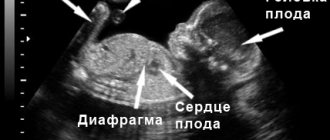
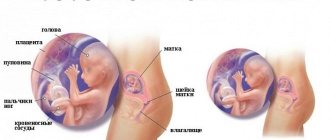
General information
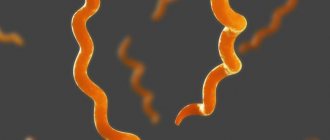
The causative agent of syphilis is Treponema pallidum. The infection is transmitted through contact of the skin and mucous membranes with infectious elements of the patient's rash. It is possible to become infected with syphilis through a blood transfusion.
There are several periods in the development of the disease:
- The incubation period is up to 30 days.
- Primary syphilis – up to 45 days.
- Secondary syphilis – from 2 to 4 years.
- Tertiary syphilis – from 5 to 15 years from the moment of infection.
A typical manifestation of primary syphilis is syphiloma. Syphiloma is a single solid round formation no larger than 1 cm in size. Syphiloma is located on the skin or mucous membranes, at the site of first contact. A deep, painless ulcer forms on the surface of syphiloma - a chancre.
When Treponema pallidum enters the bloodstream, secondary syphilis develops. Manifestations of secondary syphilis are varied and include the following symptoms:
- characteristic skin rashes;
- hair loss;
- increased body temperature;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
In the secondary period, the development of meningitis, glomerulonephritis (kidney damage) and uveitis (eye damage) is possible. Enlargement of the liver and spleen is very characteristic.
At the stage of tertiary syphilis, severe damage to internal organs and the nervous system occurs. Characteristic mental disorders appear and paralysis occurs. Currently, due to the active use of antibiotics, tertiary syphilis is extremely rare.
What are the consequences of infection
If a woman is diagnosed with syphilis during pregnancy, it is necessary to adequately assess the possible risks to the child. In some cases, abortion is the real solution. In about a quarter of cases, the fetus dies, about 60% of children are born with an existing congenital infection and characteristic defects of various kinds.
| Title and photo | Short description |
| Miscarriage
| Occurs in the early stages, the fetus exhibits abnormal development of organs, the tissues contain the causative agent of syphilis. |
| Antenatal death
| In the last weeks of pregnancy, the fetus dies as a result of damage to internal organs or cover of the placenta with scar tissue. The most common causes of death of a child are fatty degeneration of the lungs, shrinkage and hardening of the liver, and impaired blood supply. |
| Skin damage
| It can appear in the form of pemphigus, when fluid-filled rashes form on the skin. Bursting blisters form bleeding ulcers, and treponemes are released along with the liquid itself. Another option is that the skin becomes perfectly smooth, “mirror-like,” turns red, and then cracks. Radial scars form at the site of the wounds. |
| Osteochondritis
| Bone growth is inhibited, their gradual deformation occurs, and Parrot disease develops. |
| Rhinitis
| The difference between syphilitic rhinitis is that inflammation of the nasal mucosa leads to a gradual loss of the organ’s ability to function and its deformation. |
| Meningitis
| Inflammatory processes in the meninges provoke the development of hydrocephalus and curvature of the shape of the skull. In such children, the frontal lobe and brain region increase in volume. Indirect manifestations are strabismus and muscle paresis. |
| Dental dystrophy
| The shape of the teeth differs from normal; there is an expansion of the neck, while the cutting surface is significantly limited in area. |
| Hearing impairment
| Symptoms are most often detected at school age. They progress, and over time, labyrinthine deafness develops, which cannot be treated. |
| Visual impairment
| The cornea of the eye gradually becomes cloudy, and neoplasms such as plaques may be found at the bottom of the eyeball. Vision loss can be stopped if treatment is started early. |
| Infantile alopecia Congenital syphilis can lead to partial or complete baldness of the child. | The hair is lost completely or baldness is observed only in certain areas. |
If you have well-treated syphilis, and the pregnancy proceeded without complications, the likelihood of having a healthy child is very high. That is why you should not ignore even false positive test results.
There is a risk to the mother associated with impaired placental density. In some cases, it can be damaged in such a way that its particles remain in the uterus after delivery. To exclude complications, the doctor should examine the placenta for ruptures and looseness, and, if necessary, conduct a manual examination of the uterus. The woman is put under anesthesia.
Immediately after the birth of the baby, it is necessary to examine him for the presence of specific signs of congenital syphilis. After about a week, you can perform antibody tests with blood sampling. There is no point in doing this before, since up to a certain point, even in the blood of a healthy child, antibodies from an infected mother may be present.
Additionally, it is necessary to conduct an examination of the baby with consultation from the following specialists:
- ENT;
- ophthalmologist;
- radiologist;
- neurologist.
Specialists evaluate the child’s health based on specific signs. If characteristic symptoms and anomalies were identified during the examination, a series of auxiliary tests, lumbar puncture of cerebrospinal fluid and appropriate treatment are prescribed.
An important issue is not only the treatment of syphilis in pregnant women, but also the dynamic monitoring of the child after birth. The first year of life is key. Standard instructions involve regular examinations every 3 months of the child’s life.
The most important is the first infectious screening at 3 months. The child is examined by specialized specialists for developmental abnormalities, and laboratory tests are done for syphilis. If the results are positive, it is important not to skip follow-up examinations every 3 months. If the result is negative, the next visit to the venereologist can be postponed until one year of age.
If at 12 months the diagnosis of syphilis was confirmed by examination, observation continues, treatment is adjusted depending on its effectiveness at each stage. In the absence of antibodies to treponema and other suspicious manifestations, the child can be removed from the dispensary register, but it is still better to remain vigilant for the next 10 to 15 years, since some forms of the disease can appear many years later.
Further forecast
If a pregnant woman has been diagnosed with syphilis in any of its forms, treatment should not be delayed under any circumstances. If pathologies are detected in the fetus during intrauterine diagnostics, it makes sense to terminate the pregnancy.
With proper treatment, the prognosis is very favorable. A radically opposite situation occurs when the doctor’s recommendations are not followed and there is no treatment during pregnancy.
Most likely, the child will be born with pathologies and congenital infections or die in the womb. In the absence of observation and treatment after the birth of the baby, the prognosis for most sick newborns is critical - the risk of disability and death is extremely high.
But whether it is possible to get pregnant after syphilis and bear an absolutely healthy child is an entirely individual question. It all depends on the form of the disease, the timeliness and degree of effectiveness of its treatment.
Quite often, pregnancy after treated syphilis proceeds without complications, the child is born at term and has no congenital pathologies. That is why infected women should not despair and give up on dreams of motherhood.
For a more detailed look at the problem, watch the video in this article.
Treponema pallidum
The causative agent of syphilis is Treponema pallidum. Mostly, infection occurs through unprotected sexual intercourse, however, there are exceptional cases of infection through domestic means.
At the first stage of infection, syphilis does not make itself felt. No external manifestations, changes in mood, body temperature, or well-being. The incubation period of the disease lasts from one month to 5 weeks. It adapts to its new environment and “generates” infectious bodies.
Primary syphilis
The second stage of the disease is called “primary syphilis.” It occurs after the incubation period and can give the first, barely noticeable signs of the presence of pathology in the human body. A slight redness in the form of a circle or oval may appear on the body.
This spot will have a hard crust. Treatment with creams or ointments will not be effective. This spot will only increase, gradually developing first into erosion, and then into ulcerative inflammation, the diameter of which can reach 2 cm.
All such manifestations on the body do not cause inconvenience to their owner (except for the aesthetic appearance, of course). They don't hurt or itch. At the same time, the lymph nodes may become inflamed. Primary syphilis takes six to seven weeks after infection.
Secondary syphilis
Secondary syphilis (the third stage of the disease) occurs, as you already understood, from 8 weeks after infection. The duration of this stage can reach 4 years. During this period, strong changes occur in the human body.
External manifestations of the disease, such as spots, ulcers, dry crusts, spread throughout the body and are not local in nature. First of all, they appear in places with the most delicate skin: genitals, oral cavity, armpit area, “triangle” around the mouth, wrists, area under the knees, between the fingers and toes, stomach, back.
Internal organs are also severely affected, the nervous system is affected, and hair loss may also occur. Pregnancy that occurs during this period of syphilis is extremely dangerous for the fetus.
Along with the characteristic external signs of the disease, there is also its hidden form. The danger is that a person may not even suspect the presence of such a terrible “comrade” in his body, and irreversible changes have already begun inside the infected person.
Tertiary form
The most recent and perhaps critical form of syphilis is tertiary. With this diagnosis, irreversible changes in a person’s appearance are clearly visible (the body resembles a Dalmatian - there are many, many small spots on a light background), the cardiovascular system and nervous system are severely affected, and the liver is practically destroyed.
Observation after syphilis
A dermatovenerologist treats syphilis. After the illness, the patient is under dispensary observation for a long time. During this period, many women plan and give birth to children. Pregnancy cannot be ruled out directly during the acute phase of the infectious process, as well as shortly after recovery.
Pregnancy with syphilis should be planned. Until complete recovery, sexual intercourse without the use of barrier methods of contraception (condom) is prohibited. Both partners are treated simultaneously.
All women receiving treatment must undergo regular examinations for 2 years. For control, blood is taken from a vein. The analysis is done at 1, 3, 6, 12 and 24 months after completion of therapy. An adequate response to treatment is considered to be a decrease in the titer of specific antibodies by 4 times or more over the course of one year.
After suffering from neurosyphilis (damage to the nervous system), the tactics change. In addition to mandatory laboratory tests, the woman will have to undergo a spinal tap within 2 years after completion of therapy. During the puncture, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is taken for analysis. Until the diagnosis is cleared, the woman should be under the supervision of a neurologist.
A decrease in the titer of specific antibodies is a favorable sign. If the antibody titer does not decrease within 12 months, it is necessary to undergo re-treatment by a specialist.
Why doesn't the antibody titer decrease?
- false positive test result (it is necessary to retake the test);
- non-compliance with the treatment regimen prescribed by the doctor;
- inadequately selected therapy;
- re-infection through contact with an untreated partner;
- infection upon contact with a new partner.
A re-therapy regimen is developed by a dermatovenerologist taking into account all available data.
Specific treatment for syphilis
Therapy for pregnant women can be specific and preventive.
The first is prescribed to those who have a confirmed diagnosis of syphilitic infection.
The second type of therapy is carried out according to anamnestic and epidemiological indications.
With syphilitic infection there is a high risk of spontaneous abortion, stillbirth, birth of a fetus with deformities or active infection.
Therefore, a woman has the right to decide to have an artificial termination of pregnancy if she is diagnosed with a disease.
But it is also possible to preserve it.
With timely treatment, the consequences for the child can be completely avoided.
Up to 18 weeks and after this period, various antibiotic regimens are used.
Pregnant women up to 18 weeks are treated in the same way as non-pregnant women.
The pattern is determined solely by the period of syphilitic infection.
After this period, there are some peculiarities in therapy.
In particular, long-acting penicillin preparations are not used.
Although they are more convenient because they are administered once or twice a week, they are less effective.
After all, such drugs create and maintain lower concentrations of penicillin in biological fluids.
Variants of regimens for primary syphilitic infection in pregnant women after 18 weeks;
- procaine benzylpenicillin – 1,200,000 units once a day;
- novocaine benzylpenicillin – 600 thousand units, twice a day;
- benzylpenicillin sodium - 1 million units, four times a day.
Regardless of the drug chosen, the therapeutic course lasts 10 days.
During the secondary period, similar schemes are used.
The therapy differs only in duration.
It lasts twice as long.
Planning pregnancy after syphilis
Before conceiving a child, a woman must undergo the following procedures:
- examination by a gynecologist;
- examination by a dermatovenerologist;
- blood test for antibodies to syphilis (RW, RPR);
- Ultrasound of internal organs (according to indications);
- spinal puncture (after neurosyphilis).
You can plan a pregnancy no earlier than 12 months after the illness under the following conditions:
- no symptoms of syphilis;
- positive dynamics of antibody titer;
- absence of complications after syphilis (potential contraindications to conceiving a child).
Previous syphilis is not a contraindication to planning pregnancy. After proper therapy and in the absence of serious complications, it is possible to carry and give birth to a healthy child.
Preventive treatment of syphilis during pregnancy
This type of therapy is prescribed to those women who do not have a syphilitic infection.
The indication for treatment is solely based on medical history.
Preventive therapy is carried out during each pregnancy, if the woman previously had a syphilitic infection and is still registered.
It does not matter whether her serological tests are positive or negative.
Even with negative laboratory tests, preventive treatment is still prescribed.
It is also used once in those patients who were sick, cured and are no longer registered.
During all subsequent pregnancies, such therapy is no longer necessary.
Preventive therapy is prescribed to women if their partner has been diagnosed with a syphilitic infection.
The patient's test results are not taken into account when making decisions about prescribing therapy.
Even if the tests are negative, treatment is still used.
This is due to the fact that weeks may pass before the amount of antibodies sufficient to be detected in the blood is formed.
If the patient is infected, then such a long wait can lead to infection and intrauterine fetal death.
Considering that treatment with penicillin antibiotics is safe for most pregnant women, therapy is prescribed immediately, before the appropriate diagnosis is established.
A course of preventive therapy is usually prescribed at week 20.
Sometimes it is carried out much later.
Preventive treatment can be carried out immediately after specific treatment.
Procaine or novocaine salt of penicillin is used in standard doses for a ten-day course.
Complications of pregnancy after syphilis
Syphilis is a serious disease that affects internal organs and the nervous system. Against the background of syphilis, pregnancy does not always proceed well. The most dangerous period is considered to be the period of secondary syphilis in the mother, as well as the first three years after the illness. The longer the period that has passed since completion of therapy, the higher the likelihood of a successful pregnancy. Many experts recommend planning to conceive a child no earlier than 3 years after recovery.
Pregnancy after syphilis often occurs with the following complications:
- spontaneous miscarriage (mainly at 12-18 weeks);
- stillbirth;
- premature birth;
- placental insufficiency;
- fetal hypoxia and delayed development;
- oligohydramnios.
With severe damage to internal organs, secondary infertility may develop. The severity of complications largely depends on the severity of the woman’s condition, as well as on the nature of the therapy performed. With proper treatment, the likelihood of developing serious complications is minimized.
Complications
Treated syphilis and pregnancy are not mutually exclusive concepts. In the vast majority of cases, a woman carries and gives birth to a healthy child. Complications during pregnancy associated with a sexually transmitted infection occur extremely rarely. What can provoke such undesirable consequences:
- pregnancy occurring 1-1.5 years after the end of treatment;
- a woman’s refusal to undergo a full examination and (or) treatment of detected diseases, the development of which is caused by syphilis.
If pregnancy does occur within a year, then the likelihood of spontaneous miscarriage in the early stages, stillbirth, and premature delivery increases.
When a woman has been completely treated, but her body has not had time to recover, placental insufficiency may occur. The embryo does not receive enough nutrients and biologically active substances for optimal intrauterine development. This predisposes to the development of congenital pathologies, including the musculoskeletal system.
Another dangerous condition is hypoxia, or oxygen starvation. If the functioning of a girl’s respiratory and cardiovascular systems is not normalized before conception, then a deficiency of molecular oxygen occurs in the tissues of the embryo. The risk of disorders in brain development increases.
Doctors strongly recommend that former patients wait about three years for the organs affected by the disease to fully recover. After such a forced “quarantine”, healthy children are born.
Congenital syphilis
Damage to the fetus by syphilis pathogens can occur when a woman becomes infected during pregnancy. It should be borne in mind that infectious agents are not able to penetrate directly through the transplacental barrier. But only if he is healthy. As gram-negative spirochetes grow and multiply, it becomes damaged and ceases to perform its protective function. Now nothing prevents the penetration of microorganisms through the placenta.
The likelihood of a child becoming infected increases with the secondary form of syphilis, when a woman is infected long before conception. Pathogens are introduced into the fetus along with blood from the primary foci. In such cases, the first signs of intrauterine development disorders are observed before the woman has time to give birth to a child, already in the 5th month of pregnancy:
Congenital syphilis
If you are infected with syphilis directly during pregnancy or shortly before the child is conceived, intrauterine infection of the fetus is possible. Treponema pallidum easily passes through the hematoplacental barrier. Once in the fetal bloodstream, the infection quickly spreads throughout the body, leading to the development of congenital syphilis.
Symptoms of congenital syphilis rarely make themselves felt during pregnancy. The disease is detected some time after birth. In most children, the disease manifests itself 3-6 months after birth.
Symptoms of congenital syphilis:
- change in skin color to grayish-yellow;
- skin wrinkling;
- the appearance of specific rashes;
- enlarged liver and spleen;
- anemia;
- fever;
- joint damage.
Congenital syphilis is often combined with malformations of bone tissue and the organ of vision. Characterized by underdevelopment of joints, teeth, and numerous neurological disorders. If treatment is not carried out on time, blindness, deafness, and multiple damage to internal organs may develop.
Pregnancy when the fetus is infected rarely proceeds well. In 30% of women, the fetus dies in utero before 30 weeks. With timely delivery, the likelihood of asphyxia of the newborn increases. Newborn children often die in the first weeks after birth.
Pregnancy and childbirth after cured syphilis: preventive measures
Special measures to prevent syphilis are usually recommended for pregnant women with the disease treated before conception if, after the woman has completed a course of therapy, the non-treponemal test remains positive. Childbirth in such pregnant women most often takes place in a separate delivery unit or in an observation department.
If, after a course of treatment for syphilis, all non-treponemal tests taken by the patient contain negative indicators, and at the time of pregnancy the woman has already been removed from the dispensary register with a venereologist, the expectant mother is managed by a gynecologist in the usual manner, without prescribing special additional preventive measures.
Management of pregnancy after syphilis
All pregnant women who have had syphilis need to register with the antenatal clinic as soon as possible. At your first visit, you must inform the doctor about the disease, undergo all examinations and attend a consultation with a dermatovenerologist. After the examination, individual management tactics for the patient are developed, taking into account the severity of her condition and possible risks to the fetus.
Control examination for syphilis is carried out three times during pregnancy:
- at the first visit to the doctor;
- 30 weeks;
- 36 weeks.
Antibodies to Treponema pallidum persist for some time after therapy. If the infection has occurred recently, specific antibodies will be detected in the woman’s blood even in the absence of clinical symptoms. An analysis for total antibodies (YgM and YgG) will help to distinguish a fresh infection from an old one.
The likelihood of fetal infection depends on the antibody titer. Detection of YgM indicates a fresh infection and a high risk of developing congenital syphilis. The appearance of YgG indicates that the infection was suffered long enough, and immunity to Treponema pallidum has formed. In this case, the risk of infection of the fetus will be minimal.
Based on the examination results, the doctor may suggest that the woman undergo a prophylactic course of antibiotics. Antibacterial drugs are prescribed in the third trimester, when all the internal organs of the fetus are formed and the placenta is working at full capacity. To treat syphilis during pregnancy, antibiotics from the penicillin group are used, which are recognized as safe for the fetus.
History of syphilis and pregnancy
If the expectant mother undergoes a full course of therapeutic treatment and passes all the necessary tests that confirm that the disease has been defeated, her chance of a healthy pregnancy will increase significantly.
However, married couples who have completed all the necessary procedures and studies should still wait to plan a pregnancy for at least the next year or two.
After all, it will take time for the body to recover after antibiotic therapy.
Newborn monitoring
Childbirth after syphilis takes place in a regular maternity hospital. If complications develop, the doctor may refer the woman to a specialized department. The birth of a child occurs through the natural birth canal in the absence of other indications for cesarean section.
After birth, the child must be examined for syphilis. It is important to remember that maternal antibodies circulate in the baby’s blood for 4 months. The examination during this period will not be indicative. The diagnosis is made only 4 months after birth.
If signs of congenital syphilis are detected, the child receives antibacterial therapy. The course of treatment is developed by a dermatovenerologist. Therapy is carried out in a specialized hospital under 24-hour medical supervision.
If the examination results are negative, antibiotics are not prescribed. The baby comes under the supervision of a dermatovenerologist. Blood tests for antibodies to Treponema pallidum must be taken every 3 months. The period of observation of the child is 1 year.
Treatment of the disease in pregnant women
Therapy in pregnant women
Modern medicine makes it possible to treat women expecting a child without endangering the health of the baby and the mother. Therapy is carried out mainly in a hospital setting to ensure constant supervision by specialists. Doctors use a drug called penicillin. It is an antibacterial drug aimed at destroying pathogenic microorganisms.
As soon as the extent of the pathology is established, the specialist prescribes the dosage and duration of therapy with this medication. If the patient has an allergic reaction to penicillin, desensitizing treatment is recommended.
Often, pregnant women during therapy experience symptoms such as chills, headaches, high fever, and in some situations, pain in the joints and muscle tissue appears. The patient’s general condition may also worsen a couple of hours after the doctor administers the medicine. But this consequence disappears on its own after a day.
In addition, during the treatment of syphilis, the baby’s heart may beat rapidly, and the mother herself may begin to experience contractions in the second trimester. In this regard, experts urge all expectant mothers to immediately consult a doctor if they feel the onset of contractions ahead of time or the baby begins to move less in the stomach.
Of course, all women are concerned about the question: is it possible to give birth after suffering from syphilis, is it dangerous for the baby? Doctors say that it is advisable not to think about conception for 2-3 years, so you should definitely use contraceptives. After 3 years of illness, the risk of infection of the child is minimized.
If a woman wants to give birth to a healthy child, the doctor may recommend preventive treatment, taking into account the degree of development of the pathology. Therefore, it is possible to become pregnant after 3 years from the moment of recovery from syphilis. In this case, you will definitely need to take tests every trimester. After birth, the baby himself will have to be observed.
The likelihood of transmitting syphilis to a child
The likelihood that a baby will be born with congenital syphilis is quite high. After the baby is born, the following signs of syphilis may be noticed:
- Diseases of the nervous system;
- Liver pathologies;
- Prematurity;
- Skin lesions that can manifest themselves in a variety of ways;
- Bone damage.
Children with congenital syphilis are very anxious, they have problems with sleep and appetite. Late congenital syphilis is usually detected in adolescence, but sometimes it is possible as early as two years after the child is born.
Other signs of congenital late syphilis are considered to be dental deformities, eye diseases and serious hearing impairment.
How is syphilis treated during pregnancy?
Treatment of syphilis during pregnancy: forum - what does this phrase mean? The fact is that women with this infection are trying to find support online, and such forums provide them with this moral help and information.
Until four months into pregnancy, doctors usually use durant medications, which are slowly eliminated from the body. At later stages, drugs are needed that will be quickly eliminated from the body.
Primary and secondary syphilis during pregnancy is treated with courses of penicillin and bicillin. Courses of treatment are usually up to twenty days. It is the doctor who can make a decision regarding the choice of dosage and the drug itself in this case. You also need to take into account potential allergic reactions in a pregnant woman.
Latent syphilis during pregnancy (forum) - what can be said about this? Sometimes a woman who is carrying a child may develop syphilis in a latent form. This greatly complicates the situation, since she cannot notice it in time and the same goes for the gynecologist at a scheduled appointment.
What effect does syphilis have on pregnancy?
If the disease is treated almost at the moment of its occurrence, that is, with appropriate and timely diagnosis, the negative impact on the fetus can be almost completely eliminated.
Why is syphilis dangerous during pregnancy? The problem is that it causes hormonal imbalance in the female body, which can lead to:
- Freezing of a child in the womb;
- Miscarriage or threat of miscarriage;
- Premature birth.
Moreover, women who have syphilis experience late toxicosis and suffer from anemia. In addition, doctors in this case fear that the child will also be infected through the penetration of the pathogen through the placental wall. Reducing infection to zero can only be done if the woman is treated on time.
How to plan a pregnancy correctly?
After treatment for syphilis, serological tests will remain positive for a long time. During this period, venereologists recommend that patients who have recovered from the disease not become pregnant, but take care of their health. The pathology caused significant harm to the body and disrupted the functioning of almost all vital systems. Therefore, during this period it is advisable to be fully examined, and if diseases or disorders are detected, to be treated. After all, taking many pharmacological drugs during pregnancy is strictly prohibited.
This is interesting: Why can men experience pain when urinating, how to deal with them?
In order for childbirth after syphilis to be successful, the following activities must be carried out several months before the planned conception:
- a visit to a gynecologist who will issue a list of tests required;
- a visit to the venereologist who treated the woman and monitored her condition, to conduct a final full examination, including the donation of antibodies to the causative agents of syphilis.
In some cases, after suffering a sexually transmitted infection, you do not need to wait several years before conceiving. A venereologist allows you to plan a pregnancy after a year in the absence of characteristic symptoms and negative consequences, as well as with good results of biochemical studies. But still, he strongly recommends waiting as much time as possible before giving birth.
Is a relapse of the disease possible?
People who have had syphilis once can become infected again. Most often this is an infection with “new” syphilis. However, in some cases, past pathology may return if it was not completely cured at one time.
But what does this have to do with?
Syphilis is a disease that can be cured, but it takes a long time. If the treatment was chosen incorrectly, the dosage of the drugs was not followed, or the therapy schedule was violated, then treponemes may become resistant to drugs.
As a result, the bacteria will begin to transform into a stable form and will continue to remain in this position. Under favorable conditions, they will come out of hibernation and begin to attack again.
Tertiary syphilis
Can having syphilis in the past somehow affect employment in the future? Patients can work anywhere: in school, catering, police, but only if the disease has been completely treated.
How to live with syphilis and after its treatment depends on many factors. If the disease has been completely eradicated, no restrictions arise and you can safely do what you love.
Diagnostics
The presence of the disease can be determined by a blood test from a finger and a vein. To screen for syphilis, the gynecologist offers the expectant mother the following tests: RW, PB (Wassermann reaction) or MP (precipitation microreaction). The Wasserman reaction often gives incorrect results in pregnant women, so it is rarely used.
If the screening test is positive, it is necessary to undergo additional examinations to ensure the presence or absence of syphilis. The following tests are used to confirm the disease:
- immunoblotting;
- RIF (immunofluorescence reaction);
- ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay);
- RPHA (passive hemagglutination reaction);
- RIBT (treponema pallidum immobilization reaction).
First, RPGA AND RIF are prescribed. If the results are questionable, then you need to take other tests.