The belly of a pregnant woman, increasing in size along with the small growing baby inside, is not only a reason for joy and pride for the expectant mother.
Measuring its circumference is one of the most important components of diagnosis during pregnancy, so your doctor will regularly take appropriate measurements at each visit to the antenatal clinic.
The belly of a pregnant woman, increasing in size along with the small growing baby inside, is not only a reason for joy and pride for the expectant mother.
Measuring its circumference is one of the most important components of diagnosis during pregnancy, so your doctor will regularly take appropriate measurements at each visit to the antenatal clinic.
Objective examination of a pregnant woman
The examination of the expectant mother is carried out at the first appearance at the antenatal clinic and registration for pregnancy. An objective examination is carried out not only by an obstetrician-gynecologist, but also by a therapist with a dentist, an ENT doctor with an ophthalmologist, and, if indicated, an endocrinologist and surgeon, a cardiologist and a urologist. If necessary (presence of children with congenital malformations, hereditary diseases, etc.), medical genetic counseling is prescribed.
During an objective examination, the following is studied and measured:
- woman's body temperature;
- height and weight of the expectant mother (necessary for predicting future weight gain and identifying edema);
- blood pressure (measured at each visit to the antenatal clinic);
- body type (normosthenic, asthenic or hypersthenic);
- pelvic dimensions;
- color and condition of the skin and mucous membranes;
- shape of the mammary glands, their palpation;
- examination of the abdomen and palpation;
- condition of the symphysis pubis by palpation (are there any discrepancies);
- the state of the organs of the cardiovascular system and gastrointestinal tract, lungs, nervous and endocrine systems, as well as excretion;
- condition of teeth, etc.
Early attendance for registration at the dispensary is very important, since in short stages of pregnancy obesity can be diagnosed and subsequently differentiated from hidden edema. Also, the first visit to the obstetrician in early stages of pregnancy allows you to determine the woman’s “working” pressure and record its deviations from the norm in the later stages of gestation.
What should you and the doctor be wary of?
A bad sign could be excessive growth of the “bellies.” However, his serious growth retardation is also a reason to sound the alarm.
What reasons can cause “abnormal” indicators of tummy volume?
Increased numbers may indicate:
- Twins or triplets. This is not a pathology, but on the contrary, joy: two, or even three little ones are growing under your heart at once!
- That you are wearing a real hero. If at the 1st and beginning of the 2nd trimester all embryos are similar, then at the end of the 2nd and 3rd trimester each baby develops based on the genetics that you and your dad put into it. Is your husband a strong guy, 2 meters tall? It is quite possible that the son or daughter took after daddy! Although, of course, a large fruit is also a reason to get checked for a couple of diseases, and also look at your diet. Your doctor will tell you about all this in more detail.
- Polyhydramnios. There is only one child, but the amount of water in his “aquazone” is higher than normal. But this is a problem that indicates a malformation of the child or an illness of the mother.
- Poor nutrition of the expectant mother. Frequent indulgence in buns can “thicken” the layer of fat on the tummy...
- Incorrect position of the fetus, namely horizontal. Until the 2nd week of the 3rd trimester, there is still enough space in your belly for the little one to squirm and get comfortable. And if he decides to position himself horizontally, the abdominal measurements will increase sharply. By the way, if he remains in this position further (after 36 weeks), the expectant mother may be admitted to the hospital to avoid complications during childbirth.
Reduced measurement numbers indicate:
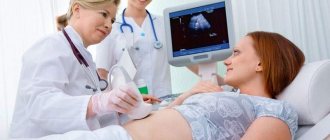
- Low water. Like excess water, not enough is a bad sign. Perhaps the water is leaking, or this phenomenon is caused by a malformation of the child. To exclude all bad suspicions, the doctor refers pregnant women with suspected oligohydramnios to an ultrasound scan.
- Not eating enough. Overeating during pregnancy is dangerous, but starving is even more dangerous! If your belly is growing slowly only because your diet is not nutritious, simply expand it.
- Fetal hypertrophy. In non-scientific terms: the fetus is too small, and this condition is considered a pathology. Of course, simple genetics may be to blame (if you have short relatives in your family), but to be on the safe side, you will be referred for a fetal blood flow test, as well as an uzist.
External obstetric examination
When conducting this examination, doctors’ tasks include examining the abdomen and pelvis (the presence of bone curvatures and displacements), measuring the size of the pelvis, measuring the abdominal circumference (at its largest size), palpating the abdomen and the convergence of the pubic bones, listening (auscultation) to the fetal heartbeat, which is possible after 20 weeks of gestation.
Pelvis measurement
Measuring the size of the pelvis is called pelviometry, which allows you to indirectly estimate the internal dimensions of the small pelvis. Determine 4 pelvic sizes (using a pelvis gauge):
Distantia spinarum
It is the distance between the anterior superior spines (easily palpable from the front) of the iliac bones and normally corresponds to 25–26 cm.
Distantia cristarum
The distance that is measured between the most distant points of the iliac crests (on the bones) and normally reaches 28 - 29 cm.
Distantia trochanterica
This is the space located between the greater trochanters of the thigh bones (they protrude from the outer surfaces of the thighs). This segment is normally 31–32 cm. If the difference between the listed transverse dimensions is no more than 3 cm, then this indicates a narrow pelvis.
Conjugata externa (external conjugate)
Refers to the straight dimensions of the pelvis. It is measured with the woman lying on her side, with the pregnant woman’s lower leg bent at the knee and hip joint. One button of the pelvis is fixed on the upper outer edge of the symphysis pubis, and the button of the other branch is pressed against the suprasacral fossa. The length of the external conjugate is normally within the range of 20 - 21 cm. If the resulting number is subtracted by 9, the approximate size of the true conjugate will be determined (11 - 12 cm).
Measuring belly size
Before measuring the size of the abdomen, the doctor must palpate the anterior abdominal wall. Why is this being done? Palpation of the anterior wall of the abdomen makes it possible to determine the elasticity of the muscles and skin of the abdomen, what condition the abdominal muscles are in, whether there are discrepancies or hernial protrusions, as well as to determine the severity of the subcutaneous fat layer, the significant thickness of which can distort the abdominal circumference (normal) indicators. The course of labor depends on the anatomical and especially functional state (muscle tone) of the abdomen. For example, in multiparous women or overweight pregnant women, the abdominal muscles are so sluggish and weakened that it can negatively affect the course of the pushing period (weakness of pushing). After all, pushing is ensured by contraction and tension of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall.
After palpation of the anterior wall of the abdomen, they proceed to palpation of the uterus, which is possible only at 13–13 weeks, when the uterus protrudes beyond the pubic symphysis. First of all, its tone is determined. Increased tone or hypertonicity indicates a threat of interruption and is determined by palpation both by the doctor and the woman herself. In this case, the uterus tenses when touched, when the fetus moves, or against the background of complete rest. Expectant mothers call this condition “stomach stones.”
Then the obstetrician takes “measurements” of the height of the fundus of the uterus and the circumference of the abdomen.
More on the topic Belly during pregnancy by weeks and months
tummy - a question for those who are not pregnant for the first time.
Girls, does the tummy appear earlier in the second (and subsequent) pregnancy? I’m almost 10 weeks pregnant - my daughter, who doesn’t know about my situation yet, says that my belly has grown.
Tummy size.
Girls, I recently read an article on one of the websites on pregnancy. They write that if the placenta is attached to the anterior wall, then the stomach grows faster and looks larger. In comparison, if the attachment is on the back wall. And then I thought about it. Is it so?
Has your stomach… risen?
Girls, could this be the case? Previously, my baby knocked mainly at the very bottom and “bulged out” only in the navel area, but now (the second day) it’s just 5 centimeters above the navel, and there’s practically no knocking at the bottom, and it feels like my belly has become higher. Or did it turn over somehow? Who had this happen?
Has your belly already appeared at the end of the first trimester?
Has anyone already developed a belly? On the contrary, I have lost weight because I can’t eat anything other than fruits, milk and a few vegetables. I look at myself and am surprised. True, this was also the case in the first pregnancy, but in the second the abdomen usually appears earlier