The situation when a woman becomes pregnant with not one, but several future babies at the same time is not such a rare occurrence and occurs in approximately 0.7 - 1.5% of cases of the total number of pregnancies. It should be noted that twin pregnancies account for 99% of the total number of multiple pregnancies and 1% are triplets. Although quadruplets and quintuplets are not excluded.
Doctors believe that the maximum number of fetuses that women can bear without threatening their own health and the health of their children is 6. An interesting fact is that a larger number of multiple pregnancies are observed on the African continent, while in China and Japan cases of twins/triplets are rare.
Pregnancy with twins, triplets...
A multiple pregnancy is called one when several fetuses simultaneously develop and grow in a woman’s sac. Multiple pregnancies are classified according to several factors. Depending on the number of fetuses, pregnancy is classified as twins, triplets, quadruplets, and so on. The number of fertilized eggs also matters, that is, multiple pregnancies can be single or double.
Fraternal twins are more common and their frequency is 70%. The mechanism of occurrence of fraternal twins comes down to the fact that 2 eggs mature in the ovary or ovaries at the same time, which can meet with sperm either during one sexual intercourse or as a result of two intercourse, provided that the period between them is no more than 7 days.
Fertilization of two eggs is possible with sperm from both one partner and (not that uncommon) from two men. A clear example of such fertilization is the film “Cuckoo”. If identical twins have exactly the same set of genes and are like two drops of water, then the similarity of fraternal children is only general, like between brothers and sisters born at different times.
Identical twins are always the same sex, while fraternal children are of different sexes. In a non-identical multiple pregnancy, each fetus has its own personal placenta and amnion, therefore such a pregnancy is called bichorionic biamniotic. In the case of a monozygotic pregnancy, the egg is divided into several after fertilization. Depending on the time period when the egg is divided, the following are distinguished:
- bichorionic biamniotic identical twins (separation occurred at the stage of movement of the fertilized egg through the tube to the uterus - the first 3 days);
- monochorionic biamniotic identical twins (division occurred within 3–8 days after conception, with 2 embryos being formed, each in its own amnion, but with a common chorion/placenta);
- monochorionic monoamniotic twins (egg division in the period 8–13 days after fertilization, while the embryos have a common chorion and are located in a common amniotic sac);
- Siamese or conjoined twins, when division occurred later than 13 days (such twins can be fused at the tailbones, lumbar spine, rib cages or skull bones).
The prognosis of pregnancy/childbirth is most unfavorable in the case of monochorionic monoamniotic twins.
Waiting Features
Pregnancy with twins, and especially triplets, requires close attention. Much of what is possible during a normal pregnancy is prohibited for expectant mothers with many children. Multiple pregnancies always have a higher risk of miscarriage or development of pathologies. Therefore, be prepared for the following:
- You need to visit a doctor and get tested much more often. After the 20th week, visits should be every 2 weeks, and starting from the 30th week - every week.
- You will have to give up intimacy even in the early stages, since your risk of miscarriage is twice as high, even in the absence of other complications.
- You need to eat for three, or even four, which is quite difficult to do with the uterus pressing on your stomach. Therefore, eat a little, but every 2-3 hours, at least 6 times a day.
- The daily calorie intake for a mother of twins is 3500 kcal, for a mother of triplets – 4500 kcal. Therefore, food should be as varied as possible. Include vegetables, fruits and nuts in your diet.
- You will have to give up your usual sports, but special gymnastics for pregnant women should become your mandatory companion.
- The longer the period, the more rest you need. For up to 20 weeks, this is a minimum of 4 hours a day, for a later period – up to 8 hours.
- You should also start wearing a prenatal bandage earlier, from about 20–22 weeks.
Why does multiple pregnancy occur?
There are many known factors that predispose to the conception of twins:
Heredity
This factor is considered the most indisputable. If the spouses were related to twins, then the likelihood of pregnancy with several fetuses increases several times. Moreover, it has been noted that twin pregnancies are passed on through generations.
Woman's age
It is noted that the older a woman is, the higher her chances of becoming pregnant with twins or triplets. This age limit is the 35th birthday, that is, on the eve of premenopause and the onset of menopause, not all menstrual cycles occur with ovulation. In turn, anovulatory cycles alternate with ovulatory ones, when a surge of hormones occurs, a powerful stimulation of ovulation occurs, as a result of which 2 or more eggs mature at the same time.
Ovulation stimulation
When prescribing infertility treatment, hormonal drugs that stimulate follicle maturation (clomiphene or gonadotropin) are usually used. Under the influence of these drugs, several follicles can mature at once.
Hormonal contraception
Often multiple pregnancies are caused by taking combined oral contraceptives. Afterwards, the ovaries become active and begin to rapidly synthesize their own hormones, which leads to the maturation of several eggs. This situation is called the rebound effect.
In Vitro Fertilization
The development of reproductive technologies, in particular IVF, is one of the reasons for multiple pregnancies. The bottom line is that after “conception in vitro,” several grown eggs are grown, and up to 4 of them are implanted with the mother. If in the 80s the percentage of multiple pregnancies after the use of assisted reproductive technologies reached 30, today it is 50%.
Parity
Most often, multiple pregnancies occur in multipregnant women. Moreover, it is noted that the greater the number of births in the anamnesis, the higher the woman’s chances of becoming the mother of twins or triplets.
A little theory, or how twins appear
Most of us still confuse the concept of twins and twins, but everything is simple there. In both cases, two male cells are present. In the case of twins, they simultaneously fertilize one female cell, as a result of which it begins to rapidly divide. That is why such children are as similar as possible to each other, they are of the same sex, because they have the same set of chromosomes.
When conceiving twins, two sperm fertilize two eggs. Thus, children are born that are different from each other, sometimes not even of the same sex. According to scientists, the average woman is more likely to give birth to twins. Do you know why? Because they are born many times more often - approximately once every 80 pregnancies (for comparison, twins are conceived 4 times less often than twins).
Interestingly, it is impossible to predict the birth of twins: the chances are very low (2% of all pregnancies). The situation is aggravated by the risk of miscarriage. It turns out that not even all women know that they were “pregnant” with twins for a couple of days, since such conceptions fail almost immediately after fertilization of the egg. Registration is achieved in one case out of 10. Twins are another matter. There, it’s easier to endure and to plan. So, if you want it, go for it!
How does a multiple pregnancy differ from a single pregnancy?
Signs of twin pregnancy
Signs appear from the very first days, and based on them, a woman may suspect that not only a single baby is developing in her womb, but two. So, the initial signs of pregnancy, such as:
- increased sense of smell, intolerance to certain odors
- the appearance of more pronounced engorgement of the mammary glands
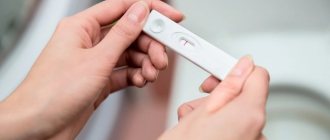
- The early appearance of pigment spots on the face alarms a woman, and she rushes to take a pregnancy test.
And here a certain surprise awaits her - the test strip is very pronounced and greasy. The described symptoms are explained by a doubling of hCG, which increases the intensity of the initial symptoms and the brightness of the test strip.
- Toxicosis
In addition, during pregnancy with twins, early toxicosis begins much earlier than during normal pregnancy, lasts more severely and longer, up to 16–17 weeks. And there is a reason for this fact. The main culprit of toxicosis is the fetus, and if there are several of them, the signs of toxicosis will be more intense. If during the pregnancy of one fetus a woman can only be bothered by heartburn and nausea, then during pregnancy with twins, unpleasant sensations are expressed in vomiting, increased salivation, excessive fatigue and drowsiness. It is rare that an expectant mother manages to avoid the manifestations of early toxicosis, which also distinguishes a pregnancy with twins from a pregnancy with one fetus.
Belly during pregnancy with twins
The abdomen begins to increase earlier, so by 12 weeks the uterus in a singleton pregnancy only protrudes slightly above the womb, and if there are several fetuses, it can almost reach the navel. Accordingly, the woman begins to feel the movement of the fetus earlier, firstly, due to the tightness of the babies, and secondly, due to overextension and thinning of the walls of the uterus.
Weight during pregnancy with twins
Weight during multiple pregnancy also deserves special attention. The weight gain in a woman pregnant with twins is more significant and increases rapidly, starting from the first weeks.
Diagnosis of fetal defects
Another feature of twin pregnancy is the result of the “triple test” - the diagnosis of congenital deformities and developmental defects of the baby. The analysis data is not indicative, since alpha-fetoprotein, human chorionic gonadotropin and placental lactogen are synthesized in greater quantities than during pregnancy with one fetus, so the results may be false positive.
Swelling, shortness of breath
As the gestational age increases during multiple pregnancy, the load on all the woman’s organs increases, so the second half of her pregnancy often proceeds with complications and extragenital diseases almost always worsen. Thus, the load on the heart increases due to a significant increase in the volume of circulating blood, the diaphragm is displaced by the rapidly growing uterus and the woman experiences shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling. Read more about edema during pregnancy.
Preeclampsia
Gestosis during pregnancy with several fetuses is diagnosed in almost half a percent of cases, and they develop earlier and are more severe. On the one hand, this is due to an increase in blood volume and increased glomerular filtration in the kidneys, which causes an increase in blood pressure, edema and proteinuria, on the other hand, the occurrence of gestosis is provoked by chronic diseases of the mother, which, as was said, are aggravated in 100% of cases.
Anemia
In addition, due to blood dilution (increasing plasma volume), hemoglobin and red blood cells decrease - a common phenomenon and is called physiological anemia during pregnancy. However, as the gestational age increases, erythiropoiesis increases in intensity, which leads to depletion of iron stores in the woman’s body and triggers the mechanism of iron deficiency anemia.
Constipation
An overstretched uterus puts pressure on the intestines, so when pregnant with twins, women often suffer from constipation and puts pressure on the urinary tract, which causes the frequent development of gestational pyelonephritis.
How can a doctor determine that a pregnant woman has twins?
In the hospital, the doctor will be able to determine the following symptoms of twins during pregnancy:
- the monitor shows 2 embryos (closer to 12 weeks);
- AFP blood test – high levels;
- the gynecologist, after measuring the uterus, discovers its significant expansion;
- Using the Doppler system, an experienced doctor will be able to hear the two embryonic pulses beating.
After a woman’s doubts are confirmed by a doctor, she can track the development of twins by week of pregnancy using a special calendar. This is how it will be easier to go through the period of intrauterine development.
Managing a twin pregnancy
Women carrying twins are at high risk and require careful monitoring throughout the entire period of expecting children. Thus, such pregnant women are prescribed visits to antenatal clinics more often than during normal pregnancy, every 14 days until 28 weeks, and then every 7 to 10 days. In addition, maternity leave is issued not at 30 weeks of pregnancy, but at 28 weeks, and sick leave lasts a total of 160 days.
Such pregnant women should pay special attention to nutrition. If the weight gain during pregnancy with one fetus is generally 9–13 kg, then during pregnancy with twins it can reach 20 kg. Accordingly, the daily caloric content of the diet increases (up to 4000 – 4500 kcal).
Given the increased demands for minerals and vitamins, it is therefore recommended to start taking vitamin and mineral complexes from the moment the fact of multiple pregnancy is confirmed.
Folic acid, which is prescribed in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy (see pregnancy period calculator by week) to prevent malformations of the brain and spinal cord at 0.4 mg/day, is prescribed for pregnant twins at 1 mg/day. Anemia is also prevented by prescribing iron-containing drugs from 15 to 20 weeks, 80 to 100 mg per day.
First trimester
- 1-4 week
As a rule, a woman does not even suspect she is pregnant yet.
After the fusion of the egg and sperm in the fallopian tube, a zygote is formed. This is a single cell from which a multicellular organism will subsequently be formed. If there were initially two eggs, and they are fertilized by two different sperm, then two zygotes will be formed, and fraternal twins will develop.
During the process of cleavage, the zygote turns into a morula. First there are 2 cells (one cell is divided in half), then 4, then successively 8, 16 and 32 cells, located in a dense cluster in the shape of a raspberry. It is at the morula stage of 32 cells that the proembryo enters the uterine cavity. It may not be implanted into the wall of the uterus immediately, but after 2-3 days.
I will dwell in more detail on the moment when one fertilized egg gives two lives. This happens if, during crushing, the morula at some point suddenly “falls apart” into two parts, and each part begins to develop further independently, forming a separate organism.
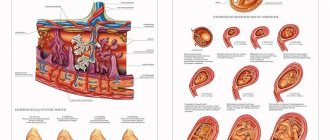
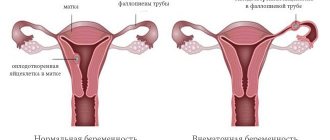
If the division of a single fertilized egg occurs in the first three days after meeting the sperm, twins develop with separate membranes and separate placentas (second column in the figure).
If this division of the egg occurs between the 3rd and 8th days after conception, the twins will have separate membranes and one placenta (third column in the figure).
If the egg decides to divide later than 8 days, but before the 13th day from the moment of fertilization, twins will develop with a single membrane and a single placenta (fourth column in the figure).
Late division of the egg (after 13 days of life) threatens the development of undivided twins (Siamese).
Before implantation, a cavity is formed between the morula cells, and it turns into a blastocyst - a hollow vesicle filled with liquid contents.
Implantation occurs approximately on the 7th day after conception. At this stage, the process of cell division is only progressing. The process of implantation of the embryo into the wall of the uterus may take a couple of days. This is considered the first critical period in the development of pregnancy.
In the second week, the formation of primary and secondary chorionic villi (the future placenta) and differentiation of the germ layers, which will subsequently give rise to all the organs and systems of the baby, occur. This is considered the second critical period in obstetrics.
Up to 14 days, the embryo looks like a vesicle consisting of three germ layers. From the third week, blood vessels form and grow into the chorionic villi. Thanks to this, when the chorionic villi come into direct contact with the mother’s blood, the fetus receives nutrients. Thus, the type of nutrition of the embryo changes to hematotrophic (through blood).
With the beginning of the third week, the formation of all organs begins (organogenesis). First, the neural tube, heart and gonads are formed, then the liver, lungs, primary intestine and primary kidney. Starting from the 3rd week, you can determine the fetal heartbeat on an ultrasound, if the permission of the device and the qualifications of the doctor allow this to be done.
At the 4th week, the nervous system continues to develop, the rudiment of the brain and spinal cord is formed. At this time, the rudiments of the upper and lower limbs are already visible in the embryo.
By the end of the 4th week, the embryos will be no larger than 2 cm in size.
- 5-8 week
During this period, organogenesis continues, that is, the formation of organs and body systems of developing children. The structure of all previously laid down organs and systems becomes more complex. Nerve fibers are formed that connect organs with the central nervous system, that is, with the brain and spinal cord. The head of the embryos at this time is disproportionately large.
At the sixth week of pregnancy, embryos can already bend and straighten their necks, changing the position of the head. Gradually, facial features emerge, eyes, ears, and mouth are formed. There is a clear difference between the upper and lower extremities, and the fingers are different.
At this stage, gender has already been formed, but gender cannot yet be determined. The genitals visible on ultrasound have yet to form.
Blood flow in the uterus and placental bed becomes more intense to ensure such intensive growth and development of embryos.
The eighth week marks the end of the embryonic period of baby development. At this time, the embryos are usually 4.5-6 cm long and weigh about 15-20 g.
- 9-12 weeks
By the ninth week, babies are fully formed to be called not embryos, but fruits. Your own blood type and Rh factor appear. With the end of the embryonic period, complete differentiation of the brain and spinal cord, central and peripheral nervous systems is observed.
The fruits swallow amniotic fluid. Their bladder and kidneys function. The movements of the fetuses become more varied - they can cover their faces with their hands, suck their thumbs, and move to the sides. The external genitalia are formed. The structure of the placenta becomes more complex. It begins to perform more and more functions (respiratory, protective, metabolic, hormonal).
At 12 weeks, the length of the babies is approximately 85-90 mm, the babies weigh up to 30 g each.
The first trimester of pregnancy has come to an end.
What changes await the expectant mother of twins in the first trimester?
The expectant mother of twins in the first trimester may experience earlier and more severe toxicosis, which may also make itself felt in the second trimester.
The uterus quickly increases in size. By the end of the first trimester, it often extends beyond the pelvis, therefore putting pressure on adjacent organs and can disrupt their normal functioning. Thus, pregnant women with twins feel a frequent urge to urinate already in the first trimester. Constipation is also a frequent (but not obligatory) companion to multiple pregnancies.
Useful: What to do if you can’t get pregnant: recommendations, reasons and myths.
In women during this period, the mammary gland actively enlarges and becomes moderately painful and sensitive. But this symptom is characteristic not only of twin pregnancy, but of any pregnancy.
A woman should visit her doctor once a month. The gynecologist, at his discretion, can set you an individual schedule of visits. Up to 12 weeks, women must undergo an ultrasound, during which all disorders and malformations of the babies are excluded.
Complications
In addition to the listed features and complications of multiple pregnancy, pregnancy with twins also has specific complications:
- the phenomenon of the death of one of the embryos or anembryony (this phenomenon occurs in 15 - 20% of cases, and the reasons are not precisely established; the fertilized egg stops developing and either undergoes reduction - resorption or remains in the uterus until birth);
- feto-fetal blood transfusion syndrome (FFH) - the presence of anastomoses between the fetoplacental systems of both fetuses (found in monozygotic monochorionic twins), redistribution of blood occurs, and one fetus gets more of it, and the other gets less, and both fetuses suffer;
- fusion of children - Siamese twins;
- antenatal death of one baby;
- congenital “deformities” in one of the twins;
- chromosomal disease in one of the children;
- reverse arterial perfusion.
Also, when pregnant with twins, a woman is advised to limit physical activity, increase daytime rest (up to 2 hours), mandatory walks in a forested area, and the indications for issuing a certificate of incapacity for work are expanded.
Example from practice : I had a 30-year-old multi-pregnant woman registered with me. She had a second, desired pregnancy, but, fortunately or unfortunately, with twins. Interestingly, the patient’s previous birth ended in a cesarean section, so she was automatically included in the high-risk group for elective surgery. When registering, the woman assumed that her period was short, in accordance with menstruation, 10 - 11 weeks. But at the very first gynecological examination, I suspected something was “off” and sent the patient for an ultrasound (the uterus was enlarged to 15-16 weeks). To our mutual joy, twins were confirmed, and the subsequent pregnancy proceeded well. However, at 22 weeks, the woman ignored the recommendations and carried bags of potatoes, which ended very badly: a late-term miscarriage. But a couple of years later, the same patient becomes pregnant again and the situation repeats: twins. Again, my colleague and I are almost blowing away specks of dust from her, but at 22–23 weeks she wanted to travel (she went to her husband by train, who was on a long business trip), disregarding our advice and warnings. And, of course, the situation repeated itself (but in a different hospital). The result is disappointing: a burdened obstetric history, a scar on the uterus, recurrent miscarriage.
Features of childbirth
Usually, in case of multiple pregnancy, doctors advise going to the maternity hospital 2-3 weeks before the expected date of birth in the case of twins, and 4 weeks in the case of triplets. Even if the pregnancy proceeded without complications and you feel well.
As for the method of delivery, everything will depend on the condition of the mother and her babies. If the pregnant woman feels well, there were no complications during the entire waiting period, all tests are normal and both babies are in the correct cephalic presentation, then a natural birth is quite possible.
With the normal development of the situation, babies are born one after another with a break of 15 minutes to 1 hour. Although usually this time does not exceed half an hour. But in the case of triplets, doctors most often resort to cesarean section.
Double or even triple births are not an easy test. It is very important to be attentive to your condition, visit a doctor on time and not ignore the symptoms that bother you, no matter how insignificant they may seem.
Twins after IVF
Many childless couples resort to trying IVF. The essence of in vitro fertilization is to remove mature eggs from a woman, fertilize them “in vitro,” as they say, in a test tube, and then introduce the fertilized eggs into the uterine cavity. Today, the introduction of one to four eggs is allowed (depending on the quality and quantity of fertilized eggs obtained in vitro).
Therefore, the percentage of multiple pregnancies after IVF reaches 70 - 80. A multiple pregnancy is already a serious test for a woman, and one that occurs after the use of assisted reproductive technologies is fraught with multiple complications due to pronounced disorders in the reproductive system and the presence of extragenital diseases and requires careful monitoring and control of the dynamics of tests .
- In the first trimester, it is important to regularly examine the hormonal levels of a woman’s body, especially hCG and estradiol levels.
- In the second/third trimesters, a twin pregnancy that occurs after IVF is at risk of developing cervical insufficiency and miscarriage. Therefore, when pregnant with more than two fetuses, a woman undergoes reduction of “extra” embryos.
Reduction (removal) is optimally performed at 9–11 weeks of pregnancy. There are 3 reduction methods: transcervical, transvaginal and transabdominal. Transabdominal reduction is considered the safest, when, under the control of ultrasound monitoring, a needle inserted into the uterus, piercing the anterior abdominal wall, punctures the embryo.
Case study: A young woman, 28 years old, after unsuccessfully trying to get pregnant and undergoing several courses of treatment, resorted to the IVF method. As a result, she had a long-awaited pregnancy with two fetuses. Until 22 weeks, the pregnancy proceeded wonderfully, without complications characteristic not only of multiple, but also of singleton pregnancies. The woman strictly followed medical recommendations, took the necessary medications and regularly attended antenatal clinics. But at 22 weeks, the patient was admitted to the hospital with broken water and severe external bleeding. It is clear that the pregnancy could not be saved.
Signs
Most often, in appearance and subjective sensations, such a pregnancy is practically no different from a singleton pregnancy. Although there are several signs by which you may suspect you have twins. Especially if you have already had such cases in your family. These include:
- A bright, clearly defined line on a pregnancy test.
- Early toxicosis, which is more severe.
- Severe fatigue that appears in the early stages, swelling of the legs and heaviness in the back, which usually appear in the second trimester.
- Large belly.
- Early and more active movement of the baby.
Such signs are very subjective and can also occur during normal pregnancy due to the individual characteristics of the body. Therefore, those that the doctor can determine will be more reliable. Namely:
- A depression at the bottom or on the anterior wall of the uterus, which occurs due to the adhesion of the fetuses to each other.
- Listening to a distinct heartbeat in different parts of the abdomen. In this case, heart sounds, as a rule, have unequal frequency.
- Phonoelectrocardiography is a study carried out at approximately 20 weeks of pregnancy, which allows you to register several heart sounds and accurately determine how many babies you are growing.
- Abnormal AFP test result. This is a blood test for alpha-fetoprotein levels, which is usually performed in the second trimester, from 16 to 18 weeks, in order to exclude various malformations.
The main method of confirming multiple pregnancy will be ultrasound, which helps determine it starting from the 6th week of pregnancy. Moreover, the accuracy of the method is 99.3%. All other studies are used only as auxiliary.
Diagnosis of twin pregnancy
How to determine pregnancy with twins?
- A doctor may suspect a multiple pregnancy already during the first gynecological examination. In this case, a soft uterus is palpated, the size of which does not coincide with the period of delayed menstruation. But an initial examination, collection of anamnesis and complaints only allows us to make a presumptive diagnosis. It is possible that the large size of the uterus is associated with the presence of myomatous nodes.
- The diagnosis is reliably confirmed only by ultrasound, during which the presence of two or more embryos is determined.
- Determining the level of hCG in early pregnancy is an indirect confirmation of multiple pregnancy, since an increase in hCG levels is also possible with trophoblastic diseases (hydatidiform mole).
- Further ultrasound examination in due time (22 - 24 and 32 - 34 weeks) allows not only to determine the number of fetuses and amniotic fluid, but also to identify signs of developmental delay in one of the babies or both, developmental abnormalities, type of placentation (mono- or dichorionic ), localization of the placenta/placenta, presence of a septum (one or two amnions), position/presentation of the fetuses. In addition, ultrasound can detect fusion between twins and helps determine delivery tactics.