Pregnancy radically changes a woman’s usual state: she develops new taste preferences, suffers from toxicosis, and her belly eventually grows! Comprehensive information about these metamorphoses today can be found in any specialized online magazine. Meanwhile, the psychological state of a woman during pregnancy is no less important than the physiological aspects. Our article will talk about neuropsychic preparation for upcoming motherhood.
A miracle happened: the pregnancy test showed two lines! From this moment on, life changes to become even better and more beautiful. But the expectant mother is not yet able to immediately comprehend the obvious - for this she will need a lot of time, namely 9 months.
The inner world of a pregnant woman is so complex and deep that her mood can change more than a dozen times a day: a minute ago she was laughing merrily, but now her eyes are wet, and there is nothing strange about that. Sensitivity, receptivity, impressionability - all types of reactions to the outside world during pregnancy are exacerbated to the limit. All expectant mothers from the moment of conception until childbirth live according to special rules of psychology.
Physiology divides pregnancy into three fundamental stages, or trimesters. The same can be done from a spiritual point of view.
First trimester
By the end of the first week of existence, there are already 250 cells in the body of the unborn baby; this formation resembles a small ball with a cavity inside and is called a blastocyst (fertilized egg). Right now, the process of connecting the unborn child with the mother’s body begins - implantation. With the help of enzymes, a depression is formed in the endometrium (the lining of the uterus), where the blastocyst falls, and the endometrial cells close over it. Implantation is complete.
The cells of the blastocyst continue their division, an embryo and extraembryonic formations are formed: the chorion is the future placenta, the amnion is the future placenta, the yolk sac is a temporary formation that will feed the baby until the uteroplacental blood flow is completely formed.
The next period is approaching, you still don’t know anything about your new position, but, nevertheless, the unborn baby is already 4 weeks old! The embryo - now we can rightfully call it an embryo - looks like a flat bluish disc consisting of several layers of cells that will subsequently develop into organs and tissues of the human body.
If menstruation does not come on time, you can take a pregnancy test or donate blood to determine beta-hCG, a hormone produced by the cells of the fertilized egg.
So, the most crucial period begins - the embryonic period. Right now, all the organs necessary for human life are being formed. It will last up to 12 weeks. Development processes during this period are very intense, the embryo is very sensitive to various damaging factors, try not to harm your baby.
The cardiovascular, respiratory, nervous systems, organs of the gastrointestinal tract, internal and then external genital organs, bones, muscles, skin, and endocrine glands begin to form.
By the 6th week, the heart is practically formed, an ultrasound examination can already detect a heartbeat, there are buds of the gonads (ovaries or testicles), and the rudiments of arms and legs appear. In addition, the embryo has a tail, which will undergo reverse development by the 10th week of pregnancy. And the length of the baby at this stage of pregnancy is 4-6 mm.
At the 8th week, the embryo’s head and pelvic ends are clearly visible, the back and abdomen can be distinguished, it makes active movements, and its length from head to tailbone is 10 mm. A little more, and in the 9th week the baby will gain his very first gram!
At the 12th week - the period of the third missed menstruation - the embryo resembles a small man. He has formed all the internal organs, arms and legs with fingers, he even has auricles and external genitalia, and the rudiments of baby teeth. Only his proportions are still funny: the size of his head is approximately equal to the size of his body. It weighs about 13-14 grams and reaches 9 cm in length.
The 1st trimester is over. During this time, a lot of changes occurred in the woman’s body. Under the influence of hormones that support pregnancy, the mammary glands become thicker, and subcutaneous fat is redistributed: without changing weight, women note an increase in the volume of the hips and abdomen. The pigmentation of the areola and labia increases, and a vertical stripe appears from the navel to the pubis. And what about early toxicosis with its nausea and vomiting! Yes, and sudden mood swings can interfere with normal life.
Second trimester
In the second trimester, further growth and development of the fetus occurs - this is what your baby is now called. I would like to remind you that it is located in the uterine cavity, lined with the amniotic membrane and surrounded by amniotic fluid. The fetus is connected to the mother's body through the umbilical cord and placenta, through which it receives the nutrients and oxygen necessary for its development. Amniotic fluid is produced by the placenta and cells of the amniotic sac. The activity of the fetal bladder is of no small importance. In preparation for life outside the womb, the fetus swallows water, which, in turn, stimulates intestinal activity and promotes the production of original feces - meconium. Amniotic fluid also performs a protective function - it protects the baby from the effects of the external environment.
During the entire second trimester, the fetus actively moves in the uterine cavity. From about 18 weeks, a woman begins to detect the movements of her baby. Now you can even communicate with him: the organ of hearing has already been formed and perceives all the sounds coming from our world.
By 20 weeks, the baby, in addition to all the organs necessary for later life, has nails, eyebrows, vellus hair, and a cheese-like lubricant appears on the skin. It weighs about 300 grams and reaches 25 cm in length. The uterus also grows with it. The fundus of the uterus can already be felt at the level of the navel.
By 24 weeks, the fetus gains the same amount and already weighs 600 grams, its length is about 30 cm. From about this time, your family can feel the baby moving by placing their hand on the stomach.
The 2nd trimester is over. What happened to the female body? Firstly, due to the addition of the uteroplacental blood flow and an increase in the volume of circulating blood (by about half a liter), the load on the heart increased. You notice that it is becoming more difficult to do your usual work, and you may experience shortness of breath after physical activity. If it doesn't go away with rest, tell your doctor. Secondly, an enlarged uterus also does not add comfort. In addition to the fact that it has become uncomfortable to sleep, you have “outgrown” your usual clothes.
Other not very pleasant symptoms also appeared. The growing uterus compresses the veins through which blood flows from the lower extremities and pelvic organs. The vascular pattern on the legs intensifies, the veins dilate - which means it’s time to wear special therapeutic compression hosiery (socks, stockings, tights), you may need to consult a specialist in vein disease - a phlebologist. For the same reason, many women develop hemorrhoids. Thirdly, due to hormones produced in large quantities that relax the muscles (primarily the uterus), the intestines begin to act up - most pregnant women suffer from constipation.
Attention to your inner world and the binary psyche of a pregnant woman
While the external activity of some expectant mothers is off the charts, others, on the contrary, focus all their attention on themselves and the baby. They do not want to attend noisy companies; they avoid difficult situations, strong emotions and spectacles. At this time, a woman can think for a long time about what her child will be like, how the birth will go, and it is difficult for her to think about something else.
Your relationship with your child becomes stronger, and psychologists have even discovered the phenomenon of the so-called “binary psyche of a pregnant woman.” By the third trimester, the expectant mother has finally gotten used to the fact that she is not alone and the unborn child has its own desires and rhythm of life. For example, a mother wants to fall asleep, but the child has a period of wakefulness. He moves, pushes, prevents you from relaxing. Or vice versa. The baby in the tummy has fallen asleep, and the mother is also uncontrollably drawn to sleep, although the day is still in full swing.
The connection between mother and baby is called the “binary psyche.” By the way, in turn, your unborn child also reacts sensitively to the fantasies, experiences and worries of the mother. Therefore, avoid films with aggressive emotions, avoid physical and emotional overload.
Third trimester
In the third trimester, all of the above symptoms will progress. Heartburn may appear (the uterus is already putting pressure on the stomach!), due to a shift in the center of gravity, the gait changes, and back pain appears. And the mammary glands are already in full swing preparing for lactation: they produce colostrum.
At 28 weeks of pregnancy, the baby is quite “big”: it weighs a little more than a kilogram, and is already about 35 cm in length. In boys, the testicles gradually begin to descend from the abdominal cavity into the scrotum. A child born at this stage, with very careful nursing, already has a chance of survival.
Then the baby actively gains weight, subcutaneous fatty tissue appears, and the skin becomes pink (previously it was bright red due to translucent blood vessels).
By 33-34 weeks, surfactant, a substance that helps with breathing, appears in the fetal lungs. So if the baby is suddenly born prematurely, he will begin to breathe on his own, and the help of resuscitators may not be required.
At 36 weeks of pregnancy, the fetus reaches a length of 45 cm, weight ranges from 2300-2600 depending on external and hereditary factors. By this time, active movements inside the uterus have ended - the limited space allows you to move only your arms and legs. The child takes his final position - presentation (ideally - head down).
You can independently calculate the approximate weight of the child: to do this, the abdominal circumference (in cm) must be multiplied by the height of the uterine fundus (in cm) - this distance is measured from the pubis to the highest point of the uterine fundus. For example, if OB = 88 cm and GMD = 35 cm, then the estimated weight of the fetus is 88 × 35 = 3080 grams.
Childbirth is ahead. I hope you have prepared for them, perhaps taken courses for young parents. A pregnancy between 37 and 42 weeks is considered full-term. When exactly the baby is born depends on hereditary predisposition (ask your mothers at what stage they gave birth) and a host of other factors.
Pain in the lower abdomen
Throughout pregnancy, the cause of poor health may be discomfort in the abdomen. They must be reported to the supervising physician. The pain varies in intensity, localization, and is accompanied by other symptoms, depending on the cause.
Immediately after fertilization, no special sensations arise due to the small size of human cells: their first divisions do not cause any symptoms.
Natural causes
After fertilization, the embryo moves to the uterus to settle there for subsequent development. Some women feel mild nagging pain at this time, sometimes similar to tingling. The phenomenon may be accompanied by a small amount of bloody discharge due to microdamage to the capillaries caused by the implantation of the fertilized egg into the uterine wall. At this stage, it is small in size and is forced to increase with the growth of the fetus. Neighboring organs are displaced, all changes are accompanied by nagging pain. This is not a pathology and does not require treatment.
More often, women who have had pelvic inflammation or have undergone surgery suffer from pain in the lower abdomen. After such pathologies, adhesions may remain that cannot stretch. As the uterus grows, they rupture, causing severe sharp pain of a pulling, pressing or cutting nature. Usually, a pregnant woman is not prescribed treatment; she is advised to remain calm and take sedatives.
After the 30th week, training contractions are possible, the uterus periodically contracts for a short period of time, and nagging pain appears in the lower abdomen. After a short rest they go away. Pain can also occur due to the baby moving.
Hormonal imbalances
During pregnancy, hormonal levels change, and various deviations can lead to pain in the abdomen and back. More often there is a lack of progesterone, which is responsible for normal tone in the uterus. It reduces its contraction, preventing the fertilized egg from being rejected. With a lack of progesterone, embryo detachment begins. If measures are not taken, spontaneous termination of pregnancy is possible.
To clarify the cause of nagging pain in the lower abdomen, an analysis of hormone levels is required.
Threat of interruption
In most cases, miscarriages and embryonic death occur in the early stages of pregnancy. They are provoked not only by external factors, but also by natural selection. In case of genetic disorders, incorrect set of chromosomes, fetal development stops. In this case, painful sensations are observed in the lower abdomen, heaviness in the lower back caused by uterine contractions.
There may be a risk of miscarriage after 22 weeks, but this is called premature birth. They are accompanied by cramping pain, bleeding, and sometimes the discharge of amniotic fluid.
The condition requires urgent hospitalization. At the early stage of the process, measures are taken to preserve the pregnancy; at the later stages of the development of premature birth, it is interrupted.
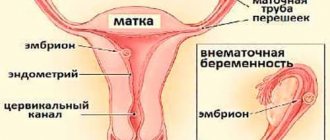
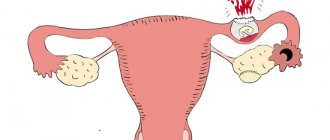
Ectopic pregnancy
In the early stages, it is difficult to diagnose pregnancy using ultrasound. Some people at this time complain of nagging pain on one side of the abdomen. Sometimes they are a symptom of an ectopic pregnancy, when the embryo implants not in the uterus, but in one of the ovaries, abdominal cavity or fallopian tubes. This is a pathology that requires surgical intervention, otherwise it can lead to irreparable consequences, including death.
An ectopic pregnancy is detected by a blood test for the level of the hormone hCG. Characteristic signs include: cramping pain, general weakness, discharge mixed with blood. If an ectopic pregnancy is determined before a significant deterioration in health, the reproductive organs can be preserved during surgery. In the acute period, the fallopian tube is usually removed, and subsequently the reproductive function of the ovary on this side is lost.
Pathological processes
A woman may experience pain that is not related to pregnancy. A common cause is intestinal problems. During pregnancy, the muscles in the abdominal cavity relax to preserve the gestating fetus. This reduces intestinal motility, and constipation, bloating, and nagging pain may appear. The condition is alleviated by proper nutrition and taking mild laxatives allowed during pregnancy.
Another cause of discomfort is inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs. They can occur in early pregnancy due to decreased immunity. The process is aimed at preserving the fetus so that the body does not perceive it as a foreign body and begins to reject it. Inflammatory diseases must be treated, otherwise they can negatively affect the course of pregnancy.
Conditions requiring surgical intervention occur less frequently. This could be appendicitis, cyst formation, or peritonitis. In such cases, the pregnant woman is bothered by pain in the lower abdomen, back, and there may be an increase in temperature. The operation is carried out in an attempt to preserve the pregnancy.
Pregnancy examinations
The word “pregnancy” comes from the word “burden.” Pregnancy is a significant burden on a woman’s entire body. Therefore, if the pregnancy is planned, try to cure your chronic diseases first. If you did not expect pregnancy, but, nevertheless, it turned out to be desired, consult a doctor as soon as possible. You will be examined, treatment will be selected and all necessary recommendations will be given for further pregnancy.
If you are healthy, you will just need to get tested.
- Analysis for syphilis, HIV infection, hepatitis B and C. The first time this test is taken is at the first visit to the antenatal clinic. You will have to retake it once every 3 months (3 times during the entire pregnancy).
- A general blood test will have to be taken monthly. The doctor will be interested in the level of hemoglobin, the number of leukocytes, platelets, and ESR.
- A biochemical blood test is also taken once a month. It can be used to judge how the internal organs function, primarily the liver and kidneys.
- A general urine test in the first and second trimesters is taken once a month, then once every 2 weeks, and after 36 weeks - weekly.
- Analysis to determine blood type and Rh factor. Rent once. However, if you have Rh negative blood and your husband has positive blood, you will have to determine the amount of Rh antibodies in your blood monthly, and more often if necessary. This is very important for identifying Rh conflict between the organisms of the mother and fetus.
- Coagulogram. Changes in the blood coagulation system are determined monthly. This is very important, because the mother’s blood provides nutrition to the baby.
- Testing for sexually transmitted diseases (chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, viral infection) is done either before pregnancy or in the early stages. If necessary, for example, if there are signs of intrauterine infection, the tests will have to be repeated.
- Ultrasound for uncomplicated pregnancy is performed at 20-24 and 36 weeks. According to indications, this study can be performed more often, since it does not have a negative effect on the mother and fetus.
- At 16-20 weeks of pregnancy, it is necessary to take an analysis for possible fetal malformations - determine the level of alpha-fetoprotein, human chorionic gonadotropin and unconjugated estriol in the blood.
- After 34 weeks of pregnancy, fetal cardiotocography (CTG) is indicated once every 2 weeks to assess its intrauterine condition.
- Pregnant women are required to be examined by a therapist, ophthalmologist, ENT doctor, or dentist.
- The need for other studies is discussed individually with the doctor leading the pregnancy.
What is the expectant mother afraid of?
The news of pregnancy always causes extreme stress for a woman. It doesn’t matter whether she planned a child or not. If pregnancy was seen as a bright prospect, the expectant mother experiences stress in a positive way - she wants to share her secrets with loved ones. If the news of imminent motherhood takes a woman by surprise, stress gives way to severe emotional shock.
In the first trimester, a pregnant woman is tormented by the fear of the unknown and change. A woman will need a lot of strength to get used to her new position, which will undoubtedly affect her studies, her work, and her life in general. The most correct step at the beginning of pregnancy is to accept yourself and the baby, which caused such emotional confusion. Once a woman can do this, she will feel incredible relief and a desire to learn to coexist with the child she carries under her heart.
Mothers who really wanted to get pregnant often begin to worry about the health of their unborn baby from the first days of this wonderful condition. Will the long-awaited child be born strong or weak, will he have any unforeseen deviations, will a strong painkiller pill taken unknowingly affect his development, how to protect himself from the harmful radiation of a computer monitor... What terrible pictures will the expectant mother draw, going over in her memory various situations when, in her opinion, she stumbled.
In the second trimester of pregnancy, all expectant mothers, as a rule, become victims of social superstitions regarding pregnancy. For example, who among the women has not heard that during pregnancy it is impossible to cut, sew or put patches, otherwise the child will have many moles? And every woman will most likely remember how she, a pregnant woman, was warned to raise her hands so that the child would not get tangled in the umbilical cord. Such beliefs do not bring anything good or useful, except increased anxiety. The surest way to get rid of them is to perceive these collective “fairy tales” as nothing other than a given of pregnancy, as one of its natural phenomena.
If unconditional trust in signs does not give the pregnant woman peace, it is better for her to turn to a professional psychologist, regular conversations with whom will put everything in its place and lead the expectant mother to peace of mind.
In the last trimester of pregnancy, a woman, consciously or not, begins to fearfully think about the upcoming test of childbirth. The most interesting thing is that these fears are not groundless: childbirth is a powerful physical and psychological experience, so all women’s fears are absolutely natural. For example, a pregnant woman may be afraid not so much of painful sensations as of the development of certain complications during childbirth. There are often cases when an expectant mother is afraid of seeming... unattractive in the eyes of her loved one and the medical staff at the time of childbirth.
However, most often a woman fears for her life and for the life of her child. Psychologists interpret these fears in their own way: a pregnant woman worries in advance about her baby, who, when born, inevitably goes through the stage of psychological death. He dies to the intrauterine world in order to be born in another, external world. Birth is the most powerful experience in a person’s entire life, and its strength is comparable only to death.
At the same time, one cannot discount the subconscious misconception that a woman should give birth in pain. Even all the latest research and techniques in the field of obstetrics and gynecology taken together will not be able to drown out the human ancestral memory with which we come into this world. We can only rely on the intelligence and adequacy of the pregnant woman herself.
To ease the moral discomfort that complicates the last weeks before giving birth, you need to properly prepare for the process of giving birth to your baby: sign up for special courses and think through the scenario of your birth down to the smallest detail - choose a maternity hospital, meet the doctor who will help in the delivery.