelihood of occurrence is usually indicated by a high level of calcitonin.
- Development occurs from paraphyllic cells or C-cells that synthesize the hormone calcitonin (responsible for the growth of bone tissue and regulation of phosphorus and calcium levels).
- It is accompanied by other diseases of the endocrine system and tends to have a family predisposition.
Anaplastic - loss of cells of their correct natural structure.
- It is mainly found in the older generation (from 67 years old).
- It is very rare, occurring in 6% of all patients with thyroid cancer.
- It has invasive growth and an aggressive nature.
- Difficult to treat.
- Occurs more often in women than in men.
Much less commonly diagnosed are lymphoma, metastatic and epidermoid cancer, sarcoma, fibrosarcoma, which occur in 2-3% of all malignant neoplasms of the endocrine system.
Among the potential causes contributing to the development of thyroid cancer are heredity, ionizing radiation, and the presence of autoimmune thyroid diseases (primarily autoimmune thyroiditis). At the same time, age is not a factor that increases the number of cases - the apogee of the incidence of follicular and papillary cancer occurs at 29-37 years. Only anaplastic is directly related to age; it is very rarely diagnosed in people under examination who are under 55 years of age.
General symptoms
At the initial stage, patients may not notice any manifestations of a thyroid tumor. The development of the presented disease over time causes obvious bulging or swelling of the neck in the Adam's apple area - on either side. As it increases, it will put pressure on the trachea, nerves and blood vessels that are located nearby.
Visually, diffuse goiter can be identified by its uniform increase. Speaking about the nodal variety, it should be noted that in the vast majority of cases it is much more enlarged on one side of the larynx. Impact on organs that are located near the throat can be manifested by the following symptoms in both benign and malignant tumors of the thyroid gland:
- difficulty breathing;
- rapidly developing change in voice, which is accompanied by severe hoarseness;
- attacks of suffocation that occur at night and begin suddenly;
- severe cough;
- difficulties in the process of swallowing food, which manifest themselves progressively;
- attacks of dizziness, palpable and constant heaviness in the temples and head.
In men, if there is an insufficient iodine ratio with a tumor of the thyroid gland, there is a weakening of sexual desire up to stable impotence. For female representatives, destabilization of the menstrual cycle may be a characteristic process. In this case, a thyroid tumor, both benign and malignant, can cause infertility and miscarriages.
Symptoms of thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer has virtually no visible manifestations and causes almost no discomfort. In many patients, thyroid hormone levels are within normal limits. For most patients, the diagnosis of thyroid cancer comes as a surprise against the background of a completely healthy body. Many patients do not experience symptoms of this disease.
However, there are signs of cancer that should be treated with caution, such as hoarseness, shortness of breath, difficulty swallowing, and the thyroid area becomes thicker and rapidly gains volume and becomes visible to the eye.
Causes of the tumor process
The development of tumor pathologies is possible in the presence of one or more provoking factors. These include:
The thyroid gland is the real cause of cancer! Endocrinologist's advice - to save yourself, drink every day... Read more »
- insufficient intake of iodine into the body;
- influence of ionizing radiation;
- disruption of the immune and neuroendocrine systems;
- hereditary predisposition;
- previous thyroid diseases.
Disease Prevention
In order to prevent the occurrence of such an oncological disease as thyroid cancer, iodine deficiency should be avoided - use kitchen salt in food with the addition of a strictly defined amount of iodine-containing salts: iodide or potassium iodide (iodized table salt), eat kelp (sea kale) as rarely as possible expose the neck and head area to x-rays.
The main measures to prevent diseases are timely treatment of the endocrine system, regular medical examinations, mainly if you are part of a risk group (live in high-risk areas, suffer from other thyroid diseases, have been exposed to frequent irradiation of the head and neck areas ).
Treatment of thyroid cancer should be carried out by specialists - a mandatory rule that is not questioned. Optimal results are achieved in a specialized endocrine surgery clinic, where the concentration of patients with this diagnosis ensures that doctors have detailed information about all the features of treatment for patients diagnosed with the corresponding types of thyroid cancer. Surgical intervention for this disease should be performed exclusively by endocrinologist surgeons who are certified as oncologists and perform more than one hundred surgical interventions annually.
Examination and diagnosis of malignant diseases
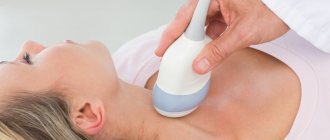
The thyroid gland can be examined using a number of techniques. Some of them are quite effective for detecting cancer, while others are completely uninformative. Let's look at them:
- The study of gland functions (hormones) is the least valuable, since most malignant tumors are not hormonally active. Only 1% of thyroid tumors may manifest as hormonal disturbances.
- Visual and manual examination by a doctor. In the early stages, a specialist can make a conclusion about the presence of a malignant formation based on the size and rate of growth of the “bump,” its structure, limited mobility, as well as a previously existing goiter, the appearance of a feeling of suffocation and tension in this area.”
Patient with papillary thyroid cancer - Ultrasonography. Allows you to detect the presence of neoplasms of even the smallest sizes, the palpation of which is impossible by palpation. This method is not suitable for determining the malignancy or benignity of a tumor, however, it is most effective from the point of view of preventive research.
- Radioisotope examination of the thyroid gland with radioactive iodine. This commonly used method allows the cancer site to be represented as a defect with a large accumulation of isotopes. However, this cannot distinguish between “cold” nodes. This research method is also used to diagnose metastases in the thyroid gland if the neoplasms are capable of accumulating iodine, and the affected organ tissue has previously been surgically excised.
- Puncture (biopsy). This method is the most accurate in diagnosing malignant and benign nodes. With its help, the affected tissue is examined, on the basis of which a conclusion is made about the histological form of the neoplasm, as well as the degree of its spread in the body.
- Laryngoscopy and bronchoscopy. They allow you to determine the degree of damage and changes in the recurrent nerves of the larynx and vocal cords, and examine the trachea for the spread of metastases and narrowings.
By the way, we recommend reading the article How to cure follicular adenoma of the thyroid gland?
Stages
The older the age, the higher the likelihood of thyroid cancer, with rapid development and death. To assess the patient’s condition, how long he will live, whether a cure is possible and what the prognosis for treatment in general is, a classification has been adopted when thyroid cancer is divided into several stages:
- At the first stage, limited growth of the formation up to 20 mm in diameter is observed, without regional and distant metastases.
- The second degree is characterized by an increase in size to 40 mm and also the absence of any metastasis.
- At the third stage, the tumor grows even more and extends beyond the thyroid gland. Secondary lesions can only be in the nearest cervical areas.
- The fourth stage has division within itself. 4A means that metastases have appeared in the regional lymph nodes of the neck and chest. 4B is the same, but there is deep growth into the tissue structures of the neck towards the spine. 4C means extensive damage to distant organs, the lymphatic system.
Photo 2. Stages of development
Causes of its occurrence or risk factors
Radiation. It has been proven that people who are often exposed to all kinds of radiation have a high chance of being diagnosed with medullary thyroid cancer. In addition, the explosion at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant in April 1986 is considered an important reason for the increase in morbidity.- Family predisposition. Scientists have found that there are genes that are responsible for the development of thyroid cancer. It can be found using a blood test. People in whom this gene has been identified can pass it on to their descendants by inheritance.
- Age and become. It has been proven that this type of disease most often occurs in adulthood and old age. Average age is 35 - 40 years. Regarding the matter, there is also a pattern: in adulthood women are more likely to get sick, but in old age it predominates in men.
- Race. It has been established that people of the Caucasian race are several times more likely to develop thyroid cancer compared to other races.
- Iodine deficiency. Very often there is a tendency towards an increase in the incidence of papillary and medullary cancer in regions with iodine deficiency in food products.
- Untreated thyroid disease. In most cases, we are talking about autoimmune diseases (for example, autoimmune thyroiditis), untreated goiter, and so on.
Signs and symptoms of thyroid disease in women
Today, many cannot determine the cause of their fatigue, irritability, and feelings of anxiety, especially for the fairer sex. Very often, the cause of such disorders in women can be diseases of the thyroid gland, which they are not even aware of. The thyroid gland is the most important organ of the endocrine system, producing hormones that are so necessary for the proper functioning of the entire body. Therefore, the slightest malfunction in its work causes many diseases. As a rule, thyroid diseases most often affect women, and the fairer sex is 5 times more susceptible to such ailments than men. This is mainly due to the physiological characteristics of the female body. Also, in addition to this, ladies are more susceptible to stress and emotional arousal. We will now try to figure out what are the symptoms of thyroid disease in women.
- The first signs of the disease
- Symptoms of thyroid disease during menopause
- Signs of thyroid cancer
The first signs of the disease
The first symptoms of thyroid disease in women are weight changes, in one direction or another. Excess weight can also indicate hypothyroidism, that is, decreased hormone levels. If there is sudden weight loss, then most often this can be caused by the fact that the gland produces more hormones than necessary.
Failure of the thyroid gland affects the general condition of the body. With hypothyroidism, signs of fatigue, depression, and depression appear. Hyperthyroidism is characterized by irritability, sleep disturbances, etc. Appetite may also increase, speech speed may increase, and emotional state may increase.
Problems with sleep appear. It becomes difficult to fall asleep, sleep is very light and superficial.
Another sign of the disease in women is causeless hair loss, which is caused by thyroid diseases. After the necessary course of therapy, the hair is restored.
Diseases of the organ also affect the process of thermoregulation in the body. Therefore, in the early stages of thyroid disease, both chills and a feeling of stuffiness, and severe sweating may occur. Palms and feet are constantly wet.
Since hormones affect the functioning of almost all organs, these diseases cause heart rhythm disturbances. A patient with low hormone levels may suffer from a slow heartbeat. And in people diagnosed with hyperthyroidism, increased blood pressure and tachycardia are often observed. Also, an increase in pulse rate in women up to 100 beats is a sign of a mild form of thyrotoxicosis, and a more severe form can be accompanied by a heart rate of up to 140 beats per minute.
In addition, women may experience enlargement of the thyroid gland, as well as the formation of nodes and tumors. This indicates the development of a disease in which it is necessary to consult a specialist.
External signs of thyroid disease
- Lethargy and pallor of the skin.
- An unusual shine in the eyes; in severe cases, bulging eyes develop.
- Increased breathing rate, slight shortness of breath.
- Periodic dizziness, a feeling of lack of oxygen are possible, airflow becomes difficult, and as a result, a strong, causeless cough may occur.
- Enlargement of the lower part of the neck and its swelling.
- Increased sweating at normal temperatures.
- Brittle nails.
- Visual impairment.
- Hand trembling.
- Diarrhea and nausea are quite common.
Symptoms of thyroid disease during menopause
Since the thyroid gland is responsible for many important processes, of course, during menopause, women can very often experience problems and diseases of the thyroid gland. This is largely due to the increased function of the organ, or, on the contrary, to a decreased level of hormones, since during menopause, almost half of women experience a malfunction of the thyroid gland, and the iodine content increases. The main signs of thyroid disease during menopause are: a depressed state, sometimes severe depression, suspiciousness, surges in blood pressure, elevated blood cholesterol levels. In many cases, with an increase in hormones, bone density decreases and joint diseases occur.
Signs of thyroid cancer
One of the most severe forms of organ disease in women is thyroid cancer. Most often, this stage is manifested by the following symptoms:
- The appearance of nodes and swelling in the neck area.
- Enlarged lymph nodes are one of the main signs of a malignant tumor.
- Hoarseness of voice and difficulty swallowing.
- Pain in the throat and neck area.
Signs of thyroid disease in women can often be mistaken for symptoms of other ailments. In this regard, it is necessary to conduct regular examinations by experienced specialists.
Treatment
Depending on the type of tumor and the presence of metastases in the organs, there are 4 treatment methods: surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy and treatment with hormonal iodine.
Surgery is the only way to remove a malignant process, provided that the pathology is detected at an operable stage. There are two options for the development of events:
- The entire thyroid gland is removed if the tumor has spread beyond the boundaries of the organ or there is a threat of exit.
- Only a malignant tumor with part of the thyroid gland is removed, provided there is no damage to the lymph nodes and the tumor extends beyond the organ.
Radiation therapy is used if the entire gland is affected or in the postoperative period to remove remnants of carcinoma. The procedure involves the use of radioactive radiation to target malignant cells. Used to eliminate anaplastic forms of tumor. It also helps prevent the development of relapses after surgery and the spread of metastases to other organs. The course lasts 2-3 weeks.
Chemotherapy is indicated for medullary cancer and undifferentiated forms of neoplasms. The drugs are administered intravenously and act on cancer cells.
Radioiodine therapy is effective for papillary and follicular cancer. It is based on the use of radioactive iodine, which is delivered to malignant cells, reaches maximum concentration and affects them. Iodine is taken in capsule form or administered intravenously.
Manifestation of thyroid cancer in the female body
As you know, the structure of the thyroid gland is very similar to a butterfly. It is located on the anterior cervical surface and is protected by the thyroid cartilage.
It is precisely because of its specific location in the body that it is very well distinguished and palpated. As a result, the process of initial examination of the organ is greatly simplified.
The very first sign of a tumor is the appearance of a small nodule on the organ. It is visible externally, most often the formation is single.
In the first stages of the development of the cancer process, this formation is elastic and not painful, but it is not very mobile. It does not grow into the skin that is located above the thyroid gland.
When swallowing, the nodule seems to roll. As cancer progresses, this formation enlarges, becomes denser and more immobile.
However, not every nodule is a tumor. In 95% of cases these are lymph nodes or formations of some other nature. It is important to monitor the appearance of nodules on the neck in children, because normally they should not appear until the age of 20.
If they are present, be sure to consult a specialist to diagnose the pathology of the cause of their appearance and the nature of the formations.
In the early stages, thyroid cancer can manifest itself as a significant increase in lymph nodes. Very often this is the only sign.
When the tumor reaches a larger size, the patient may experience other specific symptoms:
- difficulty swallowing;
- constant feeling of a lump in the throat;
- hoarseness of voice;
- pain in the neck, most often they are localized on the front surface and radiate to the ear (which one depends on the location of the area);
- breathing problems and shortness of breath;
- cough that is not caused by an allergy or cold;
- swelling of the venous vessels in the neck.
The occurrence of these symptoms is due to the fact that due to the growth of the tumor, nearby organs from the digestive and respiratory systems begin to be compressed. Changes in the patient's voice appear due to the appearance of metastases in the recurrent laryngeal nerve and vocal cords.