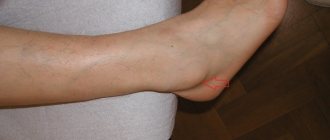
Diabetic foot syndrome characterized by a complex of symptoms (pain, swelling of the feet, decreased sensitivity, purulent-necrotic lesions) and is a complication of diabetes mellitus, which develops due to pathological changes in the arteries, nerves, bones and muscles of the foot caused by the underlying disease. As a result, purulent-necrotic processes and gangrene of the foot develop, which is an indication for amputation. This algorithm of events is partly a consequence of untimely and incorrect treatment, non-compliance with foot care rules, but most often it is determined by the severity, aggressiveness and duration of the underlying disease - diabetes mellitus.
Content:
- Classification of diabetic foot syndrome
- Wagner grades of diabetic foot
- Diabetic foot forms
- Neuropathic form
- Ischemic form
- Neuroischemic form
- Recommendations for patients with diabetes mellitus
Diabetic foot syndrome (abbr. DFS) is a complex of pathological processes in the nervous and circulatory systems, which, under the influence of diabetes mellitus, manifest themselves in the form of deformations, ulcers and destruction in the tissues of the lower extremities.
This definition was given by WHO in 1999, when DBS was not an independent disease, but was classified as a complication of diabetes mellitus. WHO studies have shown that up to 86% of patients with diabetes are at risk of developing diabetes mellitus within 5 years. Of these, 5-25% seek help from specialists when the disease has reached a dangerous stage.
Up to 60% of all limb amputations are carried out due to gangrenous infection due to diabetic foot. That is why treatment and prevention of diabetic foot syndrome should be carried out in the early stages.
Preventing feet in diabetes: what else do you need to know?
In addition to the measures described in the Memo, diabetic foot and diabetes mellitus should be reasons to strengthen the immune system.
The patient is recommended to take vitamins that stimulate the production of immunity. It is also important to try to avoid stress and prevent cardiovascular diseases.
By following these measures, the risk of developing diabetes is reduced to zero, helping you live your whole life with diabetes without serious complications.
Our online store contains the most effective and modern foot products for diabetes. We deliver throughout Russia by courier to your home, to pick-up points and by mail. Click on the image below to find out more.
Diabetic foot syndrome: classification
All over the world, when diagnosing and treating SDS, doctors use the following classification:
1. Types of diabetic foot according to the form of the disease and pathogenesis:
- neuropathic;
- neuroischemic;
- ischemic.
2. Stages of diabetic foot syndrome: from 0 to 5;
3. According to the presence of complications:
- chronic limb ischemia;
- ulcerative localizations;
- deformations of articular and osseous tissue;
- pathological fractures, etc.
Each type of disease provides its own methods of conservative, medicinal and surgical treatment. Also, for each type, doctors give their own prognosis for the development of the disease.
Treatment of diabetic ulcers
The main method of local treatment of diabetic ulcers is considered to be conditions of moist healing, thermal insulation, absence of excessive accumulation of exudate, lightweight mechanical treatments, careful use of antiseptics with a possible toxic effect. Wounds are cleaned surgically using enzyme preparations (proteolytic enzymes: papain, ribonuclease, hyaluronidase, nucleotidase and nucleosidase, ultralysine, chymopsin, trypsin, collagenase, terrilitin, etc.).
Topical medications are used - ointments on a polyethylene oxide basis, iodophor, Actovegin-gel, Acerbin spray, etc. When mycoses of the feet appear, antifungal drugs are used, for onychomycosis - Lotseril varnish, etc. In severe forms, wound coverings are widely used. There are several classes of wound dressings: semipermeable films, sponges, hydrogels, hydrocolloids, alginates, drug-loaded coatings, and biological coatings.
An analysis of scientific works in this area indicates that numerous studies have been conducted on the treatment of diabetic feet aimed at finding methods (surgical and therapeutic) and means (wound coverings, antimicrobial and reparative drugs). To eliminate and prevent the development of the infectious process and the speedy healing of already formed ulcerative defects, which is important to avoid sepsis and the need for amputation.
Wagner grades of diabetic foot
The Wagner classification is used to assess the degree of foot damage. This scale has been used in medicine since 1979.
Three main factors serve as evaluation criteria:
- the depth of damage to the epidermis and muscle tissue;
- degree of infection development;
- presence and severity of gangrene.
Diabetic foot (classification according to Wagner is mandatory to standardize the treatment plan) can have 6 stages:
Stage zero (risk stage or pre-diabetic foot). There are no signs of damage, the foot visually looks healthy. However, the patient belongs to the risk group and is diagnosed with diabetes mellitus. In this case, correct preventive measures aimed at preventing the development of the disease are of great importance.
In many ways, the prevention of diabetic foot consists of strict adherence to doctor’s recommendations and personal hygiene, leading an active lifestyle, as well as wearing comfortable and high-quality orthopedic shoes and insoles.
First stage. Superficial localized ulcers are present on the skin. There are no signs of infection. At this stage, it is important to begin treatment as early as possible to prevent the disease from spreading to soft tissues and tendons.
Treatment consists of antiseptic treatment of ulcers and normalization of blood sugar.
Second stage. The ulcers are deeper, muscle tissue and tendons are affected. There is no inflammatory process. It is at this stage that patients most often consult a doctor.
Treatment is prescribed depending on the location and type of ulcers. The most commonly prescribed topical ointments contain antibiotics. Doctors also pay great attention to the treatment of neuropathy and cardiovascular diseases that cause DFS.
Third stage. Ulcers affect the deep layers of the skin, muscles, and tendons. The patient experiences discomfort when moving, and therefore sharply limits his mobility. Multiple or single phlegmons, abscesses, and ulcers appear.
At this stage, it is no longer possible to do without serious antibiotic therapy. Surgical excision of the affected tissue is often required.
Fourth stage. The infection affects the bones, and gangrene spreads to the toes or the front of the foot. If treatment is not started promptly, gangrene will spread to healthy tissue.
The patient needs treatment with antibiotics and physiotherapy to help restore normal blood supply to the extremities.
Fifth stage. Gangrene of the entire foot. To save the patient's life, a limb is amputated.
Wagner's diabetic foot does not take into account the origin of ulcers and the form of their infection. Meanwhile, the infection can be very different. The most common infections are fungus, E. coli, salmonella, streptococci, gonococci, etc.
Surgical methods of treatment
Surgical methods are used through cutaneous transluminal angioplasty (an operation in which blood flow in the vessels is restored through a puncture in the artery), thrombarterectomy or distal vein bypass. If the soft tissues of the limb are damaged, the ulcers are treated with local antiseptics (chlorhexidine, miramistin solutions) or saline solution.
When treating the neuropathic form of diabetes mellitus, it is important to pay attention to complete unloading of the foot (immobilization or unloading of the affected limb with the possible use of orthopedic devices), careful local treatment with removal of areas of hyperkeratosis and step-by-step necrectomy (in the presence of necrotic areas).
When treating diabetic nephropathy (DN), it is necessary to restore normal innervation. One of the modern methods of treating DN is the use of drugs that have an antioxidant effect, reducing the level of neurotoxic products (free radicals). Alpha-lipoic acid preparations, Mexidol, vitamins A, E, C, and B vitamins are widely used as antioxidants.
Treatment of mixed forms
For mixed forms of the syndrome, tolperisone is also prescribed, a centrally acting muscle relaxant that enhances peripheral blood circulation. B vitamins, antidepressants, antipsychotics, aldoreductase inhibitors, g-linoleic acid. Treatment of coagulation disorders and vasodilatory effects (angioprotectors, disaggregants and rheological drugs) are carried out with the help of acetylsalicylic acid, pentoxifylline, dipyridamole, clopidogrel, ticlopidine, heparin, antispasmodics (papaverine, drotaverine, etc.).
Often, for serious forms, long-term systemic antibacterial therapy is used. A very important factor in the treatment of diabetic feet is smoking cessation, since tobacco has a negative effect on the microvascular bed. If the patient ignores the recommendations and quits smoking, the effectiveness of treatment decreases or gives only a short-term effect.
Forms of diabetic foot syndrome
Neuropathic diabetic foot occurs in 66% of patients with DFS, and the ischemic form occurs in 10%. The rest suffer from a mixed - neuroischemic form, which combines symptoms of neuropathy and vascular diseases. Let's look at the forms of diabetic foot, their signs and treatment methods in more detail.
Neuropathic form of diabetic foot
This form of DFS is one of the symptoms of neuropathy that occurs against the background of diabetes mellitus. The main cause of neuropathy is a disorder of the autonomic nervous system of the lower extremities. Damage to the nerves leads to neurotrophic ulcers, which often become infected and inflamed.
The first signs of neuropathic foot include:
- reduction or complete disappearance of sensation in the feet;
- familiar shoes become uncomfortable, calluses, chafing, and corns appear;
- legs swell regardless of the amount of fluid you drink;
- the skin of the legs becomes very dry and peels;
- ingrown nails appear;
- paresthesia of various types (feeling of numbness, “crawling insects”, trembling, tingling, restless leg syndrome, etc.).
If these signs appear, you should immediately consult a doctor to diagnose the initial stage of DFS and prevent its further development. As preventive measures, doctors prescribe a diet that normalizes metabolic processes and sugar levels, as well as physical procedures to improve blood circulation.
Maintaining good hygiene and regularly wearing comfortable shoes is of great importance. Be sure to use insoles to relieve the load on your feet.
If the disease is not treated, ulcers will appear on the skin and the bones of the foot will become deformed. In this case, treatment will depend on the stage and nature of the lesions.
As a rule, treatment for diabetic foot neuropathic form is complex and includes:
- local antibacterial ointments;
- taking antibiotics in the presence of an infection that has affected the deep layers of the epidermis;
- effective pain relief;
- physiotherapy and hirudotherapy;
- physiotherapy;
- podiatric care;
- wearing special shoes and unloading insoles.
- taking medications for neuropathy.
Neuropathic diabetic foot, the stages of which occur in patients of any age, can be successfully treated if doctors' recommendations are followed.
Personal hygiene is mandatory, the purpose of which is to prevent the development of secondary infection. To do this, you need to examine your feet daily for signs of disease. You need to wash your feet 1-2 times a day. To eliminate dryness, use a suitable nourishing cream.
Ischemic form of diabetic foot
The ischemic form develops in the presence of diseases of the heart muscle and blood vessels. The vessels of the extremities do not function properly, resulting in the following symptoms:
- constantly cold feet;
- cyanosis of fingers;
- severe pain;
- swollen blood vessels, etc.
If the underlying cardiovascular disease is not treated, ulcers and phlegmon will appear on the legs, so treatment is aimed at normalizing blood circulation in the lower extremities, as well as eliminating skin manifestations.
This form of DFS occurs quite rarely without neuropathy. Much more often, patients with diabetes mellitus have a mixed form of diabetes mellitus.
Neuroischemic form of diabetic foot
The medically accepted classification of diabetic foot considers the neuroischemic form as a combination of neuropathic and ischemic forms. Indeed, this type of SDS exhibits characteristics of both forms. This is due to the fact that patients with diabetes in 75% of cases have diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Diabetic foot syndrome (Wagner described the stages of the disease on the basis of the neuroischemic form) is characterized by an aggressive, rapid course. Ulcers formed on the skin of the feet quickly spread to neighboring tissues and penetrate into the deep layers of the epidermis, affecting the joints and bones. Very often a fungal or bacterial infection occurs, and problems with blood circulation lead to necrosis (death) of tissue.
It is also worth knowing that diabetic neuroischemic foot is almost always accompanied by edema, as a result of which deformities of the feet occur, gait changes and the patient begins to lead an inactive lifestyle, which negatively affects the course of the disease.
The neuroischemic form of diabetic foot syndrome is treated depending on the stage of the disease:
- At stages 0-1, local antiseptic ointments are used. Proper foot unloading is of utmost importance. For this, podiatrists recommend using special insoles for diabetes. Regularly wearing insoles helps reduce pressure on the feet and distribute the load evenly. The use of insoles also prevents the appearance of chafing and calluses, which is an effective prevention of ulcers.
- At stages 2-3, antibiotic treatment is carried out. Physiotherapy is used to restore normal circulation.
- Stages 4-5 of diabetic foot usually require surgical removal of the affected tissue. The recovery process after surgery is quite long and painful. When restoring motor function, it is important to prevent deformation of the legs. For this purpose, all products for diabetic feet are used, helping to form the correct position and reduce the load on the legs.
The main reasons for the development of the disease
Why are the legs at greater risk of injury in diabetes? The fact is that patients have pronounced problems with the blood vessels of the legs. Elevated sugar disrupts blood circulation in them. As a result, the skin on the lower extremities suffers from a lack of nutrients, which makes it especially sensitive to all kinds of damage.
In addition, the skin of the legs of diabetic patients does not tolerate the winter period well due to possible hypothermia, which can simply not be noticed due to a lower sensitivity threshold. For a healthy person, the same conditions pass without any problems.
The risk of damage to the lower extremities exists if a person has had diabetes for a long time and has advanced the disease without taking the necessary measures for treatment. In such a situation, even a small wound can cause serious problems, which, without healing, will begin to fester and gradually develop into gangrene.
There is such a thing as sensory neuropathy - a phenomenon when the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the feet decreases.
Due to reduced sensitivity, most diabetics may not notice leg discomfort, temperature changes, cuts or injuries. Because of this, the patient wastes time, noticing the problem when the leg tissue has already begun to rot, and surgery is inevitable.
Therefore, people with high blood sugar are recommended to examine their feet daily: feet, skin between the toes, skin under the nails.
One of the characteristic signs of diabetic neuropathy is constant dry skin, which appears to be devoid of sweating function. Against the background of dry skin, cracks begin to appear, which, when infected, easily develop into ulcers.
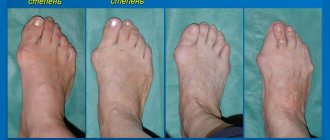
In the presence of the disease, not only the outer cover suffers, but also the internal tissues and bones. The functioning of the muscles in the feet is blocked, which leads to disturbances in the formation of muscles, and they, in turn, deform the bones of the foot. Outwardly, this can be noticed when the feet or fingers are unnaturally arched, as well as if a person’s toes have a pointed, rounded shape like a cat’s claw.
If, due to diabetes, the patient’s vision has noticeably deteriorated, then the risk of injury to the lower extremities increases, because the person does not see what he is stepping on, and sensitivity, as we have already said, is dulled.
Kidney problems are also a prerequisite for the development of diabetic foot, as the limbs swell and the feet naturally increase in size. Habitual shoes begin to crowd the foot and compress it when walking. Dry skin cracks due to constant pressure and gradually becomes covered with non-healing ulcers.
Recommendations for patients with diabetes mellitus
As you can see, SDS is a dangerous disease that is better prevented than treated. If you have been diagnosed with diabetes, you need to closely monitor for diabetic foot symptoms. If signs of SDS are detected, you should immediately contact a specialist.
It is also recommended for patients with diabetes to:
- monitor blood sugar levels;
- take medications prescribed by a doctor;
- cut your nails correctly, preventing them from becoming ingrown;
- inspect your feet daily for signs of DFS;
- lead a healthy and moderately active lifestyle;
- observe the rules of hygiene;
- wear insoles to relieve pressure on the feet.
Compliance with these recommendations, as well as constant monitoring by a podiatrist or endocrinologist, helps to identify DFS at the initial stage and prevent complications from occurring.
Features of foot care
It is much easier to prevent the disease than to carry out long-term and labor-intensive treatment of diabetic foot. The main thing in matters of prevention is special foot care, the rules of which should be known to everyone suffering from diabetes.
Foot care rules:
- Go to the hospital if you notice even minor damage to the skin of the foot.
- Wash your feet daily. When washing, do not forget about the spaces between the toes; dry your feet with a terry towel carefully, without tearing the skin.
- Inspect your feet daily for blisters, scrapes, cracks, cuts, and other damage. The easiest way to inspect soles is with a mirror.
- Monitor your foot temperature. Do not expose your feet to cold or extremely high temperatures. Avoid hypothermia, do not take too hot baths, do not steam your feet.
- Change stockings and socks every day, make sure that they are comfortable, do not rub when worn, and are not too tight.
- Avoid injuring your feet with drugs or softening chemicals. Removing calluses and growths using a razor or other cutting tools is strictly prohibited. To remove dead skin, it is better to use cosmetic files or pumice.
- Trim your nails carefully: file the corners of the nails, not cut them off, and do not allow the nail plate to grow into the skin.
- For dry skin, use special foot creams containing natural ingredients.
Patients with diabetes should pay special attention to the choice of shoes - they should be as comfortable as possible, fit well and freely on the foot. You should not buy overly tight shoes; it is recommended to wear street shoes on your toes and not on your bare feet, and avoid walking barefoot. If the foot is significantly deformed due to diabetes, it is recommended to choose special orthopedic shoes.
To eliminate the risk of possible complications from diabetes, you need to monitor the health of your blood vessels. This requires constant monitoring of blood pressure and cholesterol levels in the blood.