Menstrual cycle
A female fetus at 20 weeks of intrauterine development already has 2 million immature eggs in the ovaries. 75% of them disappear soon after the girl is born. Most women retain 500,000 eggs by reproductive age. By the beginning of puberty, they are ready for cyclical maturation.
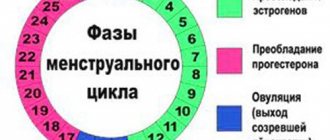
During the first two years after menarche, anovulatory cycles are common. Then the regularity of the maturation of the follicle, the release of the egg and the formation of the corpus luteum is established - the ovulation cycle. A disruption in the rhythm of this process occurs during menopause, when the release of an egg occurs less and less and then stops.
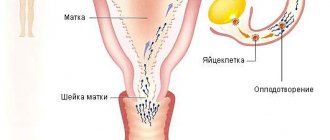
When an egg moves into the fallopian tube, it can merge with a sperm - fertilization. The resulting embryo enters the uterus. During ovulation, the uterine walls thicken and the endometrium grows, preparing for implantation of the embryo. If conception does not occur, the inner layer of the uterine wall is rejected - menstrual bleeding occurs.
On what day after menstruation does ovulation occur?
Normally, this is the middle of the cycle, taking into account the first day of menstruation. For example, if 26 days pass between the first days of each menstruation, then ovulation will occur on the 12th – 13th day, taking into account the day the period begins.
How many days does this process take?
The release of a mature germ cell occurs quickly, and hormonal changes are recorded within 1 day.
One of the misconceptions is to believe that if you have periods, then the cycle was necessarily ovulatory. Thickening of the endometrium is controlled by estrogen, and ovulation is caused by the action of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Not every menstrual cycle is accompanied by the process of ovulation. Therefore, when planning pregnancy, it is recommended to monitor the precursors of egg release and use additional tests to determine it. If anovulation lasts for a long time, you should consult a gynecologist.
Signs after ovulation
- Signs after ovulation are very difficult to track, but the best way to do this is with an ovulation test or an ovulation calendar.
- The first sign after ovulation is discharge; it is either completely absent or becomes creamy and sticky.
- Also, after ovulation, the basal temperature does not fall and is in an elevated state. This is also observed in the case of pregnancy, when the egg is fertilized.
- After ovulation, the pain and swelling of the mammary glands goes away, and the pain in the lower abdomen also stops.
- Another sign after ovulation is the disappearance of the hormonal rash. As a rule, before ovulation, small hormonal pimples appear on the face, especially on the forehead.
All signs after ovulation depend on how the ovulation process itself went and, of course, on the individual characteristics of the female body.
Signs of pregnancy after ovulation
All women have a couple of days before and after ovulation, called the fertile phase. These days are the most favorable moment for conception and pregnancy. Let's look at the main signs of pregnancy after ovulation.
- High basal temperature.
- Delayed menstruation.
- Swelling and change in breast shape, darkening of the nipples.
- Increased fatigue, morning sickness, sudden and causeless mood swings.
- Change in vaginal color.
- Frequent urge to go to the toilet and increased mucous discharge.
- Bloody discharge, gas and constipation.
- Spasms in the lower abdomen may be on one side.
- Heightened sense of smell.
- Acne and pimples.
- Mild cold and stuffy nose.
- Changes in taste and increased appetite.
Signs of fertilization after ovulation
Signs of fertilization after ovulation appear no earlier than a couple of weeks after intercourse. Let's look at the signs of sexual fertilization after ovulation.
- Implantation bleeding, which is caused by the attachment of the embryo to the uterine cavity. Bleeding occurs within one day or several hours.
- The breasts swell and become very sensitive.
- Menstruation does not occur, that is, there is a delay.
- There may be a feeling of nausea, apathy, headache, and fatigue.
- There is frequent urination and uncontrolled appetite.
All these signs are conditional and they can be caused by other reasons, for example, colds, infectious or inflammatory diseases. It is better to determine fertilization and pregnancy after menstruation has not occurred, that is, after a delay. About five weeks after sexual intercourse, at which time conception and pregnancy could occur.
Does the time of ovulation affect the possibility of conception?
Signs of conception manifest differently in every woman. So, some women begin to understand that they are pregnant after a week, others after a month, and some even only after going to the gynecologist and taking a test. Let's look at the main signs of conception.
- Signs of conception in the first days are bleeding. After conception, somewhere in the first or second week, the process of embryo implantation occurs in the body. For many women, this period is accompanied by bleeding and cramping.
- The menstrual cycle is disrupted, in other words, the woman has a delay. This is the most common sign of conception. During pregnancy, the menstrual cycle stops, but some women may experience light bleeding.
- Sensitive breasts. A couple of days after conception, the breasts swell and become hypersensitive. This is a sign of conception that cannot be ignored, since even a light touch to the breast causes discomfort.
- Nausea is also a sign of conception and occurs from 3-9 weeks after conception.
- Apathy and fatigue. Due to the fact that the body is being rebuilt to support the life of mother and child, the expectant mother may feel unwell from the first days of conception.
- Headache - appears in the first days of conception and occurs due to changes in the hormonal levels of the female body.
- Frequent urge to go to the toilet. Frequent urination appears at 6-7 weeks of conception.
- Increased appetite - after conception, a woman begins to feel constant pangs of hunger. As for products to satisfy such an appetite, these are not necessarily pickles. By the way, this symptom can persist throughout the entire period of pregnancy.
During ovulation, a woman has several days to become pregnant. That is, in the fertile phase of ovulation, successful conception is most likely. Signs of conception after ovulation look like this:
- Lack of menstrual cycle.
- Increased basal temperature.
- Increased appetite and changes in taste preferences.
- Vomiting, diarrhea, nausea.
- Breast swelling and tenderness.
- Strong sense of smell.
- Irritability.
- Apathy and fatigue.
- Change in vaginal discharge.
Please note that the lifespan of sperm in a healthy woman is from 3 to 7 days, but if there are disturbances in the female body, especially if they relate to vaginal discharge, then the likelihood of conceiving a child is reduced to a couple of hours.
If a woman has disturbances in the process of maturation of the follicle, which is responsible for the egg, then it is necessary to stimulate ovulation. For these purposes, you need to undergo an examination and consultation with a gynecologist, who will prescribe medications to restore ovulation and the possibility of conception.
Is it possible to get pregnant if you ovulate late? It is impossible to answer this question unequivocally. If the shift in the date of release of the egg is not associated with pathologies of the female reproductive system, a woman can successfully become pregnant, but she should remember that conception will occur later. It is imperative to warn the gynecologist that there is a shift in ovulation, so that he takes this feature into account when monitoring fetal development.
The fact is that due to the late release of the oocyte, the duration of the second phase of the cycle - the luteal phase - is significantly reduced (sometimes to critical values), and the female body simply “does not have time” to prepare for pregnancy.
Late ovulation. To treat or not to treat
It is important to understand that late ovulation does not mean guaranteed infertility. But it may indicate a number of other reasons.. Loparoscopic intervention is prescribed not only to eliminate the problem that caused infertility (for example, ovarian cysts), but also for diagnostic purposes
Sometimes a simple ovarian biopsy can have a positive effect on their function and stimulate them. So in the future, drug therapy is not even required.
Loparoscopic intervention is prescribed not only to eliminate the problem that caused infertility (for example, ovarian cysts), but also for diagnostic purposes. Sometimes a simple ovarian biopsy can have a positive effect on their function and stimulate them. So in the future, drug therapy is not even required.
But even if there is a need for surgical intervention, already six months after the operation the couple has the opportunity to successfully conceive a child. And the probability of getting pregnant in this case is estimated at 50-70 percent.
The menstrual cycle is a unique process inherent in the body of every woman by nature to maintain reproductive function. And ovulation, although the shortest, is quite an important moment in it. The time of its onset must be determined in accessible ways in order to control and plan conception. Late ovulation often causes difficulties in planning pregnancy.
When to take a pregnancy test after ovulation?
The instructions for the tests say that you need to be tested from the first day of the delay of critical days. This recommendation can significantly reduce the number of false results.
But not everyone has the strength and patience to wait for this moment. Moreover, in cases where conception is undesirable, women want to know the result as quickly as possible in order to take the necessary measures. Therefore, many ladies prefer to do a special test without waiting for a missed period. Some people believe that you can find out the answer two days before your period begins. And others believe that even five days before a possible delay, you can find out about pregnancy using a special test.
Women disagree so much because the sensitivity of the tests may vary, but immediately after ovulation, checking with them definitely does not make sense. Here you need to wait at least a week, 6-8 days. During this time, a special hormone is produced in the woman’s body: human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). It blocks the functioning of the ovaries, thereby eliminating the possibility of re-pregnancy.
It is by the amount of this hormone in a woman’s urine that the test gives its result. It is necessary to test after a night's sleep, because if this hormone is present in the urine, its concentration in the morning is much higher than at other times of the day.
Interesting: When Can You Have Sexual Life After Caesarean?
Tests, depending on their sensitivity, can detect hCG concentrations of both 10 units and 25. However, even highly sensitive tests on days 7-10 after ovulation and conception can show a weakly positive result when the second strip is faintly visible.
This happens because the level of hCG in the urine is very low in the early stages of pregnancy. Therefore, it is better to do a test in a couple more days, and if the second strip becomes brighter, then the answer is positive. To get a more accurate result, it is better to wait until your menstruation is late. After all, the highest concentration of hCG in a pregnant woman’s body is observed during the eighth to tenth weeks from the moment of ovulation. But you can still try a highly sensitive pregnancy test a week after ovulation.
Late cell maturation
Ovulation in any female with varying cycle lengths is observed 14 days before the onset of bleeding (menstruation). The first part of the cycle has a different duration, but the second is normally a static value.
Symptoms and concerns
With an ideal cycle, which is considered to be 28 days, the follicle ruptures on the 14th day. With other indicators, exit on days 11-16 is possible. If ovulation occurs on days 17-18 or later, it is considered late. This phenomenon causes concern among the fair sex about conception and possible infertility.
But such a delay should not worry, since the extended first phase does not affect the exit of the cell and its fertilization, it just happens later. If there are no health problems and hormone production is normal, then late ripening is not considered a problem.
Pregnancy countdown
It should be remembered that in this case, counting pregnancy on the first day of menstruation is irrelevant. The degree of embryo development on ultrasound will be less than during counting, sometimes up to 2-3 weeks.
Signs and symptoms
To detect premature egg release, you need to track your cycle for at least 3 months. With a 28-day cycle, ovulation should be expected on days 12-16, with a 30-day cycle - on days 13-17.
If a woman begins to feel the following symptoms shortly after her period, most likely she has entered the ovulatory phase earlier than usual:
- increased viscosity of cervical mucus;
- soreness of the mammary glands;
- increased sexual desire;
- aching pain in the abdomen.
Signs of premature egg release can be monitored by measuring urine LH levels using ovulation tests.
How else can you determine early ovulation?
Determining the peak of basal temperature is a reliable sign of egg release, available to any woman at home. However, this method also has disadvantages: for at least six months you need to strictly follow the measurement procedure, record the result, build a graph and analyze it together with a gynecologist.
The most accurate way to determine the release date of an egg is to measure the diameter of the follicle using ultrasound (folliculometry). For obvious reasons, this measurement is not available to all women.
An informative home method is to use the ovulation texts mentioned above. If the egg is released early, it is better to use reusable cassette devices, devices for determining ovulation by saliva, or purchase a large number of disposable test strips, starting to use them immediately after the end of menstruation.
If the failure occurs once, there is no reason to worry. Problems with conception may occur if the pathological condition persists for more than 3 months. At the same time, the menstrual cycle is shortened, and menstruation comes earlier than usual.
What to do if you ovulate late
First, you need to learn how to determine ovulation, but if the reasons for late ovulation are caused by disorders in the body, you must adhere to certain rules.
Ovulation detection
Ovulation can be detected with such maturation features in ways similar to those for any woman. Only the woman will receive a response later than expected:
- using tests (although a false result cannot be ruled out);
- by measuring basal temperature (the graph will show a decrease and then an increase in indicators with a shift towards the second phase, and not in the middle of the curve);
- examining saliva at home using devices such as microscopes (the fern leaf will be visible later than expected);
- taking a blood test for hormones;
- observing your secretions and other physiological changes;
- by performing an ultrasound as the most accurate and reliable method.
Cycle recovery
When late ovulation is established, the causes and symptoms confirm it, restoration of the normal menstrual cycle and, ultimately, the onset of favorable conception is possible, subject to certain rules:
- listen to your gynecologist’s advice on treatment;
- avoid stress;
- lead a healthy life;
- do not use dangerous and harmful substances.
Need for treatment
Late ovulation is caused by certain factors that need to be dealt with. Therefore, influencing ovulation itself is simply pointless. Currently, doctors are resorting to various measures that make it possible to correct the timing of this process. Thanks to them, you can achieve a good result - the process will proceed on time. The main thing is to identify the cause of the failure.
Quite often, miscarriage is a serious problem, due to which ovulation becomes late. Functional changes occur in the body, which have a negative impact on the process. However, after 2-3 months, restoration measures will make themselves felt, so there is no point in resorting to any medicinal methods.
However, there are also more serious reasons that need to be dealt with immediately. We are talking about diseases that are infectious in nature. In this case, doctors suggest taking a specially designed therapeutic course. Its implementation allows for effective treatment, after which the processes will stabilize and acquire normal values in terms of their course.
It makes sense to carry out therapeutic measures only when a woman cannot conceive a child and the reason for this is untimely ovulation. In some representatives of the fair sex, it may be recorded that signs of the ovulation process are completely absent. In this case, they turn to stimulation of the process under the supervision of a gynecologist. As a rule, this approach significantly increases a woman’s chances of becoming pregnant and carrying a child to term.
Late ovulation and pregnancy - when will the test show?
If pregnancy occurs, the test will be positive 12-15 days after conception, when a specific hormone, human chorionic gonadotropin, increases. It is present in the blood and urine of a pregnant woman. Test strips or devices contain a sensitive substance, the reaction of which with hCG is manifested in the form of indicator icons.
Test accuracy is 75-97%. If late ovulation occurred due to hormonal imbalance, then this value is much lower. Even a false negative result is possible. It is better to carry out testing 2-3 weeks after the release of the egg, then the reagent will be more sensitive. The following factors influence the content of the hCG hormone:
- taking hormonal drugs, diuretics;
- tumors of the pelvic organs;
- diseases of the kidneys, heart and blood vessels;
- abortions, miscarriages prior to testing.
Symptoms of egg release
Not all women experience signs of ovulation. At this moment, hormonal changes occur in the body. By carefully observing your body, you can discover the period of best fertilization ability. It is not necessary to use complex and expensive methods for predicting egg release. It is enough to detect natural symptoms in time.
Change in cervical mucus
The female body prepares for possible conception by producing cervical fluid, suitable for the transfer of sperm from the vagina to the uterine cavity. Until ovulation, this discharge is thick and viscous. They prevent sperm from entering the uterus. Before ovulation, the glands of the cervical canal begin to produce a special protein - its threads are thin, elastic and similar in properties to the protein of a chicken egg. Vaginal discharge becomes transparent and stretches well. This environment is ideal for sperm to penetrate into the uterus.
Change in vaginal moisture
Discharge from the cervix becomes more abundant. During sexual intercourse, the amount of vaginal fluid increases. A woman feels increased humidity throughout the day, which shows her readiness for fertilization.
Breast tenderness
After ovulation, progesterone levels increase. If a woman keeps a chart, she will see that her basal temperature has risen. It is caused precisely by the action of progesterone. This hormone also affects the mammary glands, so at this moment they become more sensitive. Sometimes this soreness resembles premenstrual sensations.
Changing the position of the cervix
After the end of menstruation, the cervix is closed and low. As ovulation approaches, it rises higher and softens. You can check this yourself. After thoroughly washing your hands, you need to place your foot on the edge of the toilet or bathtub and insert two fingers into the vagina. If you have to push them deep, it means your cervix has risen. It is easiest to check for this symptom immediately after menstruation, so that you can then better determine the change in the position of the cervix.
Increased sex drive
Women often notice a stronger sex drive mid-cycle. These sensations during ovulation are of natural origin and are associated with changes in hormonal levels.
Bloody issues
Sometimes in the middle of the cycle, small bloody discharge from the vagina appears. It can be assumed that this is the “residue” of blood leaving the uterus after menstruation. However, if this sign appears during suspected ovulation, it indicates rupture of the follicle. In addition, some blood may also be released from the endometrial tissue under the influence of hormones immediately before or after ovulation. This symptom indicates high fertility.
Cramp or pain on one side of the abdomen
20% of women experience pain during ovulation, which is called ovulatory syndrome. It occurs when the follicle ruptures and the fallopian tube contracts as the egg moves into the uterus. A woman feels pain or spasm on one side of her lower abdomen. These sensations after ovulation do not last long, but serve as a fairly accurate sign of fertilization ability.
Flatulence
Hormonal shifts cause slight bloating. It can be detected by clothing or a belt that has become a little tight.
Mild nausea
Hormonal changes may cause mild nausea, similar to pregnancy-like symptoms.
Headache
20% of women experience headaches or migraines before or during menstruation. The same symptom in these patients may accompany the onset of ovulation.
Anovulatory cycle
Menstrual-like bleeding may recur regularly after 24-28 days, but the egg does not leave the ovary. This cycle is called anovulatory. In the absence of ovulation, one or more follicles reach the preovulatory stage, that is, they grow, and a germ cell develops inside. However, the follicular wall does not rupture and the egg does not come out.
Soon after this, the mature follicle undergoes atresia, that is, reverse development. At this time, estrogen levels decrease, which leads to menstrual-like bleeding. In terms of external signs, it is practically indistinguishable from normal menstruation.
Why is there no ovulation?
This may be a physiological condition during puberty or premenopause. If a woman is of childbearing age, rare anovulatory cycles are normal.
Many hormonal disorders lead to an imbalance of the “hypothalamus-pituitary-ovary” system and change the timing of ovulation, in particular:
- hypothyroidism (lack of thyroid hormones);
- hyperthyroidism (excess thyroid hormones);
- hormonally active benign tumor of the pituitary gland (adenoma);
- adrenal insufficiency.
Emotional stress can prolong the ovulatory period. It leads to a decrease in the level of gonadotropin-releasing factor, a substance secreted by the hypothalamus and stimulating the synthesis of FSH in the pituitary gland.
Other possible reasons for the absence or delay of ovulation associated with hormonal imbalance:
- intense sports and physical activity;
- rapid weight loss of at least 10%;
- chemotherapy and radiation for malignant neoplasms;
- taking tranquilizers, corticosteroid hormones and some contraceptives.
The main physiological reasons for the absence of ovulation are pregnancy and menopause. During premenopause, women may continue to have more or less regular periods, but the likelihood of anovulatory cycles increases significantly.
Conception and late ovulation
Normally, the oocyte leaves the follicle 14 days after the start of menstruation at the 28th cycle. But each representative of the fair sex is unique in her own way and the menstrual cycle can vary from 21 to 35 days.
Ovulation may occur earlier than expected or be late or absent for these reasons:
- poor nutrition;
- chronic fatigue;
- climate change;
- overvoltage.
With late ovulation, the female gamete matures later than the prescribed period.
It is possible to conceive a baby in this case, but not in every case. If late ovulation occurs quite rarely, this will not prevent the sperm and egg from meeting. But if ovulation always occurs later, then the chances of success are greatly reduced. It all depends on the health of the reproductive organs. If there are no pathological changes, then you won’t have to wait long for pregnancy.
The main reasons for late ovulation
- Spontaneous abortion.
- Depression.
- The onset of the “elegant” age. In forty-year-old women, important processes occur in an altered form. In adulthood, the body begins to prepare for menopause.
- Cystitis.
- Endocrine diseases.
- Malignant tumor in the genital organs.
- Inflammation in the uterus.
- In pursuit of ideal proportions, ladies go on strict diets. Refusal of foods containing protein leads to a decrease in the production of female hormones.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the pituitary gland.
- Frequent use of emergency contraception.
- Gynecological ailments.
- Medical abortion.
- Hormonal disbalance.
- Sexual infections.
If the reason for the late release of the oocyte lies in these reasons, then you need to make an appointment with a specialist so as not to bring the situation to a critical point. Often, a gynecologist prescribes the drug Duphaston to his patients. The duration of administration and dose are set strictly individually depending on the tests obtained.
Once treatment is complete, the couple can begin planning. Expectant parents should give up smoking, alcohol and drugs.
Is it necessary to resort to treatment?
Ovulatory shifts appear against the background of certain life factors; there is no need to treat ovulation with medication. With the help of medications, you can adjust the date of ovulation. To do this, it is necessary to detect a physiological deviation as soon as possible and establish the cause of its formation.
- if failures occur due to spontaneous abortion, then the woman should delay conception for 6 months so that the body returns to normal;
- if the cause of the deviations lies in inflammation or pathogenic bacteria, then you need to undergo a therapeutic course so that the gamete matures in due time. In such a case, the patient is prescribed stimulation of oocyte maturation, as a result of which the girl has the opportunity to conceive and carry a baby.
How to correct your cycle
One of the drugs used to regulate the cycle is Duphaston.
The prescription of Duphaston for late ovulation is currently controversial. He has many opponents. For example, the product has not been produced in the UK since 2008. However, in many countries, late ovulation and Duphaston go hand in hand. It is prescribed to stimulate menstruation and regulate the cycle.
But the drug is still not recommended for those who want to get pregnant as soon as possible. This is due to the need to use the product on a schedule. Even a single mistake in the timing of administration or dosage can lead to an effect opposite to the desired one. That is, instead of the long-awaited pregnancy, menstruation will come.
Some experts in the field of medicine (Essen Institute for Medical Research and Education in Germany) argue that the use of the drug Duphaston to eliminate late ovulation is not only not justified, but can also lead to its complete absence, delaying the onset of motherhood.
Sometimes the prescription of the drug is not confirmed by the results of the analysis, but is based only on the assumption of a lack of progesterone in the blood. If you have doubts about the competence of the doctor recommending Duphaston, you should consult other specialists on this issue. It is easier to undergo additional examination than to eliminate the consequences of illiterate and inept intervention in the body.
In addition to drug treatment and following the recommendations of the attending physician, a woman herself can take measures to conceive as quickly as possible.
To get pregnant faster, you need to:
- have an active sex life with a regular partner;
- observe the work and rest schedule, do not overwork;
- avoid increased psycho-emotional stress;
- adhere to a healthy diet;
- eliminate smoking and minimize alcohol consumption;
- move a lot, walk and breathe fresh air.
Late ovulation, even if it is the result of a disease and not an individual characteristic of the female body, does not exclude the possibility of motherhood. With the help of medicine and some patience, pregnancy will definitely happen!
especially for Mama66.ru
Methods for determining the required period
The presence of late ovulation can be determined independently and there is no need to go to the hospital for this. Among the most common methods are the following:
- observing changes in basal temperature;
- special test for ovulation;
- monitoring changes occurring in the body.
To make sure that ovulation occurs later, you need to measure your basal temperature. To do this, they resort to measuring temperature values in the rectum. This method is simple and reliable. This event must be implemented regularly, otherwise it will not be able to form a real picture of ovulation.
Tests can be trusted and in most cases they give true answers, but it is impossible to be completely sure. In addition, the test answer may be erroneous due to the fact that the woman’s body is affected by a certain gynecological disease. This also includes the effect of certain medications that include certain active elements. The test must be carried out in a certain time period, which must be calculated correctly.
When ovulation occurs, most women experience specific symptomatic manifestations:
- general malaise (felt mild);
- nagging pain felt in the lower abdomen;
- headache;
- dizziness.
If you focus on the above symptoms, you can easily determine that ovulation has occurred. However, the symptoms must be pronounced. However, they can be caused by other factors that are absolutely unrelated to ovulation.
To obtain accurate data, you need to contact a medical institution. There they conduct certain studies, on the basis of which it is possible to establish the course of the process. Medical studies include:
- comprehensive examination by a gynecologist;
- ultrasound-based monitoring event;
- analysis of pituitary hormone levels.
These diagnostic measures will be reliable only if they are implemented within 3-4 cycles. This approach allows the specialist to identify all the signs characteristic of late ovulation. It is advisable to seek medical help if a woman is planning a pregnancy.
How to determine late ovulation
In most cases, treatment prescribed by a doctor helps establish a regular cycle and the onset of a long-awaited pregnancy.
Even ovulation does not occur in the middle of the cycle, this does not mean a violation. It is important that it occurs approximately 2 weeks before menstruation. When these deadlines are shifted in one direction or another, it is worth thinking about. Problems with conceiving a baby arise if the duration of the second half of the cycle is always shorter than the first.
Pregnancy with late ovulation can occur almost before menstruation. Therefore, the terms determined by ultrasound and obstetrics may differ. This must be taken into account in order to calmly respond to the alleged developmental delay of the fetus.
HCG during late ovulation is lower than it should be at the corresponding obstetric period (counting from the first day of the last menstruation). There is no need to worry about this, but after pregnancy is detected, it is advisable to observe its growth over time.
In the future, the expectant mother needs to inform the antenatal clinic doctor about the peculiarities of her menstrual cycle.
PO and pregnancy cannot be combined if the cycle shifts as a result of pathological reasons. We can talk about inflammatory, hormonal or infectious diseases. In this case, planning can begin only after the pathological factor has been eliminated. A number of diagnostic measures are carried out in advance. In order to restore the regularity of the cycle, drug therapy is carried out.
- The control strip appears when liquid (urine) gets on it.
- Test only if the liquid contains the pregnancy hormone - hCG (short for its full name - human chorionic gonadotropin).
Pregnancy test
This specific hormone begins to be produced after the fertilization of a woman's egg and its implantation into the loose wall of the uterus. After its attachment, the hCG level begins to double in some people every 24, and in others every 36 or even 48 hours.
Some women are insensitive to the proximity of the ovulatory period and do not feel any changes in their physical condition. Therefore, it is most informative to conduct home monitoring in the form of:
- charting basal temperature;
- using test strips or electronic tests;
- the use of special microscopes sold in pharmacies for the analysis of saliva and secretions.
To more accurately determine the late maturation of the egg, it is advisable to consult a doctor. Research that will help determine the cause of the phenomenon:
- examination by a specialist;
- folliculometry using ultrasound;
- blood test for hormone levels.
If deviations are recorded over several cycles, the gynecologist will prescribe appropriate treatment. You need to correct hormonal imbalance before planning a pregnancy.
The embryo becomes visible on ultrasound no earlier than 3-4 weeks. If ovulation is delayed, you need to add 2-3 weeks to it. It is worth waiting and getting tested in the 7th week of pregnancy. Otherwise, even with all the signs, the doctor will not detect the embryo and will diagnose “anembryony.”
When adjusting dates using ultrasound, the preliminary date of birth coincides with the actual one.
When does ovulation occur in women with a 28-day cycle?
? Please rate!
Pregnancy is a wonderful condition. And even better is the realization that a baby is about to appear in the house. You can bring the long-awaited moment closer by finding out the exact day of ovulation.
Calculation of the day of ovulation for cycle 28
Today, you can calculate the time of ovulation in several ways: on your own, in a clinic, using an online calculator.
Let's immediately look at independent calculation, including its advantages and disadvantages.
The girl can calculate the date of ovulation herself. If the cycle lasts 28 days, then you need to subtract 14 from this number. Thus, the 14th day is the time of ovulation.
But a girl can become pregnant a few days earlier or later, since a sperm lives in a woman’s body for several days, and a fertilized egg lives for a day.
When making your own calculations, an excellent assistant is an ovulation test, which can be purchased at any pharmacy.
If we talk about online calculations, it is simpler and better than the independent calendar method in that the program produces the following dates:
- day of ovulation;
- probable days of conception;
- “useless” days;
- for those for whom the gender of the child is important, the periods of “boy” and “girl” are emphasized.
The method of using the online calculator is very simple: you need to enter the date of the first day of menstruation, the duration of menstruation (for example, 3 days), the duration of the cycle - in our case, 28 days. Then click the “calculate” button.
Everything is quite elementary. But this test is not suitable if the cycle is not regular or ovulation is untimely (early or late).
The doctor determines the day of ovulation using ultrasound diagnostics. This method is used mainly by those girls whose cycle is disrupted, that is, difficulties arise with independent and computer calculations.
Early ovulation with a 28-day cycle
Early maturation of the egg is explained by:
- hormonal imbalances;
- unhealthy diet;
- stress;
- traumatic sex;
- abuse of alcohol and drugs;
- heavy physical labor;
- change of place of residence;
- overwork;
- postpartum period and inflammatory processes.
Signs of early ovulation are similar to those of regular ovulation:
- lower abdominal pain and bloating;
- breast swelling and pain;
- change in the consistency of vaginal discharge;
- mood swings;
- increased libido.
Early ovulation is not as scary as it might seem at first glance, although it all depends on the reasons for its occurrence. By eliminating the factor, the problem is eliminated.
Late ovulation with a 28-day cycle
If early maturation of the egg is a common case, then later maturation is almost an isolated situation. The harbingers of late ovulation are more serious than in the previous version:
- infectious diseases of the genital organs;
- abortions;
- miscarriages;
- postpartum period;
- menopause;
- hormonal dysfunction.
It is now clear that to treat late ovulation it is necessary to eliminate its source.
As for symptoms, everything is determined at the individual level - each woman is different.
Is it possible to ovulate again?
Typically the formula is: 1 cycle = 1 ovulation. But there are known exceptions, or rather:
- before the onset of menopause;
- stopping taking hormonal medications;
- increased sexual desire, which often occurs in women in the absence of regular relationships.
As has already become known, no one is immune from repeated ovulation. But it is not recommended to hope for it, even if it has arrived, since the mature egg most often dies during this period.
No ovulation
Some women throw hysterics when they learn that during the entire period from period to period, her cell did not mature. It is too early to sound the alarm if anovulation (lack of ovulation) occurs 2–3 times a year. This happens even in a healthy body.
If anovulation occurs more than four times a year, then this is a serious reason to see a doctor.
Anovulation is typical during: menopause, pregnancy, taking certain medications; hormonal disorders, infertility.
News on the topic of ovulation on the 10th day of the cycle
Read more
The most accurate method for determining ovulation
For many couples, the success of conceiving a child depends on accurately determining the woman's ovulation period. According to experts, urine testing is the most accurate way to find out the day of ovulation than the traditional calendar method.
Read more
Ovulation changes female behavior
It is known that a woman’s mood depends on her menstrual cycle. During ovulation, not only her behavior changes, but also her gait, the way she dresses and talks to men. According to experts, this is due to a subconscious desire to find a suitable partner for reproduction.
Read more
Cinnamon - an aromatic remedy for infertility
Cinnamon has been used by mankind as a spice for many centuries. But only nowadays scientists began to study its healing properties. Researchers from the United States have found that cinnamon significantly improves the condition of patients with polycystic ovary syndrome.
Read more
Smoking weed is more harmful for women than for men
Scientists from the USA, during experiments with laboratory animals, discovered that the body of females reacts to the components of marijuana in a slightly different way compared to the organisms of males. Cannabis has a more destructive effect on women's bodies.
Read more
A normal pregnancy can last ten months
Scientists have found that a normal pregnancy can last five weeks longer than the standard period of nine months.
Read more
When fate is in one stripe
Modern medicine places increasing importance on adequate and timely diagnosis. And this is understandable, since correct diagnosis of the disease is decisive for further treatment and allows a person to effectively and cost-effectively return lost health. What if we are talking about determining pregnancy? Indeed, in such a situation, the fate of many people, their family well-being depends on the diagnostic result... It is not surprising that a company that provides Ukrainian women with a convenient and reliable tool for quickly determining pregnancy enjoys the trust and gratitude of society. This is confirmed by the awarding of the honorary prize “Panacea 2009” to one of these tests. And although the company’s activities have already received various awards more than once, high praise from pharmaceutical market professionals is always a significant event.
Read more
Short intervals between periods are a sign of menopause
Shorter periods between periods may be an early sign that menopause is imminent, while heavy monthly bleeding may be due to other causes, scientists report
Changes in the timing of ovulation
The release time of the egg may vary by 1-2 days even with a regular cycle. A persistently shortened follicular phase and early ovulation can lead to problems with conception.
Early ovulation
If the release of the egg occurs 12-14 days after the start of menstruation, there is no reason to worry. However, if the basal temperature chart or test strips show that this process occurred on the 11th day or earlier, then the released egg is not developed enough for fertilization. At the same time, the mucus plug in the cervix is quite dense, and sperm cannot penetrate through it. Insufficient increase in endometrial thickness, caused by a reduction in the hormonal influence of estrogens in the developing follicle, prevents implantation of the embryo, even if fertilization has occurred.
The reasons for early ovulation are still being studied. Sometimes it happens accidentally, in one of the menstrual cycles. In other cases, pathology may be caused by the following factors:
- severe stress and disruption of the relationship between the hypothalamus and pituitary gland in the nervous system, which leads to a sudden premature increase in LH levels;
- the natural aging process, when to maintain the maturation of the egg, the body produces more FSH, which causes excessively rapid growth of the follicle;
- smoking, excessive consumption of alcohol and caffeine;
- gynecological and endocrine diseases.
Can ovulation occur immediately after menstruation?
This is possible in two cases:
- if menstruation lasts 5-7 days, and against this background a hormonal imbalance occurs, early ovulation can occur almost immediately after its completion;
- if two follicles mature at different times in different ovaries, then their cycles do not coincide; in this case, ovulation of the second follicle is timely, but occurs in the first phase in the other ovary; This is associated with cases of pregnancy during sexual intercourse during menstruation.
Late ovulation
For some women, from time to time the ovulatory phase occurs on the 20th day of the cycle or later. Most often this is caused by hormonal disorders in the complex balanced system “hypothalamus - pituitary gland - ovary”. These changes usually precede menopause and are caused by stress or certain medications (corticosteroids, antidepressants, anticancer drugs). Late ovulation increases the risk of chromosomal abnormalities in the egg, fetal malformations and early pregnancy loss.
If two follicles in each ovary do not mature at the same time, ovulation is possible before menstruation.
The cause of such a failure may be breastfeeding. Even if a woman regains her period after childbirth, she experiences a long follicular phase or anovulatory cycles for six months. This is a normal process established by nature and protects a woman from re-pregnancy.
During breastfeeding, both menstruation and ovulation are often absent for some time. But at a certain moment, the maturation of the egg begins, it is released, and it enters the uterus. And only 2 weeks after this, menstruation begins. This is how ovulation is possible without menstruation.
Often, late ovulation occurs in women who are too thin or in patients who have lost weight quickly. The amount of fat in the body is directly related to the level of sex hormones (estrogens), and a small amount of it leads to delayed egg maturation.
When is “late” ovulation a normal option, and when is it a symptom of pathology?
Various gynecological diseases.- Infectious diseases.
- Hormonal imbalances - with low estradiol or high testosterone, follicle maturation occurs at a slower rate. Lack of progesterone may also play a role.
- The period after childbirth or miscarriage (abortion).
- The period before the onset of menopause.
- Constant stress.
- Change of climate or time zones.
Thus, late ovulation can occur both in absolutely healthy women and in women whose bodies are exposed to various factors that can, one way or another, shift ovulation to a later date. Therefore, late ovulation itself cannot cause a woman’s infertility, since it is quite possible that this is an individual feature of the body.
Late ovulation can be associated with the inability to get pregnant only when it is a clear sign and consequence of some disorder in the body. For a healthy woman, late ovulation, provided its timing is determined, will not become an obstacle to achieving the cherished goal, namely, pregnancy.
According to examinations of many women and approximate statistics, late ovulation most often does not in any way affect the possibility of fertilization of an egg by a sperm and its further development. The only downside is that women with late ovulation have a slightly less chance of conceiving a child than others, since the egg does not mature every month, but once every 35-40 days. There are healthy women who ovulate more rarely – once every one and a half to two months.
In a healthy woman of reproductive age, ovulation occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle. With a classic 28-day cycle, the egg leaves the follicle on the 14th day, but if a woman’s regular cycle lasts 32 days, it can be expected on the 16th day. If the egg leaves the follicle with a delay of 3–5 days (for example, on days 20–25), then there is reason to say that the woman is experiencing late ovulation.
In some cases, the egg is “late” not due to illness, but due to physiological reasons. Failure of the menstrual cycle and its displacement are considered normal in the postpartum period; usually the condition of a young mother normalizes itself over time. The following factors can also cause late ovulation:
- concomitant diseases - an infectious disease, a cold, aggravated chronic pathology can lead not only to a delay in timing, but also to an anovulatory cycle (after recovery, everything will return to normal);
- frequent changes of time zones and/or long flights;
- adaptation to a changing climate;
- constant overwork;
- strong feelings.
In most cases, such a violation is the result of diseases, which include:
- pathologies of the endocrine system leading to hormonal imbalance;
- polycystic ovaries;
- infections of the reproductive system;
- adenomyosis;
- endometriosis;
- inflammation of the organs of the female reproductive system, acute or chronic.
For couples planning to have a child, determining the date of oocyte maturation is of particular importance. However, if the egg leaves the follicle later than normal or the woman has an irregular menstrual cycle, then you cannot rely on calculation alone, so you should also pay attention to the characteristic symptoms and use methods such as measuring basal temperature, ultrasound of the ovaries, and an ovulation test.
In most women, ovulation is accompanied by characteristic symptoms, which helps determine readiness to conceive even if ovulation shifts. Rupture of the follicle may be accompanied by mild pain in the lower abdomen, which quickly passes. By the time of ovulation, the amount of discharge increases, which becomes similar in consistency to raw egg yolk.
Another sign of ovulation is premenstrual syndrome (a woman becomes irritable and very emotional, her mood often and suddenly changes).
To determine ovulation by basal temperature, you will first need to build a temperature graph. To do this, you need to measure your temperature rectally every morning at the same time (before getting out of bed) for 3-4 months, and record the results in a special table. Before the egg leaves the follicle, basal temperature values increase within 0.5–1 degrees.
Ultrasound examination of the ovaries is one of the most accurate ways to determine ovulation. Usually the doctor prescribes the test, but when planning a pregnancy, a woman can ask the doctor to write out a referral for an ultrasound scan. To prepare for pregnancy, research begins on the 8th day of the cycle, and by the middle of it it becomes possible to detect ovulation.
Ovulation tests
Ovulation tests, which are sold in pharmacies, show high accuracy. According to the principle of action, they are similar to tests for determining pregnancy, but the special substance with which the strip is impregnated reacts not to hCG, but to LH (luteinizing hormone, the level of which increases during ovulation). If the egg has left the follicle and the body is ready for conception, the test will show 2 stripes.
If a woman knows that ovulation came “late,” this fact should be taken into account when confirming conception. Since fertilization of the egg during late ovulation does not occur in the middle of the cycle, but closer to its end, if there is a delay of several days, doing a test will be useless - even if the woman is pregnant, the level of hCG in her body will not yet reach high enough values.
In order for the reagent of a conventional pharmacy pregnancy test to detect an increase in the level of the hCG hormone in a woman’s urine, at least 2 weeks must pass from the moment the egg is released. It is possible to determine that conception has occurred using a test strip if you calculate when it is best to carry out the test.
When calculating, you need to take into account the date of release of the egg (you can focus on the signs and symptoms of ovulation and your own feelings, but the calculation will be more accurate if the woman has undergone tests or relevant tests). The embryo does not implant in the uterine cavity immediately - about 6–8 days pass between fertilization and attachment. The level of the hCG hormone begins to rise only after the fertilized egg has consolidated and the development of the embryo has begun.
It is recommended to carry out a pregnancy test during normal periods of ovulation in the absence of menstruation for at least 3 days after the expected date of their arrival. For women whose egg release occurs later than normal, the recommended day to use the test strip is no earlier than a week after the expected date of menstruation. If you need to determine pregnancy earlier, it is better to use highly sensitive digital tests.
When ovulation is late, a pregnant woman may get her period. This happens if fertilization occurred at the very end of the cycle, and the fertilized egg simply did not have time to “get” to the uterus by the start date of menstruation. Regulations can begin at the right time and go away as usual or look like scanty spotting.
Using ultrasound
Ultrasound examinations are performed several times during pregnancy - this is an effective way to monitor the development of the fetus and identify many abnormalities in the early stages. It is possible to confirm the fact that a woman will soon become a mother with the help of such a study, but there is no need to sign up for the study in the first week of the delay - even the most experienced specialist will not see anything on the screen.
For the doctor to be able to view the fertilized egg on the monitor, at least 4 weeks must have passed from the moment of fertilization. If modern equipment is installed in the ultrasound room, the doctor conducting the examination is experienced and highly qualified, and the woman’s uterus is completely healthy and no inflammatory processes occur in it, you can see the embryo at a period of 3–3.5 weeks.
In most cases, the study is carried out no earlier than the 5th week from the moment of alleged conception. At this time, the doctor will be able to examine the fertilized egg, hear the baby’s heart beating, and conclude that the pregnancy is developing normally and no abnormalities have been identified. For this reason, we can talk about confirming pregnancy using ultrasound during late ovulation only if there is a delay of at least 3 weeks.
Typically, gynecologists take the date of the last menstruation as the “reference point” for pregnancy. This approach can be considered rational during normal ovulation, but if the oocyte leaves the follicle later, the calculation will be incorrect. As a result, the doctor will receive a significant calculation error - up to 3 weeks.
Based on erroneous data, a gynecologist during pregnancy may conclude that the fetus is developing too slowly, with a delay, and will not be able to correctly determine the date of birth. Based on the assumption that the child is lagging behind in development, the gynecologist may prescribe the woman to take hormonal medications that are actually unnecessary, which will negatively affect both her condition and the health of the baby.
The gynecologist should be informed about late ovulation (even if there is only suspicion). Then the doctor will calculate the gestational age based on the results of the ultrasound. The doctor will determine the degree of maturity of the fetus, measure its parameters and be able to draw fairly accurate conclusions about the gestational age.
A feature of pregnancy with this phenomenon is the discrepancy between the actual and obstetric dates. The doctor determines the period based on the date of the last menstruation.
With an average cycle of 28 days, pregnancy is calculated from the date of expected ovulation. In fact, conception and implantation of the egg could have occurred much later. It is imperative to inform your doctor about the signs of hormonal imbalance.
The difference is estimated at two to three weeks. For an obstetrician, this is a sign of fetal developmental delay. A pregnant woman begins to worry, although there is no real reason for this.
Causes of late ovulation
Most of the factors that cause a late ovulatory period can be corrected with special medications or lifestyle changes. It is enough to identify the circumstances that caused the cycle disruption and eliminate them. Difficulty may arise in the presence of diseases of the reproductive organs. In this case, it will be necessary to undergo a full course of treatment.
The reasons for the delayed formation of the egg may be the following factors:
- recent medical abortion;
- taking certain potent drugs;
- consequences of miscarriage;
- recent birth;
- constant stress or abnormalities in the functioning of the nervous system;
- infections of the body's reproductive system;
- a sharp change in hormonal levels;
- taking contraceptives;
- approaching menopause;
- changes in climatic conditions;
- past infectious or viral diseases.