When a brain tumor is diagnosed, its treatment largely depends on the degree of malignancy and advanced stage of the disease. The success of therapy is also affected by the type of tumors localized in the cranium - extracerebral, affecting the membranes of the brain, or intracerebral, which is an atypical formation of brain cells.
Types and symptoms of tumors
With a brain tumor, the cells of tissues, membranes, blood vessels, and nerve endings rapidly divide. Cancer can be primary, growing in a part of the brain, or secondary, formed by metastasis from another organ damaged by the disease.
Primary tumors are divided into:
- Astrocytomas, consisting of astrocyte cells that nourish and ensure the development of neurons.
- Oligodendrogliomas, formed from cells that protect neurons.
- Ependymomas that develop from the membrane cells lining the walls of the ventricles of the brain.
- Mixed gliomas containing pathologically altered cells of astrocytes and oligodendrocytes.
- Adenomas of the pituitary gland, which is responsible for the production of hormones.
- Lymphomas of the central nervous system, in which atypical cells form in the lymphatic vessels located in the skull.
- Meningiomas that develop from mutated cells of the meninges.
Pronounced symptoms during extracerebral formation can be called:
- Fainting.
- Difficulty speaking.
- Loss of coordination.
- Memory loss.
- Cramps.
- Hallucinations.
At the first signs of illness, you should see a doctor in order to identify the cause of its occurrence. The earlier treatment for brain cancer is started, the greater the chance of recovery.
Intracerebral tumors localized in tissues manifest themselves less actively. The first thing that should alert the patient is morning headache attacks, accompanied by nausea and sometimes vomiting.
Classification of uterine fibroids
Externally, the tumor consists of one or several nodes (seals) of different sizes, consisting of smooth muscle fibers. The most common are multiple myomatous nodes (up to 80% of cases). The size of fibroids can vary from a few millimeters to 20-25 cm. Depending on the location of the tumor in the uterus, the following types of fibroids are distinguished:
- Subserous fibroid . It develops from the outer muscular layer of the uterus and grows above the surface, towards the peritoneum.
- Submucosal (submucosal) fibroid. It occurs under the mucous membrane and grows deep into the uterine cavity (endometrium). This form of tumor is characterized by rapid growth and pronounced symptoms (severe bleeding, severe pain, etc.).
- Interstitial (intermuscular) fibroids are the most common form. The tumor grows into the thickness of the uterine wall, thereby greatly increasing its size.
In approximately 95% of cases, the tumor develops in the body of the uterus, very rarely in the cervix.
Reasons for tumor development
Doctors cannot say for sure why cancer occurs. The only proven cause of cancer in adults is radiation. Some experts see the causes of the disease in infrared, ionizing, electromagnetic radiation.
Risk factors that contribute to the proliferation of pathological cells include:
- Age.
- Heredity.
- Genetically modified foods.
- Intoxication with chemicals (pesticides, vinyl chloride).
- Papillomatosis viruses.
The tumor can form at any age, but most often doctors detect it in people after 45 years of age. The risk of getting a brain tumor increases:
- In men from 58 to 69 years old.
- Participants in the liquidation of the Chernobyl accident.
- People who abuse mobile phone conversations.
- Workers in highly toxic enterprises. When a person comes into daily contact with harmful substances (lead, arsenic, gasoline, mercury, pesticides), the risk of developing cancer increases significantly.
- In organ transplant recipients.
- HIV-infected people.
- Those who have undergone chemotherapy treatment.
Genetic abnormalities are the main cause of the development of cancer in children. It is known that cells capable of increased division undergo atypical changes. And in a child’s body (not excluding the fetus developing in the womb) there are much more of them than in an adult.
Dimensions of uterine fibroids
Often, fibroids are multiple and range in size from tiny to huge, occupying most of the abdominal cavity. Myoma begins with the formation of a nodule in the muscular wall of the uterus; it can remain stable in size for a long time, or it can begin to grow slowly or quickly.
Depending on the location of the myomatous nodes relative to the thickness of the muscular wall of the uterus (myometrium), they are distinguished:
- Intramural (intermuscular, interstitial) uterine fibroids, which are located deep in the wall of the organ; occurs most often. Until this type of fibroid reaches a critical size, it usually does not cause symptoms.
- Submucosal (submucosal) fibroid. Located under the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity. Submucous fibroids can be broad-based or pedunculated; they grow into the uterine cavity or are “born” through the cervical canal into the vagina. It is these fibroids that lead to heavy menstruation, during which a woman loses a lot of blood, uterine bleeding, infertility, miscarriages, and premature birth.
- Subserous (subperitoneal) myoma. It is located under the serous membrane covering the outside of the uterus, from the abdominal cavity. Subserous fibroids can also be broad-based or pedunculated. When we talk about giant fibroids, the size of a melon or a watermelon, they usually mean subserous nodes.
There are also mixed forms (intramural-subserous, intramural-submucous).
Diagnostic methods
Before prescribing treatment, a brain tumor is diagnosed. The patient must undergo:
- Neurological monitoring of reflexes, coordination, hearing and vision. If pathologies are noticed, the specialist will be able to determine the approximate location of the formation.
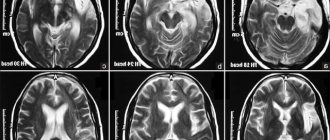
- Magnetic resonance imaging, which allows you to obtain a clear layer-by-layer image of the brain, assess the size, location, and degree of growth of the tumor.
- Computed tomography, radiography, and ultrasound examination of other organs are performed if the tumor in the brain is secondary.
- A biopsy is done to determine the type of tumor based on its cellular composition. The procedure is performed during surgery or by inserting a special needle into a small drilled hole in the skull.
Symptoms of uterine fibroids
Sometimes uterine fibroids are asymptomatic and are detected only by ultrasound. But it is often accompanied by:
- menstrual irregularities - heavy and prolonged menstruation, uterine bleeding. With severe blood loss, anemia develops;
- pain in the lower abdomen and lower back;
- infertility and miscarriage. This is due to impaired maturation of the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity (endometrium) due to hormonal disorders, deformation of the uterine cavity, changes in the contractility of the uterine muscle (myometrium);
- dysfunction of neighboring organs. With large fibroids, compression of neighboring organs occurs - the ureters, bladder, rectum, and urination and stool are impaired.
Uterine fibroids may undergo reverse development and shrink during menopause, and become calcified (impregnated with calcium salts).
One of the complications of uterine fibroids is a malnutrition of the node - when the leg of the node is torsed or thrombosis of the vessels supplying the node with blood, tissue necrosis occurs. This causes abdominal pain, increased body temperature, often vomiting, a symptom of “acute abdomen” (symptoms of peritoneal irritation).
This complication requires surgical intervention and removal of the necrotic node . With the rapid growth of a uterine fibroid node, especially in menopause, there is a suspicion of a malignant tumor - sarcoma.
The diagnosis of uterine fibroids is made on the basis of a gynecological examination and ultrasound examination (abdominal and transvaginal sensors are used).
With submucosal (submucosal) localization of the node, the diagnosis can be made by hysteroscopy.
In some cases, magnetic resonance imaging of the pelvic organs (MRI) is performed if ultrasound data is insufficient.
Brain tumor treatment methods
Treatment of brain cancer is carried out using methods such as:
- Drug therapy that eliminates symptoms and alleviates the patient’s condition.
- Surgery is the most effective step in the fight against the disease.
- Radiation therapy is carried out when damaged tissue is in a hard-to-reach place and cannot be removed surgically.
- Chemotherapy is used as an adjuvant treatment after surgery.
An integrated approach is considered the most effective, when observation is carried out by several specialists: a neurosurgeon, oncologist, radiologist, and attending physician. They tell the patient how to treat a brain tumor and whether surgery can be avoided. Much depends on the nature of the formation - whether it is malignant or benign.
- A malignant neoplasm is characterized by the presence of pathological tissues and structures in the main organ of the nervous system. They are capable of rapidly increasing, growing deeply into structures and the skull. Experts say that drug treatment here is auxiliary. When the tumor strongly compresses neurons and nearby structures, unbearable pressing headaches occur. For such symptoms, painkillers and medications that reduce swelling are prescribed.
- If a patient is diagnosed with a benign brain tumor, radical treatment is a little easier. After all, such neoplasms have clear outlines and are located on the surface of the brain, do not penetrate deep into its tissues and do not metastasize. Having reached a certain size, a benign tumor stops growing. But, as in the case of malignant tumors, relapse is possible after its removal. It is believed that benign tumors in the human body do not threaten his life and health. Tumors in the skull are dangerous because they compress the brain, damage healthy cells, and cause inflammation.
Surgery
A brain tumor, the treatment of which is based on surgery, requires the patient to be in the hospital of the neurosurgical department. In advanced cases, surgery is performed immediately.
Surgical intervention is divided into 2 categories:
- Radical surgery with absolute elimination of the tumor.
- A palliative operation that improves the patient's condition by removing part of the tumor compressing the brain. The patient’s well-being stabilizes, he is no longer tormented by attacks of pain in the head, and brain functions are restored.
Surgery to remove a tumor in the brain involves trepanation and excision of cancerous tissue. Doctors try to remove as much tumor as possible and preserve healthy cells as much as possible. Modern neurosurgeons use the latest techniques for this:
- Craniotomy , which involves making holes in the skull to access the brain.
- Endoscopic trephination , which allows radical treatment of brain cancer without opening the skull.
- Stereotactic radiosurgery supplemented with biopsy.
Special microscopes, which are used by surgeons during operations, make it possible to carry out complex interventions in the brain with minimal trauma to surrounding tissues.
In the postoperative period, the patient needs to be monitored by a neurologist. Pathologies of the nervous system cause serious complications. Restoring brain function requires a lot of time, scrupulous implementation of doctors’ recommendations, and careful attitude to health after discharge from the hospital.
The attending physician selects a comprehensive treatment that improves blood circulation, normalizes blood pressure, and reduces autonomic disorders. Treatment of brain cancer involves taking supportive and restorative medications, physiotherapeutic procedures, massage sessions, and recreational exercises.
Radiation therapy and chemotherapy
Radiation therapy treatment uses high-energy X-rays to destroy abnormal cells. There are two types of this therapy:
- Treatment with a special device that directs a radiation beam to the location of the cancerous tumor.
- Internal therapy that uses a radioactive component. It is in capsules and is inserted into the affected area with a needle, catheter or needles.
Chemotherapy is used in conjunction with radiation exposure. The technique involves taking medications that stop the growth of atypical cells and destroy them. After entering the patient’s body, the drugs begin to work intensively, affecting cancer cells. If medications are injected directly into an organ or spine, the chances of a positive treatment outcome increase significantly.
In parallel, the patient is prescribed dietary supplements - dietary supplements. They help cope with side effects that may occur during the course of treatment. Only a specialist can prescribe drugs for chemotherapy, based on the type of tumor.
Traditional methods
If brain cancer is detected, treatment with healing infusions and decoctions to reduce tumor growth, maintain the body, and strengthen its protective functions requires prior consultation with a doctor. Conservative treatment in this case is the main one, and non-traditional treatment is an auxiliary method. Popular recipes:
- Taking 1 teaspoon of aloe juice twice a day will help reduce swelling.
- Pour 3 g of dried white mistletoe flowers into a glass of goat milk.
- 2 tbsp. l fresh chestnut flowers and 1 tbsp. pour a glass of boiling water over dried flowers and let stand for 6-8 hours. After straining, the drug is drunk one sip at a time throughout the day.
Treatment of uterine fibroids
Depending on the results of the diagnostic examination, the optimal types of treatment for each patient are determined.
Today, there is non-surgical treatment (medication, conservative) and surgical treatment of uterine fibroids.
For small tumors, it is advisable to prescribe drug therapy (hormone therapy, herbal medicine). In some cases, treatment is not prescribed at all, but systemic monitoring of existing fibroids is carried out (the “watchful waiting” method). For example, with the onset of menopause, the symptoms of fibroids may disappear.
If drug therapy is ineffective, surgical treatment methods are prescribed.
The main indications for surgical treatment of uterine fibroids are rapid growth of nodes, severe bleeding, and large fibroids.
There are two types of surgical treatment: organ-preserving and radical .
Organ-preserving surgical treatment methods include:
Laparoscopic myomectomy . Organ-preserving surgery aimed at removing nodes. The operation is performed under general anesthesia, through a micro-incision in the abdomen, using a laparoscope. Myomectomy makes it possible to preserve the body and cervix, which will allow the patient to give birth to children in the future.
Hysteroscopic myomectomy . The nodes are removed through the vagina using a hysteroscope. Used in the treatment of submucosal fibroids.
Abdomial (open) myomectomy . A traditional operation to remove myomatous nodes, during which two incisions are made: one on the abdominal wall for free access to the uterus, the second on the uterus itself. Surgery is prescribed for multiple fibroids or large tumors.
Radical surgical excision of fibroids is carried out by performing a hysterectomy. Hysterectomy – complete removal of the uterus. This radical method is carried out when it is impossible to use other methods of surgical intervention, as well as when there are signs of malignant degeneration of the tumor.
minimally invasive treatment methods have been increasingly used to treat uterine fibroids . These include:
- Uterine artery embolization (UAE). The procedure is based on puncture of the femoral artery and the introduction of a special drug that blocks blood flow in the myomatous nodes.
- Focused ultrasound ablation (FUS ablation) . Destruction of uterine fibroids with ultrasonic rays. The procedure is controlled by a magnetic resonance imaging scanner.
- Transabdominal MRI-guided cryotherapy. The methodology is at the research stage.
The basis for preventing uterine fibroids is preventing the disease. A timely visit to a gynecologist and early diagnosis will help avoid severe disease and complications (miscarriages, infertility, malignant processes).
Forecasts
Malignant gliomas are a common diagnosis, accounting for 60% of common primary brain tumors. They are divided into 4 degrees of malignancy. The more advanced the disease, the higher the degree of malignancy, the less chance the patient has of returning to normal life and recovering.
Already at stage 3 of malignancy, the tumor is considered inoperable. Treatment of such patients consists of eliminating symptoms and alleviating their condition. Narcotic drugs that have a calming and analgesic effect help relieve a person from severe headaches.
Doctors use the term “five-year survival rate” for some types of cancer. Many patients live longer if the type and grade of malignancy allows surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy to treat early-stage brain cancer.