According to statistics, approximately 60% of adults in the world suffer from disorders of the digestive system. Pathologies are accompanied by unpleasant symptoms: nausea, vomiting, pain of varying intensity, and bowel disorders. With gastritis, an inflammatory process develops in the mucous layer of the stomach, leading to dangerous complications if left untreated. This article describes in detail what gastritis is, what its symptoms are and how treatment is carried out in adults.
What is gastritis?
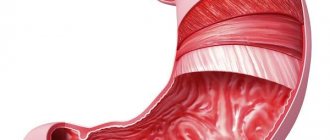
Gastritis is an acute inflammatory process that affects the gastric mucosa. The disease leads to interruptions in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, which loses the ability to properly digest food and absorb nutrients. This, in turn, leads to undesirable consequences.
Inflammation can occur in acute or chronic form. In both cases, the person experiences noticeable pain and needs immediate treatment. Acute gastritis occurs rapidly and painfully, while chronic gastritis manifests itself at times, which makes it difficult to diagnose the disease in the early stages.
Advanced gastritis can result not only in exacerbations, severe pain and serious disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system, but also become the main cause of tumor development with subsequent death.
Gastritis has code K29.0 - K29.7 according to ICD-10. ICD - International Classification of Diseases - a universal classifier developed by the World Health Organization.
Photo: Complications of gastritis
Treatment of acute gastritis
Before starting treatment for acute gastritis, experts recommend cleansing the intestines and stomach. In situations with an infectious etiology of gastritis, antibacterial drugs and absorbent substances are prescribed: kaolin, activated carbon and others.
Antihistamines have a good effect in acute allergic gastritis. A pronounced pain syndrome requires the use of antispasmodics and anticholinergic drugs. Proper nutrition is also necessary. In particular, in the first one or two days you need to completely give up food, however, it is not forbidden to drink strong tea.
On the second and third days, the patient can indulge in porridge made from semolina and rice, low-fat broth, jelly, and slimy soup. After about ten days, the patient can return to a normal diet.
An attack of acute gastritis can be alleviated by washing the stomach with a solution of baking soda or mineral water. Cleansing the stomach occurs through a special enema or taking a laxative. It is useful to place a warm heating pad or a warming compress in the stomach area, and then maintain bed rest for two to three days.
In situations with an infectious etiology of acute gastritis, antibacterial drugs and absorbent substances are prescribed
If the symptoms continue to bother you, you need the help of a specialist - a gastroenterologist. In critical cases, the patient may be admitted to hospital, while in mild cases, outpatient treatment is acceptable. However, even in this case, everything should take place under the strict supervision of a doctor.
Prescribed drugs can be aimed at achieving the following goals:
- reduction of intoxication and reduction of harmful substances in the body: this is facilitated by activated carbon, droppers with saline and glucose, Smecta, Enterosgel, Kaolin, Polysorb, Gastrolit, Polyphepan, Filtrum STI and other means;
- anti-allergy medications: Zodak, Suprastin, Tavegil, Diazolin, Allegra, Xyzal, Claritin and others;
- reducing the pain syndrome of acute gastritis: Atropine, Baralgin, Noshpa, Analgin, Papaverine;
- for hemostatic action: Zantac, Kvamatel, Losek, Sucralfate;
- to normalize acidity in the stomach: Maalox, Almagel, Phosphalugel, Gastralugel, Almalog, Adzhiflux, Altacid and others;
- to restore microflora: Linex, Bifiform, Bifidumbacterin, Acipol, Biosporin and others;
- to improve digestion: Pancreatin, Mezim, Festal, Panzinorm, etc.
Causes of gastritis
Acute and chronic gastritis can occur for different, unrelated reasons, so it would be more appropriate to consider the causes of these two forms of the disease separately.
Causes of acute gastritis in adults
- regular alcohol abuse;
- use of anti-inflammatory drugs such as Ibuprofen, Aspirin, Diclofenac and others;
- eating expired foods or foods contaminated with harmful microorganisms;
- infections (gastritis often occurs due to infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori);
- irritating chemicals (acids, alkalis) and poisons that enter the stomach with food or liquid;
- dysbacteriosis;
- against the background of some other diseases.
Causes of chronic gastritis
- poor diet, frequent dry snacks;
- addiction to spicy and fatty foods;
- habit of eating dishes very hot;
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking;
- parasitic and helminthic infestations;
- intestinal infections;
- constant stress, depression, nervous breakdowns;
- kidney diseases leading to intoxication;
- living in an industrial area contaminated with radiation or chemicals;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- avitaminosis;
- heredity.
Often even the youngest are affected by the disease. Gastritis in children is explained by the fact that the stomach of children under 7 years of age is not yet fully formed. In addition, it is more sensitive to irritants compared to the stomach of an adult.
Reflux
The cause of gastritis can be duodenogastric reflux. With reflux, a malfunction of the digestive organs occurs - the contents of the intestine, along with bile, are thrown back into the stomach. Bile dissolves the mucus that protects the inner surface of the stomach and acidic gastric juice causes a chemical burn to the mucous membrane.
An inflammatory process develops, which leads to the destruction of the mucous membrane, the development of dystrophic and necrobiotic changes in the tissues of the gastric walls. A similar cause of gastritis is typical for nervous and emotional people. In addition, cholecystitis or pancreatitis can cause reflux.
International classification of gastritis
Each form of gastritis comes in several types. Each type of disease occurs for certain reasons and requires its own approach to treatment.
Types of acute gastritis
- Fibrinous (diphtheric) gastritis is the result of penetration of various acids or mercury vapor into the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, fibrinous gastritis can be a consequence of an intestinal infection or an object entering the stomach. This gastritis is accompanied by elevated body temperature and acute pain.
- Catarrhal gastritis (also called banal) - occurs as a result of neglecting the rules of proper nutrition, with helicobacteriosis, food poisoning or allergies. Damage to the mucous membrane in this case does not cause much concern. Banal gastritis is accompanied by stomach pain, bloating, nausea and vomiting, constipation or diarrhea, weakness, heartburn, headache and dizziness, and poor appetite.
- Corrosive (necrotic) gastritis appears when highly concentrated alkalis or acids enter the gastrointestinal tract. The problem may also be poisoning with heavy metal salts. In this case, the patient experiences severe nausea, accompanied by blood, severe pain in the abdomen and stomach. An unpleasant taste and difficulty breathing appear. Help for corrosive gastritis of the stomach consists of immediate hospitalization of the patient, followed by surgical intervention.
- Phlegmonous (purulent) gastritis develops as a consequence of an ulcer or tumor of the stomach. Another reason may be mechanical damage to the stomach. Phlegmonous gastritis is accompanied by unbearable pain and high fever. This type of gastritis requires immediate medical intervention.
Classification of chronic gastritis of the stomach
The varieties look like this:
- Type A: autoimmune (fundic) form of gastritis. Occurs as a result of an attack by the immune system against the stomach.
- Type B: bacterial (antral) gastritis. Caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
- Type C: reflux gastritis. Occurs as a result of the release of bile into the stomach.
Mixed types
In addition to the main types, there are also mixed (for example, AB) or additional types of chronic gastritis:
- Surface.
- Atrophic.
- Radiation.
- Hypertrophic.
- Eosinophilic.
- Lymphocytic.
- Polypous.
Stress and bad habits
A long-term negative state, for example, increased mental or excessive physical stress, destabilizes the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for the coordinated functioning of many body systems (including the gastrointestinal tract). Severe nervous tension can cause inhibition of blood supply to the mucous protective tissues. This makes the mucosa vulnerable to the aggressive action of the acid contained in the gastric juice.
Nicotine affects stomach functions in a similar way. When nicotine enters the lungs when smoking along with smoke, it spreads throughout the body and causes vascular spasms. This disrupts the motor functions of the stomach and blood supply to the walls. In addition, nicotine enters the smoker’s body with saliva.
Alcohol affects the walls of the stomach like a chemical burn, and also increases the acidity level of the stomach. The higher the concentration of ethanol in the drink, the stronger the body will react to it. Mucous tissues become irritated, protective barriers are broken, and inflammation begins.
To prevent negative consequences for the body caused by stress and bad habits, you need to change your lifestyle.
Why is gastritis dangerous?
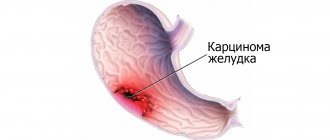
If you do not start treating gastritis in a timely manner, the area of damage to the gastric mucosa will only become larger over time. This can lead to the development of peptic ulcers, which are much more difficult to treat. Very often, a peptic ulcer can lead the patient straight to the surgical table.
A more severe consequence of advanced gastritis is the development of a cancerous tumor. Oncological diseases are life-threatening and almost always end:
- surgical intervention;
- long recovery period.
Gastritis during pregnancy is greatly aggravated and causes great inconvenience to the expectant mother. Due to the disease, toxicosis often occurs, which in chronic gastritis can last up to 17 weeks instead of the required 12.
Why gastritis of the stomach develops, symptoms of the disease and treatment of all its types
Author: Doctor_N · Published 02/19/2019 · Updated 10/21/2019
Gastritis pain
For gastritis of the stomach, the symptoms of the disease are taken into account, and treatment is prescribed in accordance with the diagnosis. Gastritis is a lesion of the gastric mucosa combined with its inflammation, often extending into deeper tissues. The stomach ceases to function effectively, and the patient’s quality of life noticeably decreases. The disease is characterized by temporary exacerbations and the risk of various complications, including cancer. Both adults and children suffer from disorders of the mucous membrane, and the number of patients with this diagnosis tends to constantly increase.
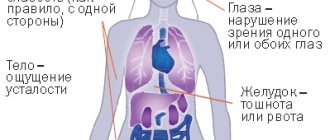
Symptoms and signs of gastritis
The earlier a patient suspects something is wrong and consults a doctor, the greater his chances of successful treatment and recovery. Gastritis can be diagnosed by the following signs:
- discomfort in the stomach;
- pain after eating;
- heartburn;
- poor appetite;
- bloating;
- flatulence;
- nausea and vomiting;
- feeling of heaviness after eating;
- dizziness and headaches;
- general weakness, fatigue;
- yellowish or whitish coating on the tongue;
- frequent belching;
- increased or decreased acidity;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- increased salivation or dry mouth;
- drowsiness, irritability;
- constipation or diarrhea;
- stomach pain on an empty stomach.
Diagnostics
Acute gastritis, due to its main symptoms, can be confused with other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and abdominal cavity, and some infections:
- Stomach ulcer - periodic pain after eating and at night on an empty stomach;
- Acute pancreatitis - severe and persistent abdominal pain, serious condition;
- Acute cholecystitis - intense cramping pain on the right side of the body, high temperature;
- Myocardial infarction - high blood pressure, angina, chest pain;
- Typhoid fever;
- Scarlet fever;
- Meningitis.
Differential diagnosis will allow you to exclude other diseases and clarify the true diagnosis. A complete blood count and alpha-amylase test will be required for a more complete history.
The doctor examines the patient, finds out what medications he took, and analyzes his diet. Nutrition plays a decisive role here, but if the patient’s diet is more or less correct, then it is worth looking for the cause in alcohol abuse, smoking, and uncontrolled use of certain medications. Provoking factors will be infections, mechanical damage and inflammation of the mucous membrane, chemical burns, and toxin poisoning.
In acute gastritis, the skin will be dry and pale. Palpation in the epigastric region is accompanied by painful sensations of moderate tolerance. There is an unpleasant odor from the mouth, and there is a gray coating on the tongue.
Standard tests include blood, urine and feces. The latter can be used to determine occult blood. Sometimes acute gastritis is accompanied by anemia. Blood biochemistry reveals disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys, liver, and pancreas.
Gastroscopy and a Helicobacter breath test will be complemented by an endoscopic biopsy for a detailed examination of gastric tissue. X-ray and MSCT will complement the overall picture of the disease.
Diagnostic methods
Fibrogastroduodenoendoscopy
To determine gastritis, doctors most often use:
- fibrogastroduodenoendoscopy (FGS);
- FGDS;
- gastroscopy.
The doctor uses a probe to assess the condition of the stomach lining. To obtain a more accurate result, the doctor may take a piece of mucous membrane.
Blood analysis
To diagnose Helicobacteriosis, it is necessary to do a blood test, the results of which will show the level of antibodies to the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
Stool analysis
Chronic gastritis may be accompanied by bleeding, so to detect it, the patient is prescribed a stool examination.
Diagnosis of gastritis
A therapeutic diet helps to successfully treat gastritis at home.
Diagnosis of gastritis consists of several stages:
- Analysis of patient complaints, collection of a detailed medical history, visual examination.
- General and biochemical blood test.
- Analysis of urine.
- Stool tests for blood and for the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection.
- Endoscopy with biopsy. The following are determined: the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, the characteristics of inflammation of the gastric mucosa, the presence/absence of precancerous changes. For biopsy, at least five samples of mucous tissue are taken (2 fragments from the antrum, 2 from the body of the organ, 1 from the angle of the stomach).
- Breath test. Determines the presence of Helicobacter pylori.
- Intragastric pH-metry. Determines the level of secretory functions and diagnoses functional disorders.
- Ultrasound. The liver, gall bladder, and pancreas are examined to identify concomitant gastrointestinal diseases.
- Manometry. The upper gastrointestinal tract is examined to determine the presence or absence of reflux gastritis.
- Electrogastroenterography. The motor and evacuation functions of the gastrointestinal tract are examined to determine duodenogastric reflux.
Treatment of the disease
After gastritis has been diagnosed, the doctor must prescribe treatment. When choosing a treatment method, people usually turn to traditional or folk medicine. Effective treatment of gastritis consists in eliminating the factors that provoke its development and appearance. The entire treatment complex includes the following steps:
- Taking medications.
- Stimulation of the restoration processes of the mucous membrane.
- Special diet.
- Preventive measures to prevent relapse.
Treatment should be prescribed by a specialist doctor after a thorough examination of the patient’s condition. The choice of medication depends on the cause of the disease. For example, gastritis caused by pathogenic microorganisms entering the stomach is treated with antibiotics.
The drug Bismuth
Sometimes the doctor may additionally prescribe bismuth preparations, which form a protective shell around the damaged area, preventing further development of the disease.
Photo: disease with increased secretion
Vomiting as one of the recovery options
In case of acute gastritis, it is necessary to induce vomiting. To do this, the patient needs to drink 2-3 glasses of warm water. In severe cases, a special probe is used to lavage the stomach.
Antispasmodics
Antispasmodics help dull pain. Also, for gastritis, it is recommended to take enterosorbents.
Non-traditional treatments
Fans of alternative medicine can try treatment using various herbs. Treatment with folk remedies involves the use of decoctions, which should help the patient feel better. Taking these decoctions will help with gastritis with high acidity.
Traditional treatment
Healers and healers claim that potato juice is a great remedy for such a scourge. It can be obtained using a juicer. If you don’t have a juicer, you can grate the potatoes on a fine grater and then squeeze out the juice.
To begin with, you need to take about 25 grams of juice (half a 50 g glass) 3 times a day half an hour before meals. Gradually the amount of juice increases to 100 grams at a time. You need to continue the course of treatment for 3 weeks. This remedy will help eliminate minor inflammation.
When do you need specialist help?
Every person should closely monitor their health and promptly respond to any disruptions in their work:
- If he notices alarming symptoms that do not go away on their own within a week, he should immediately make an appointment with a gastroenterologist.
- It is recommended to contact specialized specialists even after undergoing drug treatment. In this case, timely diagnosis will help to stop inflammatory processes on the mucous membrane at a very early stage and prevent the progression of the pathology.
- If there is a person in the family or close circle who has gastritis, then everyone who has been in contact with him needs to be examined. If the pathogenic bacterium Helicobacter provoked the development of pathology in a patient, then everyone who had household contact with him could become infected with it.
- Those people who have bad habits should undergo regular examinations. In their case, everything can be much more serious, since nicotine and alcohol often cause the development of ulcerative pathologies.
Diet and nutrition for gastritis
The diet, as well as the treatment, should be prescribed by a doctor, based on the patient’s well-being, his physical condition and the causes of gastritis.
Allowed foods
In acute gastritis, the patient is not given food for the first two days. You are allowed to drink warm tea with lemon or rosehip decoction. On the third day, liquid food is introduced into the menu:
- kefir;
- delicate cream soups;
- light vegetable or chicken broths.
After this you can eat:
- liquid semolina porridge;
- jelly and jelly;
- oatmeal;
- crushed rice porridge;
- boiled eggs.
You need to eat often, but in small portions.
Prohibited foods
Drinking alcohol and smoking are completely excluded. At the end of the diet, the patient must adhere to the principles of rational nutrition and ensure that the diet is varied and provides the body with all the necessary vitamins.
To prevent a recurrent attack of gastritis, avoid the following foods:
- fatty, fried, smoked and spicy foods;
- chocolate;
- flour products, baked goods;
- coffee, carbonated drinks;
- semi-finished products;
- products that cause fermentation.
Therapeutic diet table No. 2
If a patient suffers from chronic gastritis, he is prescribed a long-term medical diet table No. 2, which consists of the following dishes:
- lean boiled chicken and white fish;
- second water broths and soups;
- boiled eggs;
- pasta and porridge (milk possible);
- stewed or boiled vegetables;
- jelly, mousse, jelly;
- baked apples;
- diet cookies or biscuits;
- greenery;
- Rye bread;
- low-fat cheese;
- fresh juices.
During the diet, you should exclude the following foods from your diet:
- fatty, spicy, smoked and fried foods;
- fatty soups and broths;
- instant food products;
- store-bought sauces and marinades;
- coffee;
- strong black tea, sweet soda, alcoholic drinks;
- canned food;
- bakery products.
We also recommend that you read the articles about therapeutic diets:
- table No. 1;
- table number 4.
Is it possible to protect yourself from gastritis?
To protect themselves from such a dangerous disease as gastritis, people should regularly take preventive measures.
It is extremely important to monitor the quality of food
It is necessary to consume only high-quality and healthy products. It should be remembered that coarse, spicy, fatty, smoked, salted and fried foods are one of the main irritants for the gastric mucosa. To avoid overloading it, experts recommend using safe cooking technologies, for example, boiling, baking, steaming. You should also use only those products when creating a menu that are on the approved list.
If people manage to radically change their diet, they are unlikely to experience gastritis for this reason.
Prevention of gastritis
Prevention will help prevent gastritis of the stomach:
- In the morning you need to have a hearty and healthy breakfast. The best option is oatmeal with water, fruits, yogurt, eggs. It is not recommended to drink coffee, strong tea and sour juices on an empty stomach.
- Avoid eating fast food.
- Avoid fatty, spicy and smoked foods, and do not eat overcooked foods with a dark crust.
- Eat small meals 4-6 times a day.
- Try not to use large amounts of spices and hot seasonings when cooking.
- Avoid sweet carbonated water and, if possible, alcohol and cigarettes.
Gastritis is a very unpleasant disease, which is often the result of an unhealthy lifestyle. If a person carefully monitors his diet, personal hygiene and habits, then gastritis and complications after illness will never bother him.
Project consultant, co-author of the article: Ovchinnikova Natalya Ivanovna | Gastroenterologist, Hepatologist, Infectious disease specialist 30 years of experience / Doctor of the highest category, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Education:
Diploma in General Medicine, Novosibirsk State Medical Institute (1988), Residency in Gastroenterology, Russian Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education (1997)
Why does he appear?
When gastritis occurs, a person begins to experience pain in the stomach, which can be associated with the process of eating food.
As the pathology progresses, the patient’s general health worsens and symptoms characteristic of this disease appear:
- nausea;
- belching;
- heartburn;
- disruption of defecation processes;
- bloating;
- feeling of fullness in the stomach, etc.
If these signs appear, people should immediately contact a medical facility for advice. If they manage to receive adequate help in a timely manner, then most likely the disease will very quickly go into remission. In the future, they need to monitor their diet and eliminate all factors that could provoke an exacerbation of the pathology.
Regular coffee consumption
The caffeine present in this invigorating drink can act as an irritant to the gastric mucosa. If a person drinks coffee in small quantities, it will not bring any harm to his body. If the drink is consumed on an empty stomach, or in unlimited quantities throughout the day, then signs of acute gastritis will appear very quickly.
Pathogenic microflora
Modern medicine considers the pathogenic bacterium Helicobacter as the main provoking factor that can cause any form of gastritis. It can enter the human body due to simple lack of personal hygiene. Infection can also occur by eating poorly washed fruits and vegetables, as well as through household contact with a sick person. To prevent Helicobacter infection, people should always wash their hands before eating and after visiting public areas. You should not eat from other people's dishes or drink from other people's cups, and you should always use your own personal hygiene products and towels.
Food intolerance
Probably every person loves milk, so they try to introduce it into their diet in different forms. Unfortunately, some people have individual lactose intolerance, which they may not even be aware of. When drinking milk, they begin to experience heartburn and discomfort after a short period of time, but do not remove it from their diet. Over time, this healthy drink causes gastritis, as it complicates the digestion process and severely irritates the gastric mucosa.
In addition to milk, people may have individual intolerance to sugar, gluten, spicy foods and other foods.
Bad habits
Alcohol-containing drinks, as well as nicotine, have a detrimental effect on all human organs and systems. In people who have these addictions, the gastric mucosa constantly suffers, since it has to come into contact with strong irritants. According to statistics, almost every smoker and people who regularly drink alcohol are diagnosed with gastritis.
Long-term use of medications
When treating any disease, specialists usually prescribe different types of drugs to their patients. If the course of drug therapy includes antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and aspirin, then they will begin to have stomach problems while taking them. The components present in these drugs have a detrimental effect on the mucous membrane. Most often, gastritis appears during drug treatment in people with a very sensitive stomach.
Diseases
In some cases, a pathology such as gastritis develops against the background of autoimmune diseases. In this category of patients, immune cells begin to have a negative effect on the gastric mucosa, thereby provoking the development of inflammatory processes and erosive changes.
People who have diseases such as diabetes are at risk of getting gastritis.
Poor nutrition
Most often, those people who do not monitor their diet and do not follow a diet suffer from gastritis.
They regularly consume the following foods:
- fat;
- spicy;
- smoked;
- fried;
- salty;
- fast food;
- instant food products;
- energy;
- sweet soda;
- products that lack fiber necessary for digestive processes.
Mechanical, chemical and thermal damage
People may develop this pathology for the following reasons:
- previous surgical interventions;
- eating too hot foods and drinks;
- chemical or food poisoning;
- stomach injury;
- strong physical activity, etc.
Reflux (bile)
In some people, bile leaks directly into the stomach. Modern medicine classifies this pathological process as reflux (bile). It is considered as one of the reasons for the development of gastritis.
Prevention
To protect yourself from gastritis, it is important to build the right diet for yourself. Diet and the quality of food eaten play an important role in preventing the disease. Reduce the amount of alcohol and tobacco consumed.
Stress is one of the causes of gastritis - eat slowly, in a good environment and with positive thoughts. Do not use harmful chemicals.
Video on the topic: Gastritis: causes, symptoms and treatment
Clinical picture of chronic gastritis
Chronic inflammation of the mucous membranes covering the walls of the stomach can be caused by a huge number of reasons. Previous infectious diseases, helminthic infestations, and endocrine diseases increase the risk of developing pathology several times. Stomach tissue can be destroyed in some autoimmune disorders. Various poisonings, neurological pathologies, unhealthy diet, stress - all these factors negatively affect the condition of the mucous membranes and can cause inflammation, which, if left untreated, can become chronic.
Chronic gastritis from the inside
The symptoms of chronic gastritis in adults are rather mild and appear mainly during the period of exacerbation. Pain in this form of the disease is of moderate intensity and occurs mainly under the influence of the following factors:
- binge eating;
- consumption of carbonated drinks, fast food, sausages and other harmful products;
- long period of fasting (more than 6 hours).
After eating even a small amount of fatty food, the patient feels heaviness in the stomach and bloating. He may belch with a metallic taste, and heartburn may worsen. There is a constant unpleasant odor from the mouth, despite the absence of carious teeth and other oral diseases, as well as careful hygiene. Even the use of mouth rinses and mouth fresheners solves the problem for no more than 2-3 hours.
Localization of various forms of gastritis
Other clinical symptoms of the disease include:
- increased activity of the salivary glands and the formation of large amounts of saliva;
- periodic stool disorders not related to food intake;
- decreased appetite;
- change in taste preferences.
If chronic gastritis is not treated on time, it can develop into more serious pathologies, such as peptic ulcers. To prevent the disease, it is necessary to eat properly, ensure sufficient oxygen supply and monitor the supply of essential nutrients and beneficial elements.
How does alcohol affect the lining of the stomach?