Encephalopathy is a malfunction of the brain that can manifest itself in a person even before birth, or can develop as a result of exposure to unfavorable factors on the body. Brain cells die when oxygen metabolism is disrupted. This phenomenon does not occur on its own; it is most often caused by a malfunction of other organs.
Treatment of cerebral encephalopathy in adults is usually long-term, but if strictly adhered to, it helps restore the proper functioning of brain systems. Where does this problem come from? What are the signs of illness? Is there a classification of encephalopathy? Why do newborns suffer and which stages and forms are most dangerous? Let's try to answer these important questions.
What is encephalopathy and what happens?
Encephalopathy can be congenital (perinatal) or one that arises as a result of other pathologies in the body (acquired).
Where does it come from in people who are healthy from birth? Under the influence of certain unfavorable factors, brain cells are destroyed. Further, the brain structures fail and cannot perform their functions normally. This pathology does not occur on its own, but is caused by other reasons. In general, the disease develops slowly and is successfully treated in the early stages. If the root cause is diagnosed in time, therapy will have a positive result.
If the necessary measures are not taken, types of encephalopathy such as hepatic, diabetic or toxic will lead to serious consequences, including death.
The brain is very sensitive to lack of oxygen. Its functions are disrupted if oxygen is not supplied in sufficient quantities for several minutes.
Oxygen deficiency (in medicine this condition is called “brain tissue hypoxia”) inevitably leads to the loss of brain cells. A delay of more than 5 minutes in the supply of O2 results in brain death.
What you need to know about cardiopathy?
Cardiopathy refers to a number of non-inflammatory diseases in which reversible and irreversible inflammatory processes occur in the muscles of the heart. These diseases are usually not associated with rheumatism and heart defects.
- Basic information about the disease
- The occurrence of the disease in children
- Types of disease
- Symptoms
- Features of treatment
Basic information about the disease
There are several types of cardiopathy, each of which is based on specific causes. Among them, functional cardiopathy occupies a special place. Often this form of the disease develops in children, especially adolescents. The disease is characterized by aching pain in the heart area. The discomfort may pass quickly, but there are times when the pain continues for quite a long time. Sometimes they last for several days.
One of the diagnostic methods that detect cardiopathy is echocardiography. Treatment is carried out under the condition of absolute abstinence from alcohol. Women who have metabolic disorders due to dishormonal cardiopathy may experience problems with the functioning of the ovaries. In addition, the pain associated with this form of the disease is in no way related to physical stress on the body. The treatment process occurs with the help of adrenergic blockers and psychotropic substances.
In case of increased production of thyroid hormones, thyrotoxicosis cardiopathy may occur. In this case, the heart expands, the rhythm of work gets lost, and arrhythmia is also noted. During treatment, it is very important to restore normal functioning of the thyroid gland. This eliminates the failure of the heart muscles.
The occurrence of the disease in children
Cardiopathy in children is, unfortunately, a very common phenomenon. The disease can be either congenital or acquired during the period of growth and development of the body. Most often, the disease manifests itself in schoolchildren. When the cause of cardiopathy is a congenital heart defect, the first symptoms may appear immediately after birth.
While a teenager is growing, he experiences serious hormonal imbalances. This leads to increased fatigue, as well as slow metabolism of nutrients and ultimately to heart failure. Among the consequences, one should highlight a fairly common problem - sudden weight loss. Shortness of breath may also occur even when walking slowly.
To determine whether a child has heart problems, you should monitor him especially closely during and after outdoor play. If there is the slightest suspicion of cardiopathy, you should immediately consult a doctor. In addition, doctors recommend at least once a year an examination by a cardiologist, taking readings from an electrocardiogram. It is important to remember that it is not always possible to listen to the manifestation of a murmur in the heart. You should be extremely careful about stages such as extrasystole.
The appearance of cardiopathy is associated with problems such as:
- enlargement of the septum between the ventricles;
- defective development of the ventricles;
- anastomosis;
- stenosis;
- reduction of heart valves.
Types of disease
Today, medicine knows several types of cardiopathy. Most of them can occur in childhood. The most common:
- congenital;
- secondary;
- functional;
- dysplastic.
Functional cardiopathy is the child’s body’s response to increased physical activity. For example, it develops in schoolchildren who are taught physical education incorrectly. In this case, it is necessary to take into account both the age of each student and their level of preparation for certain types of loads. To prevent the disease at such a young age, you should correctly calculate the load that the child can withstand during classes.
Children suffering from rheumatism may also develop dysplastic cardiopathy. In general, this disease is not associated with the functional characteristics of the child’s body. It is characterized by damage to heart tissue, which is then replaced by new, inelastic fibers. Since the affected tissue does not have time to cope with its functional responsibilities, this can lead to a common phenomenon - heart failure.
Another type of disease is secondary cardiopathy. It is a consequence of a long-term cold. It can develop rapidly if there is chronic inflammation in the body. As a result, disease of any organ leads to secondary cardiopathy.
Mostly this syndrome is the main manifestation of diseases such as:
- asthma;
- myocarditis (including rheumatoid);
- endocarditis;
- pneumonia.
As a rule, secondary cardiopathy is much easier to identify than in other cases, since the child is continuously monitored for the cause of the primary disease.
Symptoms
Depending on how strong the destructive processes are, as well as where exactly the problem is localized and what its form is (for example, functional cardiopathy), symptoms can manifest themselves in different places and in different ways. It could be:
- weakness;
- rapid onset of fatigue;
- heartache;
- too rapid pulse;
- pale skin.
If the right heart is affected, pulmonary failure occurs:
- heavy sweating;
- dyspnea;
- edema;
- causeless cough;
- unpleasant heaviness near the heart.
Classification
Depending on what causes encephalopathy, its classification is different. A constant or acute lack of oxygen can be caused by:
- temporary stoppage of the heartbeat (as a result of which blood does not circulate properly throughout the body and oxygen supply is interrupted);
- respiratory dysfunction;
- improper blood circulation in the brain.
Toxic damage can be caused by the following factors:
- substances that poison the body for a long time (alcohol, potent medications, drugs);
- intoxication due to serious illnesses.
Any serious illness can lead to such an unpleasant complication as cerebral encephalopathy.
Description of the syndrome
Brain tissue is very dependent on the transport of oxygen along with the blood flow. If they do not receive proper nutrition, neurons are not able to survive more than 6 minutes. Nerve tissues are quite susceptible to toxic components produced by viruses and bacteria, or coming from the outside. Also, diffuse neuronal damage can be caused by dysfunctions of various organs.
This condition is also called psychoorganic syndrome. There are several types of them, differing depending on the reason why the massive death of brain neurons began. Symptoms and changes in the patient’s mental state are also important. According to etiology, the syndrome is classified as follows:
- Hypoxic. This condition is based on a lack of oxygen or metabolic disorders in the nerve cells of the brain. Such encephalopathy can be perinatal, occurring during the birth process, asphyxia, caused by suffocation, as well as post-resuscitation, that is, caused by resuscitation measures.
- Post-traumatic. Occurs immediately after brain injury or as a result of long-term consequences. An example is Marfan syndrome, an encephalopathy of people involved in boxing.
- Angioencephalopathy. This is a type of psychoorganic syndrome that occurs according to the dyscirculatory type. This condition develops with cerebral ischemia due to atherosclerosis or hypertension.
- Toxic. Occurs due to intoxication with toxic substances. These may be chloroform, lead compounds, carbon monoxide. Possible factors include the use of drugs, alcohol and a number of medications.
- Toxic-metabolic. It develops with the prolonged presence of toxic products in the body, when the process of their elimination and breakdown is disrupted, and also if they are produced in large quantities.
There are other variants of the course of the syndrome. Among them there are both basic and combined ones. Types can be distinguished:
- Apathetic. Accompanied by weakness, asthenia, and increased fatigue. As the syndrome progresses, a person may experience euphoria, emotional lability, decreased self-criticism, and disturbances in mental activity.
- Euphoric. Initially it leads to an increase in mood, a decrease in critical attitude towards oneself, the absence of inhibition and any barriers to communication.
- Explosive. Here there is affective lability, decreased criticism, increased irritability, excitability and rudeness. A person’s range of interests is narrowed, disturbances in adaptation and the phenomenon of sociopathy are observed.
The focal form is accompanied by damage to individual areas of brain tissue. Depending on the timing of the appearance of the first symptoms, congenital forms that formed during intrauterine development are classified. They appear with malformations of the central nervous system, metabolic disorders. Another form is acquired, when symptoms appear throughout a person’s life.
The most common types of brain dysfunction are encephalopathy and chronic ischemia. In older people, the syndrome can occur against the background of hemorrhage in brain tissue, stroke, or coronary artery disease. There are specific forms. For example, encephaloreconditioning occurs due to a lack of blood sugar. Disseminated encephalomyelitis is a type of autoimmune disease.
Types of pathology
Depending on the nature of the pathology, the following types are distinguished:
- Hypoxic. Formed when oxygen supply to the brain is intermittent. This may be congenital encephalopathy, post-resuscitation encephalopathy, or the result of suffocation.
- Toxic. This brain condition is provoked by frequent use of alcohol and/or drugs, treatment or abuse of potent medications, etc.
- Encephalopathy. It is the result of improper (too fast or slow) blood movement in the vessels of the brain. This is a common encephalopathy of the brain in the elderly.
- Metabolic encephalopathy. This type of disorder is triggered by various ailments that lead to the formation of toxic breakdown products. Depending on the location of the disease, such encephalopathy can be hepatic, bilirubin, or uremic. Diabetes can also be the root cause of this pathology - it causes a hypo- or hyperglycemic form of the pathology.
- Post-traumatic. This encephalopathy in adults is usually triggered by external damage to the skull and brain (trauma and/or concussion).
- Radial. Disturbance due to harmful radiation.
Reasons for the development of the disease
Damage, destruction of brain cells, leading to metabolic disorders and cerebral circulation, is caused by various reasons. The factors that lead to gray or white matter damage may differ between children and adults.
In adults
Brain encephalopathy in an adult can be caused by:
- Hypoxia. Oxygen starvation leads to the death of brain cells. Lack of oxygen can be caused by cardiac arrest, impaired blood flow (due to the formation of a blood clot), mechanical suffocation, or impaired ventilation.
- Poisoning. Toxic substances that have a long-term effect on brain cells lead to their death and pathological vasoconstriction. Negatively affect blood vessels: nicotine, alcohol, drugs, internal toxins that are not eliminated from the human body in the usual way (for example, when the urinary system is disrupted).
- Impaired blood flow. Impaired cerebral circulation occurs due to narrowing and stenosis of blood vessels caused by atherosclerosis, thrombosis, and varicose veins.
- Traumatic brain injury. Concussions and open skull fractures also cause the death of gray cells and disruption of nerve connections in the head.
- Irradiation. Exposure of the brain to ionizing radiation can lead to encephalopathy.
Elderly people are most often susceptible to this pathology. Certain categories of patients are at risk:
- Athletes: football players, karatekas, boxers.
- Patients with alcohol, drug, nicotine addiction.
- HIV-infected.
- Diabetics.
With encephalopathy, the number of nerve cells in the brain decreases and tissue necrosis develops. If encephalopathy is not treated, as a result of ischemia, the gray matter swells and internal hemorrhages appear.
In children
Why does encephalopathy occur, what kind of disease is it? The development of pathology can begin even before the baby is born.
During pregnancy, damage to the gray matter is provoked by:
- Infectious colds suffered by the mother: rubella, chickenpox, measles, swine flu.
- Stressful situations, neuroses, depressive states.
- Smoking, alcohol addiction in a pregnant woman.
- Severe toxicosis, gestosis.
- Chronic diseases of a pregnant woman: diabetes, kidney failure.
- Insufficiency of placental and uterine circulation.
- Intrauterine infections.
The baby's brain cells can be damaged during childbirth:
- During rapid labor.
- If labor is delayed, it lasts longer than a day.
- If the child experiences a long period of waterlessness.
- In case of premature birth.
- With placental abruption.
- If the child is subjected to mechanical asphyxia, entanglement with the umbilical cord.
In the first week of a baby's life, the cause of encephalopathy can be brain damage that causes:
- Infection.
- Disease of the child's circulatory system.
- Head injury.
- Surgical interventions.
The threat of miscarriage, uterine hypertonicity, and low water levels can provoke a disruption of the intrauterine blood supply to the baby’s brain and lead to the development of pathology. Trauma to the child's head during childbirth, by decision of specialists, is excluded from the list of factors leading to encephalopathy.
The disease is diagnosed by a neonatologist in the maternity hospital or by a pediatrician during examination of the baby. To clarify the diagnosis, a survey of the mother is conducted. To assess the severity of encephalopathy, a number of studies are carried out:
- General, biochemical blood test for gas composition.
- Analysis of the composition of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Ultrasound of the brain.
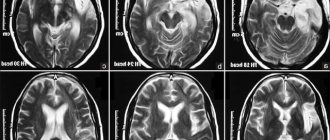
- MRI of the head.
- Dopplerography of the vessels of the brain and neck.
- EEG of the brain (if there is severe convulsive syndrome).
The newborn is examined by a neurologist, and an ophthalmologist examines the condition of the fundus. Based on the examination results, a diagnosis is made and treatment for encephalopathy is prescribed.
Forms of pathology
The following forms of pathology are also distinguished:
- Focal encephalopathy is a disease that affects specific areas of the brain. It can go unnoticed in the initial stages, especially if the patient has a weakened immune system;
- angioencephalopathy of the brain is formed due to chronic hypoxia caused by constant disruption of blood circulation. It is typical for adults, and the symptoms are often mild;
- encephalopathy in newborns can occur in the womb or during childbirth;
Perinatal encephalopathy can be triggered by unfavorable circumstances that affect the development of the fetus:
- prolonged and incurable illnesses of the mother (heart pathologies, kidney inflammation, diabetes, etc.);
- infectious and viral diseases that a woman suffered during pregnancy (for example, pneumonia);
- regular use of alcohol and drugs during pregnancy, smoking;
- excessive nervousness;
- placental insufficiency in chronic form;
- problems with pregnancy.
As you can see, the problem can arise at any stage of a person’s life.
PE in babies
Often, signs of such a pathology appear immediately after experiencing hypoxic shock.
PE in babies
There is also congenital PE, which is associated with poor blood supply to the brain in the womb, during labor or after it. The main reasons that can cause this disease are neuroinfections (diseases affecting the nervous system that could be caused by infectious agents), hypoxia, trauma during childbirth, and fetal intoxication. The most common cause of this pathology is cesarean section.
Read: You need to get tested for hidden infections to make sure you are healthy
Many experts claim that this disease is the main cause of neurological pathologies in children, but not many agree with this.
In some cases, this pathology resolves without serious complications, but often it carries serious consequences, namely hydrocephalus and cerebral palsy. The disease provokes an increase in intracranial pressure, which subsequently leads to epilepsy and brain dysfunction.
Often, the severity of the baby’s damage is assessed using the Apgar score and the presence of the baby’s original feces in the amniotic fluid.
Perinatal PE can often be detected from the first day of a baby’s life, primarily by disturbances in motor activity. There are three degrees of severity of the pathology. Below we will describe each of them in more detail with symptoms.
Mild degree of PE:
- Increased muscle tone
- Drowsiness
- Anxiety
- Weak sucking reflex
- Irritability
As a rule, after a few days, such signs return to normal.
Severe degree of pathology:
- The baby is in a state of lethargy, i.e. he is too lethargic, muscle tone is significantly reduced
- Severely reduced sucking and grasping reflex
- The baby may experience respiratory arrest
- Seizures occur
After two weeks, slight improvements may be observed, but after this period a sharp deterioration may follow. Severe cramps may occur.
Severe degree of pathology:
- The child does not respond to stimuli
- The baby is in a stupor or coma
- Because breathing is irregular, you may need a ventilator
- Decreased muscle tone
- Severely reduced tendon reflex
- Lack of normal reflexes
- Examination of cranial nerves may detect oculomotor disorders
Cramps occur early and are extremely intense and conventional treatments have no effect on them. There is a gradual depression of consciousness, the fontanel becomes tense and this may indicate cerebral edema.
If your baby has been diagnosed with PE, you should not become hysterical.
It is important to understand that this disease can be prevented rather than treated in the future. It is recommended to prevent this pathology in babies during pregnancy.
During this period, a woman needs to lead a correct lifestyle:
- Stick to proper nutrition
- Take air baths for at least an hour a day
- Adhere to personal hygiene rules
Very often, the cause of PE in a baby is the mother’s incorrect behavior:
- Excessive abuse of alcohol, drugs
- Use of certain medications
- Exposure to toxic substances
In addition, there are other factors that can influence the occurrence of this disease:
- The baby was born too early or too late
- Abortions and miscarriages
- Long-term therapy for infertility
- Women's diseases
- Risk of miscarriage
Now good results have been achieved in this direction, but, contrary to this, this pathology in children occurs with a frequency of approximately two cases per 1000 children.
Read: Rash on the labia and its possible causes
Encephalopathy in children under one year of age: comments from a neurologist on video.
Risk of acquiring encephalopathy during childbirth and the first weeks of life
Encephalopathy can also occur during childbirth as a result of:
- asphyxia of the newborn;
- prolonged waterless period;
- long or too rapid labor process;
- premature separation of the placenta;
- child swallowing intrauterine fluids.
The first week of life is a period when the body, and the brain in particular, is especially sensitive to external and internal negative factors. If the child’s body has been affected by a virus or infection these days, this can lead to a malfunction such as encephalopathy, the consequences of which can bother the person throughout his life. Also, pathology can form some time after the operation, if one has taken place.
How the disease manifests itself at different stages
Symptoms of encephalopathy are often similar to signs of other diseases or to a temporary deterioration in well-being due to changing weather - headache, depression, dizziness, etc. Therefore, it is difficult to recognize the pathology and there is a risk of triggering the disease, which can lead to serious complications and even death.
For a disorder such as cerebral encephalopathy, symptoms vary - much depends on the form in which the disease manifests itself and the severity.
Patients experience encephalopathic syndrome, which has common symptoms:
- frequent mood swings;
- weakness and malaise;
- constant fatigue;
- irritability;
- depression;
- sleep problems;
- confusion;
- forgetfulness;
- tearfulness;
- suicidal tendencies.
During a conversation, the patient has difficulty pronouncing words, in life he is apathetic and lacking initiative, constantly wants to sleep (regardless of the time of day).
Rare symptoms
The disease encephalopathy, in addition to general symptoms, in different forms and stages is accompanied by various signs:
- In the first stage of toxic encephalopathy, the patient experiences a loss of coordination of movements, he is aggressive, restless and excited. This may cause hallucinations and seizures. Further, if the pathology is not detected in time, it all develops into lethargy, confusion, and drowsiness. For someone who suffers from this form of the disease, in an advanced stage, reflexes may disappear over time, which is why adynamia develops. Mental disorders occur, which manifest themselves in the form of delusions and hallucinations. The patient may suffer from epilepsy.
- Discirculatory encephalopathy can also progress. Initially, the patient feels discomfort and pain in the head, which may be accompanied by dizziness and tinnitus; constant anxiety and fatigue. Such a patient has poor performance and memory, he suffers from insomnia or, conversely, increased drowsiness. Hypertension occurs from time to time. At the end of the day, all unpleasant sensations intensify and are temporarily absent after rest. Then the patient only gets worse - he often loses consciousness, suffers from epileptic seizures, walking gets worse, he feels fear and cannot absorb information. Encephalopathic syndrome is manifested by a decrease in intelligence, as a result of which dementia progresses - a process irreversible for the brain.
- Angioencephalopathy, if left untreated, usually leads to inhibition of higher brain processes. This leads to dementia (dementia), disorientation in space, deterioration of vision, speech, swallowing, etc. This form rarely occurs in the form of epilepsy or deterioration of the vestibular apparatus.
- Metabolic encephalopathy of the brain. This disease is expressed by confusion, systematic and uncontrollable absent-mindedness, and constant interruptions in sleep. A person who suffers from this type of brain encephalopathy cannot adequately perceive the world around him. The disease in an advanced state can lead to the development of coma.
- Post-traumatic encephalopathy of the brain is characterized by the following symptoms: unreasonable and sudden changes in behavior, absent-mindedness, amnesia or memory distortion, complications of thought processes, mental regression. This type of disease is dangerous because symptoms may not appear immediately (the so-called latent course).
In the advanced stage of a disease such as encephalopathy, the symptoms become more vivid.
Symptoms and signs
The clinical picture of encephalopathy can be very variable and largely depends on the nature of the pathological process that led to brain damage. The most common symptoms in patients with this pathology are:
- dizziness;
- headache;
- irritability and mental instability;
- sleep disturbance;
- noise in the head;
- memory loss;
- increased fatigue;
- loss of ability to concentrate;
- narrowing the range of interests;
- tendency to depression or, on the contrary, to euphoria and disinhibition with a lack of criticism of one’s condition;
- personality change;
- disruption of innervation of various areas of the body;
- hand tremors;
- sexual function disorder;
- violation of facial expressions and sound pronunciation;
- movement coordination disorder;
- the appearance of pathological reflexes;
- decreased hearing and vision;
- disorders of consciousness.
Diagnostics
It is carried out using a number of instrumental techniques:
rheoencephalography is a non-invasive examination method that allows you to obtain information about the condition of the walls of the blood vessels in the brain. Carrying out an REG is a simple way to obtain sufficient information about the functioning of the arterial and venous vessels of the central nervous system;- Doppler ultrasound is a safe and highly informative method for diagnosing vascular disorders underlying the development of encephalopathy. When performing ultrasound examination, the specialist pays special attention to the study of the carotid, vertebral, subclavian and main arteries of the brain;
- MRI is an indispensable method for examining patients with signs of encephalopathy. To obtain complete information for certain clinical symptoms, it may be necessary to perform MRI of the vessels of the brain, head and neck (MRI angiography), cranial nerves, pituitary gland, eyeball, orbits. MRI tractography makes it possible to detect pathology of the white matter of the brain caused by congenital and acquired diseases;
- diagnosis of the underlying disease - undoubtedly, in order to prescribe effective treatment, it is necessary to determine the exact cause of the development of encephalopathy. For this purpose, the clinic uses a wide variety of research methods, from a general blood test to a liver biopsy.
Perinatal encephalopathy
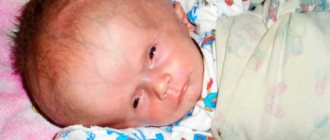
Encephalopathy of the brain - what is it and what does it look like in newborns?
In children who have just been born, the characteristic features of the disorder look like this:
- With a mild degree of encephalopathy, the baby is too excitable. This is reflected by poor sleep, restless loud crying, loss of appetite (the baby is reluctant to take the breast), increased (or decreased) muscle tone. Some children at this stage of the disease even have slightly slanted pupils towards each other.
- The average severity of the disease is characterized by more obvious symptoms - a syndrome of depression of the nervous system and motor disorders. In addition, infants suffer from seizures, decreased muscle tone, and hydrocephalus. Despite the fact that general muscle activity is reduced, the flexor muscles of the arms and legs, on the contrary, are overly tense, so the limbs of such a child are constantly bent. Externally, you can notice strabismus, marbling of the skin and a large fontanel that pulsates intensely. The baby sleeps little and eats poorly, or refuses to eat at all, screams from time to time in his sleep, and cries for a long time.
- In severe cases, brain functions fail and the child may fall into a coma.
Course of PEP and possible prognosis
During PEP, three periods are distinguished: acute (1st month of life), recovery (from 1 month to 1 year in full-term infants, up to 2 years in premature infants) and outcome of the disease. In each period of PEP, various syndromes are distinguished. More often there is a combination of several syndromes. This classification is appropriate, since it allows us to distinguish syndromes depending on the age of the child. For each syndrome, appropriate treatment tactics have been developed. The severity of each syndrome and their combination make it possible to determine the severity of the condition, correctly prescribe therapy, and make prognoses. I would like to note that even minimal manifestations of perinatal encephalopathy require appropriate treatment to prevent adverse outcomes.
Let us list the main syndromes of PEP.
Acute period:
- CNS depression syndrome.
- Comatose syndrome.
- Syndrome of increased neuro-reflex excitability.
- Convulsive syndrome.
- Hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome.
Recovery period:
- Syndrome of increased neuro-reflex excitability.
- Epileptic syndrome.
- Hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome.
- Syndrome of vegetative-visceral dysfunctions.
- Movement impairment syndrome.
- Psychomotor development delay syndrome.
Outcomes:
- Full recovery.
- Delayed mental, motor or speech development.
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (minimal brain dysfunction).
- Neurotic reactions.
- Autonomic-visceral dysfunctions.
- Epilepsy.
- Hydrocephalus.
- Cerebral palsy.
All patients with severe and moderate brain damage require hospital treatment. Children with mild impairments are discharged from the maternity hospital under outpatient supervision by a neurologist.
Let us dwell in more detail on the clinical manifestations of individual PEP syndromes, which are most often encountered in outpatient settings.
The syndrome of increased neuro-reflex excitability is manifested by increased spontaneous motor activity, restless shallow sleep, prolongation of the period of active wakefulness, difficulty falling asleep, frequent unmotivated crying, revival of unconditioned innate reflexes, variable muscle tone, tremor (twitching) of the limbs and chin. In premature infants, this syndrome in most cases reflects a lowering of the threshold for convulsive readiness, that is, it indicates that the baby can easily develop convulsions, for example, when the temperature rises or when exposed to other irritants. With a favorable course, the severity of symptoms gradually decreases and disappears within a period of 4-6 months to 1 year. If the course of the disease is unfavorable and there is no timely treatment, epileptic syndrome may develop.
Convulsive (epileptic) syndrome can manifest itself at any age. In infancy it is characterized by a variety of forms. An imitation of unconditioned motor reflexes is often observed in the form of paroxysmal bending and tilting of the head with tension in the arms and legs, turning the head to the side and straightening the arms and legs of the same name; episodes of shuddering, paroxysmal twitching of the limbs, imitations of sucking movements, etc. Sometimes it is difficult even for a specialist to determine the nature of the convulsive conditions that arise without additional research methods.
Hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome is characterized by excess fluid in the spaces of the brain containing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which leads to increased intracranial pressure. Doctors often call this disorder to parents exactly that - they say that the baby has increased intracranial pressure. The mechanism of occurrence of this syndrome can be different: excessive production of cerebrospinal fluid, impaired absorption of excess cerebrospinal fluid into the bloodstream, or a combination of both. The main symptoms of hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome, which doctors focus on and which parents can control, are the rate of increase in the child’s head circumference and the size and condition of the large fontanel. For most full-term newborns, the normal head circumference at birth is 34 - 35 cm. On average, in the first half of the year, the monthly increase in head circumference is 1.5 cm (in the first month - up to 2.5 cm), reaching about 44 cm by 6 months. In the second half of the year, the growth rate decreases; by one year, head circumference is 47-48 cm. Restless sleep, frequent profuse regurgitation, monotonous crying combined with bulging, increased pulsation of the large fontanel and throwing the head back are the most typical manifestations of this syndrome.
However, large head sizes often occur in absolutely healthy babies and are determined by constitutional and family characteristics. The large size of the fontanel and the “delay” in its closure are often observed with rickets. The small size of the fontanel at birth increases the risk of intracranial hypertension in various unfavorable situations (overheating, increased body temperature, etc.). Carrying out a neurosonographic examination of the brain makes it possible to correctly diagnose such patients and determine treatment tactics. In the vast majority of cases, by the end of the first six months of a child’s life, normal growth of head circumference is noted. In some sick children, hydrocephalic syndrome persists by 8-12 months without signs of increased intracranial pressure. In severe cases, the development of hydrocephalus is noted.
Comatose syndrome is a manifestation of the serious condition of the newborn, which is assessed by 1-4 points on the Apgar scale. Sick children exhibit severe lethargy, decreased motor activity up to its complete absence, and all vital functions are depressed: breathing, cardiac activity. Seizures may occur. The severe condition persists for 10-15 days, with no sucking or swallowing reflexes.
The syndrome of vegetative-visceral dysfunctions, as a rule, manifests itself after the first month of life against the background of increased nervous excitability and hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome. Frequent regurgitation, delayed weight gain, disturbances in cardiac and respiratory rhythm, thermoregulation, changes in the color and temperature of the skin, marbling of the skin, and dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract are noted. Often this syndrome can be combined with enteritis, enterocolitis (inflammation of the small and large intestines, manifested by stool upset, impaired weight gain), caused by pathogenic microorganisms, with rickets, aggravating their course.
The syndrome of movement disorders is detected from the first weeks of life. From birth, a violation of muscle tone can be observed, both in the direction of its decrease and increase, its asymmetry can be detected, and there is a decrease or excessive increase in spontaneous motor activity. Often the syndrome of motor disorders is combined with a delay in psychomotor and speech development, because disturbances in muscle tone and the presence of pathological motor activity (hyperkinesis) interfere with purposeful movements, the formation of normal motor functions, and mastery of speech.
With delayed psychomotor development, the child later begins to hold his head up, sit, crawl, and walk. A predominant disorder of mental development can be suspected in the presence of a weak monotonous cry, impaired articulation, poor facial expressions, late appearance of a smile, and delayed visual-auditory reactions.
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a neurological disease that occurs as a result of early damage to the central nervous system. In cerebral palsy, developmental disorders usually have a complex structure, combining motor disorders, speech disorders, and mental retardation. Motor disorders in cerebral palsy are expressed in damage to the upper and lower extremities; fine motor skills, articulatory muscles, and oculomotor muscles suffer. Speech disorders are detected in most patients: from mild (erased) forms to completely unintelligible speech. 20 - 25% of children have characteristic visual impairments: convergent and divergent strabismus, nystagmus, limitation of visual fields. Most children have mental retardation. Some children have intellectual impairments (mental retardation).
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder is a behavioral disorder associated with the child's poor control of his attention. It is difficult for such children to concentrate on any task, especially if it is not very interesting: they fidget and cannot sit still calmly, and are constantly distracted even by trifles. Their activity is often too violent and chaotic.
Diagnostics
Congenital pathology is detected during examination of the child immediately after his birth. A neurologist, neonatologist or ophthalmologist may suspect abnormalities. Next, the baby may be referred for examination to a neurosurgeon, who will prescribe other examinations.
When diagnosing different types of encephalopathy, the possible causes of its occurrence and development are taken into account:
- congenital pathology;
- probable intoxication or radiation;
- possible metabolic failures as a result of liver and kidney disease;
- atherosclerosis;
- hypertension and vascular disorders;
- interruptions in the functioning of the respiratory system, etc.
What examinations do doctors prescribe?
First of all, this is electroencephalography, which is used to record the failure of the bioelectric rhythms of the brain and the presence of slow waves (pathological), as well as convulsive activity.
Another method of diagnosis and detailed examination of the patient is magnetic resonance imaging. In this way, the main signs of brain exhaustion, etc. are revealed.
A test of blood and other body fluids shows the amount of oxygen in the blood and the presence of toxic agents. This helps to identify the cause of the disease.
In addition, they prescribe:
- biochemical blood test - to determine blood lipid levels;
- a metabolic test that will show the level of electrolytes, oxygen and other gases in the blood;
- blood pressure measurement;
- drug test;
- Doppler ultrasound - monitoring blood circulation in the body, etc.
Treatment of posthypoxic disease
The methodology of therapeutic interventions is aimed at:
- Combating impaired blood circulation: restoring the volume of circulating blood, treating hypotension, avoiding vascular pinching.
- Treatment of neurological disorders: monitoring the functioning of restored areas of the brain.
- Treatment of symptoms that have developed against the background of cerebral hypoxia: disruption of the heart and other vital organs.
- Normalization of hypoergosis and blood chemical parameters.
To bring blood counts back to normal, antihypoxants are prescribed.
These include:
- Neotone;
- Mexico;
- Actovegin;
- combination drug Cytoflavin.
Also indicated for use are nootropic drugs to stimulate metabolism and antioxidants.
In addition to medications, you need to eat more foods rich in vitamin E, C, and fiber. Grapes, nuts, kiwi, and red berries have these properties. It is not recommended to drink drinks containing alcohol.
In pregnant women, existing diseases may worsen or pathologies to which there is a predisposition may arise. Encephalopathy in pregnant women occurs against the background of changes in the body of the expectant mother.
We will talk about the symptoms and treatment of dysmetabolic encephalopathy in this article.
You need to try to get more rest, often walk in the fresh air, and avoid nervous tension. Such measures significantly improve the condition of nerve cells, which is very important for recovery. Moderate physical activity also has a positive effect on health.
Therapy
Can encephalopathy be cured? Nowadays, doctors use various methods to treat this disease. It all depends on how early the diagnosis was made, the severity and age of the patient. For example, encephalopathy in older people is more difficult to treat, given the fact that metabolic and recovery processes in their bodies occur slowly. In addition, diagnosing the disease in older people is more difficult.
Be that as it may, with a disorder such as cerebral encephalopathy, treatment is always complex and quite long-term.
It includes:
- Medicines are neuroprotectors. Prescribed drugs for encephalopathy improve blood circulation and normalize brain function. This treatment lasts at least a month. The course of treatment is repeated, if necessary.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures: electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, acupuncture or blood irradiation.
- Surgery to improve blood flow to the brain.
Features of the treatment of cerebral encephalopathy
Brain damage always causes the development of a pathological process in the body. Fighting the underlying disease, and not its consequences, will help get rid of the existing problem.
Medicines against encephalopathy
The use of medications by patients in case of brain cell death should be strictly controlled by a specialist. In most cases, encephalopathy is treated with the following drugs:
- Nootropic substances
. They are intended to regulate metabolism and improve blood supply. Among the huge range of drugs in this pharmacological group, experts usually recommend that a patient with a similar diagnosis take Piracetam and Pyriditol. - Antiplatelet agents
. To prevent blood clots from forming during encephalopathy and to thin the blood, the patient is prescribed medications in the form of Aspirin or Pentoxifylline. - Vitamins
. In this case, it is best to take retinol (improving vision when it is lost due to the death of brain cells) and tocopherol (protection against heart attack and stroke). The aforementioned vitamins A and E are found not only in medicines, but also in potatoes, carrots, beef liver, eggs and milk. - Angioprotectors
. Treatment of cardiovascular diseases is not complete without these drugs. For encephalopathy, nicotinic acid and Cavinton are usually prescribed. - Biostimulants
. A similar gift of nature in the form of extracts of aloe, ginseng, Schisandra chinensis and high algae helps the body fight long-standing diseases that can cause brain damage. - Essential amino acids
. Methionine is prescribed in cases of metabolic and toxic encephalopathy. It helps the liver to function at the proper level in the presence of unfavorable factors. - Adaptogens
. The most popular among them are plant-based preparations that speed up the functioning of cell membranes. Eleutherococcus, a plant with a tonic effect, is prescribed for radiation, toxic and metabolic encephalopathy. - Drugs that regulate lipid metabolism
. In this case, we are talking about Cetamifene and Essential, which are prescribed to patients with the death of brain cells due to the underlying disease in the form of dysfunction of the biliary tract and liver.
Therapeutic procedures to combat encephalopathy
In addition to the aforementioned drug treatment, the patient is prescribed the following set of rehabilitation measures:
- Massage
. Such a reflex effect on a person’s muscular system has a beneficial effect on his overall well-being during progressive migraines and tremors of the limbs. - Manual therapy
. Some incompetent people confuse these sessions with massage, in which only the patient’s muscles are developed without involving the joints. Practice shows that manual therapy significantly reduces headaches in a patient suffering from encephalopathy. - Acupuncture
. Experts believe that this technique is more suitable for women. If a person has no contraindications to this procedure in the form of pathological pregnancy, infectious diseases, cancer and mental disorders, then acupuncture will alleviate the symptoms of encephalopathy. - Physiotherapy
. Electrophoresis helps the injured party to turn on the body's defenses. Magnetotherapy allows you to correct the patient’s physical and mental state. UVR (ultraviolet of blood) is a necessary method for a beneficial effect on the human body at the cellular level, which is so important for encephalopathy. - Physiotherapy
. The so-called exercise therapy is selected individually for each patient. A special set of exercises serves both for preventive purposes and in the case of stage 3 of the disease, when the patient becomes disabled.
Restrictions during treatment
If a diagnosis of encephalopathy has been established, treatment will only work if the patient adheres to the strict restrictions prescribed by the doctor:
- giving up bad habits - drinking alcohol and drugs, smoking;
- refusal of fatty and salty foods;
- avoidance of stressful situations.
Remember that the consequences of encephalopathy, if not detected and treated in time, are very serious - dementia, coma and even death. Therefore, if you suspect a disorder, you should pay a visit to a neurologist, who will refer you for examination and then prescribe the correct therapy. Treatment with folk remedies without a doctor's advice can be harmful to you.