- Chiari syndrome. Impaired circulation of cerebrospinal fluid occurs due to the fact that the fetus’s brain does not develop properly: the brain stem and cerebellum descend into the foramen magnum. The brain may grow too quickly, becoming much larger than the skull.
- Edwards syndrome. A chromosomal disorder affecting girls, characterized by abnormal development of many organs, the brain, malfunction of all systems, and the occurrence of dropsy. Children suffering from this syndrome die in the first months of life.
- Asymmetry of the lateral ventricles, in which the free outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the cranium is disrupted.
- A congenital narrowing of the tubule through which cerebrospinal fluid drains from the brain.
- Anomalies of brain development: asymmetry of the cerebral ventricles, narrowing of the cerebral aqueduct, underdevelopment of the openings for the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Neoplasm in the head , leading to displacement of brain structures, defects in the blood vessels of the head and neck.
- Trauma during childbirth, which causes intraventricular stroke or cerebral hemorrhage, oxygen starvation, asphyxia.
- Meningitis.
- Encephalitis.
- Improper development of the vascular system.
- Infectious diseases.
- Brain hemorrhage, intracranial hematoma.
- Cyst.
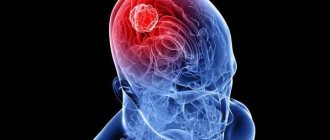
- Neoplasm in brain tissue, skull bones.
- Spinal cord cancer.
- Head and neck injuries: bruises, fractures of the skull, spine, falls from a great height, whiplash.
In a baby
Most often, hydrocephalus of the brain in children under one year of age develops due to infections in utero (80% of patients). Other reasons:
Dropsy often develops in premature, low birth weight babies. Due to the fact that all organs and systems (cardiac, vascular, digestive, nervous) are not fully formed in the baby, an incorrect reaction of the body to the environment may develop, such as increased production of cerebrospinal fluid.
If the child is over a year old
In the age group of children from 1 year and older, the cause of the pathology may be:
Hydrocephalus of the brain in children can occur due to genetic abnormalities in the development of internal organs.
Classification of pathology
It is needed for the doctor to determine treatment tactics. The classification is formed by many factors: the reasons for its appearance, the state of the cerebrospinal fluid tract, the level of intracranial pressure, and some other factors.
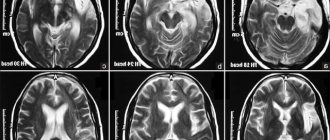
The first picture is normal, the second is hydrocephalus
The distribution into individual types of the disease is based on the localization of the cerebrospinal fluid in a specific area of the brain.
- Outer. The accumulation is observed under the shells. This type is considered to be congenital, the development of which is facilitated by birth injuries. Treatment is medicinal, allowing to stabilize the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. In the absence of positive dynamics, surgical intervention is prescribed.
- Interior. Accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid is observed in the ventricles of the brain. This type of disease can be either acquired or congenital. Initial treatment is conservative; in the absence of positive results, surgical treatment.
- Mixed. Fluid accumulates under the membranes of the brain and in the ventricles.
- Hypertension-hydrocephalic syndrome. Characterized by increased intracranial pressure, there is an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the spaces of the brain, in particular in the ventricles.
Dropsy is classified according to numerous criteria. The most commonly used:
- By location. Divided into external and internal hydrocephalus. The internal one is localized in the ventricles, the external one - in the subarachnoid space. There are mixed types.
- According to the form. Open and closed dropsy are determined. When the form is open, nothing prevents the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid; when it is closed, there are adhesions and neoplasms. It is called occlusal. The occlusive form of hydrocephalus affects infants with brain tumors.
- According to the nature of the course, four forms are distinguished. Acute symptoms appear very quickly: within a few days. With this development, surgical intervention is necessary. Symptoms of the chronic form are blurred and visible after 6 months. With compensated dropsy, the cavities remain dilated, but the pressure drops. In this form, dropsy returns after injury to the skull. External dropsy is easily identified. It is large, the fontanel protrudes above the skin. With this form, the baby often throws back his head and arches his back. The internal closed form of leakage is considered dangerous.
How is hydrocephalus formed?
Hydrocephalus occurs when the balance between the production of cerebrospinal fluid and its absorption is disrupted. Let's explain what this means.
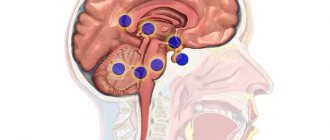
The brain is a solid, richly supplied structure with dense elastic properties, in which there are several cavities. They are called the ventricles of the brain. They are lined with a kind of “moss” of vessels, and it is this (this is called “plexuses”) that is responsible for the formation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
The ventricles communicate with each other, and the cerebrospinal fluid leaves the brain substance through them. Next, he needs to wash the spinal cord and get into the gap between the middle and inner membranes, which cover both the spinal cord and the brain. In this gap (it is called the subarachnoid space), which is found both in the cranial cavity and in the spine, there are vessels that absorb cerebrospinal fluid, which by this time already contains metabolites that have been processed and released by the brain structures.
Next, the cerebrospinal fluid must enter the special veins that exist in the cranial cavity. They are called venous sinuses and their peculiarity is that they do not collapse, having a special attachment to the cranial bones. The absorption of cerebrospinal fluid into the venous sinuses depends on the difference in pressure: the pressure in the sinuses must be lower than the intracranial pressure.
Liquor performs the following functions:
- being an incompressible fluid, it protects the brain from injury;
- removes certain substances from both parts of the central nervous system;
- maintains constant intracranial pressure;
- ensures balance between the water-electrolyte composition of the circulatory system and this fluid;
- oscillatory movements of the cerebrospinal fluid affect the autonomic nervous system.
Cerebrospinal fluid is produced continuously. Depending on age, it is synthesized from 40 to 150 ml per day (for comparison, in adults - up to 1.5 l/day). This fluid contains some leukocytes in the form of lymphocytes, a certain amount of protein, and electrolytes. The level of gases and sugar correlates with that contained in the blood: for example, the glucose content in the cerebrospinal fluid should be half as much as in the blood.
If a violation occurs:
- formation of cerebrospinal fluid (its excess is synthesized);
- its absorption;
- flow of cerebrospinal fluid along the designated paths,
hydrocephalus develops. Depending on the level at which the disorder occurs, as well as the pressure that is created in the cranial cavity, there is a classification of the disease, which we will consider below. Doctors use it to guide the treatment of pathology.
When the balance between the formation and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid is disturbed, or its circulation suffers, then in order to achieve this absorption at all, the cerebrospinal fluid must be “pushed” into the vessels that utilize it, that is, intracranial pressure must be increased. This leads to expansion of the liquor spaces. The volume of the skull can only be changed in infants in the first months of life (as long as there are fontanelles and the interosseous sutures have not fused), therefore the expansion of the spaces where the cerebrospinal fluid circulates forces the brain to decrease in size.
Hydrocephalus is water on the brain. In the process of brain activity, metabolic processes occur. For their implementation, liquid is required. It contains essential nutrients. It circulates inside the skull, washing the brain, and is constantly renewed.
The liquid is called cerebrospinal fluid. The child's volume is 50 ml. In adults, this figure is 3 times higher (120-150). It is constantly updated. In infants - 8 times a day, in adults - 3. The hematopoietic system, spinal cord and brain are involved in production. In the brain, the ventricles are responsible for the renewal function. The veins in the parietal region are responsible for absorption.
Liquor nourishes and protects the brain from mechanical shocks and injuries, and creates the necessary microenvironment. It maintains the pressure necessary for life, which ranges from 70 to 180 mm Hg. Art. If changes occur in the body, circulation is disrupted and fluid is poorly absorbed. The amount of liquid increases. Hydrocephalus in a child occurs from an excess of cerebrospinal fluid in the skull.
Probable Causes
Trauma during childbirth can cause hydrocephalus
The main factors influencing the development of the disease include:
- previous intrauterine infections;
- inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system;
- birth, as well as head injuries in the postpartum period;
- brain tumor.
You need to know that the reasons why hydrocephalus occurs may differ depending on the age of the child.
- In the fetus during intrauterine development:
- almost always this is a developmental defect of the nervous system;
- less often - genetic pathologies;
- infections during the prenatal period.
- In newborns:
- in almost 81% of all cases it is the result of infections during the prenatal period, in particular malformations of the brain, both spinal and brain;
- birth trauma causing the development of meningitis is less common;
- result of intracranial hemorrhage;
- even more rarely, vascular defects;
- tumors.
- For children over one year of age:
- spinal or brain tumors;
- consequences of meningitis;
- result of hemorrhages;
- consequences of traumatic brain injury;
- genetic problems;
- malformation of blood vessels or the brain itself.
You can separately consider the causes of infectious and non-infectious nature.
Infectious include:
- herpes;
- rubella;
- cytomegalovirus infection;
- neurosyphilis;
- Pneumococcus;
- toxoplasmosis;
- meningococcus;
- parotitis;
- Haemophilus influenzae.
Defects that cause hydrocephalus include:
- Dandy-Walker syndrome;
- a narrowed canal that connects the brain to the ventricles;
- Arnold Chiari syndrome;
- congenital underdevelopment of the openings necessary for the outflow of fluid;
- cerebral vascular abnormality.
Oncological processes:
- papillomas;
- vascular plexus meningiomas;
- skull tumors;
- brain, brain or spinal cancer;
- oncology of the cerebral ventricles.
Factors that place a child at risk are also identified:
- birth of the baby before the beginning of the 35th week;
- newborn weight up to 1.5 kg;
- narrow pelvis of the expectant mother;
- the use of special instruments during labor, for example, forceps or a vacuum;
- asphyxia or hypoxia of the fetus at the time of birth;
- the presence of intrauterine diseases due to infectious pathologies suffered by the expectant mother, in particular toxoplasmosis or mononucleosis;
- the presence of bad habits in a woman during pregnancy.
Possible complications
If left untreated, the disease will progress in most cases. This can lead to negative consequences, including death to the patient.
The main complications of hydrocephalus:
- cerebral edema,
- Brain displacement
- Epileptic seizures,
- Coma,
- Stroke,
- Respiratory failure.
With hydrocephalus in infants, the formation of new brain tissue slows or stops. And this leads to a lag in the mental, mental and emotional development of the child.
Parents should understand that hydrocephalus of the brain in children under one year of age affects the excessive formation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain area, which creates disruptions in the natural processes of nervous activity. This disease causes increased intracranial pressure, which contributes to disruption of brain nutrition, slowing down the blood circulation process, which means that the cells of the main organ of the nervous system may die.
In addition, the disease can be complicated by a congenital severe form of this disease.
Hydrocephalus of the brain in children, consequences of the disease:
- disability in the baby: cerebral palsy, delay in the development of fine and gross motor skills, convulsive condition, physical incapacity may be observed;
- mental retardation, mental disorders, degrees of debility, personality disorders may be observed, in 10% of cases attacks of anger, irritation, and euphoria are possible;
- speech impairment, visual impairment, hearing loss due to brain damage.
When there is an urgent need for surgical intervention, the risk of consequences cannot be excluded:
- epileptic seizures;
- hematoma formation;
- shunt dysfunction;
- pseudocysts;
- lethal outcome when seeking help late.
Treatment
Treatment of hydrocephalus in children can be conservative and surgical. Conservative treatment is effective in cases with open, non-progressive hydrocephalus.
In order to reduce the production of cerebrospinal fluid and improve cerebrospinal fluid dynamics in children, it is allowed to use diacarb (acetazolamide), furosemide (Lasix), mannitol, glycerin (convenient because it is taken orally). If there is no effect from taking medications, as well as in cases where the disease progresses, in the presence of closed hydrocephalus, surgical treatment is indicated.
External ventricular drainage is performed in urgent cases when increasing symptoms of increased intracranial pressure threaten the child’s life.
If the cause of the disturbance in the flow of cerebrospinal fluid is a tumor or hematoma, then its removal is indicated, which in itself allows restoring normal cerebrospinal fluid dynamics.
CSF shunting operations (ventriculoperitoneal, ventriculoatrial, lumboperitoneal shunting) are routinely performed. With the help of systems of tubes and valves, it is possible to drain excess cerebrospinal fluid from the brain into the body cavity (abdominal, pelvic, atrium). Of course, these are very traumatic operations, but if they are performed successfully, the child gets the opportunity to live a full life and does not suffer from physical and intellectual development.
Prevention
In order to minimize the chance of developing hydrocephalus, follow these rules:
- Protect your child from head injuries in every possible way: wear helmets for rollerblading/scooter/bicycle skating, carry him in a car seat, and do not walk in places where there is a danger of injury.
- During pregnancy, a woman should be examined for the TORCH complex of infections, followed by consultation with an infectious disease specialist.
- If ARVI, rubella or any other disease occurs during pregnancy, additionally undergo an ultrasound scan of the fetus and consult with a medical geneticist and infectious disease specialist about the further management of the period of gestation.
- It is imperative to undergo routine examinations by a neurologist, ultrasound or MRI if the child was born premature.
- The previous rule applies to conditions after meningitis, meningoncephalitis, intracranial hemorrhages, and head injuries. Do not neglect visiting a doctor.
- Protect your baby from head injuries.
- During the period of bearing a child, it is necessary to undergo examination for TORCH - infections.
- If during pregnancy the expectant mother becomes infected, for example, with rubella or she gets sick with ARVI, then it is recommended to undergo an additional ultrasound examination and also visit an infectious disease specialist and a geneticist.
It is important to visit a neurologist, MRI or ultrasound if your baby was born prematurely or if he suffered an intracranial hemorrhage, meningoencephalitis, head injury or meningitis.
Now you know what hydrocephalus is in a child and the symptoms of the disease. Remember that by following simple preventive measures, you can prevent the development of pathology. The task of parents is to notice the disturbance in the baby’s body in time and take him to a doctor’s appointment in a timely manner.
Diagnostics
A child with signs of hydrocephalus should be seen by a doctor immediately. To establish a diagnosis and the cause of why there may be excess water in a child’s head, doctors recommend conducting a thorough examination, including ultrasound, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, and measurement of intracranial pressure.
Risk factors for hydrocephalus in a child
The risk increases:
- in prematurely born children;
- in infants weighing up to 1500 g;
- if the woman in labor has a narrow pelvis;
- forceps and vacuum were used during childbirth;
- oxygen starvation of the fetus;
- intrauterine diseases of internal organs;
- bad habits of a woman in labor;
- past infections of the expectant mother.
The likelihood of developing hydrocele in utero is influenced by many things, but primarily by unfavorable conditions for fetal development. These factors include Rh conflict between mother and fetus.
To be fair, it is worth noting that not every Rh-conflict pregnancy ends in the birth of a child with congenital hydrocephalus. However, if the mother has a negative Rh factor, and the baby is positive, and the antibody titer in the woman’s blood is high, then doctors will definitely consider this possibility.
Risk factors include infectious diseases that a woman can contract during pregnancy.
Often, hydrocephalic changes are closely related to a concomitant diagnosis of genetic disorders in the fetus. Often children with Down, Turner, and Edwards syndromes appear with severe congenital hydrocephalus.
Preeclampsia also poses a certain danger during pregnancy; diabetes mellitus, as well as severe anemia in the expectant mother, can also play a role. If you are pregnant with twins and the child is diagnosed with gross malformations of the heart, circulatory system, or kidneys, the risk of having a hydrocephalus increases.
For boys and girls, the postnatal period is also important in the prospect of hydrocephalus. Premature birth, a long anhydrous period, rapid labor, during which the baby may experience cerebral hemorrhages, are dangerous. Some birth injuries, infection in early newborns with meningitis and encephalitis can also cause the development of hydrocephalus.
Can dropsy cause other diseases?
As medical practice shows, after dropsy, children often develop infectious diseases of the reproductive and urinary system. The disease can also lead to decreased potency, premature ejaculation, or even unintentional erection.
But this only applies to those cases where the child has been diagnosed with a chronic form of the disease. However, it will be possible to identify all these problems only after puberty, when the prostate gland and pituitary gland begin to more actively synthesize sex hormones. And this occurs around 11-14 years.
As for varicocele (varicose veins of the venous node of the scrotum), these diseases have little in common with dropsy, despite similar symptoms. Dropsy can become a provoking factor for varicocele, but does not lead to its appearance. Varicose veins are a consequence of internal thrombosis of blood vessels or plaques entering them that impair blood flow.
Forecasts
The prognosis is influenced by timely diagnosis and therapeutic treatment. A child with such a diagnosis will be healthy and develop well. If therapy was carried out late in infancy, this subsequently affects his mental and physical development.
There are no universal prognoses for hydrocephalus in children. Everything is individual, and there are as many forecasts as there are patients themselves. The most positive prognosis is given with great caution to children with communicating hydrocephalus. With occlusive dropsy, cure without consequences does not happen so often.
Congenital hydrocephalus, if detected in time, is faster and easier to treat than an acquired disease. Hydrocephalus of the first degree is less likely to leave irreversible consequences than extensive and severe cerebral hydrocephalus. The prognosis is more positive the earlier doctors identified the disease and the sooner medical assistance was provided.
Unfortunately, a large number of children who have suffered severe forms of hydrocephalus subsequently develop debility, mental retardation, and mental and personality disorders. Among the lesions of the nervous system, the leading ones are cerebral palsy, as well as lack of coordination of movements.
Children whose parents treat diligently and consciously live much longer than abandoned children with congenital hydrocephalus. Dropsy of the brain is curable. Only the consequences of the disease can be total.
How long and how a child with hydrocephalus will live depends on the cause and type of the disease, as well as the time during which the diagnosis was made. Communicating forms of hydrocephalus have a more favorable prognosis, and congenital, timely diagnosed pathology is easier than acquired.
If treatment is started on time and adequate surgery is chosen, the child’s life continues, but its quality may suffer when various restrictions appear associated with impaired speech, vision, movement, hearing or coordination.
The prognosis for hydrocephalus depends on how quickly and promptly the diagnosis is made and treatment is started. Children with hydrocephalus can live a normal life, although they may face some problems with the maintenance of their shunts. If treatment of the disease in an infant is not started in a timely manner, then its development threatens the child with developmental delays, speech impairment, as well as irreversible changes in the brain leading to disability.
Classification of disease and varieties
By origin, hydrocele in a newborn can be congenital or acquired. The first type is detected in patients in the first month of life. Diagnose:
- acute form – duration does not exceed 3 days;
- subacute – the development period ranges from 3 months to six months;
- chronic - the length varies from 6 months to one year.
In addition, experts classify several types of dropsy of the brain.
Communicating dropsy
The process is characterized by excessive formation of fluid, while it is not able to be absorbed in optimal quantities. The circulation of cerebrospinal fluid is not disrupted. The process is associated with diagnosing metastases of cancer in a patient, identifying sarcoidosis, detecting meningitis or various types of hemorrhages.
Closed hydrocephalus
It occurs due to blockage through cystic formations, scars, and as a result of hemorrhages.
Depending on the location of the pathological focus, the disease can be external or internal. The first type is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in special expansions at the base of the brain, and the second - directly in the ventricles. In case of timely treatment of dropsy, the chance of minor damage to vital processes increases significantly. This gives a good prognosis for subsequent recovery.
The classification of pathology is also carried out on the basis of the manifestation of certain disturbances of processes in the brain:
- compensated - the disease is detected without accompanying symptomatic signs and manifestations, while the child’s development occurs without any deviations;
- decompensated – clearly expressed violations of the patient’s general health are detected.
Based on the severity of the identified deviations, hydrocephalus is distinguished between moderate (minor deviations from normal values) and severe (significant increase in the cerebrospinal fluid tract and brain substance).
Rehabilitation
Even after successful treatment, the child will need several years of rehabilitation.
There, speech therapists, neurologists, and massage therapists work with the child. Chinese clinics that practice laser therapy sessions show excellent results in treatment and rehabilitation. There are also rehabilitation centers in Israel.
In Russia and abroad there are many sanatoriums that are ready to accept children from 2-3 years old - after undergoing bypass surgery or endoscopic plastic surgery of the ventricles of the brain.
Courses in rehabilitation centers and trips to sanatoriums do not replace daily intensive training with such children, because they require much more attention and patience.
How does the disease manifest?
In children under 2 years of age
In children under 2 years of age, the presence of the first signs will indicate the presence of hydrocephalus. This:
- deterioration of appetite and sleep;
- refusal of breastfeeding;
- moodiness, nervousness;
- decreased vision, squint, rolling of the eyeball;
- thin, shiny skin of the head with pronounced blood vessels;
- abnormal size of the skull;
- convulsions;
- muscle weakness;
- difficulty holding the head;
- growth retardation.
An experienced doctor will be able to identify dropsy based on the presence of minor symptoms. For minor problems, medication treatment is sufficient. For more severe symptoms, surgery is necessary.
It happens that the disease begins later. The symptoms are characterized by intracranial pressure. The child has:
- severe pain in the head;
- vomit;
- violation of movement coordination;
- fatigue and drowsiness;
- nervousness;
- vision loss and blindness.
School-age children do not adapt well to a group, have difficulty understanding the program, study poorly, and lose their memory. They suffer from nervous disorders. The causes may be various types of lesions:
- tumors;
- meningitis;
- aneurysm;
- renal failure;
- heart and vascular disease;
- hypertension;
- skull injuries.
Signs of hydrocephalus differ between children under 2 years of age and older children.
In children under 2 years of age
At this age, congenital hydrocephalus usually appears. This pathology is severe, the child’s condition quickly deteriorates, and damage to brain structures develops. In some cases, hydrocephalus is a consequence of meningitis or encephalitis, then it has a chronic course.
The peculiarity of the course of the disease in children of this age is due to the fact that the bones of the skull at this age are not yet tightly fused and can move relative to each other, making it possible for additional volume to appear in the skull for an increased amount of fluid. Therefore, the main symptom is an enlargement of the head, which progresses: more than 1.5 cm per month for at least 3 months in a row and more than 9 mm from 3 to 12 months of life.
A child is normally born with a head circumference that is 1-2 cm larger than the chest circumference; by 6 months the ratio should change. If the head remains larger than the chest, it may indicate hydrocephalus.
| Child's age | Normal head circumference, cm |
| Up to 29 days of life | 34-35 |
| 1 month | 36-37 |
| 2 months | 38-39 |
| 3 months | 40-41 |
| 6 months | 43-44 |
| 9 months | 45-46 |
| 12 months | 46-47 |
| 24 months | 48-49 |
| 3 years | 49 |
Other symptoms will be:
- blue-green veins are visible on the frontal, temporal and occipital parts of the head;
- the child is capricious, whiny, sleeps poorly;
- the baby is not gaining weight well;
- after 3 months he begins to hold his head up;
- does not know how to smile;
- begins to sit up late, crawl, walk;
- the skin on the head becomes thin and shiny;
- a pliable place at the top of the head - the fontanel - protrudes above the bones of the skull and pulsates;
- forehead increased in size;
- the pupil cannot stay in one place when fixing the gaze - it will make wide or small fluctuations up and down or left and right;
- the brow ridges hang over the facial skull, making the eyes appear deep-set;
- divergent strabismus is noted;
- frequent regurgitation during feeding;
- throwing back the head;
- it is difficult to straighten your legs, they are bent at the knee joints;
- drooping eyelids;
- when blinking or looking down, a white stripe of sclera appears between the upper eyelid and the upper edge of the iris;
- the child eats little by little, sucks sluggishly, reluctantly.
With rapid progression, which requires immediate hospitalization in a children's multidisciplinary hospital, where there are departments of neurology and neurosurgery, the following signs appear:
- convulsions;
- vomiting;
- crying on one note;
- drowsiness;
- previously acquired skills (sitting, walking, tracking toys) are lost;
- the impossibility (complete or partial) of independent movements in the limbs may develop.
Cyst in the head - causes
Good afternoon, a neurosonography was done a month ago and showed that there was water in the baby’s head, the indicator was 5, they prescribed treatment with pantogams 3 times a day for a month, massage, electrophoresis and magnetic therapy, the treatment was carried out, we went and tested again, the intracranial pressure became 18 and was 7 and increased the amount of water increased to 11, the interhemispheric groove also increased, it was 5 now 7. Treatment was prescribed by a gastroenterologist because there was mucus in the stool and supposedly because of this the fluid could increase, they also prescribed massage, pantogam, and lingonberry leaf or knotweed. Is the treatment correct? Login Register. Questions about children's health. Hydroencephalopathy and High intracranial pressure in the infant.
Useful tips
- If a child has a confirmed diagnosis of hydrocephalus, there is no need to despair. After all, during this difficult period, the baby needs a strong, reasonable and self-possessed mother who will help him overcome the disease. There are many forums on the Internet for parents whose children have successfully recovered from hydrocephalus, and for those who are yet to do so.
- There is no need to look for those to blame; sometimes this illness does not depend in any way on the parents and their correct or incorrect actions.
- During pregnancy, you should definitely attend an antenatal clinic. Many studies and tests that are prescribed to expectant mothers will help you learn about risk factors in advance.
- Before pregnancy, a woman should visit an infectious disease specialist at least once to find out, by donating blood, what diseases she has suffered from, and what antibodies to what dangerous infections she has in her body.
- If during pregnancy (especially in the early stages) a woman gets sick with rubella, measles or another infection, she should definitely agree to additional studies of the fetus’s condition and visit a geneticist in order to make a further (very painful) decision about bearing a child. You need to know about the risks of pathologies and treatment during pregnancy.
- If a child was born prematurely, you should not miss a single mandatory medical examination or routine visit to the doctor.
- Babies over one year old should be protected from head injuries. If you bought him a bicycle, be sure to give him a helmet. If a child is transported in a car, then it is imperative to use a car seat.
- All viral infectious diseases that infect a child cannot be treated independently - according to grandmother’s recipes, viburnum and burdock. You should definitely consult a doctor, get tested, and take medications only as prescribed by a qualified doctor.
You will learn more about this disease from the video below.