Author: A. Olesya Valerievna, candidate of medical sciences, practicing physician, teacher at a medical university, especially for SosudInfo.ru (about the authors)
Vascular encephalopathy is damage to brain tissue against the background of a long-term, progressive decrease in arterial circulation. It manifests itself in a combination of various disorders of the intellectual sphere, behavior, and emotional background. Over time, disturbances in motor function and the functioning of internal organs develop, and independent existence and self-care become more difficult.
Vascular encephalopathy is extremely common. The majority of patients with this disease are elderly people suffering from atherosclerosis, hypertension, and disorders of carbohydrate and fat metabolism. Among all vascular lesions of the brain, including strokes and aneurysms, encephalopathy has taken a strong leading position, and it is diagnosed in at least 5% of adult residents of Russia, although the real incidence figures are much higher.
In recent years, vascular pathology of the brain has shown a tendency towards rejuvenation. This is due to the increasing incidence of cardiovascular diseases in young and mature people, and encephalopathy has become increasingly evident in people under 40 years of age.
The significance of the problem of vascular encephalopathy is due not only to the significant costs of treating a chronic progressive disease, but also to high rates of disability and death, which can occur both from dementia - an extreme degree of encephalopathy, and from acute circulatory disorders in the brain against the background of chronic ischemia.
Social disadaptation, loss of ability to work, irreversible changes in behavior and the need for care place a heavy burden on both the state and the patient’s family, which has been forced to fight for the life of a loved one for many years.
The disease, having arisen gradually, steadily progresses, and it is no longer possible to completely eliminate it. The efforts of specialists and patients themselves are aimed at containing vascular disorders and reducing negative symptoms through the use of conservative and surgical treatment, if possible.
Risk area
The first signs of dyscirculatory encephalopathy are headaches, weakness, memory loss and depression. Brain changes at this stage can still be reversed if treatment is started in a timely manner. The diagnosis is made not by the local attending physician, but by a neurologist. And before this, the patient will need to undergo a thorough examination. Diagnostics includes:
- cardiogram;
- examination of the vascular system of the head and neck;
- electroencephalography;
- fundus examination;
- MRI;
- psychological tests for memory, emotionality and thinking.
Important! Dyscirculatory encephalopathy of the brain will be recorded as a diagnosis if the changes have developed for more than six months with a gradual deterioration in well-being.
The disease is common among the elderly and people over 45 years of age. Mental workers are at particular risk because their brains often work at the limit of their capabilities, but without physical exertion. The older a person is, the higher the chance that he will be diagnosed with dyscirculatory encephalopathy. It is this that leads to senile dementia or ischemic stroke. Dyscirculatory encephalopathy is rightly called dangerous, because disability and mortality due to it are the most common around the world.
The disease develops faster if there is:
- unbalanced diet;
- overweight;
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking;
- hormonal disbalance;
- stable, high blood pressure;
- diabetes;
- head or neck injuries;
- atherosclerosis;
- improper treatment of cervical and spinal diseases.
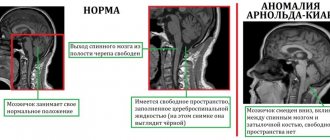
VBI can be cured because it is a reversible process. This type of deficiency is common. The vertebrobasilar apparatus easily returns to normal if you follow the doctor’s recommendations. But if irreversible processes occur in the VBD due to improper treatment or lack thereof, the consequences can be dire. The situation is even worse when the entire CVB suffers. The prognosis for such patients is always disappointing.
Stages and degrees of disease development
To function normally, the brain needs constant and adequate nutrition. All this directly depends on cerebral circulation. Any disruption of this system leads to serious problems. And discirculatory cerebral encephalopathy is no exception. The disease begins when the capillaries of some part of the brain do not bring a sufficient volume of blood. This leads to loss of functionality of the vessel wall, which in turn leads to the leakage of various fluids into the brain. Due to swelling, neurons do not receive normal nutrition and die. And this is already a microinfarction of the brain.
The disease strikes the first blow to the subcortical white matter. This means that it will be more difficult for the brain to process signals from the limbs and control them. The gray matter is the next to suffer, due to the death of which people suffer from thought disorders. Almost half of the cells in the frontal and temporal lobes die. This leads to the formation of foci of necrosis and death.
Discirculatory encephalopathy has 3 stages, which largely influence the clinical picture, treatment methods and prognosis:
Discirculatory encephalopathy of the 1st degree is characterized by:
- mild headaches;
- lack of vital energy;
- insomnia;
- a sharp change in mood from tears to extreme aggression;
- dizziness;
- disruptions in hearing, vision and speech;
- slight numbness in the arms or legs.
At this stage, the brain can still independently regulate situations, and the symptoms of dyscirculatory encephalopathy disappear within a day.
Discirculatory encephalopathy of the 2nd degree leads to an even greater deterioration of the patient’s condition. The above signs are joined by:
- noise in ears;
- the intensity of vertigo and headaches increases;
- constant drowsiness and weakness;
- memory impairment;
- inability to perceive speech;
- complete change of behavioral habits;
- voice change;
- lips begin to twitch.
Dyscirculatory encephalopathy of the 3rd degree is characterized by an even greater deterioration in well-being, but the person himself does not even understand what is happening to him. Moral values become unimportant, there is constant irritability and aggression. Vision or hearing decreases or completely disappears. The gait becomes shaky and uncertain. Dementia syndrome develops. Without outside help a person cannot even serve himself.
Often the diagnosis of “grade 3 dyscirculatory encephalopathy” raises the question: how long can you live with it? Everything is individual, but such a patient is definitely guaranteed to have a disability. The worst thing is if dyscirculatory encephalopathy of mixed origin is diagnosed. It is more difficult to treat, and the prognosis is often disappointing.
Treatment prognosis and possible complications
Discirculatory encephalopathy is a chronic progressive disease with a steady course. Despite the efforts of doctors, not everyone is able to completely get rid of its symptoms. If the disease is detected at an early stage, the prognosis for treatment is most favorable. In the case when the patient turned to the doctor too late, all that remains is to maintain his condition at a certain level and protect the body from the development of complications. The presence of other chronic or acute illnesses in the patient is also of particular importance. It is known that patients with diabetes and people suffering from high blood pressure suffer from dyscirculatory encephalopathy much more severely than others.
In his clinical practice, the author of the article came across a fifty-nine-year-old patient who was able to quite successfully fight this disease. After the diagnosis was made and confirmed, the man began to actively attend physiotherapeutic procedures, therapeutic exercises, followed a diet, took all medications and regularly consulted with a psychologist. At home, he constantly gave his brain simple exercises: he solved crosswords and equations, and solved Sudoku. Such actions helped the victim recover quite quickly and maintain his health within normal limits. After several years of this lifestyle, he began to feel much better, which greatly affected his psycho-emotional state.
What complications may occur in patients with dyscirculatory encephalopathy:
- Hemorrhagic stroke is bleeding in the brain. This is an extremely severe pathological condition, during which the vast majority of patients fall into a coma. Neurosurgeons are involved in his treatment, and the rehabilitation process can take several years.
- Impaired coordination of movements and absent-mindedness often become the causes of the development of domestic and industrial injuries. People lose the ability to self-care, and when handling cutlery they can injure or burn themselves. That is why it is so important that a loved one is always next to a patient with dyscirculatory encephalopathy.
- Hemorrhage into the eyeball and visual impairment. This disease can develop spontaneously due to a sharp jump in blood pressure. At such moments, it is necessary to immediately take the patient to the ophthalmology department, where the doctor can remove the accumulated blood without harm to the eyeball.
Photo gallery: complications of the disease
A stroke is a buildup of blood in a specific area of the brain.
Burns are the most common injuries. characteristic of patients with DEP
Bleeding in the eye can lead to vision loss
How long can you live with the disease?
With early diagnosis and timely treatment, patients do not have to fear for their health. On average, it takes from two to five years to transition from one stage of dyscirculatory encephalopathy. Life expectancy in patients with second and third degrees of cerebral vascular damage is reduced by seven to twelve years.
What causes illness?
Diagnostic measures are designed not only to identify the disease, but also to find the cause that provoked it. Any damage to the vascular system contributes to the development of cerebral encephalopathy. Most often this happens due to:
- Atherosclerosis, which blocks blood vessels with cholesterol plaques. The lumen is either seriously reduced or completely blocked. Blood does not reach the brain area, which provokes its starvation. Atherosclerotic cause is the most common cause of the diagnosis of cerebral venous discirculation.
- Arterial hypertension injures the vessel, which leads to flooding of the brain area with blood or plasma and its swelling.
- Hypotension, in which there is a lack of blood in the vessels, and due to its slow movement, the cells starve.
- High viscosity blood also leads to poor circulation, which provokes the formation of blood clots, which cause necrosis.
- Osteochondrosis, in which bone spurs or spasms compress an artery in the spine, resulting in insufficient blood flow to the brain.
- Trauma to the brain or spine, which causes hematomas to form. They compress the vascular system of the damaged area and lead to a failure in the nutrition of brain cells.
- Abnormal development of the body's circulatory system.
- Tobacco smoking, which provokes cerebral vascular spasms.
- Diseases of the circulatory and vascular systems.
- Hormonal disbalance. It causes improper production of hormones that are responsible for the normal functioning of the entire body.
Medications
Treatment of grade 2-3 dyscirculatory encephalopathy is carried out comprehensively, with a clear medication regimen. The most commonly prescribed drugs are:
- lowering blood pressure
, such as Lisinopril, if the cause of the disease is hypertension. They block a certain enzyme that increases blood pressure. The smooth muscles of the blood vessels relax, expanding the lumen, which leads to a decrease in pressure; - calcium inhibitors
like Nimodipine. Often, grade 3 discirculatory encephalopathy, like the second, occurs due to its excess. When taking the medicine, vascular tone decreases, they relax and expand the lumen, which provides the brain with the necessary amount of blood. At the initial stage, the drug is prescribed intravenously, and then in tablet form; - beta blockers
like Atenolol. It normalizes heart function, lowers blood pressure and pulse rate, which leads to normal blood flow to the brain. In addition, sodium salt and excess water are removed from the body; - tablets for protecting and strengthening blood vessels
, like Curantil. It helps to expand capillaries and increase their lumen. The brain begins to receive enough blood without platelets sticking together; - diuretics
, which reduce blood volume and blood pressure; - blood thinners
. A commonly used drug is Aspirin. Platelets do not stick to it, which is the best prevention of thrombosis; - lowering cholesterol levels in the blood
, such as nicotinic acid, which improves the nutrition of brain cells and blood vessels; - to improve memory and thinking.
Electrophoresis is usually used for these agents. In addition to their main purpose, they are powerful antioxidants that protect a person from the harm of free radicals. They normalize the connections of nerve cells and the transmission of impulses along them.
Encephalopathy of the second and third degrees is treated with a specially developed drug Vasobral, which not only improves blood flow to the brain, but also restores its functions. It reduces the number of clots and normalizes the metabolic process in cells, which leads to the brain’s resistance to oxygen starvation. The risk of swelling at stage 2 is reduced by 74%.
What examinations do doctors prescribe?
First of all, this is electroencephalography, which is used to record the failure of the bioelectric rhythms of the brain and the presence of slow waves (pathological), as well as convulsive activity.
Another method of diagnosis and detailed examination of the patient is magnetic resonance imaging. In this way, the main signs of brain exhaustion, etc. are revealed.
A test of blood and other body fluids shows the amount of oxygen in the blood and the presence of toxic agents. This helps to identify the cause of the disease.
In addition, they prescribe:
- biochemical blood test - to determine blood lipid levels;
- a metabolic test that will show the level of electrolytes, oxygen and other gases in the blood;
- blood pressure measurement;
- drug test;
- Doppler ultrasound - monitoring blood circulation in the body, etc.
Physiotherapy
How to treat a disease without pills? If this is the initial stage, then you can get by with diet and physical therapy. But if the cause of the disease was chronic and led to the formation of encephalopathy of complex origin, then it is necessary to treat only in tandem, combining pills, diet and physiotherapy - the impact on the body of physical factors that have a therapeutic effect. The minimum course for the treatment of cerebral discirculatory encephalopathy is 10 procedures.
Elimination of dyscirculatory encephalopathy is carried out:
- Electrosleep, which stimulates brain activity with electricity. It has low frequency and strength. Current penetration is carried out through the eyelids. With this procedure, metabolic processes are improved and neural connections between nerve endings are normalized.
- Galvanotherapy , which affects the neck and shoulders with a weak current. Decompensation of capillaries is normalized, blood flow into them increases. The procedure is often enhanced with iodine and potassium orotate.
- UHF therapy , in which a high-frequency electromagnetic field forms an ion current in the blood. This enhances its movement through small capillaries, enriching the brain with oxygen. Any negative manifestations of the cephalgic type disappear or decrease.
- Laser , which restores the functioning of dysfunctional areas in the cervical-collar area. Nerve cells work better, blood flow increases, the blood thins out, which increases the speed of its movement.
- Therapeutic baths, which are oxygen, carbon dioxide and radon. After the first procedure, sleep normalizes, vertigo and tinnitus go away.
- Therapeutic massage , which can be acupuncture, lymphatic drainage and conventional in the cervical-collar area. In the first case, the effect is on specific points that normalize brain function. Swelling is well removed by lymphatic drainage type massage, and regular massage relieves spasms that affect the arteries.
ENCEPHALOPATHY
(Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels).
Dyscirculatory encephalopathy is a gradually progressive organic change in brain tissue due to chronic cerebral vascular insufficiency caused by various vascular diseases - hypertension, atherosclerosis, etc.
Etiology.
Based on the etiological factor, there are:
A synonym for atherosclerotic encephalopathy is the term “atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels.” Dyscirculatory encephalopathy, which occurs in various diseases, has much in common both in the nature of the clinical manifestations and in the course, however, some of its features still depend on the etiological factor.
Clinical picture.
The initial period of the disease is characterized by pseudoneurasthenic syndrome: emotional instability, irritability, memory impairment, headache, dizziness, sleep disturbance, tinnitus and other symptoms. Increased vascular reactivity and instability of blood pressure are often observed, especially in hypertension, which is characterized at this stage by transient increases in blood pressure. Signs of organic damage to the nervous system are usually not detected. In the fundus there is a narrowing of the retinal arteries. The performance of patients at this stage periodically decreases; treatment and preventive measures can contribute to stable compensation.
With an unfavorable course of the disease, especially when exposed to various exogenous factors, clinical symptoms become more severe. Increased fatigue, headache, dizziness, sleep disturbance are persistent; Fainting often occurs. Emotional instability increases.
A neurological examination reveals mild organic symptoms: asymmetry of cranial innervation, tendon reflexes, muscle tone, unclear pyramidal signs, etc. Autonomic-vascular lability is noted, cerebral vascular crises often occur, after which organic symptoms (“traces”) intensify.
The psyche often changes: self-doubt, a tendency to a hypochondriacal state, and phobias appear; explosiveness, egocentrism, weakness; Memory disorders worsen, especially for current events. Changes in the fundus become more significant and are in the nature of atherosclerotic or hypertensive angiosclerosis. The ability of patients to work decreases.
With pronounced dyscirculatory encephalopathy, due to the increase in morphological changes in the brain tissue, the clinical picture becomes more severe. The decline in memory and attention progresses, the range of interests narrows, and dementia gradually develops. The course of the disease is aggravated by repeated cerebral crises and strokes. In the neurological status during this period, distinct organic symptoms are noted: insufficiency of cranial innervation, nystagmus, signs of pyramidal insufficiency, sometimes speech disorders, paresis of the limbs, sensory disturbances and pelvic disorders.
Pseudobulbar syndrome is often observed dysphonia, dysarthria and dysphagia, combined with symptoms of oral automatism, increased pharyngeal and mandibular reflexes, forced crying and laughter. Pseudobulbar syndrome is caused by multiple small focal changes in the white matter of both hemispheres of the brain or brain stem, destroying the supranuclear fibers of both sides.
When the subcortical nodes are damaged, various extrapyramidal symptoms occur, which can rarely reach the level of parkinsonism. In the fundus of the eye at this stage, gross changes are noted: with atherosclerosis - sclerosis of the retinal vessels, sometimes symptoms of copper and silver wire, with hypertension - hypertensive angiosclerosis and retinopathy with the phenomenon of arteriovenous crossing (Salus symptom I-II-III), Gvist phenomenon, sometimes hemorrhages.
TREATMENT.
Therapeutic and preventive measures are aimed at treating the underlying disease and eliminating disorders of brain function.
- For atherosclerotic encephalopathy, a diet limited in fat and salt is prescribed.
- Systematic use of vitamins, especially ascorbic acid, is necessary.
- Hypocholesterolemic drugs are prescribed cetamifene, linetol, statins (simvastatin, rosuvastatin and atorvastatin).
- is also used : thyroidin, testosterone propionate, 1 ml of 1% solution under the skin 2-3 times a week, for a course of 15 injections; diethylstilbestrol propionate, 1 ml of 1% solution every other day, intramuscularly, for a course of up to 20 injections.
- For hypertensive encephalopathy - treatment of hypertension (see).
- For all types of dyscirculatory encephalopathy, repeated courses of vasoactive agents ( xanthinol nicotinate, stugeron, nicotinic acid, Cavinton, trental, etc.) are indicated.
- Prescribed drugs that improve the metabolism of brain tissue: nootropic and psychostimulant (citicoline, piracetam, aminalon, pyriditol, or encephabol, acephen).
- Symptomatic treatment: for insomnia - radedorm, reladorm, phenazepam;
- for irritability and anxiety - sibazon, elenium, tazepam, rudotel, grandaxin, trioxazin;
- For headaches - analgesics;
- For dizziness - belloid, cavinton, stugeron, torekan, dedalon.
- Psychotherapy is also of considerable importance . Rational employment of patients and their observance of work and rest schedules are very important.
ethnoscience
Treatment of dyscirculatory encephalopathy with folk remedies has been used for a long time and gives good results. Symptoms and treatment will be related, but you need to understand that these methods are applicable if dyscirculatory encephalopathy needs prevention. Treatment with folk remedies at a severe stage can be additional to the main therapy. Most often, DEP is treated:
- Collections of herbs. They use, for example, the “Crimean Collection”, consisting of rose hips, sweet clover petals, birch leaves, coltsfoot, plantain, licorice, linden flowers, oregano, raspberry and rose hips, all taken in equal proportions. Tea is prepared from a tablespoon of the mixture and a glass of boiling water. The course of treatment is 3 months. A sedative mixture consisting of chamomile, mint, lemon balm, valerian and lemon zest helps well against cerebrovascular encephalopathy. Duration of treatment is from 2 to 3 months.
- Caucasian balsam, which is prepared from propolis, Dioscorea caucasica and red clover. The clinic returns to normal already in the second week of admission. The person feels an extraordinary surge of strength.
- Hawthorn, which is a powerful stimulant for the heart and blood. It is eaten both raw and used for infusions and decoctions. With the right approach, headaches go away after 7 days of use.
Forecast
If vertebrobasilar anomalies lead to the fact that a person cannot work and take care of himself, then he will be assigned a disability. In this case, the stage of the disease must be 2 or 3. The disability group is assigned as follows:
- Group 3
- the disease has stage 2, the patient can self-care, but work is impossible, help from outsiders is selective; - Group 2
- disease stage 2-3, limited life activity, memory problems, severe neuralgic disturbances, repeated strokes; - Group 1
- stage 3, which rapidly progresses, causing disruption in motor functions, blood circulation, and pronounced dementia and aggressiveness.
The prognosis for patients with stage 1-2 with proper treatment is often positive, and they can live for quite a long time. The second stage of the disease can be stopped in development for 5-7 years. If there is no treatment, then disability is guaranteed. The higher the stage, the greater the risk of complications and deterioration in quality of life. At stage 3, the disease progresses quickly, which makes therapy difficult and costly. But it can delay death. Death in this case most often occurs due to heart attacks, ischemic strokes and cardiovascular collapse. If you ignore the doctor’s recommendations, then a new attack of dyscirculatory encephalopathy and its transition to a new stage has an interval of 1.5-2 years. But it’s best to just take care of your health, eat right, and do exercises, which is the best remedy for dyscirculatory encephalopathy.
Symptoms of vascular dementia
Signs of developing vascular encephalopathy can be divided into several broad groups.
Cognitive (having cognitive significance):
- memory loss;
- impaired thinking and judgment;
- impairment of orientation, speech and learning ability;
- weak cognition.
Behavioral (related to behavior):
- personality disorders, emotionality;
- depression, anxiety;
- delusions, hallucinations;
- identification violation;
- behavioral disorders;
- sleep disorders.
Functional:
- difficulties in complex activities;
- difficulties in housework;
- self-care on a daily basis;
- continuity disorders;
- communication disorders;
- gait disturbance.
Symptoms of vascular encephalopathy often begin suddenly, often after a stroke. A person may have a history of high blood pressure, vascular disease, or previous strokes or heart attacks.
The disease may, but should not, progress over time, depending on whether the person has additional assumptions about it. In some cases, symptoms may subside over time. If the disease progresses, its symptoms often occur in steps, with sudden changes in intensity.
Vascular encephalopathy with damage to the midbrain, however, can lead to a gradual, progressive decline in cognitive function that can look like Alzheimer's disease. Unlike people with AD, people with SE often maintain their personality and normal levels of emotional reactivity into later stages of the disease.