The disease occurs in waves: periods of exacerbation with severe symptoms are replaced by latent phases, when there are no signs of syphilis, and only positive blood tests indicate the presence of infection.
What symptoms and signs in women indicate syphilis in the early stages and later? Find out in this article.
More than 50% of cases of syphilis in women are diagnosed in the early childbearing period, between the ages of 18 and 29 years . Up to 100% of newborns from sick mothers are infected, and 30% are stillborn.
Infection with syphilis mainly occurs through sexual contact and through kissing, much less often through close household contact, through household items. Since the causative agent of syphilis remains pathogenic for some time in a humid environment, it can be infected through dental and hairdressing instruments, endoscopic devices, and enema tips.
Symptoms of syphilis in women appear, on average, 3 to 4 weeks from the moment of infection , this is how long the incubation period lasts.
Symptoms of syphilis in women: the very first signs
When and how does syphilis manifest in women? Usually a month after infection , sometimes this period is reduced to 9 days or extended to six months.
The disease begins with the formation of a flat, compacted papule at the site of penetration of the pathogen:
- on the oral mucosa;
- facial skin;
- in the corners of the lips;
- on the nipples of the mammary glands;
- on the mucous membrane of the genital organs: cervix, vagina, vulva, clitoris.
Often the disease in women is diagnosed only in the secondary period , if chancroid appears on the cervix and vagina.
Since syphiloma is painless, women usually do not feel it when it is located inside the vagina and hidden from view.
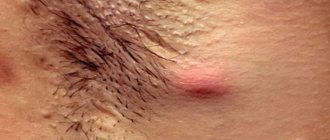
Some time after the first signs of syphilis in women, the papule turns into a round or oval ulcer, the color of red meat, with a diameter of up to 2 cm. It is moist, dense and painless to the touch . In the center, the ulcer has a dirty yellow color, resembling a purulent mass.
Carefully! The photo is not for the faint of heart - symptoms of the primary form of syphilis in women
Symptoms of progression of the primary form
About a week after the formation of hard chancre, patients' lymph nodes in the areas where syphiloma is localized become enlarged. When a chancre forms on the genitals, the pelvic lymph nodes increase, on the oral mucosa - submandibular, on the mammary glands - axillary. The nodes are mobile and painless, and can increase to the size of a walnut.
And only 3–4 weeks after the formation of syphiloma, the RW blood test shows a positive result .
In the absence of treatment, the course of the primary period ends with a general malaise of the body:
- increased body temperature;
- febrile manifestations;
- pain in bones and joints;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes.
These symptoms indicate the spread of tryponema pallidum throughout the body, to other tissues and organs. From this moment the secondary period begins.
Domestic infection
Less commonly, the disease can occur through everyday life.
Infection can occur through the personal belongings of an infected person, as well as through contact with objects on which traces of the patient’s secretions could remain. Conditions under which infection can occur are:
- if the secretion of the sick person contains a huge number of syphilis pathogens;
- in case of violation of the integrity of the mucous membranes or skin (presence of scratches, abrasions or wounds) of a healthy person.
The causative agent of syphilis is not transmitted if personal hygiene rules are observed and there is no physical contact with an infected person.
In addition to a sexually transmitted sexually transmitted disease (syphilis on the genitals), in the modern world you can also find a household version of the disease. Sometimes it can form in the mouth. You can become infected with household syphilis through household items used by an infected person. This includes any utensils used by the infected person, lipstick, can of soda, etc.
During the incubation period, a person does not yet know that he has become infected, but already at this moment he is dangerous to those close to him. Relatives, close friends, and also a partner can easily become infected with household syphilis without even knowing it.
Secondary period of the disease
Secondary syphilis develops 2 months after the formation of chancre and is characterized by rashes on the skin and mucous membranes. The following types of rash are distinguished :
- Syphilitic roseola - flat spots, 0.5 to 1 cm in diameter, pink or pale pink, localized on the skin of the trunk and limbs. The rash does not manifest itself with accompanying symptoms - there is no itching, peeling, or burning.
- Lenticular syphilide - round, dense, copper-red elements that rise above the skin.
- Meliary syphilides are small, millet grain-sized, dense brownish papules localized on the skin of the body. They usually gather in groups, forming rings, arcs and plaques.
- Coin-shaped syphilides are large spots, up to 2.5 cm in diameter, red or brown in color, slightly raised above the skin.
- Weeping syphilide is wet, round, eroded spots that form in the groin area and axillary folds. Accompanied by moderate itching.
- Condylomas lata are soft, pale pink papules that rise above the skin and resemble papillomas in appearance. Localized in the perineum and around the mouth.
- Pustular syphilide - small pustular papules with a yellowish crust at the end. Localized on the trunk, limbs and face.
All elements of the rash, with the exception of roseola, have clear boundaries and are located randomly. Most often, the rash affects the skin of the torso, but can occur on the scalp, face, neck and palms.
After 2–3 weeks, the rash goes away suddenly , leaving no spots or scars. The secondary period of syphilis lasts up to 5 years, during which time rashes periodically appear, which disappear on their own after some time.
The first wave of the rash is characterized by a brighter course: multiple skin lesions, the elements are brightly colored. Subsequently, the papules have darker pigmentation and are localized in individual areas of the skin, often forming in groups.
Photos of secondary syphilis in women
Therapy for intolerance to basic antibacterial drugs
In case of hypersensitivity to penicillin drugs, the patient is prescribed Ceftriaxone, Tetracycline or Doxycycline. Erythromycin can be used:
- Ingredients: erythromycin.
- Therapeutic effect: antibacterial effect.
- Indications for use: primary syphilis, gonorrhea, allergy to penicillin.
- Daily dosage: for adults – 200-400 mg every 6 hours, for children – 40 mg/kg for 2-4 doses.
- Advantages: can be used to treat a child, minimum contraindications and side effects.
Article on the topic: Candiderm - instructions for using ointment
These medications are prescribed in higher dosages for a course of 14-30 days. For fresh forms of the disease, treatment can be carried out with Sumamed. If the patient has intolerance to penicillin, erythromycin and tetracycline, then Cefazolin is allowed to be used:
- Ingredients: cefazolin.
- Therapeutic effect: bactericidal.
- Indications for use: sexually transmitted diseases.
- Dosage per day: 1-6 g for 2-3 injections.
- Advantages: minimum contraindications (age up to 1 month, individual intolerance.
Tertiary infection
Thanks to annual medical examination, in which an RW blood test is mandatory, tertiary syphilis is diagnosed extremely rarely .
The tertiary period of the disease develops 4–5 years after Treponema pallidum enters the body. This period is characterized by damage to the skin, mucous membranes, bones, and internal organs .
It is manifested by the appearance of tubercles, plaques and nodules, often single, brown or red-brown in color on the arms, back and face.
The plaque has irregular borders , rises slightly above the skin and is covered with ulcers and crusts.
With a later course, an isolated gumma forms in the subcutaneous tissue - a hard node, the size of a walnut, with an ulcer in the center.
Most often it occurs on the scalp, chest, face . Gummas and tubercles, localized on the mucous membrane of the mouth, larynx and nose, lead to tissue destruction and deformation of the soft palate. Against this background, the following complications develop:
- destruction of the nasal septum, deformation of the nose;
- hoarseness and hoarseness;
- impaired tongue mobility.
Spreading to other tissues and organs, syphilis affects the nervous, vascular and skeletal systems, manifesting itself as syphilitic meningitis, hydrocephalus, and progressive paralysis.
Internal organs (liver, kidneys, lungs, heart) are deformed and their function is impaired.
Photo of tertiary syphilis in women
Treatment of neurosyphilis
Upon learning of the disease, it is necessary to stop all sexual relations. Intimate partners and family members should definitely get tested. The tests are not expensive, and many hospitals and institutions provide them free of charge.
Further terms and costs depend on the stage of the disease, the chosen medications and the regimen.
Drug treatment in the early stages takes 2-4 weeks with infections once a day or twice a week. Advanced variants of syphilis are fought from several months in a hospital to a year on an outpatient basis.
As for the cost, as of 2020, the price for bicillin 3 in Moscow averages 649 rubles. for 600,000 units, 50 pcs. Ceftriaxone in 1 gram packaging – 24 rubles. Swiss "Rocephin" will cost 550 rubles. per gram.
Giving preference to quick recovery with the help of imported drugs, you will have to pay more. The desired therapeutic effect can be achieved quite cheaply with local tablets and injections.
Later stages are much more expensive due to the duration of the course and additional complexes to eliminate the harm caused by the disease.
When treating syphilis, it is important to understand that the course cannot be interrupted, and the disappearance of symptoms does not indicate complete recovery.
Failure to comply with the medication schedule will lead to temporary improvement, and then to relapse and transition from the primary stage to the secondary stage.
A person can be considered cured of syphilis only after an appropriate doctor’s conclusion.
There are several types of treatment for syphilis:
- Specific. Once the diagnosis is made, treatment is carried out with antibiotics. But since they kill not only harmful, but also beneficial microbes, vitamins and drugs that increase the body’s immune defense are prescribed.
- Preventative. It is prescribed to persons who have been in contact with a patient with syphilis during the infectious stage of the disease.
- Preventive. Applies to pregnant women who have previously had syphilis or currently have this disease. And also to children whose mothers were infected during pregnancy.
- Trial. Prescribed for suspected specific damage to internal organs in the absence of the ability to confirm the diagnosis with convincing laboratory data.
- Epidemiological or syndromic. It is carried out on the basis of anamnesis and clinical picture in the complete absence of laboratory diagnostics.
How to treat syphilis in a woman if she is pregnant? Therapy can only be used up to 32 weeks. Follow-up therapy, if necessary, is prescribed after the birth of the child. After successful and timely treatment, healthy babies are most often born in the first half of pregnancy. And later therapy complicates the recovery of a pregnant woman.
How long does it take to treat syphilis at different stages? In any case, therapy takes a long time. Even at the first stage, the treatment process takes from two to three months. Moreover, therapy should be continuous. If the second stage has occurred, then the treatment will be longer - up to two years or more. During this time, sexual intercourse is prohibited.
If the disease is detected in a partner, he is also required to undergo a full course of therapy. Treatment time will depend on the stage of the disease. All family members should undergo preventive treatment at the same time as the sick person. The treatment time for neurosyphilis depends on the severity of the disease and the characteristics of the patient’s body.
How long does it take to treat syphilis? Preventive treatment is prescribed to people who had household or sexual contact with a patient during the infectious stage of the disease. But if no more than 3 months have passed from this moment. Treatment begins with injections of medications containing penicillin. The course of therapy is carried out for 14 days.
How to treat syphilis if a person consults a doctor after a few months? If the period of treatment is from 3 to 6 months after contact with a patient with syphilis, then the examination is carried out twice, with an interval of 2 months. And treatment will be prescribed only when the disease is detected. If more than six months have passed since contact with a person with syphilis, then only one examination is sufficient.
Neurosyphilis is one of the advanced stages of syphilis that affects the nervous system. It has two types - early and late. Treatment of the early stage is identical to the treatment of secondary relapse. The only difference is that at the secondary stage the concentration of antibiotics in the cerebrospinal fluid increases. For this purpose, drugs are used that slow down their removal from the body.
Treatment of late neurosyphilis is selected taking into account the degree of brain damage. Courses of antibiotic therapy are combined with immunomodulators, vitamin complexes and symptomatic treatment. During treatment, the patient’s condition is additionally monitored by a neurologist and an ophthalmologist.
Ceftriaxone is a reserve drug. Doctors use it if a patient is intolerant to penicillin. Ceftriaxone treats syphilis much more effectively, as it quickly penetrates into the cerebrospinal fluid. This antibiotic has high treponemocidal activity. The fastest effect is achieved with injections into the muscles.
The drug is effective at any stage of syphilis disease. It can be taken by pregnant women. When treated with Ceftriaxone, there is no harmful effect on the body, which distinguishes it from other antibiotics. The medicine acts on bacterial cell membranes, inhibiting their synthesis. How to treat syphilis with Ceftriaxone?
Treponema pallidum cannot be defeated without antibacterial drugs. The duration of antibiotic therapy is determined by the doctor based on the stage and form of the disease: the process can last from weeks to several years. Which doctor treats syphilis and monitors the treatment of syphilis? Venereologist or syphilidologist.
Syphilis in its active form is treated in a hospital; in latent cases, outpatient treatment is indicated. In both cases, it is unacceptable to interrupt the course: the full course of treatment ends with a mandatory re-examination.
The effect of antibiotics is usually enhanced by the prescription of physiotherapeutic procedures, immunomodulators, probiotics and vitamin and mineral supplements. The patient is required to exclude alcohol and sexual intercourse for the duration of treatment.
When choosing a treatment method for syphilis, the venereologist takes into account all factors together:
- form and stage of the disease;
- the presence of chronic pathologies;
- tolerance to specific medications;
- patient's age;
- his physical/psychological condition;
- his living conditions.
Ultra short circuit
It is applicable to combat Treponema pallidum if no more than 48 hours have passed since it entered the body. The doctor makes the decision to administer medications based on the patient's information about potentially dangerous sexual contact. Treatment according to an ultra-short regimen includes a single intramuscular injection of benzathine benzylpenicillin/retarpen in a volume of 2.4 million units.
For preventive treatment
This model is similar to the ultra-short scheme, but involves two injections of bicillin-1 in a volume of 2 million 400 thousand units. (each).
For specific treatment
You cannot do without it if the disease has already taken hold in the body, and doctors talk about early manifested/latent, secondary or secondary recurrent syphilis. For early latent and secondary recurrent syphilis, they are treated with retarpen, bicillin-1 or benzathine penicillin G, 2 million 400 thousand units (a total of 6 injections). For primary and secondary fresh syphilis, the same medications are indicated: injection into the muscle of 2.4 million units every 5 days.
For the treatment of pregnant women
Bicillin-1 is recommended for women at different stages of pregnancy (in the absence of allergic manifestations to the drug). It is administered intramuscularly 2 times a week. The single dose is reduced to 1 million 200 thousand units. The course consists of 7 injections.
Drugs
Medicines against syphilis are available in tablets or in powder form for injection.
Azithromycin
In the early stages of infection, Azithromycin in the treatment of syphilis is equal in effectiveness to benzylpenicillin, which is recognized as perhaps the most effective remedy against treponema pallidum. In addition, this semi-synthetic antibiotic does not have any noticeable side effects on the body. The price is about 65 rubles.
As a prophylactic measure, Azithromycin, a single dose of which is determined by the doctor, is taken for 2 weeks after contact with an infected person. Complete cure with the use of Azithromycin occurs quickly if the patient does not have a “bouquet” of other sexually transmitted diseases.
Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin in the treatment of syphilis is part of the group of semisynthetic penicillins that can actively inhibit the synthesis of cell walls of Treponema pallidum. The tablets are taken without reference to food intake, washed down with drinking still water. Price from 62 to 489 rubles.
The daily dose is calculated by the attending physician: usually it is 500-1000 mg at a time (2 times a day). Treatment with Amoxicillin takes from 5 to 14 days. The time interval between medication doses for people with kidney pathologies is also determined by the doctor.
Tetracycline
How to treat syphilis with Tetracycline? Its derivatives are recognized as the most toxic of antibiotics and are indicated in the early stages of both primary and secondary syphilis. Price from 28 to 51 rubles.
Non-cutaneous symptoms
In addition to skin rashes, the course may be accompanied by other manifestations of syphilis in women. They occur mainly in the secondary period of syphilis:
- Baldness . Increased hair loss in certain areas of the head (cicatricial alopecia) or evenly throughout the entire area (diffuse alopecia). Loss of eyelashes and eyebrows may also occur. Hair growth resumes after 1 – 2 months.
- Erythematous tonsillitis . Unlike tonsillitis, it is expressed by a sore throat, but there is no pain.
- Syphilitic meningitis . The membranes and blood vessels of the brain are affected. Patients complain of headache, tinnitus, dizziness.
- Hydrocephalus . Manifested by headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, confusion. Speech disturbances and epileptic seizures are possible.
- Myocardial damage . Characterized by toxic dystrophy, functional cardiac disorders are observed.
- Liver damage . Anicteric forms of hepatitis occur, with enlargement of the liver and spleen.
- Stomach damage . It occurs in the form of gastritis and peptic ulcer.
- Kidney damage . It is asymptomatic without swelling and increased blood pressure. In a general urine test, an increased number of red blood cells and protein is observed.
Impaired function of internal organs is observed in 25% of patients in the secondary period of syphilis.
We invite you to find out what kind of discharge occurs in women with syphilis. And in another article there is a detailed description of all periods of infection.
Diagnosis, which doctor to contact
If a painless ulcer is detected on the genitals or if the lymph nodes in the pelvic area are enlarged, a woman should visit a gynecologist at the antenatal clinic.
He will conduct a diagnostic examination, and if syphilis is suspected, he will write out directions for blood tests using ELISA and RW methods and send you for further examination to a dermatovenerologist.
In case of rashes, you should immediately seek advice from a dermatovenerologist. Laboratory diagnostics will be carried out:
- serological blood tests using ELISA, RIF, RPGA, RV methods;
- diagnostics of chancre contents and rash elements for the detection of treponema pallidum using dark-field microscopy;
- study of syphilides using the PCR method;
- examination of cerebrospinal fluid if neurosyphilis is suspected.
If positive results are obtained, the patient will be immediately sent to a specialized facility for treatment of the disease.