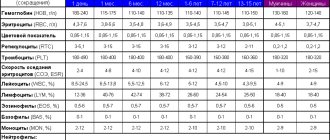
Mechanism of development of ear pain
The syndrome occurs against the background of various ailments. In most cases, ear pain develops as a complication of sinusitis. In this case, the patency of the auditory tube is disrupted. Poor ventilation of the ear cavities is the main cause of the unpleasant symptom.
Inflammation of the Eustachian tube - the canal connecting the middle ear cavity with the pharynx - is accompanied by swelling of the mucous membrane and a decrease in pressure inside the tympanic cavity. Impaired ventilation leads to inflammation and pain. When a foreign body gets inside the ear, the lumen of the auditory tube is blocked and inflammation occurs. The syndrome develops similarly when there are sulfur plugs.
Pain inside the ear can appear against the background of a sharp increase in pressure inside the tympanic cavity. The so-called barotrauma occurs when there are sudden loud sounds. Soreness often indicates neurological diseases. The mechanism of development of the symptom is not well understood. It is assumed that the syndrome occurs due to impaired blood circulation in the nerves of the auditory analyzer.
Why is ear pain dangerous?
Constant inflammation threatens to become chronic. In this case, the pain goes away, but purulent discharge appears. Lack of adequate treatment can result in rupture of the eardrum – perforation. Among other dangerous consequences of otalgia, experts call:
- meningitis;
- deafness;
- severe brain damage;
- death.
Associated symptoms
If swelling of the ear cavity occurs due to infectious inflammation, in such cases the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- systematic aching pain, which intensifies with palpation of the ear;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes located behind the ear;
- hearing loss;
- purulent discharge;
- feeling of stuffiness;
- general weakness, nausea, lethargy, chills;
- the ear is very red;
- elevated body temperature.
If a child has become capricious, his ear has turned red, he is constantly fiddling with it, scratching it - this is a direct reason to consult an otolaryngologist.
Ear pain as a sign of pathology
Otalgia is characteristic of many diseases. Depending on the etiology, pain inside the ear can be shooting, pulsating, cutting. As a rule, it is accompanied by other symptoms (itching, discharge). To determine the root cause, the syndrome must be considered in conjunction with other manifestations.
Inflammatory processes
The most common cause of ear pain is otitis media. Symptoms of pathology depend on its form. Depending on the location of the inflammatory focus, otitis media can be external, middle or internal:
| Form of otitis | Clinical picture |
| External - inflammatory disease affecting the auricle, external auditory canal |
|
| Middle – causes inflammation of the middle ear cavity |
|
| Internal – affects the bony labyrinth (cochlea and semicircular canals) |
|
Fungal infections
The infection affects the walls of the outer and middle ear. At first, the symptoms of fungal infection (otomycosis) are mild. The patient feels slight itching and tingling inside the ear. Then soreness and gray, dirty-black discharge appears.
Pathologies of neighboring organs
Diagnosis of inflammatory ear diseases is not difficult. The situation is more complicated with the secondary form of otalgia, when the syndrome is caused by pathologies of neighboring organs:
| Diseases of neighboring organs | Clinical picture |
| Diseases of the temporomandibular joint - located behind the anterior wall of the ear canal, susceptible to arthrosis, arthritis |
|
| Dental problems (caries, inflammation) are a common cause of otalgia. |
|
| Pathology of the cervical spine (osteochondrosis, myofascial syndrome) – accompanied by ear pain due to common innervation pathways |
|
| Sinusitis – inflammation of the paranasal sinuses |
|
| Mumps is a viral disease with non-purulent damage to glandular organs (salivary glands, testes, pancreas) |
|
| Mastoiditis – inflammation of the mastoid process of the temporal bone |
|
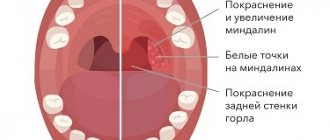
| Sore throat (tonsillitis), pharyngitis |
|
| Neuralgia of the trigeminal or glossopharyngeal nerve - |
|
Articles on the topic
- Blood from the ear - causes and possible symptoms, treatment methods, complications
- Bloody discharge from the ear - why it appears in children and adults, therapy
- Blood from the ear with otitis in adults - why it appears and what the symptom indicates
Throbbing ear pain after injury
Such symptoms indicate damage to the auditory organ. Sometimes the pulsation is caused by a traumatic brain injury. The intensity of the noise depends on the severity of the injury and the amount of swelling. The syndrome has a unilateral localization, accompanied by dizziness and vomiting.
Throbbing pain inside the ear is an alarming symptom that may indicate damage to brain structures.
Other reasons
Sometimes ear pain can be caused by intracranial tumors. Acoustic neuroma is a benign tumor of the auditory nerve. The disease manifests itself as noise, ear pain, and hearing loss. In addition, the cause of the syndrome can be rheumatic diseases. In this case, the spread of inflammation to the ear artery causes pain.
Eagle syndrome is a rare disease. The reason for its development is the elongation of the styloid process of the temporal bone. The growth irritates the glossopharyngeal nerve, causing pain inside the ear. Eagle syndrome is manifested by the following symptoms:
- unilateral sore throat;
- difficulty swallowing;
- facial pain;
- noise.
Injury
If the auricle hurts, then it is quite possible that the cause is an injury to the hearing organ. Tissue damage, cartilage puncture, strong blow or inflammatory process - all this will be accompanied by pain.
Painful sensations can be provoked by the following factors:
- Frostbite;
- Burn;
- Exposure to chemicals;
- Exposure to cold wind.
In this case, various treatment methods can be used, ranging from the use of an antiseptic to the use of ointment to relieve the tumor. When the injury begins to heal, the process will be accompanied by itching. Sometimes it can be very strong, causing a person to experience great discomfort. In this case, the specialist prescribes antihistamines to the patient.
If a serious injury to the auditory organ occurs, antibacterial drugs may be required to avoid infection.
Painful sensations can also provoke partial separation of the auricle. In some cases, its complete separation is diagnosed. In this case, urgent surgical intervention is necessary. You need to act as quickly as possible, as an inflammatory process may begin to develop, which will negatively affect the result of the operation.
Methods for determining the cause of ear pain
Otalgia accompanies many diseases. The following diagnostic methods help to identify the cause of the syndrome:
| Disease | Diagnostic methods |
| Otitis, eustachitis |
|
| Mastoiditis |
|
| Contusion, foreign body penetration, perforation of the eardrum |
|
| Arthritis or arthrosis of the temporomandibular joint |
|
| Barotrauma | Otoscopy |
| Pulpitis | X-ray of a tooth |
How to treat ear pain
Treatment methods are determined by the doctor. The choice of treatment tactics depends on the cause of the pain. If fluid accumulates in the ear cavity, the eardrum is punctured. In a situation where the symptom is caused by intracranial tumors, surgery is performed. In other cases, medications are prescribed:
- analgesics – suppress pain sensitivity (Ketorolac, Paracetamol, Otipax);
- antipyretics – reduce temperature (Nurofen, Mefenamic acid);
- vasoconstrictor drugs - reduce swelling of the mucous membrane (Polydex, Vibrocil);
- antihistamines – eliminate itching, redness (Cetrin, Diazolin);
- antibiotics - suppress bacterial infection (Tsipromed, Sofradex, Amoxicillin, Cefazolin);
- anti-inflammatory drugs - inhibit the production of inflammatory mediators (Prednisolone, Dexomethasone);
- antimycotics – inhibit the development of fungal flora in otomycosis (Griseofulvin, Natamycin).
Treating ear pain with physical therapy is also effective. Electrophoresis and pneumomassage are indicated if the pain syndrome is caused by osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. Pain inside the ear due to pulpitis and caries goes away on its own after the main problem is eliminated.
First aid
Otalgia can be primary or secondary. It is important to make sure that the syndrome is caused by an ENT disease. If the pain intensifies when pressing on the tragus of the ear, there is no doubt about it.
First aid in the form of a painkiller tablet should be provided immediately after calling a doctor.
Folk remedies for ear pain
Self-prepared ointments and drops should be used as an addition to the main treatment. Folk remedies will help temporarily relieve pain. It will not be possible to completely eliminate the problem using only compresses and infusions. Before using recipes, it is important to make sure that you are not allergic to individual components.
Compresses
The product is applied externally to the auricle. Compresses warm and accelerate regeneration processes. For this purpose, use a heated bag of salt or a simple bottle of warm water. Discharge of pus and temperature are contraindications for the procedure. For the compress you need:
- take a piece of fabric;
- cut a hole according to the size of the ear;
- soak in the solution;
- squeezing out excess liquid, place the flap around the ear;
- Place a cotton ball inside the ear;
- place a similar cellophane blank on top;
- wrap your head in a warm scarf.
A properly placed compress quickly relieves pain. It is dangerous to warm the ear with purulent otitis media. This can cause the infection to spread and lead to serious complications. For ear pain caused by inflammation, use:
- Compress with camphor alcohol. Dilute the product 1:1 with warm water. Soak the fabric blank with the solution and then place it on the ear. Place polyethylene on top according to the shape of the workpiece. Leave the compress for 1–2 hours. Carry out the procedures until complete healing.
- Oil compress. Heat the vegetable oil in a water bath to 38 °C. Saturate the fabric with it. After all layers of the compress have been placed, leave it for 6–8 hours. Apply the product until the condition improves.
- Dry compress. Wrap a bag of warm sand in cloth and place it on the ear for 15–0 minutes. Repeat the procedure 3-4 times a day until the patient’s condition improves.
- Compress with kombucha infusion. Take a 12-day infusion. Moisten the fabric blank with it. Then place the remaining layers. Keep the compress for 8-9 hours daily until recovery.
Drops
The product easily penetrates the ear canal. In view of this, the drops should not have an aggressive composition: a high concentration of acids. alcohols If the eardrum is perforated, the product should not be used. Drops based on:
- Olive oil. Place 3-4 drops of warm oil into the ear canal. Treat for a week.
- Hydrogen peroxide. In Art. l. Dilute 15 drops of 3% peroxide in warm water. Draw the solution into a syringe and inject it into the sore ear. After 10 minutes, remove the remaining product with a cotton swab. Apply peroxide twice a day before recovery.
- Baked onion juice. Bake the onion in the oven. Place the juice squeezed out of it into the ear canal. Carry out the procedure 3-4 times a day. Treat until pain disappears.
- Garlic oil. Chop a clove of garlic. Add to 15 ml olive oil. Leave for 20 minutes. Instill 3-4 drops of the finished product 4-5 times a day. The course of treatment is a week.
Prevention
Photo 2. To prevent diseases, you need to take care of ear hygiene.
Source: Flickr (Jason Carroll) In order to prevent the development of the infectious process, experts recommend following these tips:
- carefully observe the rules of ear hygiene - rinse with warm water or herbal infusion at least once a month;
- To prevent otitis, it is recommended to avoid getting water in the ears ;
- Since otitis media often manifests itself as a complication after a cold, it is important to treat illnesses in a timely manner until complete recovery.