How is weight determined using ultrasound?
Accurate determination and assessment of fetal weight norms week by week is only possible through ultrasound. In this case, important diagnostic indicators are:
- gestational age in weeks;
- length of the fetal body and limbs;
- Head circumference;
- hip size;
- abdominal circumference.
However, it is not possible to constantly carry out this study and analyze the weight of the fetus by ultrasound week by week. In this regard, doctors have developed methods for determining the body weight of the fetus by assessing the size of the pregnant woman’s abdomen and uterus. There are several modifications of these methods that allow you to calculate fetal weight by week of pregnancy. The simplest and most frequently used are:
- Zhordania formula - the weight of the fetus by week is determined by multiplying the abdominal circumference of the expectant mother and the height of the uterine fundus (in centimeters).
- Yakubova's method is an improved version of the method discussed above. When calculating, special coefficients are used. The formula is as follows: OJ (abdominal circumference) VDM (bottom standing height) x 100/4.
The estimated fetal weight in the early stages is calculated using ultrasound. At a later stage, the doctor, thanks to measurements of the abdominal circumference and the height of the uterus, can calculate this indicator.
When a woman develops a baby in the womb, she wants to know as much as possible about him: what the baby looks like, what color his hair and eyes are, and of course, what his height and weight are.
The weight of the fetus and the rate of its increase are issues that concern not only future parents, but also the attending physician, because this parameter can tell a lot about the condition of the fetus.
Too little or too much weight at one stage or another of development may indicate problems in the body of a woman or her child.
In the first trimester, it is very difficult to determine the baby’s weight, because he is still very small. And doctors are still of little interest in this indicator.
In the first weeks of pregnancy, the most complex processes of the formation of all the tissues and organs of the baby occur, so during the examination, doctors will first of all look at the presence/absence of all vital structures in his body.
Although the rate of weight gain in the first months of life is impressive: from 1∙10-6 g (the weight of the cell formed as a result of the fusion of sperm and egg) to 10-13 g at the end of the 12th week of gestation.
That is, the mass of the new little man increases hundreds of thousands of times in just a few weeks!
In the future, the rate of growth will not be so colossal, and if you count the weight gain per week, then it will be greater the closer the moment the child is born.
However, just before birth, in the last 2 weeks, fetal weight changes more slowly.
In the second and third trimesters, the child’s weight by week normally has the following values:
- At week 13, when the child has already formed all the organs and their systems, his weight is 14-20 g with a height of approximately 60 mm.
But even though he can move, the mother will not yet feel his kicks.
- From 14 to 20 weeks, smaller details of the baby’s structure are formed (finger patterns, hair), weight is 220-270 g. The fetus is already large enough for its movements to become noticeable to the mother.
- In the next 4 weeks (from 20 to 24), the weight of the fetus reaches 550-600 g. The woman feels its active movements.
In case of premature birth, the fetus can survive if its weight is at least 500 g. - By the end of the 26th week, the baby's organs have completed the main stages of formation, so the baby has a high chance of life if premature birth occurs. Now its mass is 750-850 g.
- By the thirtieth week, most babies are already turning their head down, preparing for a natural birth. The length of the fetus at this time reaches 24 cm, and its weight is 1100-1300 g.
- At about 34 weeks, another ultrasound examination is usually scheduled, during which measuring the approximate weight of the fetus will be a mandatory item. Normally it should be 2100-2300 g.
- From 34 to 38 weeks, the baby grows quickly, gaining approximately 200 g every 7 days. If childbirth occurs at the end of this period, the pregnancy can already be considered full-term. Fruit weight – 3100-3200 g.
- By the end of the 40th week, it is time for the baby to be born. Most women give birth during this period. The weight of a child at birth usually reaches 3200-3600 g, and his height is about 50 cm.
- If labor does not occur, the pregnancy is considered post-term. In the absence of labor, it is induced artificially. Within 41-42 weeks the baby grows to 3500-3800 g.
- K=12, if the woman’s weight is more than 90 kg;
- K=11 if less than 90.
The baby's weight by week of pregnancy may differ from the figures given, and this does not necessarily indicate any problems in his health.
1 Hereditary predisposition. If the parents (especially the mother) have low weight and height, their baby will probably not be of great size either.
2 Insufficient or improper nutrition of the mother, which may be accompanied by a disruption in the flow of nutrients and oxygen through the vessels of the placenta.
3 Bad habits, especially smoking, affect the diameter of the lumen of the placental vessels. As in the previous case, the nutrients necessary for the growth of the fetus are supplied to it in smaller quantities.
4 Infectious and chronic diseases of the mother, her nervous stress negatively affect metabolism, and thereby limit the nutrition of the baby in her womb.
5Fetal weight at birth will understandably depend on the degree of term.
The greater it is during premature birth, the higher the chances of the baby’s life.
6 The likelihood of fetal malnutrition also depends on the age of the expectant mother: it increases in women who are too young (under 18 years old) and in the case of late pregnancy (after 35 years old).
7 Child underweight is often found in women suffering from anemia - a lack of hemoglobin in the blood. Both mother and child suffer from oxygen starvation, especially in recent weeks.
1 Excessive and irrational nutrition of the mother, consumption of large amounts of flour and sweets, as well as liquids, lack of vegetables and fruits in the daily diet.
2 A common cause of fetal hypertrophy is maternal diabetes. The child's body receives a lot of carbohydrates and produces large doses of insulin, storing excessive amounts of adipose tissue.
3 Excess body weight in a baby can be caused by many other metabolic disorders in the mother or child that are not related to diabetes.
4 As in the case of malnutrition, excess weight may be due to heredity if parents also have an innate tendency to be overweight.
An interesting pattern: very often second and subsequent children are born with more weight than the previous ones. The reason for this is unclear, but the fact is clear: first-born children have less chance of hypertrophy.
5 Congenital developmental disorders of the baby (Sotos syndrome, or cerebral gigantism, as well as Beckwith syndrome, manifested by dysfunction and excessive enlargement of some body organs).
6 There is also imaginary hypertrophy, when the child’s body weight is increased not due to his fatness, but due to the increased fluid content in his body (edema develops).
A child who weighs more than 4-4.5 kg at birth will be considered large. The body weight of newborns in some cases can exceed 10 kg.
The most common way to determine fetal body weight is to calculate it during an ultrasound examination.
However, the figures obtained will be approximate; even such a modern diagnostic method is often mistaken.
Gynecologists can calculate the approximate weight of the child based on the height of the uterine fundus and abdominal circumference.
But the results in this case will be even more inaccurate. Although experienced doctors are often able to determine the approximate weight with enviable accuracy.
Very inquisitive mothers find other, more unusual calculation methods. For example, in some cases, when determining a child’s weight, the circumference of the expectant mother’s wrist is taken into account.
But such connections between parameters are not sufficiently substantiated, which means that the accuracy of the calculation will be low.
If a pregnant woman takes care of her health and follows an appropriate regimen, her baby will have less problems gaining weight. In cases where there are already deviations in body weight, careful monitoring of the baby’s condition by a doctor is necessary.
There are several methods that will help calculate the baby’s weight before birth.
Let us denote the weight of the fetus, further in the formulas, by the letters VP.
Calculations using formulas will be informative after 32 weeks of pregnancy.
Lankowitz formula
This method of calculating weight is considered one of the most accurate.
VP = (VDM coolant V P) x 10
To use the formula, a woman needs to know 2 important indicators - the height of the uterine fundus (UFH) and the abdominal circumference (AC). They can be found on the exchange card after each doctor's visit.
The indicators add up. To them you need to add the weight of the pregnant woman in kg (B) and her height in cm (P). Multiply the resulting amount by 10.
The error in the calculation is 500 g. Therefore, the formula should be used no earlier than the end of the 2nd trimester of pregnancy.
Bublichenko formula
You need to take the weight of the expectant mother in kg (B), divide it by 200 and multiply by 10.
Recently, this technique has been used quite rarely, because the error in calculations is almost 1 kg.
Yakubova's formula
We need the same indicators that are used for calculations using the Lankowitz formula - OZH and VDM. They need to be added and then divided by 4. Another 100 is added to the result.
Jordania formula
Coolant and air flow indicators are again needed. To get the result you just need to multiply them by each other.
According to Johnson
To use this method, you only need to know the VDM parameter.
A coefficient (K) is subtracted from this parameter:
The resulting difference must be multiplied by 155.
Solovyov's method
How does fetal weight change over the weeks of pregnancy? Norms and deviations from them
The weight of the fetus changes every day, and after 30-32 weeks the increase becomes more noticeable. What does this depend on? The process occurs at a rapid pace due to the ability of the uterus to stretch significantly.
In its normal state, the size of the female reproductive organ reaches 6-8 cm, weight - about 60 grams. By 32-34 weeks of gestation, the uterus increases to almost 30 cm, and by 38-40 weeks it reaches 40 cm and weighs more than a kilogram. This unique ability of the organ is inherent in nature itself, due to which suitable conditions are created for the full formation and growth of the baby inside the womb.
Many pregnant women are concerned about the question of how much weight the baby gains by week and what to do if weight gain is bad? Sometimes, in order to increase the baby’s weight at 34-36 weeks, specialists prescribe special mixtures to the woman. They help the baby gain the necessary indicators before birth.
In the first trimester
Doctors determine fetal growth and weight using ultrasound. The embryo is visible on the device monitor only from the 8th week of gestation. Until this time, it is tiny in size.
Starting from the 8th week of pregnancy, the embryo becomes human-like. It has a large head, a small body with the rudiments of arms and legs. By week 4, the weight of the embryo is approximately 1.5-2 g. After 30 days, the weight increases 5 times, although the embryo still remains tiny.
In the second trimester
From the 20th week, the baby’s organs are actively forming, and muscle tissue is also appearing. He grows in length, the proportions of his body change. The limbs take on the correct shape. In the period from 18 to 20 weeks, the expectant mother begins to feel the first movements of the child.
In the second trimester, the child’s weight increases approximately 50 times and at 24 weeks reaches 0.5-0.6 kg (see also: weight and height of the child at 26 weeks of pregnancy). It follows from this that the fetus gains about 60 grams per week.
In the third trimester
The third trimester (starting from the 30th week) is characterized by increased muscle mass gain, since all vital organs are already formed (see also: 30th week of pregnancy - how many months is it?). The baby gains on average 200 g per week. In general, starting from 7 months, its weight increases 6 times during the entire third trimester. During this period, the fetus rapidly gains weight and by the end of the 37th week already weighs 2.5-3 kg.
The weight of the unborn baby is influenced by many factors, for example, the poor health of the mother or her illness during pregnancy. The most common causes of low birth weight of a newborn:
- If one of the parents has a frail build and short stature, the child may be born with low weight.
- When a woman is diagnosed with anemia. This condition negatively affects the formation of the placenta, which affects the provision of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus. As a result, the baby is born very small and may lag behind in development.
- Inappropriate lifestyle of the expectant mother. If a woman does not pay due attention to her diet, drinks alcohol or smokes, all this affects the growth and development of her child.
The weight of a newborn in 10% of cases is above normal and can reach 5 kg. The reasons for such deviations are:
- Maternal diabetes mellitus. The disease affects the intrauterine development of the child. The fetus receives a large amount of insulin, due to which its weight increases significantly. Prenatal obesity may even develop. Women with this diagnosis must adhere to a special diet and follow all the recommendations of specialists, then the baby will be born healthy.
- Poor nutrition during pregnancy. If a woman eats a lot of carbohydrates (baked goods, sweets), this affects not only her weight, but also the weight of the baby.
- Severe toxicosis in the first and third trimesters. This condition is accompanied by edema, which does not have the best effect on the condition of the fetus.
- Hemolytic disease of a child. This pathology appears even before birth due to Rh conflict. If a woman is Rh negative and her husband is positive, the child will inherit Rh from the father. The condition is characterized by the formation of edema in the body cavity. Due to this accumulation of fluid, the mass increases.
According to statistics, a large baby is born in those families where there are already one or two children. This is explained by the fact that a woman is already more aware and in control of her condition during her second or third pregnancy. The expectant mother worries less and does not make the same mistakes associated with her lifestyle, so the fetus grows better and gains weight.
Deviations from the norm in a larger direction in the weight of the child at birth do not have the best effect on the birth process. A large fetus can cause many problems during childbirth:
- discrepancy between the size of the child’s head and the woman’s pelvis;
- ruptures are possible when the fetus passes through the birth canal;
- the likelihood of postpartum hemorrhage (possible due to insufficient contractile function of the uterus after delivery).
To avoid such unpleasant consequences, doctors prescribe a caesarean section. It can be planned or emergency.
Fetal weight indicators are important throughout the entire 40 weeks of pregnancy. Deviations from the norm may indicate the presence of developmental pathologies and improper course of the gestation period. You will learn about what weight is normal for a baby and what can affect his development by reading this article.
The normal weight with which a child is born is considered to be 3000-3600 g.
Deviations from the normative indicators of fetal weight are possible in 2 options.
Underweight
This is what they say about children who gain less than 2 kg at the time of birth.
A child's low weight causes concern among parents much more often than a child's excess weight, and this is not entirely correct.
There is no need to start panicking in advance, because lack of weight does not always indicate that the child’s body is underdeveloped.
At the present stage, doctors can fully assess the condition of the child even before birth. If the baby does not have developmental pathologies, the organs and body proportions are normally formed, the expectant mother feels well during pregnancy, eats properly and is sufficiently active, then most likely this deviation is physiological.
It happens that children with low weight are born weak, but thanks to the efforts of doctors and the responsibility of parents, by six months they are almost not behind their peers. At the current level of development of medicine, even children born weighing less than 1 kg gain the necessary weight in artificially created conditions.
It’s another matter if the child’s internal organs are not sufficiently formed due to lack of weight. Such children are more often susceptible to various diseases, so they require more careful monitoring by doctors.
Already during pregnancy, a woman whose fetus is underweight may be prescribed specialized treatment that will help influence the growth and development of the baby.
Exceeding weight
Excess body weight is observed in children born weighing more than 4 kg.
If the reason for a child’s overweight is the physique of the parents, then in most cases such children are born absolutely healthy.
But if the reason for the deviations is the presence of endocrine or other pathologies in the mother, then this is already a reason to pay special attention to his health.
During pregnancy, special attention should be paid to the weight of the fetus. Timely detection of deviations will help to take measures to correct the baby’s body size. It should be remembered that the mother’s lifestyle and her responsible attitude towards her special situation have a significant impact on the course of pregnancy and the health of the child.
Features of pregnancy with twins at 32 weeks
When the development of babies reaches 32 weeks, the doctor can assess their general condition, identify possible pathologies, and also set a date for an early birth. An ultrasound examination during this period makes it possible to examine both placentas and find out their condition and location. According to the norm, by 32 weeks the twins should have decided on their position and be ready for birth.
A special feature of such a pregnancy is the need for a control ultrasound examination in the maternity ward. Thanks to this, the doctor will analyze important indicators and make a decision regarding delivery tactics. By 32 weeks, each baby's weight should be within 1.6 kg.
In such cramped and uncomfortable conditions, twins will gain weight at a slower rate. In this regard, by the time twins are born, they will weigh less than if an ordinary, average baby was born. Therefore, twins have to develop much faster so that by the time of birth all vital systems and organs are functioning normally. Knowledge about earlier birth pushes babies’ bodies towards accelerated development.
Throughout the entire period of pregnancy, you should remember about safety and treat yourself and your unborn child with special attention and caution. Remember the basic rules: you should not freeze and stay in the sun for too long, you need to choose comfortable clothes taking into account weather conditions, ensure your feet are constantly warm, and avoid falls and excessive fatigue from work. Remember that lying around constantly without doing anything is also not allowed.
Remember that you can’t lie down all the time doing nothing either.
What should a pregnant woman do? Firstly, you need to regularly visit your local gynecologist. Secondly, you should undergo all prescribed examinations, such as ultrasound and tests. Thirdly, do not forget about weight control. During pregnancy, including at 32 weeks, stressful situations should not be allowed. Create a calm environment around you: pleasant music, close and dear people, absence of noise and screams. Do not forget about the dangers of nicotine, so you should avoid being near people who smoke. Remember that during the entire period of bearing a child, it is not recommended to use any drops or tablets without the permission of a doctor. You can eliminate any danger only by paying close attention to your own body.
Fetal weight is greater than normal
When assessing a child’s weight by week of gestation, doctors are often faced with a situation where the values obtained during examination are higher than normal. If the pregnancy process proceeds normally, there are no complications, then doctors associate the possible deviation with heredity. Tall parents with a dense build are more likely to give birth to large babies. However, in some cases, an indicator exceeding the permissible norm values is a sign of pregnancy complications.
According to statistics, in approximately 10% of all pregnancies the weight of the newborn reaches 5 kg. By assessing how weight changes week by week, recording excess values of the norm, doctors try to exclude the following complications of pregnancy:
- Diabetes mellitus in pregnancy. With this pathology, the fetus receives more insulin, which leads to an increase in body weight. In some cases, intrauterine obesity is possible.
- Violation of the diet of a pregnant woman. A large amount of carbohydrates and sweets in the daily menu of the expectant mother contributes to rapid weight gain not only by the mother herself, but also by the fetus.
- Hemolytic disease of the fetus - develops as a result of Rh conflict, when a woman is Rh negative and her husband is Rh positive, and the baby inherits the father's Rh. This leads to the formation of edema; excess fluid in the body leads to weight gain.
If the fetal weight is more than normal, doctors advise the pregnant woman to adjust her diet and lifestyle. The menu strictly limits carbohydrates - pastries, sweets, flour and bakery products are kept to a minimum. Preference should be given to lean meats, vegetables, and fruits. The diet should contain:
- beef (veal);
- poultry meat;
- zucchini;
- cabbage;
- legumes;
- greens (parsley, dill, lettuce);
- river and sea fish (hake, carp, pollock).
How to gain baby weight during pregnancy?
When the doctor determines that the fetus is small, it is necessary, first of all, to adjust the diet.
Products should be as healthy as possible, with plenty of vitamins and minerals. A complete abstinence from alcohol and tobacco products is provided to avoid fetal hypoxia. Some experts recommend special nutritional mixtures, such as Nutrizon, which helps the baby gain weight during pregnancy and reduces the risk factor for developing various pathologies.
Additionally, the main reasons that led to the decrease are determined. Then, most often in a hospital setting, compensatory therapy is prescribed to stimulate weight gain in the fetus.
Fetal weight is below normal
Having learned how much the fetus should weigh at the current stage, pregnant women panic if it is below normal. In most cases, this situation indicates a delay in fetal development and pregnancy pathology. However, before making such a conclusion, estimating the weight of the growing fetus week by week, it is necessary to make sure that the gestational age is set correctly.
If the child’s weight is below normal, doctors initially try to exclude developmental delays. At the same time, they take into account the fact that numerous factors influence the weight of the future baby. Thus, even poor health of a pregnant woman or a mild cold can cause a decrease in fetal weight. Among the main reasons for the underweight of the unborn child are the following:
- One of the parents is short or frail.
- Presence of anemia in a pregnant woman. The pathology negatively affects the formation of the placenta, as a result of which the baby does not receive enough oxygen and nutrients.
- Wrong image of a woman. Insufficient nutrition, adherence to diets, lack of meat products in the diet (vegetarianism) often leads to the fact that the baby is born low-weight or has developmental delays.
If the baby's weight is below normal during pregnancy, first you need to find out the reason. When this is not associated with pathology of fetal development, doctors advise the woman to adjust her diet. A pregnant woman's daily menu should include meat dishes and dairy products in sufficient quantities. Protein promotes rapid muscle gain. The diet should contain:
- meat;
- cottage cheese;
- flour products (in limited quantities);
- dairy products;
- vegetables and fruits.
Prevention of deviations
Prevention in this case will be thoughtful preparation for the process of bearing a child. Below is a list of recommendations for the expectant mother:
- Try to cure all your diseases. Any chronic disease of a pregnant woman poses a danger to the child, therefore, even before pregnancy, the expectant mother needs to undergo a comprehensive examination and try to cure all her “sores”. If it is completely impossible to get rid of a disease, you need to consult a doctor about how to minimize the harm from it to the fetus.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle. Before and during pregnancy, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right, not overwork yourself and be less nervous. All this will help you give birth to a healthy baby.
- Be careful when taking any medications. Before taking any medicine, you should consult your doctor. This also applies to products that you safely use in everyday life. Ideally, you need to get used to taking only the medications that are prescribed to you.
- Get medical tests regularly. If you have any suspicious condition, you should immediately contact a gynecologist. Any frequency of visits to the hospital is justified when it comes to the child’s health. Remember that only a doctor can identify abnormalities in the development of the fetus, and therefore begin the necessary treatment or at least compensate for the harm.
What determines the weight of the fetus during pregnancy?
The weight of the child depends on the functioning of the placenta and the incoming nutrients with oxygen. Starting from the second trimester, the fetus increases to 80 grams. In the later stages, the seven-day gain reaches 200 grams, but before labor the pace slows down significantly due to the death of the placenta.
The indicator also depends on the following factors:
- unbalanced maternal diet;
- stressful situations during pregnancy;
- chronic diseases;
- toxicosis;
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- genetic predisposition.
The weight of the baby during intrauterine development also depends on gender. Boys are born larger than girls.
Formulas for calculating fetal weight
| Calculation method | Preliminary data | Formula | Notes |
| Jordania formula | Pregnant woman's abdominal circumference (AB), uterine fundus height (UF), all parameters are measured in centimeters | Weight (g) = Coolant x HP | For a more accurate calculation, the doctor uses special coefficients |
| Yakubova's method | The parameters are the same | Weight = (VDM coolant) x 100/4 | An improved version of the Jordania formula |
| Johnson calculation | In addition to the above parameters, the Solovyov coefficient is used, which is calculated based on the woman’s weight. If body weight is less than 90 kg, the coefficient will be 11, if more than 90 kg, then 12. | Fetal weight = (VD-coefficient) x 155 | |
| Solovyov's method | It is necessary to measure the height of the uterine fundus and wrist circumference. If the last parameter is less than 16 cm, the coefficient will be 12; if the wrist is more than 16 cm in circumference, the Solovyov coefficient will be 11. | The formula is the same | |
| Dobrovolsky's technique | Mother's height, 0.5 coefficient applied | Fetal weight = (woman’s height – 96)x0.5 | |
| Lankowitz formula | It is considered one of the most difficult methods. A woman’s height, weight, abdominal circumference, fundus height | Fetal weight = (WL height weight) x 10 | In half the cases, Lankowitz's formula gives accurate results. In other cases, calculation errors are possible (approximately 200-500 g) |
| Bublichenko method | The simplest and most uncomplicated method, where you only need one parameter - the mother’s weight | Baby's weight = Mother's weight / 20 |
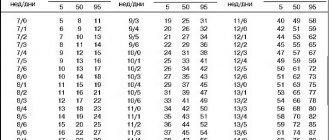
Average components of weight gain during pregnancy
| A week | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| Weight, g | 1 | 2 | 4 | 7 | 9 | 14 | 21 | 30 | 40 |
| A week | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| Weight, g | 50 | 140 | 200 | 220 | 280 | 400 | 460 | 550 | 650 |
| A week | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 |
| Weight, g | 750 | 800 | 950 | 1000 | 1100 | 1300 | 1600 | 1900 | 2100 |
| A week | 35 | 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 | |||
| Weight, g | 2300 | 2500 | 2800 | 3100 | 3200 | 3200 |
Deviations in a child’s birth weight are not only due to gender. This indicator is also affected by:
- heredity;
- chronic diseases of women;
- fetal malformations;
- placental insufficiency;
- lifestyle of the expectant mother.
- Heredity. A child's weight gain largely depends on the build of the parents. If dad and mom have a fairly large build, then the child’s weight will be significantly greater than that of parents with an average body size. But if the parents are thin and short, then the baby will be born with low weight.
An important indicator is the weight of the parents at birth.
- Nutrition. During pregnancy, a woman should consume the entire range of useful vitamins and elements that her baby will receive with her. This has a beneficial effect on the development of its mass.
Abuse of fried, fatty and floury foods can lead to a lack of important substances for the child and developmental delays.
Excessive intake of vitamins can negatively affect growth.
- Bad habits. When the fetus consumes alcohol, nicotine and narcotic substances during pregnancy, not only is there insufficient weight, but also various developmental pathologies.
- Stress. If the expectant mother often worries and is nervous, this cannot but affect the baby’s weight gain.
- Chronic diseases. For example, women with diabetes are more likely to give birth to children with excess body weight, and with heart pathologies, on the contrary, there is a lack of weight.
- Extreme conditions. If the pregnancy is difficult and there is a constant threat to the baby’s life, then it is most likely that he will lose weight.
- Multiple pregnancy. If a woman is carrying 2 or more children, their weight will deviate from the norm. But in this case it is considered natural.
- Condition of the placenta. If the uteroplacental blood flow is disrupted, the baby does not receive enough oxygen and its growth slows down.
- Age of the pregnant woman. Particular attention should be paid to women in labor under 18 and after 35 years. They are more likely to have insufficient fetal weight.
- Taking medications. Some medications, especially antibiotics, can have a serious effect on the growth and development of the fetus. The most dangerous period is the 1st trimester, since at this time the baby is developing important structures.
- Pregnancy order. It is known that the size of the first child may be slightly smaller than in subsequent pregnancies.
Exceeding weight
Starting point - pre-pregnancy weight
A woman’s weight before pregnancy is the so-called reference point, to which we will add grams. First of all, you need to decide what is considered the norm. As a rule, they proceed from the ratio of height minus 110. That is, with a height of 170 cm, your optimal weight should be 60 kg (170-110 = 60). This is the norm.
Many women, who were quite happy with their pre-pregnancy weight, are terrified of losing their slim figure and losing weight. They limit themselves in food and take vitamins, believing that they are enough for the development of a healthy child. Of course, they may preserve their figure in this way (but not always), but the baby’s health is jeopardized. Remember, now nothing is more important to you than the health of your unborn child and you have no right to deprive him of essential nutrients for fear of getting fat. In addition, problems with returning to one’s prenatal size arise not because of “pregnant” weight gain, but because of hormonal changes occurring in the body of a young mother. If your weight before pregnancy fluctuates within the normal range, then for the normal course of pregnancy and childbirth you need to monitor your weight gain so that it does not exceed the norm and does not fall below 9 kg.
If your pre-pregnancy weight is more than 20% higher than normal, you should carefully monitor your diet and not overeat (especially in the first trimester). But you also cannot go on a strict diet during pregnancy - the child will not be able to grow only due to the mother’s fat deposits, since they do not contain the necessary set of nutrients. Your task is to gain no more than 6-10 kg during pregnancy, but no less. Overweight women should try to gain no more than 300 g per week in the first trimester, 300 g per week in the second trimester, and 200 g per week in the third trimester.
If at the time of pregnancy your weight is significantly less than normal, then during the first trimester you should eat more calories so that the second trimester starts off normal. To avoid the risk of having a baby with a low body weight, you should add about 11-16 kilograms during pregnancy, otherwise your body, which does not have its own reserves, will not supply the child with everything necessary, but will fight with it for vitamins and nutrients. The weight gain pattern for underweight women is as follows: first trimester - 800 g per month, second trimester - 2400 g per month and third trimester - 2000 g per month.