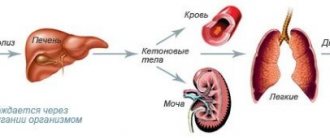
Diabetic nephropathy is a process of pathological changes in the renal vessels, which is caused by diabetes mellitus. This disease leads to the development of chronic renal failure and there is a high risk of death. The diagnosis is made through not only a physical examination of the patient, but also requires laboratory and instrumental examination methods.
Online consultation on the disease “Diabetic nephropathy”. Ask a question to the specialists for free: Endocrinologist.
- Etiology
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention
In most cases, diabetic nephropathy is treated through medication and diet. In more complex cases, patients are prescribed hemodialysis, and a kidney transplant may also be required.
According to the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, diabetic nephropathy has two meanings. Thus, the ICD-10 code would be E10-14.2 (diabetes mellitus with kidney damage) and N08.3 (glomerular lesions in diabetes mellitus).
It is noted that the development of such a complication is most often diagnosed in the insulin-dependent type of diabetes mellitus. In 40-50%, diabetic nephropathy is fatal.
What is diabetic nephropathy
One of the dangerous complications of diabetes is nephropathy, which is a violation or complete loss of kidney function. The pathogenesis of the disease is determined by several factors:
- Hyperglycemia - disruption of the structure and function of proteins in the kidney membranes, activation of free radicals that have a cytotoxic effect.
- Hyperlipidemia - similar to atherosclerosis, plaque formation occurs in the renal vessels, which can lead to blockage.
- Intraglomerular hypertension - manifested by hyperfiltration, then the cleansing function of the kidneys decreases, and the proportion of connective tissue increases.
Nephropathy of diabetic origin in the patient's medical history is designated as chronic kidney disease with an indication of the stage. According to ICD-10, the disease has the following codes:
- with an insulin-dependent form of diabetes complicated by kidney diseases - E 10.2;
- for renal failure and insulin dependence – E 11.2;
- if in diabetes there is insufficient nutrition, affected kidneys - E 12.2;
- for nephropathic disorders against the background of a specified form of the disease - E 13.2;
- for an unspecified form of diabetes with kidney damage – E 14.2.
Epidemiology
According to the International Diabetes Federation, the total number of people with diabetes is 387,000,000 people. 40% of them subsequently develop kidney disease, which leads to kidney failure.
The occurrence of diabetic nephropathy is caused by many factors and varies numerically even within European countries. The incidence among German patients admitted for renal replacement therapy exceeds data from the USA and Russia. In Heidelberg (south-west Germany), 59% of patients undergoing blood purification procedures due to renal failure in 1995 had diabetes, 90% of the cases being type 2.
A Dutch study found that the prevalence of diabetic nephropathy is underestimated. During autopsy sampling of kidney tissue, the team was able to detect histopathological changes associated with diabetic kidney disease in 106 of 168 patients. However, 20 of 106 patients did not experience clinical manifestations of the disease during their lifetime.
Symptoms
Clinical manifestations of the disease depend on the stage of the disease. At the initial stage, nonspecific symptoms occur:
- decreased performance, increased fatigue;
- the occurrence of general weakness;
- poor tolerance to physical activity;
- occasional dizziness, headaches;
- the appearance of a feeling of a stale head.
As Kimmelstiel Wilson syndrome progresses, its manifestations expand. The following clinical signs of the disease are observed:
- the appearance of facial swelling in the morning;
- increased frequency and pain of urination;
- dull pain in the lumbar region;
- constant thirst;
- increased blood pressure;
- cramps in the calf muscles, pain, pathological fractures;
- nausea and loss of appetite.
Features of the disease during pregnancy
The first stages of diabetic nephropathy occur unnoticed, so regular visits to the doctor are the main thing that helps to detect the disease in time. The condition of a pregnant woman can worsen significantly as the pathology moves to later stages of development. This is manifested by the following symptoms:
- severe shortness of breath when standing for a long time;
- swelling around the eyes, legs and arms;
- loss of appetite;
- general weakness;
- poor sleep quality;
- vomiting and nausea, which indicates intoxication.
If these symptoms appear, you should seek medical help. This should be done even in cases where the signs are mild: pregnancy is a big burden for the body, so timely detection and treatment of nephropathy will avoid a decrease in the performance of already loaded kidneys.
During pregnancy, the kidneys are exposed to enormous stress, so early diagnosis and treatment of nephropathy are extremely important for the health of the expectant mother and her child.
Causes
High plasma glucose levels are the main cause of diabetic nephropathy. Deposits of the substance on the vascular wall cause some pathological changes:
- Local edema and structural changes in blood vessels that occur during the formation of glucose metabolic products in the kidney, which accumulate in the inner layers of blood vessels.
- Glomerular hypertension is a constantly progressive increase in pressure in the nephrons.
- Disorders of the functions of podocytes, which provide filtration processes in the renal corpuscles.
- Activation of the renin-angiotensin system, which is designed to prevent an increase in blood pressure.
- Diabetic neuropathy - affected vessels of the peripheral nervous system are transformed into scar tissue, causing kidney dysfunction.
It is important for patients with diabetes to constantly monitor their health. There are several risk factors that lead to the formation of nephropathy:
- poor glycemic control;
- smoking (maximum risk occurs when consuming more than 30 cigarettes/day);
- early development of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus;
- stable increase in blood pressure indicators;
- the presence of aggravating factors in the family history;
- hypercholesterolemia;
- anemia.
Diabetes and blood pressure surges will be a thing of the past
Diabetes is the cause of almost 80% of all strokes and amputations. 7 out of 10 people die due to blockages in the arteries of the heart or brain. In almost all cases, the reason for such a terrible end is the same - high blood sugar.
You can and should beat sugar, there is no other way. But this in no way cures the disease itself, but only helps fight the consequence, not the cause of the disease.
The only medicine that is officially recommended for the treatment of diabetes and is also used by endocrinologists in their work is.
The effectiveness of the drug, calculated according to the standard method (the number of recovered patients to the total number of patients in a group of 100 people undergoing treatment) was:
- Normalization of sugar – 95%
- Elimination of vein thrombosis – 70%
- Eliminate palpitations – 90%
- Relief from high blood pressure - 92%
- Increased vigor during the day, improved sleep at night - 97%
Manufacturers are not a commercial organization and are financed with government support. Therefore, now every resident has the opportunity.
In addition to the increase in pressure and destruction of blood vessels due to hyperglycemia, sugar also affects metabolic processes, causing a number of biochemical disorders. Proteins, including those inside the kidney membranes, are glycosylated (react with glucose, sugared), the activity of enzymes increases, which increase the permeability of the vascular walls, and the formation of free radicals increases. These processes accelerate the development of diabetic nephropathy.
In addition to the main cause of nephropathy - excessive amounts of glucose in the blood, scientists identify other factors that influence the likelihood and speed of development of the disease:
- Genetic predisposition. It is believed that diabetic nephropathy occurs only in individuals with genetic background. In some patients, there are no changes in the kidneys even with a long-term absence of compensation for diabetes mellitus;
- High blood pressure;
- Infectious diseases of the urinary tract;
- Obesity;
- Male gender;
- Smoking.
Classification by stages
Without treatment, nephropathy constantly progresses. Diabetic glomerulosclerosis has the following stages:
- Hyperfunction of the kidneys. The disorder occurs when diabetes is first diagnosed. This stage is characterized by an increase in the size of the organ cells, increased urine output, and increased filtration. The protein is not detected in the tests, and there are no external manifestations of the disease.
- Initial structural changes. At this stage, symptoms of nephropathy do not appear. Thickening of the walls of the renal vessels gradually develops. Kimmelstiel Wilson syndrome at this stage occurs approximately 2 years after the diagnosis of diabetes in the patient.
- Incipient diabetic nephropathy. It is characterized by significant damage to the blood vessels of the kidneys. Glomerulosclerosis can be determined by routine urine testing. Protein inclusions appear in the liquid (30-300 mg/day). The stage occurs after 5 years of diabetes progression. In addition, a characteristic indicator of nephropathy is an increase in glomerular filtration rate. The third stage of the disease is the last stage at which the disease is considered reversible.
- Severe nephropathy in diabetes mellitus. At this stage, clinical signs of pathology clearly appear. Proteinuria (release of large amounts of protein) is detected. The protein content in the blood decreases sharply. The patient develops swelling on the face and lower extremities. With further progression of nephropathy, the phenomenon becomes widespread. Fluid accumulates in the abdominal and chest cavities and pericardium. If severe kidney damage is detected and diuretics do not provide the desired effect, a puncture is prescribed. As the body begins to break down its own proteins, patients rapidly lose weight. Patients complain of nausea, thirst, general weakness, increased blood pressure, pain in the heart and head.
- Uremic. The final stage of diabetic nephropathy is end-stage renal failure. The organ completely ceases to function due to total vascular sclerosis. Symptoms characteristic of stage 4 progress, threatening the patient’s life. The Dan-Zabroda phenomenon is noted, manifested in an imaginary improvement in the condition. It is possible to get rid of the dangerous late complications of diabetes mellitus only with the help of peritoneal dialysis, hemodialysis and kidney transplantation.
Diet features
It is important that the products have a low GI and are properly cooked. It is forbidden to add too much salt to food; it is better to reduce salt consumption to a minimum. Avoid starvation and overeating. These two factors provoke spikes in blood sugar. Meals should be in small portions, five to six times a day.
If the feeling of hunger is great, then you are allowed to have a light snack, for example, a small portion of vegetable salad or a glass of fermented milk product. Sample menu for the day:
- first breakfast - fruit salad;
- second breakfast - an omelet of proteins and vegetables, green tea with a slice of rye bread;
- lunch - vegetable soup, barley with fish cutlet, green coffee with cream;
- afternoon snack - vegetable salad, tea;
- first dinner - sweet peppers stuffed with minced chicken with brown rice, tea;
- second dinner - half a glass of yogurt.
Diagnostics
For successful treatment of the disease, it is necessary to identify it in time. As part of the early diagnosis of diabetic glomerulosclerosis, general and biochemical tests of urine and blood, Zimnitsky and Reberg tests, and ultrasound examination of the renal vessels are performed. The presence of the disease is manifested by microalbuminuria and glomerular filtration rate.
When a patient with diabetes undergoes annual screening, the ratio of albumin and creatinine in morning urine is examined. If an elevated protein level is detected, doctors diagnose the disease in the stage of microalbuminuria. The further development of diabetic nephropathy is determined by the control of proteinuria. To do this, specialists conduct multiple urine tests. In case of a positive result, the stage of proteinuria is stated.
Nephropathy in diabetes mellitus is diagnosed in the presence of protein in the urine, arterial hypertension, damage to the ocular vessels leading to visual impairment, and a persistent decrease in the glomerular filtration rate. The disease must be differentiated from other kidney diseases: tuberculosis, glomerulonephritis, chronic pyelonephritis, diabetic retinopathy. To do this, urine is examined for microflora, organ ultrasound, and excretory urography. In some cases, a kidney biopsy is indicated.
Diet for complications of diabetes on the kidneys
In many cases of diabetic kidney problems, limiting salt intake can help lower blood pressure, reduce swelling, and slow the progression of diabetic nephropathy. If your blood pressure is normal, then eat no more than 5-6 grams of salt per day. If you already have hypertension, then limit your salt intake to 2-3 grams per day.
Now the most important thing. Official medicine recommends a “balanced” diet for diabetes, and even lower protein intake for diabetic nephropathy. We suggest that you consider using a low-carbohydrate diet to effectively lower your blood sugar to normal. This can be done when the glomerular filtration rate is above 40-60 ml/min/1.73 m2. The article “Diet for Kidneys in Diabetes” describes this important topic in detail.
Treatment of diabetic nephropathy
Therapy of the disease is based on the use of medications, special nutrition and auxiliary folk remedies. In the later stages of the disease, the use of hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis is required to replace kidney function. In extreme cases of organ damage, transplantation is required. All treatment measures must be prescribed by a doctor after examining the patient.
Drugs
Taking medications is an essential part of the complex treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Specialists can prescribe the following groups of medications:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors.
Enalapril. The drug has a vasodilating effect and improves renal blood flow. Indications for taking the drug include the prevention of ischemia and the treatment of arterial hypertension. Enalapril can be used in the early stages of diabetic nephropathy, since the medicine is contraindicated in renal failure.
- Angiotensin receptor antagonists.
Losartan is a drug that has a hypotensive effect. Among its indications is kidney protection in type 2 diabetes. The effect of the drug for nephropathy is to reduce the rate of progression of chronic renal failure. The medicine has a large list of adverse reactions, so consultation with a specialist is necessary before use.
- Diuretics (thiazide, loop).
Indapamide is a thiazide diuretic that helps remove excess fluid from the body and fight swelling in diabetic nephropathy. The medication has many contraindications, so it must be taken as prescribed by a doctor.
- Slow calcium channel blockers.
Verapamil is a medication that has antianginal, antiarrhythmic and antihypertensive effects. Used for nephropathy to lower blood pressure. The drug is excreted by the kidneys and has no contraindications associated with this organ.
- Alpha-, beta-blockers.
Concor is a drug whose active ingredient is bisoprolol. The medicine belongs to beta-blockers. It should be prescribed with caution to patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. The medication has no contraindications regarding kidney function.
Diet
Compliance with a diet is an integral part of the complex treatment of Kimmelstiel-Wilson syndrome. The list of foods that can or cannot be consumed is determined by the doctor and depends on the stage of progression of the kidney disease. Experts identify several general principles of nutrition for nephropathy of diabetic origin:
- It is necessary to reduce your daily protein intake to reduce the concentration of toxins in the body. The patient is supposed to switch to dietary varieties of fish and meat. Then you should only consume proteins of plant origin.
- For nephropathy of diabetic origin, it is often recommended to limit salt intake. To make it easier to cope with dietary changes, you should include onions, garlic, celery stalks, lemon and tomato juice in your diet.
- The possibility of eating foods rich in potassium is determined by the doctor, based on test results.
- If a patient with nephropathy is bothered by severe swelling, he is advised to limit his drinking regimen.
- Steaming or boiling should be used for cooking.
Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis
The dialysis procedure is the purification of blood using a special device or through the peritoneum. This method does not help treat the kidneys; its use is aimed at replacing the functions of the organ. A dialyzer is used for hemodialysis. Blood entering this device is cleansed of excess fluid and toxins. The process helps maintain normal blood pressure levels, electrolyte and alkaline balance. The procedure for nephropathy is carried out 3 times a week, its duration is 4-5 hours.
Peritoneal dialysis involves purifying blood through the abdominal cavity. This procedure can be carried out in a medical setting or at home. For peritoneal dialysis, the following indications are established for which hemodialysis is impossible:
- bleeding disorders;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- inability to access blood vessels.
If for some reason a doctor refuses to provide a patient with such renal therapy for nephropathy, he must justify his decision. Some contraindications may serve as factors for a negative answer:
- oncological diseases;
- mental disorders;
- liver failure, cirrhosis;
- leukemia;
- a combination of cardiovascular pathologies and previous myocardial infarction.
Normalization of blood pressure indicators
When pathological changes occur in the kidneys, it is very important to normalize blood pressure readings and eliminate even their minimal excess.
At an early stage of development of the disease, pressure should not exceed 130/85 mm Hg. Art. and be not lower than 120/70 mmHg. Art.
Blood pressure that is most consistent with the norm allows you to slow down the development of pathological processes in the kidneys.
When choosing medications, it is necessary to take into account their effect on the affected organ. As a rule, specialists resort to the following groups of drugs:
- ACE inhibitors (lisinopril, enalapril). Medicines are used at all stages of pathology. It is advisable that the duration of their exposure does not exceed 10–12 hours. When treating with ACE inhibitors, it is necessary to reduce the consumption of table salt to 5 g per day and potassium-containing products.
- Angiotensin receptor blockers (Irbesartan, Losartan, Eprosartan, Olmesartan). The drugs help reduce both total arterial and intraglomerular pressure in the kidneys.
- Saluretics (Furosemide, Indapamide).
- Calcium channel blockers (Verapamil, etc.). The drugs inhibit the penetration of calcium into the body's cells. This effect helps to dilate coronary vessels, improve blood flow in the heart muscle and, as a result, eliminate arterial hypertension.
Prognosis and prevention
Only the first 3 stages of diabetic nephropathy have a favorable prognosis with timely treatment. With the development of proteinuria, it is only possible to prevent further progression of chronic renal failure. The terminal stage of the disease serves as an indication for replacement therapy or organ transplantation. To avoid nephropathy, patients with diabetes need to follow these recommendations:
- Constantly monitor blood glucose levels;
- prevent the development of atherosclerosis;
- follow the diet prescribed by the doctor;
- take measures to normalize blood pressure.
Normalization of sugar levels
Normalization of glucose levels in the body comes to the fore in the treatment of nephropathy, because It is the high sugar level that is the main cause of the development of the disease.
Clinical studies have established: if for a long period the glycohemoglobin level does not exceed 6.9%, it is possible to prevent the development of nephropathy.
Experts allow glycated hemoglobin levels exceeding 7% with a high risk of hypoglycemic conditions, as well as in patients with severe heart pathologies.
To correct insulin therapy, it is necessary to: review the drugs used, their administration regimen and dosage.
As a rule, the following scheme is used: long-acting insulin is administered 1-2 times a day, a short-acting drug is administered before each meal.
The choice of glucose-lowering drugs for kidney disease is limited. The use of drugs that are excreted through the kidneys, as well as those that have undesirable effects on the organ, is undesirable.
In case of kidney pathology, the use of:
- biguanides, which can cause lactic acidosis coma;
- thiazolindiones, which promote fluid retention in the body;
- glibenclamide due to the risk of a critical decrease in blood glucose.
For type 2 diabetics, it is recommended to use the safest oral medications that have a low percentage of excretion through the kidneys:
If it is not possible to achieve satisfactory compensation with tablets in type 2 diabetics, specialists resort to combination treatment using long-acting insulin. In extreme cases, the patient is completely transferred to insulin therapy.