The endometrium is the inner mucous layer of the uterus, equipped with blood vessels. It is responsible for creating favorable conditions for the implantation of a fertilized egg. If pregnancy does not occur, the function of the endometrium is to remove the unfertilized egg from the body along with menstrual blood. Any pathologies of the mucous layer (thickening, thinning) lead to failure in pregnancy. On average, its norm for unhindered implantation of the egg is 0.7 cm.
p, blockquote 1,0,0,0,0 —>
p, blockquote 2,0,0,0,0 —>
A thin layer of the endometrium is one of the common pathologies observed in women of reproductive age. Often this problem causes infertility.
p, blockquote 3,0,0,0,0 —>
p, blockquote 4,0,0,0,0 —>
Causes and signs of pathology
p, blockquote 5,0,0,0,0 —>
The thickness of the mucous layer can vary and depends on the day of the menstrual cycle. In the first days it does not exceed 0.5-0.9 cm, and a few days before the start of menstruation it reaches 1.3 cm. If the thickness is below 0.5 cm, we are talking about hypoplasia (thinning) of the endometrium.
p, blockquote 6,0,0,0,0 —>
Why is the endometrium thinned?
p, blockquote 7,0,0,0,0 —>
Predisposing factors include:
p, blockquote 8,0,0,0,0 —>
- hormonal imbalance;
- endocrine diseases;
- congenital disorders in the blood supply to the uterus;
- chronic inflammatory processes in the genital organs;
- presence of polycystic ovary syndrome;
- underdevelopment of the uterus;
- frequent use of emergency contraception (Postinor).
It is necessary to note the negative impact of surgical manipulations that were performed on the uterus. The consequences of curettage performed during abortions are especially dangerous. Some women with thin endometrium experience underdevelopment of the mammary glands, narrow pelvis, short stature, and later menarche.
p, blockquote 9,0,0,0,0 —>
The disease has no specific signs, so many women who are not planning a pregnancy may not even be aware of the presence of a problem. Typically, the diagnosis of hypoplasia is established in the process of determining the reason why pregnancy either does not occur or is terminated in the early stages.
p, blockquote 10,0,0,0,0 —>
Thinning may be indicated by scanty periods and irregular menstrual cycles. Painful periods, the presence of large clots in the blood, and discharge in the middle of the menstrual cycle should also alert you. Sometimes during reproductive age, uterine bleeding may occur. The listed symptoms should be the basis for a visit to the gynecologist.
p, blockquote 11,0,1,0,0 —>
p, blockquote 12,0,0,0,0 —>
Physiotherapeutic methods for enlarging the endometrium
To build up the endometrium, physiotherapeutic methods can be used that improve blood supply to the female genital organs. Among them are:
- therapeutic exercises;
- massage (impact on certain areas of the body using hands);
- acupuncture (exposure to certain points of the body with special needles);
- hirudotherapy (treatment with leeches);
- electropulse therapy;
- magnetic therapy on the lower abdomen.
Any physical activity can help improve blood circulation in the pelvic organs: swimming, yoga, and running. Exercises for strengthening the pelvic floor muscles from wumbling and belly dancing are especially useful.
The likelihood of pregnancy with this pathology
In most cases, thinning of the uterine mucosa worries women who are planning to conceive or those who have had a long-awaited pregnancy after previous failures. What to do if the endometrium is thin and how does this affect the development of the fetus?
p, blockquote 13,0,0,0,0 —>
First of all, women are reduced in their ability to become pregnant naturally, since the thin mucous layer of the uterus prevents the implantation of the fertilized egg.
p, blockquote 14,0,0,0,0 —>
Is it possible to get pregnant with a thin endometrium?
p, blockquote 15,0,0,0,0 —>
Medicine knows of cases where conception occurred even with a thickness of 0.4 cm. But if pregnancy does occur, the risk of early termination, toxicosis, bleeding, subsequent weakness of labor and other complications during childbirth increases.
p, blockquote 16,0,0,0,0 —>
After conception has occurred, the endometrium continues to grow. In the first trimester, its thickness reaches 2 cm or more. Often, it is its significant increase that allows the doctor to determine pregnancy on an ultrasound, since the fertilized egg itself may not yet be noticeable. In the early stages of pregnancy, a thin endometrium requires increased attention from doctors and immediate treatment, since a miscarriage can occur at any time.
p, blockquote 17,0,0,0,0 —>
Separate mention should be made of the IVF procedure when diagnosing thin endometrium. This procedure is extremely undesirable for such pathology, since the chances of the embryo being successfully implanted in the uterus are extremely low. The probability of pregnancy with a thickness below 0.7 cm is no more than 15%. Therefore, the patient is advised to postpone the procedure and take appropriate measures.
p, blockquote 18,0,0,0,0 —>
p, blockquote 19,0,0,0,0 —>
What signs indicate a thick endometrium and the development of a polyp?
- irregular menstruation;
- heavy bleeding, when one pad/tampon lasts for 2-3 hours;
- bleeding between cycles;
- painful menstruation;
- pain during sex.
What is the cause of thickening of the endometrium?
- With hormonal imbalance and absence of menstruation, the endometrium is not renewed, which leads to its thickening. Proliferation of the endometrium and an increase in the number of estrogen receptors are observed with the development of endometriosis, which may be accompanied by retrograde menstruation. In this case, endometrial particles with reverse blood flow enter the peritoneal cavity and not the vagina. This leads to the proliferation of endometrial cells in the abdominal cavity.
- Another common manifestation of estrogen and progesterone imbalance is polyps. This is the growth of a separate area of the endometrium in the uterus or in the cervix. Polyps often appear with weight gain, when estrogen begins to be more actively produced by fat cells. We get estrogen dominance, and as a result, PCOS. Pelvic infections, pelvic congestion. During pregnancy, the lining of the uterus naturally thickens to support the fetus.
Here is a story from my life.
In 2010, an ultrasound scan diagnosed me with enlarged endometrium in the uterus. Then, with the ultrasound doctor, we regarded this as a possibility of implantation of the fertilized egg, but a week passed, there was no implantation, a second one began and a slight bleeding began, which did not stop, but intensified. The story ended with increased bleeding, a diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy, and hospitalization. Another ultrasound in the hospital helped avoid curettage, which is usually prescribed in this case. For me it was a nightmare, since I was planning a pregnancy and was expecting a happy motherhood. This outcome made me think and start working on myself. I began to learn to understand my body and its desires, because I did not want a repetition of this condition. I wanted to become a mother.
Diagnosis and treatment
p, blockquote 20,0,0,0,0 —>
After studying the general symptoms, the patient is prescribed:
p, blockquote 21,0,0,0,0 —>
- Ultrasound of the uterus, which is performed several times at different phases of the cycle;
- general urine and blood tests;
- analysis to determine the level of hormones responsible for the onset and successful course of pregnancy;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- taking samples of uterine tissue for histological examination;
- biopsy of the uterine body.
These studies make it possible not only to establish the fact of endometrial thinning, but also to determine the causes of the pathology.
p, blockquote 22,0,0,0,0 —>
Treatment for thin endometrium depends on the reasons that caused it. In most cases, this is an imbalance of the hormonal system. Therefore, pregnant women with this pathology need hormonal therapy with drugs containing progesterone. Treatment regimens, dosage, and duration of therapy are carried out exclusively by the attending physician on an individual basis.
p, blockquote 23,1,0,0,0 —>
If hypoplasia is caused by chronic inflammatory diseases of the genital organs, drug therapy should be aimed at eliminating the source of inflammation. In some cases, there may be indications for surgical treatment. It consists of removing the inner layer and further hormone therapy. These methods help to renew the mucous layer of the uterus and normalize its thickness.
Effective ways to grow the endometrium: medications
medications are usually used . It should be noted that thin endometrium is difficult to treat.
Since the growth of the endometrium directly depends on estrogen, accordingly, the following is prescribed:
- Hormonal treatment: as a rule, these are injections of estradiol, Divigel.
- Hormel drops are a homeopathic medicine that is used to regulate a woman’s hormonal conditions. Its action is aimed at activating estrogen production. The effect of the drug is quite mild and effective.
It is believed that drugs such as Duphaston and Utrozhestan increase the endometrium. This is not true. These drugs help the endometrium to form and mature. These drugs contain progesterone: Duphaston consists of synthesized progesterone and has no side effects, Utrozhestan is made of natural progesterone.
Ways to increase progesterone levels
Our readers successfully use Monastic tea to treat the thyroid gland. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
Progesterone is a female hormone responsible for the normal course of pregnancy and the transformation of the mammary glands for milk production. If a woman experiences progesterone deficiency, this can lead to pregnancy failure - spontaneous miscarriage or fetal death. What are the causes of this problem?
What changes with endometrial hyperplasia?
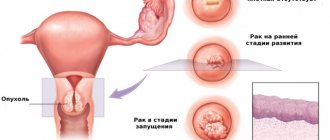
Excessive proliferation of endometrial cells is not typical for a healthy woman; only with pathology, the uterine mucosa loses its functional purpose - creating favorable conditions for implantation of the embryo after conception. Endometrial hyperplasia is a sharp increase in its volume, excessive thickness of the mucous layer. In healthy women, the endometrium grows only during the first phase of the female cycle, since its growth is stimulated by the action of estrogens. Then, in the second phase, it is stably maintained in a certain state by the hormone progesterone. If we are talking about endometrial hyperplasia, then hormones influence it excessively, this can lead to focal growth, forming a polyp, or lining the entire inner surface of the uterus. Naturally, endometrial hyperplasia then affects menstrual function and the ability to conceive is impaired.
Description of the disease
Endometrial hyperplasia is excessive proliferation (overgrowth) of the uterine mucosa. Typically, the endometrium grows during the menstrual cycle, preparing a bed for future fertilization of the egg.
If pregnancy does not occur, the mucous membrane peels off and comes out along with menstrual flow. Such cyclical changes occur every month.
Sometimes the mucous membrane grows too much and the endometrium thickens. If abnormal growth of the mucous membrane is observed, this pathology is called endometrial hyperplasia.
On this basis, the disease is distinguished from endometriosis, when, with excessive growth of the mucous membrane, its cellular structure does not change.
Forms
Based on the results of histological analysis, the following forms of pathology are distinguished:
- atypical (adenomatosis);
- simple.
The atypical form is rare, but it is the most dangerous.
With atypical pathology in the overgrown mucous membrane, structural changes occur in the cells (atypical nuclei, multinucleolar cells, etc.), this is revealed by histological examination of the tissue.
Modern medicine considers this form of the disease a precancerous condition. However, this is not a death sentence, and not in all cases the violation develops into carcinoma. According to statistics, endometrial cancer develops in approximately one in ten women diagnosed with adenomatosis.
In the case of a simple form of the disease, there are no atypical cells. It, in turn, is divided into glandular and glandular-cystic.
Glandular endometrial hyperplasia is an excessive proliferation of glandular endometrial tissue. Glandular cystic hyperplasia is a cystic form of glandular endometrial hyperplasia.
The most common diagnosis is simple glandular hyperplasia.
Types
Based on localization, there are two types of disease:
- diffuse;
- focal.
With diffuse growth of the mucous membrane occurs evenly over the entire surface of the uterus. In focal cases, cells grow only in a limited area. In this case, so-called polyps are often formed. Both diffuse and focal types can be simple and atypical.
The role of hormones in the genesis of hyperplasia
The leading reason for the formation of endometrial hyperplasia is considered to be the influence of hormones, or more precisely, an imbalance between estrogen and progesterone. It is believed that the stimulus for excessive growth of the endometrium is an excess of estrogen hormones with a relative deficiency of progesterone. Any conditions that provoke hormonal imbalance can become an impetus for the development of hyperplasia. In the first phase, hormones have a ratio in favor of estrogens, which stimulates the growth of the endometrium to a certain limit. After ovulation, progesterone should take first place, while estrogen hormones decrease. As the level of estrogen decreases towards the end of the cycle, the rejection of the outdated endometrium begins, a new cycle begins - the old endometrium is rejected, bleeding begins, and a new one forms in its place. If disruptions occur in this mechanism due to inflammation of the ovaries, endocrine changes or problems with the pituitary gland, endometrial hyperplasia may develop.
Folk remedies
You can restore the endometrium using traditional medicine. The use of herbal preparations is based on the fact that their use helps normalize a woman’s hormonal levels. And achieving endocrine balance stimulates an increase in endometrial thickness. For this purpose, sage, red brush, hops, clover, hogweed, etc. are used. One of the methods is to alternately use herbs in the following order: in the first half of the cycle, a decoction of red brush is used, and in the second, hogweed is used.
To improve the condition of the uterine mucosa, it is recommended to adhere to a special diet. It is recommended to use products rich in:
- vitamin C (black currant, pineapple, grapefruit, lemon, etc.) to strengthen the vascular wall;
- vitamin E (raspberry leaves, flax seeds, fresh vegetables, etc.);
- salicylates (honey, strawberries, cherries, cranberries, etc.) to thin the blood and prevent blood clots;
- omega-3 fatty acids (salmon, trout, etc.).
Pumpkin is often used for endometrial growth. This product is very popular due to its availability and ability to be used in various dishes. There is a drug called Tykveol, containing pumpkin seed oil for the endometrium and the treatment of other pathological conditions.
Causes of pathology: inflammation of the ovaries, metabolic pathologies
Hormonal imbalance can be provoked by both external factors and certain endocrine-metabolic pathologies of the body. First of all, it is worth noting the use of estrogen drugs, but without the addition of progesterone, as well as the development of polycystic ovary syndrome. Hyperplasia may be present at the onset of menopause or if there is chronic inflammation of the ovaries. This is not typical for an acute inflammatory process, since edematous and exudative processes predominate, but chronic inflammation of the ovaries, including cystic lesions, can lead to an imbalance of hormones. Possible endometrial hyperplasia due to obesity, during adolescence.
It is often detected in young girls who have not yet given birth, or during premenopause. Hyperplasia is often accompanied by thyroid pathologies, adrenal dysfunction or diabetes. Often problems in the structure of the mammary gland are also identified.
How to treat focal hyperplasia?
Are there signs of endometrial polyps? You have a chance to protect yourself from complications and get rid of unwanted symptoms. The On Clinic medical center in Almaty employs qualified gynecologists. A specialist will conduct an examination. Based on its results, he will prescribe treatment. The treatment program is compiled individually for each patient. This takes into account symptoms, the presence of concomitant diseases, age and individual characteristics of the body. The final cost depends on the drugs used.
The medicines used by On Clinic doctors have maximum effectiveness and minimal side effects.
Treatment of focal hyperplasia is complex. It is aimed at eliminating symptoms, restoring the hormonal levels of the female body and normalizing reproductive function.
Endometrial polyps are treated with conservative and surgical methods. Conservative treatment includes drug therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Stop bleeding. The method of eliminating bloody discharge from the uterus is selected taking into account the state of the body and the volume of blood released.
- Stopping further growth of polyps. Effective treatment involves stopping or slowing the growth of polypotous cells.
- Restoration of hormonal levels. Hormone imbalances are corrected by taking hormone-based medications.
- In the absence of ovulation, when the egg does not leave the ovary, the patient is prescribed stimulation of this process.
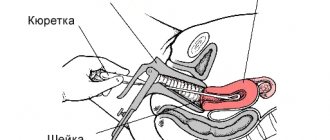
Treatment of polyps begins with hysteroscopy. Please note that this procedure is not performed in adolescents. During this procedure, biomaterial is selected for laboratory testing. After diagnosis, On Clinic specialists will give a referral for diagnostic curettage. After this procedure is performed, the patient is advised to visit a gynecologist to receive corrective treatment.
If conservative treatment is ineffective, which often happens with multiple endometrial polyps, it is advisable to remove them. In severe cases, with multiple lesions, the only effective way to cure is to remove the uterus.
Many gynecological diseases, including focal hyperplasia, occur without obvious symptoms. That is why, for the purpose of early diagnosis and timely treatment, it is recommended to visit a gynecologist at least once every six months. Endometrial polyps are often detected during a routine examination.
Do you need a good doctor in Almaty? Contact the On Clinic medical center. The clinic has qualified specialists and modern equipment. Thanks to this, the diagnosis will be accurate and the treatment effective.
Benefits of treatment at On Clinic
- Experienced gynecologists
- Individual approach and complete confidentiality
- Gynecological treatment (hardware sanitation, ointment tampons, etc.)
- Effective physiotherapeutic procedures
- Modern equipment that increases the effectiveness of treatment
- Certified original medications that are given to the patient for the period of treatment in individually selected dosages
- Treatment control, the doctor is always in touch with the patient until a positive result is obtained
- At On Clinic we use only disposable sterile instruments
- Analyzes are submitted to an independent Moscow laboratory
- All medical procedures: sanitation, IVs, physiotherapy and repeat appointments are included in one price
To avoid inconvenient queues, it is better to make an appointment with a doctor online. Fill out the appointment form on the website to visit a gynecologist on a day convenient for you. Registration through the website gives a discount to every patient!