Dacryocystitis in children often develops under the influence of infection with pathogenic bacterial microflora. Inflammation of the lacrimal sac occurs when a young mother violates the basic sanitary and hygienic rules for organizing care for a newborn and infant. Typical symptoms of dacryocystitis and treatment of this pathology with etiotropic pharmacological drugs are discussed in detail in the proposed material. The probable causes of eye disease and laboratory diagnostic methods are also described in detail here.
Compliance with basic rules of personal hygiene, using only sterile materials to care for the eyes of a newborn - all these preventive measures will help avoid inflammation of the lacrimal sac in children.
The essence of the problem
Inflammation of the lacrimal sac occurs as a result of the outflow of fluid in the canal being disrupted. As with any stagnation, pathogenic microflora begins to multiply there. If dacryocystitis in a child is not treated, complications may arise not only in the nasal canal, but also in the brain.
The human organs of vision are constantly moistened; tears are released not only at the moment of crying, but also so that a film covers the surface of the eye and prevents the mucous membrane from drying out. When it dries out, which happens when working at a computer for a long time, dry eye syndrome occurs. It is familiar to many - it feels like sand has been poured into the eyes.
The main tear duct is located near the corner of the eye. Smaller and auxiliary ones are located in the conjunctiva. The main channel has 2 holes, they are directed in the opposite direction from each other - one to the upper eyelid, the other to the lower.
Dacryocystitis
Dacryocystitis in children occurs due to the fact that there is a violation of the deformation of the germinal film. When the baby is still in the uterus, the outlet of the nasolacrimal canal is blocked by a film, which breaks after the baby is born. If this does not happen, the child develops dacryocystitis. The disease occurs due to the accumulation of epithelial cells, detritus and mucus in the closed lacrimal sac. Ultimately, this leads to an inflammatory process.
In addition, the patency of the lacrimal canal may be impaired due to pathological intrauterine development or due to injuries that occurred during childbirth. For example, the baby’s nasolacrimal canal has narrowed, agenesis of the ducts has occurred, they are too narrow or curved, etc.
Dacryocystitis can be not only congenital, but also acquired. Frequent rhinitis, pathogenic microbes - Staphylococcus aureus, streptococcus or Pseudomonas aeruginosa - can also lead to the development of pathology in a child.
Symptoms of inflammation of the lacrimal sac (dacryocystitis)
Some mothers of my little patients bring their child to an appointment already when the disease, as they say, is in full bloom. And this happens because for a long time mothers tried to cure the disease on their own, at home, with the help of over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs, mistaking the symptoms of inflammation of the lacrimal sac for conjunctivitis. But with conjunctivitis there is no tearing, and the amount of pus does not increase when pressing on the lacrimal sac.
Another common mistake is massaging the lacrimal sac area. If the patency of the lacrimal canal is impaired, the only thing that can be achieved with such “treatment” is an intensification and greater spread of the purulent-inflammatory process.
Do not engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication! Dacryocystitis (and conjunctivitis too) cannot be treated with the first drugs you come across in a pharmacy or read on the Internet. In addition, dacryocystitis cannot be cured with anti-inflammatory drugs alone. Remember that pus in the eye is extremely dangerous! Run to the doctor at the first signs of illness.
The thing is that the lacrimal sac, in which tears accumulate, performs the function of a pump. When we blink, it contracts and unclenches, pumping tear fluid into the nasolacrimal duct. If acute dacryocystitis goes untreated for a long time, then under the influence of the purulent-inflammatory process the lacrimal sac becomes flabby and loses its pumping functions. This leads to the fact that even after successful treatment of acute dacryocystitis, the child will continue to have a high risk of recurrence of the disease due to congestion in the lacrimal sac. If clinical symptoms of dacryocystitis appear, immediately seek medical help from an ophthalmologist.
Acute dacryocystitis without treatment can turn into a phlegmonous form - severe purulent inflammation, threatening the loss of the eyeball.
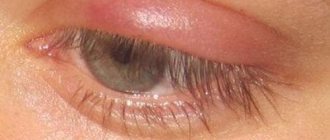
See what inflammation of the lacrimal sac looks like - the photo shows characteristic clinical symptoms:
Dacryocystitis in newborns
In the first months of life, a child's eye should be moisturized very generously. While in the mother's womb, the baby's organs of vision were filled with viscous masses resembling gelatin, and the entrance to the canal was blocked. After birth, the baby's eyes have to get used to new conditions, so tearing is usually very strong.
However, if the membrane has not ruptured and the tear duct has not opened, then about a week after birth, the baby can see redness and swelling of the skin near the inner corner of the eye, and copious and continuous tear production.
When you press on the area near the tear duct (in the inner corner of the eye), purulent fluid may be released. Typically, dacryocystitis in children is unilateral, but if the newborn suffers from bilateral inflammation, the severity of the disease is greatly complicated.
Forms of the disease
Dacryocystitis can be:
- sharp;
- chronic;
- infectious.
In the first case, the clinical picture and symptoms are clearly expressed. The chronic form is characterized by blurred symptoms; if the infection spreads further, for example to the epithelium located nearby, phlegmon of the eye may occur.
Dacryocystitis in newborns
For this type of pathology, there is also a certain gradation - it can be a simple form, stenotic, ectatic-catarrhal and empyema (phlegmous). Infectious dacryocystitis is divided into post-traumatic, parasitic, viral or bacterial, depending on the type of infection that affected the canal.
Forms of the disease
Symptoms and diagnosis
- Common symptoms of dacryocystitis are weakness, slight fever, headache, and depression.
- As for local changes, this is severe lacrimation, the inner corner of the eye is swollen, red and painful.
- When you press on the lacrimal sac, purulent or mucous fluid is released.
- With severe swelling, the palpebral fissure narrows.
- After 2 days, the infiltrate softens, bloody-purulent discharge may appear, and an abscess occurs, which can open on its own without surgical intervention.
Treatment of the disease
The acute form of the disease is treated inpatiently. At the beginning of the disease, while there is still no fluctuation, the child is indicated for UHF therapy. Additionally, vitamins are prescribed.
After the symptoms of fluctuation appear, it is necessary to open the phlegmon. Further measures include drainage with sodium chlorine solution. Within a week, the wound will need to be washed with a solution of Dioxidin or another antiseptic.
To clean the wound for 7 days, several times a day, it is necessary to treat with agents that improve the healing process. Methyluracil ointment is usually used for this purpose. In addition to this, magnetotherapy can be used.
For about 10 days, you need to drip antimicrobial drugs into the conjunctival sac - these can be solutions:
- Levomycetin;
- Sulfacyl sodium;
- Gentamicin;
- Miramistina;
- Tsipromed;
- Colbiocin;
- Trimethoprim.
At night for a week, tetracycline or erythromycin ointment must be placed in the conjunctival sac. The patient should be given antibiotics or sulfa drugs orally or by injection.
Treatment tactics
Treatment
Both conservative and surgical treatment can be prescribed. All possible medical actions for dacryocystitis:
- massage;
- application of drops;
- taking antibiotics;
- probing;
- dacryocystorhinostomy.
In the acute course of the disease and the formation of fluctuations, that is, the accumulation of fluid with purulent contents. The phlegmon is opened, drainage is placed, and a sodium chloride solution (ten percent) is used. For at least two, maximum five days, wash with antiseptic solutions. At this time, the wound tightens and heals. Therapy is accompanied by taking multivitamins and antibiotics, and sometimes magnetic therapy is used.
If the disease is detected in a timely manner in the early stages, the baby begins to undergo therapeutic massage and early probing. If a diagnosis is not made in time or the wrong treatment is started, the process can be complicated by terrible pathologies or become chronic.
The child may be prescribed the following antibiotics:
- penicillins;
- aminoglycosides;
- cephalosparins;
- sulfa drugs.
Using eye drops
Drops for dacryocystitis in newborns are prescribed by an ophthalmologist, based on the child’s health condition and the presence of characteristic symptoms. The baby will be prescribed medications containing antibiotics, for example, Tobrex. The product is prescribed one drop up to five times a day and is used for a maximum of a week, but not less than five days. Sometimes, a positive effect occurs within the next day, and some parents stop using the drops. However, this should not be done. Such actions increase the risk of exacerbation or early relapse of the disease.
Massage treatments
Massage for dacryocystitis in newborns is necessary to cleanse the lacrimal sacs of accumulated pus. In recently born babies, this is a fairly effective way to open the tubules. Pressure is applied up to ten times a day for two weeks.
You can entrust this procedure to a specialist, or you can learn it yourself and carry it out at home.
- Wash your hands and trim your nails first. You can use sterile gloves. However, do not forget to disinfect or use new gloves for each subsequent procedure.
- It is necessary to rinse the eye with a solution of furatsilin. We draw from the outer to the inner edge. Now you need to wipe off the released pus using a sponge or bandage, but be sure to use a sterile one.
- It is necessary to gently press with your finger (pad) on the inner corner of the eye (from the bridge of the nose).
- Apply pressure on the lacrimal sac using forward, jerky movements. This promotes the release of purulent contents and tear fluid. It must be taken into account that too light pressure will not produce the desired effect; too much pressure will damage the integrity of the nasal cartilage of a newborn baby.
- Place strong tea leaves, furatsilin solution or chamomile decoction into the sore eye. Use a clean sponge to wipe away the secretion.
- Swipe again from top to bottom from the inner edge along the base of the wing of the nose using pressing and vibrating movements. This will help break through the film that did not break during the birth of the child.
- The procedure of squeezing and cleansing is repeated up to five times a day. Each time after this, the eye is instilled with Levomycetin or Vigamox, Tobrex.
I bring to your attention dacryocystitis in newborns, a video of a massage.
Application of the probe
If the child’s condition has not improved through conservative treatment, then, starting from the age of two months, he is prescribed sounding.
The baby is given local anesthesia using analgesic drops. A probe is inserted into the lacrimal canal, with the help of which the gelatin film is pushed out.
After this procedure, the lacrimal ducts are washed with an antiseptic solution.
Probing takes literally a few minutes. The baby's crying has a positive effect on accelerating the breakthrough of the film and promotes the opening of the tear duct.
This procedure is successful in 95% of cases. Parents will immediately notice the onset of a positive effect, because pus and mucus will stop secreting, and normal clear tears will be observed when crying.
Operation
Surgery is prescribed if a positive effect has not been achieved from taking antibacterial drops, massage, and even after probing.
As a rule, two years are expected, after which a dacryocystorhinostomy is performed, the main purpose of which is to create an outflow tract.
Today, the procedure can be performed endoscopically, which is a more gentle method of surgery.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine preparations may be prescribed as additional therapy, but only after consultation with the attending physician:
- compresses with decoctions of dill, mint or chamomile;
- freshly squeezed Kalanchoe juice is used as lotions or drops (one drop three times a day);
- used black tea bags (without flavorings and all kinds of additives) are applied to the sore eye after cooling.
Now you know what dacryocystitis in newborns is and the treatment of this disease. It is very important that the disease was diagnosed on time and treatment procedures were provided. Remember that an neglected condition can lead to the development of serious consequences and severe complications. Take care of your baby's health from the first months of his life!
Antibiotics for children
A bactericidal effect can be achieved using Penicillin (course up to two weeks), Ampicillin can be given orally, and Oxacillin can be administered intramuscularly. Aminoglycosides and cephalosporins also have a bactericidal effect. If the symptoms are pronounced, the doctor may recommend droppers with Hemodez, glucose with ascorbic acid. You should also alternate injections of calcium chloride and methenamine.
Massage of the tear duct is recommended for newborns; the doctor will explain and show you how to do it. The procedure must be carried out 3 times a day for 2 weeks. After the massage, antiseptics should be dripped into the conjunctival sac. This could be Miramistin, Furacilin or Picloxidin. Passive rinsing of the lacrimal ducts with antiseptics is necessary for 1-2 weeks.
If there is no result, doctors prescribe a probing procedure. When the symptoms of the disease stop appearing, lacrimation may still continue. If it does not go away for too long, then surgery is necessary to restore the outflow of tears.
Diagnostics
- Personal examination of the child, collecting complaints, finding out the time of onset of symptoms and possible causes:
- the doctor will evaluate the absence or presence of lacrimation, protrusion of the corner of the eye;
- examine the condition of the skin near the eyelids;
- look at the growth of eyelashes and the presence of lacrimal openings;
- assess the nature of the discharge from the lacrimal sac. Necessary to confirm or exclude an infectious process.
- A nasal test is performed to assess the patency of the lacrimal canals. Three percent collargol (2 drops) is dropped into the baby's eye. After this, a cotton pad is inserted into the nose to a depth of 2 cm. If, five minutes after instillation of the eye, paint appears on the turundum, then the lacrimal ducts are functioning normally, the reaction is positive. If 10 minutes pass, but staining still occurs, this indicates a slow process. If more than 10 minutes pass and no color appears, then there is a blockage.
- The tubular test is carried out to assess the suction function of the lacrimal tubules, puncta and sac. During this procedure, the eye is also instilled with collargol (three percent) - two drops. If the color on the eye disappears after 5 minutes, then everything is fine, if it takes up to 10 minutes, then the process is slow, and if it lingers for more than 10 minutes, then the outflow of tears is severely impaired.
- Clinical analysis of urine and blood.
- Laboratory examination of discharge in case of suspected infectious process to identify the pathogen and determine its sensitivity to groups of antibiotics.
In addition, additional studies may be carried out, which include:
- endoscopy of the nasal cavity;
- washing and probing of the lacrimal ducts.
Complications of the disease
If treatment for dacryocystitis was started on time and carried out correctly, then there should be no complications or consequences. If the disease is advanced, stretching of the lacrimal sac may occur, and a dacryocystocele may also form. Visually, it will look like a bump in the inner corner of the eye.
A complication of dacryocystitis can be phlegmon of the lacrimal sac. This is a dangerous purulent inflammation. If the patient is not promptly provided with qualified assistance, the disease can be fatal.
Complications
One of the complications is phlegmon of the eyelid and orbital tissue. Purulent inflammation can spread to the entire eye area (panophthalmitis), and over time this can lead to significant visual impairment or even complete blindness.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies for the treatment of dacryocystitis can be used, but always after consultation with a specialist, especially if we are talking about a newborn. Under no circumstances should you put breast milk (or urine, which is even more dangerous) into a child’s eye: this can lead to additional microbes getting into the eyesight, which will only aggravate the course of the disease. Herbal compresses include dill, mint, chamomile, and tea lotions.
Some people believe that dacryocystitis will go away on its own. The tear sac and its ducts grow with the baby, and the membrane that prevents tears from going in the right direction can burst. This can lead to the fact that after the age of 1 year the child will get rid of the pathology on his own. But if this does not happen before 2 years, then, most likely, you will have to do probing.
Massage for dacryocystitis
It is important to understand that if a child has an acute disease, there is purulent discharge and an elevated temperature, then waiting 2 years is at least dangerous. You need to bathe your baby with caution, carefully ensure that water does not get into the eyes; when walking, you also need to pay attention to ensure that strong winds do not blow dust into the organs of vision. In addition, it is necessary to ensure that the baby does not rub his eyes with dirty hands.
Surgical methods
If after the first stage of treatment signs of the disease persist, surgical methods are prescribed.
Probing
Parents are wary of this method, but they should remember that the procedure is painless and is performed only under local anesthesia .
The essence of the procedure:
- A special probe is passed along the natural course of the lacrimal duct, pushing out the membrane and the resulting plug.
- The lacrimal ducts are washed with an antiseptic solution.
- The procedure takes up to 3 minutes.
- Local antibacterial therapy is prescribed for 6–7 days.
- There are cases when repeated probing is performed (the hole is closed with a lump of pus or mucus).
The procedure is performed on children aged 2–3 months according to the indications of a specialist. Delay can cause complications (the film thickens over time), relapses and the formation of adhesions in the lacrimal sac are possible.
Expert opinion
Ermolaeva Tatyana Borisovna
Ophthalmologist of the highest category, Candidate of Medical Sciences
The baby will not feel any pain at all, but may cry due to the bright light aimed at the open eye. After the procedure, the child will not experience discomfort.
Physiotherapy with probing
Massage, rinsing, baths are accompanying procedures that help quickly get rid of canal blockage.
Is it possible to be cured without this procedure?
In 90 cases out of 100, regular massage and drops give the desired result - the ducts are freed from the plug. If symptoms persist for a month, it is advisable not to delay probing.
Bougienage
Bougienage is a type of sounding. The procedure is safe, performed with anesthesia, lasts 5–6 minutes . It is prescribed only when at the first stage of treatment (rinsing, massage) the gelatin plug could not be broken, the canal is still clogged.
The operation is performed in the first year of the baby’s life (up to 5–6 months). Blood tests for coagulation are taken first. During the procedure, the walls of the lacrimal canal are moved apart with a special instrument (bougie), the canal is pierced, and then washed with a special solution.
Operative surgery
Expert opinion
Ermolaeva Tatyana Borisovna
Ophthalmologist of the highest category, Candidate of Medical Sciences
These methods are used in severe (chronic or acute) forms of the disease, taking into account the child’s age, neglect or repeated signs of canal blockage. Surgical operations completely restore the function of tear secretion.
Using a laser
A special laser endoscope is used to make a hole in the nasal bone connecting the nasal canals with the lacrimal sac.
Using an endoscope
A similar procedure involves using an endoscope to make a passage between the nasal cavity and the lacrimal canaliculus (the site of the blockage is cut).
Fracture of the nasal bone, without displacement of fragments
The method is rarely used (in 1 - 2% of cases). During the operation, the patency of the lacrimal canaliculus is restored by destroying the nasal bone (if pathologies are identified).
Balloon dacryocystoplasty
During the operation, a guide with a special balloon is attached to the tear duct through an opening in the corner of the eye. The balloon is filled with liquid and expands, clearing the tear duct.
Dacryocystorhinostomy
Conducted for children aged 10 years and older. During the operation, a temporary (for 1.5 - 2 months) prosthesis is installed - a tube through which tears flow into the nose, bypassing the blocked passage. The prosthesis is installed through the lacrimal sac, and a hole is made in the nasal bone.
Preventive measures
To prevent dacryocystitis, newborns are given antibacterial drops in their eyes and the nasolacrimal duct is massaged. But if, nevertheless, alarming signs of this disease are observed in a child, there is no need to be alarmed; you need to visit a doctor as soon as possible.
Chamomile is a proven antiseptic that can be used from infancy
Some mothers do not want to use antibiotic therapy for their baby, but here it is necessary to remember that any untreated process will most likely lead to surgery. In any case, parents should listen to the recommendations of the ophthalmologist and follow all the prescriptions he makes.
Treatment of dacryocystitis
To eliminate the disease and prevent complications, comprehensive treatment is carried out, which includes:
- ingestion of antibacterial and immunostimulating drugs;
- topical preparations, mainly in the form of ointments, emulsions;
- physiotherapeutic effects - UHF lamps, warming up;
- special massage, which is carried out up to 5-7 times a day, to open the lacrimal duct and remove the contents of the lacrimal sac;
- opening the abscess, washing and treating with antiseptic agents;
- formation of a new channel if necessary, if it itself has not recovered.
In the case of chronic dacryocystitis, it is possible to use a surgical method - widening the duct and forming the nasolacrimal duct. If the cause of the chronic form is deformation of the new cavity as a result of trauma, the help of a maxillofacial surgeon is required.
The following methods are used to treat newborns and infants:
- probing of the nasolacrimal duct - used if the prenatal membrane itself has not resolved;
- washing the eyes with special solutions;
- massage to squeeze out contents from the nasolacrimal ducts. Often, massage effectively removes the membrane that interferes with the outflow of tears;
If conservative methods do not help after three months of age, surgical intervention is possible to open the nasolacrimal duct.
In case of dacryocystitis, it is very important to exclude mechanical irritation of the eyeball. If the patient has vision problems and wears contact lenses, it is necessary to abandon them for the duration of treatment and use glasses. Contact lenses irritate the already damaged mucous membrane of the eye, which can lead to a purulent process on the conjunctiva and injury.