- To GET RID of herpes, drink a glass of... read more >>
Any type of sore throat, where herpetic is no exception, is an infectious disease that affects the mucous membrane of the throat, palate, tonsils and the entire larynx. It is worth noting that in this case it is in no way connected with the herpes virus, for this reason this type of sore throat has other names in medical terminology.
For example, if we are talking about vesicular and aphthous tonsillitis, then you should know that they are the same thing. In order to get rid of this disease, it is necessary to have a clear understanding of what it is, what signs exist, what causative factors influence its occurrence and development, and what modern medications and folk remedies are considered the most effective in treatment.
Causes of the disease in adults
This type of sore throat in adults occurs when the Coxsackie virus or herpes enters the body , but the disease does not develop when the immune system is normal.
Carefully! Factors such as a previous cold or flu can provoke the progression of the disease, after which the body’s protective functions are noticeably weakened.
Herpangina pathogens can be transmitted in the following ways:
- Contact. In this case, viruses are transmitted through direct contact between a person and a sick person. When kissing, pathogens pass from person to person through saliva.
- Airborne. Viruses are spread in the environment by sneezing and coughing.
- Fecal-oral . Infection occurs through the use of objects with which the patient has been in contact.
Possibility of complications after suffering herpetic sore throat
In severe cases of herpetic sore throat, generalization of the infection may occur. In adults, in most cases, there is an insufficient degree of reactivity, which also contributes to the aggravation of the situation.
Generalization of infection is that viruses spread to other organs, which leads to complications such as:
- encephalitis,
- pyelonephritis - kidney damage,
- serous meningitis - inflammation of the brain,
- myocarditis - infectious heart disease,
- hemorrhagic conjunctivitis - inflammation of the conjunctiva of the eyes with hemorrhages.
If herpangina appears with meningitis, the clinical picture is complicated by trismus of the masticatory muscles, as well as rigidity of the occipital muscles.
As a rule, after competent and timely treatment, the doctor makes a favorable prognosis. If myocarditis is present, the prognosis is worse. All complications of herpetic sore throat require immediate medical intervention, which is described in detail in the video in this article.
Symptoms
Herpes sore throat is characterized by the following distinctive symptoms and signs:
- increase in body temperature;
- general malaise and weakness ;
- inflammatory processes spreading to the mouth, throat and tonsils;
- formation of small blisters on the laryngeal mucosa , similar to those that appear with herpes;
- pain when swallowing;
- muscle pain , which lasts approximately during the first week of the development of the disease, and then completely disappears.
Throughout the entire period of development of the disease, there is a possibility that the virus can spread to people around the patient.
Therefore, a person sick with herpangina must be isolated, and treatment should begin from the first day of the development of the disease.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of herpetic sore throat is established on the basis of previous serological and virological studies. Pharyngeal swabs collected during the first 5 days of the disease are used as material for virological research. Serological testing is based on the examination of serum collected during the first days of the onset of the disease, as well as 2-3 weeks after that. The most informative diagnostic method in this case is the immunofluorescence method.
Differential diagnosis is based on data in the form of the child’s age, the characteristics of the disease in terms of its seasonality, and the localization of the elements of the rash in the oral cavity. Herpetic sore throat is not accompanied by the appearance of a herpetic rash on the face, the mucous membrane does not bleed, and gingivitis does not develop. In frequent cases, herpetic sore throat is accompanied by the appearance of a symptom such as pain in the abdominal area, which is caused by myalgia of the diaphragm that is relevant to it.
Main areas of diagnostics: blood test; determination of the pathogen (examination of smears, nasopharyngeal swabs).
Diagnostics
Reference! Diagnosis and differentiation of herpes sore throat begins with a visual external examination. After this, the patient is prescribed a virological and serological test, in which a smear is taken from the affected mucosa.
Such material, when analyzed, makes it possible to accurately identify the causative agent of the disease and prescribe appropriate adequate treatment.
The patient also needs to undergo a general blood test : with herpes sore throat, an increased level of leukocytes can be seen in the blood.
It is important to differentiate the disease from other ailments, since in the early stages the symptoms of herpangina are similar to those of intestinal dyspepsia, ARVI or influenza.
How does herpangina occur?
Unlike other types of sore throat, the herpes type occurs with two development peaks .
The first of them occurs on the first day, and the second on the third day after infection.
The causative agent of the disease settles not only on the surfaces of the throat and tonsils, but also penetrates the intestinal lymph nodes .
After this, during the incubation period you should wait for the development of the disease and the first peak - this can take from two days to two weeks.
During this period, the virus manages to spread to muscle and nerve tissues.
The disease is generally characterized by a favorable prognosis with timely treatment, and after a person recovers from herpangina, he develops immunity to the pathogens that caused it.
Preventive measures
To avoid infection, actions aimed at strengthening the immune system are recommended, as well as reducing the likelihood of encountering an infection. Prevention of herpetic sore throat includes:
- proper nutrition and taking vitamins;
- hardening, moderate physical activity;
- accommodation, recreation in environmentally friendly areas;
- compliance with the rules of personal hygiene and sanitary standards in the home;
- refusal to visit crowded places during disease outbreaks;
- isolation of sick family members.
Herpetic sore throat is common among children. In adults, the disease develops rarely, mainly against the background of severely weakened immunity. Despite its acute course with high fever, in 97% of cases, herpangina has a favorable prognosis. Treatment is based on the use of symptomatic remedies: rinsing solutions, lozenges, sprays, antipyretic drugs. On average, the patient recovers in 7–10 days. Repeated cases of herpangina are possible when infected with another strain of the virus. The disease is highly contagious and requires isolation.
Treatment of herpes sore throat in adults
When treating herpes sore throat, the following nuances must be taken into account:
- The patient must strictly adhere to bed rest until complete recovery.
- consumed by the patient during treatment should not be hard, tough, too hot or cold . In these cases, food can irritate the affected mucous membrane, slowing down the healing process.
- It is important to constantly drink more fluid, which will subsequently remove a certain number of pathogenic microorganisms from the body.
Need to know! Considering that the causative agent of the disease is viruses, antibiotic drugs intended to fight bacteria and infections are not used in this case due to ineffectiveness.
Basically, symptomatic treatment is prescribed , the purpose of which is to relieve symptoms and relieve inflammation. For this purpose, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs .
As an additional measure, you can gargle, thanks to which the affected tissues heal and pathogenic microflora is washed away.
Sometimes patients with herpangina are prescribed analgesics.
In most cases, treatment occurs at home, but if pathologies such as meningitis and myocarditis develop against the background of the disease, hospitalization may be necessary.
Also, hospital treatment is a prerequisite for severe forms of the disease and if we are talking about small children (under the age of one year).
Viferon and suprastin (a strong antihistamine) are prescribed as an antiviral drug for the treatment of herpes sore throat
Acyclovir , which effectively fights bacteria, is useless as a therapeutic drug for herpes sore throat, but it can be used to lubricate the throat when ulcers appear on it (acyclovir promotes their healing).
Treatment of the disease must be comprehensive , so the patient is prescribed several types of medications:
- antipyretics (ibuprofen, paracetamol);
- antihistamines to relieve swelling and inflammation (fenkarol, claritin, diphenhydramine);
- some antibiotic drugs (only for clinical manifestations of herpangina);
- analgesic bactericidal agents (used topically when rashes appear), which include tantum verde, ingalipt, Lugol's solution and hexoral;
- antiseptic solutions for rinsing (chlorhexidine, miramistin, furatsilin, hydrogen peroxide).
Additionally, physiotherapeutic procedures, inhalations, applications and compresses .
What folk remedies can be used?
Traditional medicine is not the best method of treatment for herpes sore throat , but such measures can be resorted to, using them as a supplement to the main course of treatment.
In particular, you can gargle not only with medications and solutions, but also with decoctions based on chamomile, calendula, sage, plantain or oak bark.
Remember! These products can be used individually or as part of a herbal mixture, in which all these herbs are mixed in equal proportions and a teaspoon of this mixture is poured into a glass of boiling water, which is used for rinsing after cooling.
also lubricate the throat with propolis or irrigate with beet juice , but using soda-salt solutions when ulcerations form on the surface of the throat is not recommended, since these drugs can irritate the affected tissues.
Clinical picture
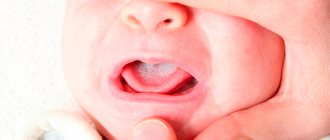
A distinctive symptom of herpetic sore throat is the presence of painful blisters with liquid on the surface of the inflamed red mucous membrane of the pharynx.
The vesicles have a diameter of 1-2 mm and cover the palate, tonsils, pharyngeal ring and tongue. At the beginning of the disease, vesicles are visible as red dots. It seems that they are filled with blood. What early papules look like with herpes sore throat in a child and an adult can be seen in photo 1.
Within a few hours the bubbles lighten. And it seems that there is not blood in them, but water. Redness remains around the vesicles (Figure 2).
Papules last 2-4 days. And then they burst, forming ulcers, on the surface of which crusts form. The ulcers hurt no less than the blisters themselves.
The severity of herpes sore throat in adults and children can be determined by the number of vesicles: the more there are, the more severe the disease.
After 5-6 days from the onset of the disease, the crusts from the ulcers disappear, leaving no traces of their presence on the mucous membrane.
A typical manifestation of herpangina is acute stabbing pain in the throat. Since the disease is essentially pharyngitis, and not tonsillitis, the pain with it differs from pain with other types of tonsillitis. It does not squeeze the throat, does not shoot into the ears and does not pulsate. But swallowing solid and liquid food can be much more painful than with bacterial tonsillitis.
Besides the throat, Coxsackie viruses most strongly affect the digestive system. Therefore, the symptoms of the disease, primarily in children, are:
- pain in the abdominal area;
- nausea and vomiting;
- bowel disorder.
Herpetic sore throat occurs in several stages.
- The first stage takes 1-2 days. Characterized by a high temperature of up to 39-41 degrees, acute sore throat, runny nose, and weakness. Often intoxication - vomiting, diarrhea, muscle pain. There are no vesicles in the throat.
- By the end of the 2nd day of illness, the general symptoms of the disease weaken somewhat. The temperature drops slightly. But bright red bubbles appear on the palate and tonsils.
- On the third day of illness, the temperature rises again to 39-41 degrees. General symptoms increase. The bubbles turn from red to transparent.
- On the 4th day the final phase begins. The vesicles gradually open. The temperature is decreasing. The general condition is improving.
Until the 7-8th day of the disease, the throat is cleared of crusts covering the ulcers. The condition is returning to normal.
This is how the classic form of herpes sore throat occurs. However, there are also atypical cases of the disease in which bubbles in the throat either do not form at all or form several times.
In general, the clinical picture in adults and children with herpetic tonsillitis is similar. But children get sick more seriously.