3757
Candidal stomatitis is a fairly rare pathology that affects the oral mucosa. To eliminate this problem, complex therapy is used. It includes medications of both local and general action, as well as traditional methods of home treatment.
What causes the development of the disease?
Before you begin treatment for candidal stomatitis, you need to know what affects its appearance. This will help you better understand what to avoid to prevent illness.
So, the main reasons:
- Weakened immunity that does not fully suppress the growth of the fungus.
- Any allergy (the appearance of which can also be influenced by a weakened immune system).
- Long-term use of medications that cause dysbacteriosis.
- Dehydration due to severe diarrhea.
- Lack of vitamins, especially vitamins A, B, C, E.
- Hormonal changes in the body (for example, during pregnancy in a woman) or other problems with hormonal levels.
- Oral health problems: diseases of the gums and teeth (gingivitis, caries, tartar).
- Toothpastes containing sodium lauryl sulfate, which is designed to clean the oral cavity and freshen breath, but leads to dehydration and the rapid development of stomatitis.
- Long stressful loads.
- Hereditary predisposition to diseases of the oral cavity often requires almost constant treatment of candidal stomatitis.
- Long-term chemotherapy associated with malignant neoplasms, which also weakens the immune system.
Due to one or more of the above factors, a favorable environment is created for the proliferation of fungi of the genus Candida.
There is also a systemic cause of candidal stomatitis, which requires treatment from several medical specialists at once - this is thrush affecting the entire body or its occurrence on the vaginal mucosa of a woman.
A child becomes infected with a fungus of the genus Candida as a result of passage through the birth canal or due to non-compliance with hygiene standards.
A common cause is dysbiosis
Candidal or fungal stomatitis occurs when candidiasis is an infection also caused by yeast-like fungi, primarily from the genus Candida albicans (thrush).
All microscopic organisms belonging to the genus Candida are considered opportunistic, that is, capable of causing disease only under certain conditions. Often, candidal stomatitis is preceded by dysbiosis in the mouth - a condition in which the composition of the microflora of the oral cavity changes. The number of beneficial microorganisms decreases, and the number of pathogenic microorganisms increases. The following factors can lead to dysbiosis:
- poor oral care;
- getting dirt or additional amounts of yeast-like fungi into the mouth through unwashed hands, dirty objects, food;
- side effect of potent drugs, for example, antibiotics, diuretics;
- long-term use of toothpaste or mouthwash containing sodium lauryl sulfate, a foam-forming substance;
- prolonged diarrhea (diarrhea);
- severe blood loss;
- dehydration of the body;
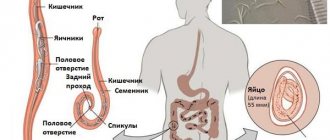
- vital activity of worms.
Worms can cause dysbacteriosis
Stages of development of candidal stomatitis
Treatment of candidal stomatitis depends on the degree of its progression. The entire disease can be divided into several stages based on its symptoms, depending on how late it is detected:
- Stage one. The mildest symptoms of oral candidiasis are the appearance of red sores on the mucous membranes: cheeks, lips, as well as on the gums, tongue and tonsils. At this stage, treatment of candidal stomatitis is difficult due to the fact that the disease is still barely noticeable and may not cause serious discomfort, which is why the patient does not see a doctor. The first stage can last quite a long time and not develop into subsequent ones.
- Stage two. A white cheesy coating appears at the sites of the ulcers, which can be removed. When scraped, red and rather painful wounds form at the site of the ulcers. At this stage, the temperature may rise, but only slightly and quite rarely.
- Stage three. The white cheesy coating becomes very difficult to scrape off, the wounds bleed and hurt a lot. This period is dangerous because microorganisms can get into bleeding wounds, which will cause bacterial stomatitis, the course of which is more severe and is accompanied by a very high temperature.
- Stage four. Severe form of candidal stomatitis, requiring immediate action. The upper respiratory tract may be affected, so only a specialist can determine how exactly to treat candidal stomatitis. At this stage, the disease is very dangerous for children.
In addition, it is also important to know that candidal stomatitis is a contagious disease that is transmitted through kissing and even through sharing utensils. We recommend that you undergo full treatment for candidal stomatitis and avoid such contact with other people during your illness.
Types of disease
The external manifestations of the disease may vary not only depending on the cause of its occurrence, but also on the age of the patient, the presence of concomitant diseases, the level of immunity, etc.
There are the following types of oral candidiasis:
- spicy;
- chronic.
Acute candidiasis
As it develops, you may notice symptoms such as increased body temperature, general malaise, lethargy, fatigue, etc. The symptoms of the disease are quite pronounced. In the absence of proper treatment, this type of oral thrush most often develops into a chronic form.
Acute type of stomatitis is divided into the following subtypes:
- atrophic - a more complex form, developing most often after taking antibiotics and other hormonal medications. Patients complain of pain, burning and dry mouth. There is no white coating. Cortical formations are possible on the reddened and inflamed surface of the lips and mouth. As a rule, patients with the disease lose taste sensitivity;
- pseudomembranous is the most common subtype of the disease. This form affects small children, premature babies, infants, as well as adults with the following diseases: AIDS, diabetes mellitus and various blood diseases.
The symptoms are quite pronounced. If there is no treatment in adults and children, the lesion may become atrophic.
In mild cases of the disease, small white plaque formations resembling a cheesy mass are observed. As a result of their removal, foci of inflammation form in place.
In more severe conditions, plaque is scraped off with great difficulty, leaving behind ulcers, often accompanied by bleeding.
Sick children often become lethargic and refuse to eat. Adults experience dry mouth and some pain while eating.
Chronic candidiasis
Formed as a result of lack of treatment of the acute form. As a rule, the symptoms are quite mild. There are two subspecies:
- hyperplastic - a disease that occurs in humans while taking antibiotics, as well as in patients with tuberculosis, AIDS and some blood diseases. White plaques form, gradually merging into large spots. Over time, the white color becomes slightly yellowish. It is quite difficult to scrape off plaque. Patients indicate ulcers, dryness and burning in the mouth, pain;
- atrophic - observed in people who regularly use false teeth. Underneath them, the oral mucosa may begin to dry out and swell. Patients complain of painful feelings, burning and dry mouth. You can see a whitish coating locally in the folds of the mouth and under the tongue.
Treatment of candidal stomatitis in adults
How to treat the disease “candidal stomatitis”?
First of all, at the first signs of the appearance of red sores, it is necessary to contact a specialist who must correctly diagnose the disease and prescribe treatment. Quick and timely diagnosis is the key to successfully overcoming the disease and eliminating discomfort.
Most often, in the treatment of candidal stomatitis, drugs from the group of antifungal agents are prescribed. Depending on the stage and form of the disease, they are taken 4-7 times a day until any signs of thrush completely disappear. Be sure to consult your doctor before using any medications!
Also during treatment it is necessary to use local antifungal agents, such as:
- A solution of baking soda in water (a teaspoon per glass of water). For better dissolution, the water should be warmed up a little.
- Drops with nystatin.
- Lotions with potassium permanganate. Potassium permanganate dissolves at a rate of 1 to 10,000.
- Asepta rinse solution. It contains an anesthetic component that relieves discomfort. The rinse aid is convenient because it does not require preparation and is immediately ready for use. You can take it with you to work and periodically rinse your mouth with it throughout the day. The solution has an excellent disinfectant effect and relieves burning sensation.
Treatment with drugs
The complex of therapeutic measures for candidiasis includes eliminating symptoms and taking antifungal drugs :
- The doctor prescribes Nystatin , Amphotericin B , Miconazole , Ciclopirox as the main remedy .
- To sanitize the oral cavity and relieve symptoms rinses are used. The most commonly used is a 20% solution of sodium tetraborate in glycerin .
- To treat severe forms additional restorative drugs and immunotherapy are prescribed .
Consumer Reviews
Maria Shamenkova (24review.ru)
“Unfortunately, I learned about the Asepta Active mouthwash late, when I was already sick with stomatitis. Unpleasant itchy ulcers appeared in the mouth. I was forced to even be on a liquid diet for some time. I lost a couple of kilos, and there really is no silver lining. However, the ulcers did not want to go away on their own, and the doctor told me to rinse my mouth at least twice a day with Asepta. The taste is pleasant, minty, so this treatment did not cause me any discomfort at all. The soreness has gone away, and now I just automatically use their Fresh mouthwash to keep my breath fresh.”
Polynina Evgenia (24review.ru)
“The Asepta Active mouthwash helped me a lot in a situation where, due to the eruption of a wisdom tooth, I was climbing on the wall in pain. The dentist said that the tooth is growing normally, it does not need to be removed, and he recommended this rinse for discomfort. Often in such a situation, purely instinctively, you don’t take out the toothbrush for fear of pain, and, accordingly, the germs remain. The mouthwash penetrates into the most inaccessible places and cleanses the oral cavity 100%. When I started rinsing my mouth with Asepta, the pain went away. For this, we should also thank benzydamine, an anti-inflammatory analgesic component in the mouthwash.”
In addition, certain foods promote the growth of fungus. Therefore, to successfully suppress its reproduction, it is necessary to follow a diet, completely or maximally eliminating fatty, sweet and starchy foods from your diet. Sour and sweet foods can irritate the oral mucosa and lead to the appearance of new ulcers, which makes the treatment of candidal stomatitis difficult even for adults, as it brings severe discomfort. The diet should consist of boiled, pureed dishes and continue throughout the entire period of illness.
It is also important to know that even after the visible disappearance of all symptoms of Candida infection, it is necessary to continue treatment for several more days to avoid relapse of the disease. Therefore, an adult needs to carefully monitor the treatment process for candidal stomatitis and avoid unauthorized withdrawal of medications, even if it seems that the condition has already improved. It is necessary to completely complete the course and carefully listen to the doctor’s advice.
In certain cases, at the discretion of the specialist, an additional single dose of an antifungal agent may be prescribed once a year to prevent recurrence of the disease.
In addition, during treatment it is also necessary to more carefully monitor the general condition of your body, take vitamin and mineral complexes, strengthen the body by hardening, play sports, and give up bad habits. We recommend the Asepta complex, which contains vitamins and minerals necessary for a person. It also contains coral calcium, which helps strengthen teeth, as well as coenzyme Q10, which stimulates the regeneration of the oral mucosa.
Therapeutic measures
Therapeutic measures for this disease consist not only of complex treatment of candidiasis, but also of strengthening the immune system, treating concomitant diseases and normalizing the microflora of the oral cavity.
General treatment
Fungal diseases, which include candidiasis, respond well to treatment with a combination of local remedies and general therapy drugs. The doctor prescribes antifungal drugs for acute and chronic disease, with extensive damage to the mucous membrane.
- medications are Diflucan or Nystatin.
- If there is excessive dryness in the mouth, a three percent solution of potassium iodide is prescribed. Iodine destroys fungus and increases salivation .
- To strengthen the immune system and as supportive therapy, vitamins, iron and calcium supplements are prescribed.
Local treatment
Antifungal drugs in the form of ointments, lozenges, gels, rinses and applications help destroy the fungus at its location. Antimycotics should be applied to areas affected by the fungus after first rinsing the mouth with regular warm water.
During rinsing, the Candida fungus is mechanically removed from the surface, after which it is more susceptible to the action of drugs. Nystatin ointment or Clotrimazole should be used for at least 10 days.
For adults
During the treatment period (it is at least two weeks), adults are recommended to pay special attention to oral hygiene. In addition to regular brushing of your teeth, be sure to rinse your mouth several times a day: after meals and at night.
For this purpose, antiseptic solutions are used. Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, Sangviritrin or Rotokan protect the mucous membranes from infections, prevent bacterial stomatitis and reduce inflammation caused by fungus.
For children
For children, rinsing is replaced with irrigation, while the child's head is tilted down so that the liquid flows out immediately. Aqueous solutions of Sangviritrin or Rotocan are used as antimicrobial drugs.
Almost all antifungal drugs are contraindicated for use in children under 12 years of age, so therapy is carried out with an aqueous solution of Pimafucin . Three tablets are dissolved in a glass of water and irrigated into the mouth or applied to the Candida lesions with a cotton swab. Iodinol and aniline dye are also applied with a cotton swab.
Traditional medicine recipes
Folk remedies for the treatment of candidal stomatitis are very effective and are quite capable of replacing antiseptics and pharmaceutical antifungal drugs.
The recipes are based on herbs that have an astringent and antibacterial effect, fresh juices and berry purees, and natural phytoncides of onion and garlic.
- Lingonberry leaf, bearberry or oak bark are brewed with boiling water and left in a water bath for about thirty minutes. Before rinsing, dilute with warm water in half. If you carry out the treatment without diluting the broth, the effect will be much greater. Concentrated herbal infusions can be used in the form of applications.
- Freshly squeezed juices of viburnum, cranberries or carrots are used for rinsing the mouth. Freshly squeezed juices of berries and vegetables are taken orally as a vitamin supplement.
- Rosehip or sea buckthorn oil is applied to a cotton pad and applied for half an hour to the place where Candida plaques are located. These oils have anti-inflammatory and regenerating effects.
- The pungent substances contained in garlic and onions can slow down the growth of the fungus, so during illness it is advisable to consume these vegetables fresh as often as possible.
How to treat candidal stomatitis in childhood?
In terms of symptoms, candidal stomatitis in children is no different from that in adults. The main difficulty in diagnosis and treatment is that the child cannot explain what exactly is bothering him and where exactly it hurts; his signals to parents about problems are that he refuses to eat, sleeps restlessly, cries more often and is capricious.
It is necessary to approach the treatment of newborns who were infected with candida during childbirth very responsibly and carefully, since candidal stomatitis occurs very quickly in them. In this case, there is also a risk of difficulty feeding due to pain, dryness and burning. The child also becomes restless and cries often. The most striking signs of damage to the mucous membrane of a newborn is the formation of a white coating, which later turns into a film. The temperature in mild forms of candidal stomatitis does not rise above 38 degrees and is usually very rare.
If a nursing mother detects in a timely manner that she has thrush, then infection of the baby can be avoided. To do this, we present here the main signs of damage to the mother’s nipples by the Candida fungus:
- Redness in the nipple area.
- Itching sensation.
- Severe peeling of the skin.
- Feeling pain when breastfeeding.
- Tingling sensations in the nipples and chest.
After each meal, it is necessary to give the child a few sips of clean water, and also treat the oral mucosa locally with antifungal drugs. Also very useful are rinses, which a child at a certain age can do independently. In this case, quickly suppressing the growth of the fungus will not be difficult.
If candidal stomatitis affects a small child, then during treatment it is necessary to wrap a cotton swab around your finger and treat the wounds with an antifungal agent. You can also use cotton swabs and pieces of sterile bandage. All this must be done with all precautions so as not to harm the child or cause him to experience stress.
Treating your baby's mouth can be easier if you purchase a special antifungal spray. The treatment procedure is quite unpleasant, but necessary for the successful treatment of candidal stomatitis in a child.
The course of treatment, in this case, as in adults, lasts until the symptoms completely disappear, and it should also be continued for several more days to prevent relapse of the disease. During the treatment process, it is important to observe increased hygiene precautions and treat the pacifier or breast with a soda solution before each feeding. This is done in order to remove possible traces of fungus remaining on them.
How and what can you treat candidal stomatitis in a child?
- A solution of baking soda at the rate of 1 teaspoon per glass of warm water.
- Creams and gels with an antifungal effect (they also have an analgesic effect, which eliminates discomfort in the mouth and helps restore the baby’s appetite).
- Aniline dyes.
Important! You cannot treat a child’s wounds with brilliant green or hydrogen peroxide, as they irritate the mucous membrane and can only aggravate the disease, but not cure it. You should also not give your child honey, since sweets only promote the growth and reproduction of the fungus. The most effective remedies in this case are special antifungal drugs that really help cope with the disease.
Also, in addition to local treatment, treatment with drugs for internal use with antifungal action is indicated. You should consult your doctor before using any of them.
It is also important to know the initial cause of the disease, so that by eliminating it, you can also eliminate the conditions for the growth of the fungus. If candidal stomatitis is caused by long-term use of antibiotics, then its treatment should be accompanied by the inclusion in the course of probiotics and drugs that improve the growth and reproduction of beneficial flora. Since, if the problem with dysbacteriosis persists, then when antifungal drugs are discontinued, a relapse of the disease may occur, and this may happen repeatedly.
It is also worth knowing that, in addition to the use of medications, it is necessary to carefully ensure that the child drinks plenty of fluids. Juices (orange, birch), herbal teas, cranberry juice, lingonberry juice - all this can and should be given to the child during treatment in order to replenish the dehydrated body and support it in the fight against the disease.
Like adults, when treating candidal stomatitis, children need to carefully follow a diet. It is necessary to completely exclude sweets, candies, and chocolate from the diet - they help create the most favorable conditions for the fungus. Fatty and spicy foods are also extremely undesirable; they not only help the fungus grow, but also irritate the mucous membrane, which leads to worsening of the condition and delays in treatment. All food for a child should be boiled, ground and gentle. These can be puree soups, porridges, omelets, cottage cheeses and the like.
In addition, along with vitamin and mineral complexes, we also recommend taking some medications to stimulate the immune system. However, you should not prescribe them to yourself, and especially to your child; it is better to visit a doctor and get advice on which drug is suitable for you and your baby personally.
What is it and what does it look like
About 30 species of microflora constantly live in the mouth, forming a biological balance - a balance of microflora, which is controlled by saliva. When the protective functions of saliva are weakened, the rapid development of opportunistic organisms begins - these include a fungus like Candida Albicans, which accounts for 95% of candidiasis diseases.
Conditions for the development of Candida fungus
Candida Albicans is a single-celled yeast fungus; under normal conditions it is harmless and even beneficial: it decomposes dead tissue and prevents intoxication. If there are foci of inflammation and tissue necrosis in the body, this will give impetus to an increase in the fungal colony of Candida. The optimal temperature for the life of the fungus is 37°, the nutrient medium is glucose; Excess sugar in the body can provoke its rapid reproduction. Lactobacilli and bifidobacteria, on the contrary, inhibit the development of Candida; the deficiency of these bacteria or their destruction by antibiotics creates conditions for candidiasis - the so-called damage to the mucous membranes and skin by overgrown colonies of the fungus. Candidal stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa caused by the proliferation of Candida fungi.
Why is candidiasis called thrush?
Candidal stomatitis in children, like vaginal candidiasis in women, is often called thrush. Colonies of the fungus form a white coating on the mucous membrane, curdled plaques have a sour smell - all this is associated with fermented milk products. Rashes with stomatitis are localized on the inner surface of the oral cavity, on the tongue. Signs of candidal stomatitis in adults (pictured below): a cheesy coating, limited foci of inflammation, the presence of ulcers and erosions - make it possible to differentiate the disease from tonsillitis and other non-fungal inflammations.
Helpful: Symptoms of a broken jaw
How to treat candidal stomatitis at home?
Treatment of candidal stomatitis is carried out at home with the help of appropriate medications prescribed by a doctor. It is important to treat the affected areas with creams and lotions in a timely manner and not to miss taking medications on time at the same time. Also, you should not cancel the course on your own, even if it seemed to you that you are already absolutely healthy. Moreover, to prevent the reappearance of candidal stomatitis, it is necessary to take a single antifungal agent after one to two months.
Despite the fact that a strict regime for the treatment of candidal stomatitis may not be followed, it is important to carefully maintain hygiene, treat surfaces with a disinfectant solution, wash toys with soap, and boil dishes without fail. This will help you avoid delaying treatment due to re-infection with fungus from your used items.
Prevention of candidal stomatitis
Prevention here is very simple - hygiene and thorough cleaning. It is important to strengthen your immunity with vitamins and walks in the fresh air, and for young mothers to maintain breast hygiene when feeding their baby and approach the issue of their health and immunity with special care.
Remember that stress, excessive physical activity, long-term underlying diseases and their inadequate treatment can provoke stomatitis. Take care of your health and well-being, maintain hygiene with the help of modern drugs!
Sources:
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- The use of adhesive balm "Asepta®" in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases L.Yu. OREKHOVA*, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor, Head of Department V.V. CHPP**, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor, Head of Department S.B. ULITOVSKY*, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor A.A. LEONTIEV*, dentist A.A. DOMORAD**, O.M. YAKOVLEV** SPbSMU named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, St. Petersburg - *Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, **Department of Microbiology
- https://cyberleninka.ru/article/v/puti-sovershenstvovaniya-pervichnoy-profilaktiki-zabolevaniy-parodonta Acute herpetic stomatitis in children, Baranaeva E.A. Merkulova E.P. magazine "Medicine and Healthcare"
- https://cyberleninka.ru/article/v/osobennosti-protivoretsidivnogo-lecheniya-allergicheskogo-stomatita Acute stomatitis in children, Drobotko L.N., Strakhova S.Yu.
For an accurate diagnosis, contact a specialist.