Mycelix - for diabetes. Hurry up to get it for free! More details
Maintaining normal blood glucose levels in diabetes mellitus is considered the main goal of treatment. Reducing and stabilizing blood glucose levels is achieved through an integrated approach and often requires the patient to change their lifestyle and diet.
Following a diet and rational physical activity help stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce the dose of glucose-lowering drugs or insulin.
This insidious diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disease in which the pancreas produces enough insulin, but it is rejected by the body's cells. As a result, the receptors lose sensitivity to the hormone, glucose is not absorbed by the cells, and its concentration in the blood increases.
The essence of the problem
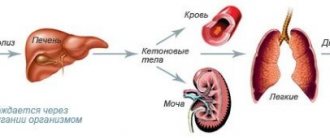
Thus, hyperglycemia is the main syndrome that accompanies diabetes mellitus: blood sugar levels - the table below reflects physiological indicators.
Table: Blood sugar levels:
| Age | Concentration, mmol/l |
| 2-31 days | 2,8-4,4 |
| 1 month-14 years | 3,3-5,6 |
| 15-60 years | 4,1-5,9 |
| 60-90 years | 4,6-6,4 |
| Over 90 years old | 4,2-6,7 |
During the development of the disease, all metabolic processes are disrupted. In this case, many organs and systems are affected, primarily the heart muscle and blood vessels.
This can lead to many serious complications:
- coronary heart disease,
- ACS, myocardial infarction,
- stroke of ischemic type,
- trophic disorders in the lower extremities, kidneys, organs of vision, etc.
Vessels wear out quickly in diabetes
. Please note! According to statistics, ineffective treatment of T2DM leads to a decrease in life expectancy in men by an average of 12 years, and in women by 20 years.
This is why diabetes can and should be treated. The main thing is to follow the recommendations of your doctor and not interrupt the therapeutic course.
Pathogenesis
The human body contains a 0.1 percent glucose solution.
This substance is consumed by cells, replenishing energy reserves. Also, the reserve of sugar may be in the liver for carbohydrate glycogen. If a person is healthy and eats properly, then the balance of sugar intake and consumption is normal. To find out your sugar status, you need to donate blood from a finger or vein on an empty stomach. If the doctor notices an increase in the norm, do not immediately get upset. Perhaps this condition is preceded by stress, a course of therapy. But such a deviation should not be left unattended; you need to visit your doctor for a consultation and start a therapy regimen.
Once a diagnosis of diabetes is confirmed, a person is required to take medications for the rest of his life. Self-medication is inappropriate, as life-threatening complications may develop.
General principles of therapy
Drug lowering blood sugar is far from the only treatment method.
Modern comprehensive care for a patient with diabetes should be provided on the following principles:
- Dieting. The correct selection of products will help not only achieve normoglycemia, but also reduce weight. Remember that one of the risk factors for developing T2DM is obesity.
- Sufficient physical activity, the type of which should be selected together with your doctor. Not everyone is suitable for gym or aerobics, but exercise therapy and daily walking will be useful for everyone.
- Medicines to lower blood sugar. The tablets allow most patients with T2DM to achieve target glucose levels.
- Insulin therapy. In rare cases, when glycemia is not controlled with medication, patients are transferred to insulin injections.
If the doctor decides to transfer the patient to insulin injections, he will most likely prescribe either genetically engineered human insulins or insulin analogues. The most modern are insulin analogues. Their advantage is that they are convenient to use for the patient, provide a stable effect and the required duration of action, and have fewer side effects. Previously, in Russian therapeutic practice, only original analogues of foreign-made insulin were used, such as, for example, Humalog (Eli Lilly, insulin lispro), Lantus (Sanofi, insulin glargine), Novorapid (Novo Nordisk, insulin aspart) and others. Today, the segment also includes Russian biosimilars of some drugs. For example, in 2020, the Geropharm company, after conducting all the necessary preclinical and clinical studies that confirmed their similarity with the original drugs, safety and effectiveness, registered the drugs RinLiz (biosimilar to Humalog), RinLiz Mix 25 (biosimilar to Humalog Mix 25), RinGlar (biosimilar Lantus).
Fresh vegetables and herbs will only bring benefits
Pastries, sweets and large amounts of fruit can trigger a sharp rise in sugar
Note! Unlike type 2 diabetes, patients with the insulin-dependent form of the disease should receive adequate insulin therapy immediately after diagnosis.
Free drugs
Preferential drugs are issued only with a prescription from an endocrinologist. First of all, insulin is provided to diabetics suffering from type 2 diabetes.
Table 6. Insulin for patients with type 2 diabetes:
| Form of the drug | Preparation-1 | Preparation-2 |
| Solution for subcutaneous administration | Glargine | Detemir |
| Ampoules for injections | Lizpro | Aspart |
| Suspensions for injections | 2-phase Aspart | Isofran |
List of documents
To receive preferential medications you must provide:
- identification document,
- SNILS,
- certificate from the Pension Fund,
- health insurance.
Vitamin preparations
The sign lists free vitamins for people with type 2 diabetes.
Table 7. Free vitamin preparations:
| Vitamin preparation | Description |
| Analogue of vitamin D. Refers to a vital drug for diabetics. Maintains homeostasis of calcium-phosphorus metabolism. Helps stimulate active absorption of phosphates and calcium from the lumens of the small intestine. |
| A fat-soluble vitamin that plays a critical role in redox processes. Synthesizes lipids, proteins and mucopolysaccharides. |
| Regulates calcium and phosphate metabolism. The drug also has a stimulating effect on all stages of calcium absorption in the intestine. |
| Vitamin D3. Helps accelerate the absorption of calcium in the digestive tract, and also accompanies the activation of phosphorus reabsorption in the kidney channels. It has a stimulating effect on ossification processes. |
| Replenishes vitamin B6 deficiency and normalizes lipid metabolism. Takes an active part in the metabolic processes of tryptophan, cysteine, glutamic, methionine and other amino acids. |
| Water-soluble vitamin B1. Plays a significant role in the metabolism of fats, proteins, carbohydrates, as well as in the processes of nerve excitation in synapses. |
| Replenishes the lack of calcium ions. It has a beneficial effect on the processes of transmission of nerve impulses. |
Medicines to normalize metabolism
Patients are prescribed the use of amino acids and enzyme medications.
Table 8. Drugs that normalize metabolism:
| Medicine | Description |
| It has choleretic and cholekinetic, detoxifying, regenerating, antioxidant, antifibrosing and neuroprotective effects. |
| Helps catalyze the hydrolysis of globotriaosylceramide and other neutral glycosphingolipids with the alpha-galactyl radical. |
| It is a recombinant human alpha-galactosidase A. It is used in enzyme replacement therapy. |
| Glycoprotein. Replaces or enhances the effect of the enzyme beta-glucocerebrosidase, which accelerates the hydrolysis of glucocerebroside with the formation of glucose and ceramide in lysosomes. |
| It is a purified form of the lysosomal enzyme iduronate-2-sulfatase. Intended to compensate for the deficiency of iduronate-2-sulfatase. |
| It is an analogue of human lysosomal beta-glucocerebrosidase. Helps enhance the hydrolysis of the glycolipid glucocerebroside to ceramide and glucose. Stops the accumulation of glucocerebroside in macrophages. |
| It is an inhibitor of glucosylceramide synthase. This enzyme is responsible for the first step in the synthesis of most glycosphingolipids. |
Antithrombotic drugs
The list of recommended drugs is presented in the tablet.
Table 9. Antithrombotic drugs:
| Medicine | Description |
| It is an indirect anticoagulant. Helps suppress the synthesis of vitamin K-dependent blood clotting factors in the liver. The effect of the medicine occurs 3-5 days after the start of administration. |
| Refers to low molecular weight heparins. Has a pronounced antithrombotic effect. Not recommended for people suffering from uncontrolled bleeding. |
| Medium molecular heparin. Accelerates the anticoagulant effect of antithrombin III. It has a hypolipidemic effect, promotes the activation of lipoprotein lipase, and reduces the activity of GM hyaluronidase. Helps increase cerebral vascular resistance and increase renal blood flow. |
| Specific and active inhibitor of platelet aggregation. Has a coronary dilation effect. Selectively reduces the binding of ADP to platelet receptors. |
| Recombinant human plasminogen activator. It is prescribed with caution to patients who have crossed the 70-year-old threshold. |
| Fibrinolytic agent, single-chain urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Converts profibrinolysin into fibrinolysin, which lyses fibrin clots. |
| Oral anticoagulant, direct factor Xa inhibitor. Has a powerful anticoagulant effect. |
Medicines that normalize blood pressure
The sign contains a list of free medications that normalize blood pressure.
Table 10. Free drugs that normalize blood pressure:
| Medicine | Description |
| Centrally acting antihypertensive agent. Reduces peripheral vascular resistance, reduces cardiac output and heart rate. Helps increase GFR and renal blood flow. Also has a calming effect. |
| Belongs to the group of imidazoline derivatives. Promotes stimulation of alpha-2 adrenergic receptors and central imidizazoline receptors. Has a hypotensive and sedative effect. |
| Selective agonist of imidazoline receptors. Responsible for tonic and reflex control of the sympathetic nervous system. Has an antihypertensive effect. |
| Has central and peripheral effects. Blocks postsynaptic alpha-adrenergic receptors. Against this background, a decrease in OPSS is observed. The drug also helps lower upper and lower blood pressure. Post- and preload on the heart is reduced. |
| Non-selective endothelin receptor antagonist. Helps reduce pulmonary and systemic vascular resistance. |
Recommended diuretics
The table provides a list of free diuretics provided to people with type 2 diabetes.
Table 11. Diuretic drugs:
| Medicine | What is |
| Thiazide diuretic. Promotes disruption of the reabsorption of sodium ions, chlorine and water in the distal tubules of the nephron. Accompanies an increase in the excretion of potassium and magnesium ions, as well as bicarbonate. Thanks to this medicine, calcium ions are retained in the body. The onset of the diuretic effect occurs after 120 minutes. |
| Sulfonamide derivative. It has a moderate saluretic and diuretic effect. |
| A loop diuretic that blocks the reabsorption of sodium and chloride ions in the proximal and distal portions of the renal tubules. It has a diuretic, natriuretic and chloruretic effect. |
| Potassium-, magnesium-sparing diuretic drug. Competitive aldosterone antagonist. It has an inconsistent hypotensive effect. |
Classification of diabetes medications
All drugs that lower blood sugar in diabetes can be divided into five large groups:
- Enhancing insulin secretion in the pancreas.
- Increases sensitivity to insulin.
- Reducing the formation of glucose in the liver.
- Reducing the absorption of carbohydrates in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Strengthening the excretion of excess sugar in the urine.
Let's take a closer look at each.
Drugs that enhance insulin production
This large group includes several classes of drugs:
- sulfonylurea derivatives,
- meglitinides,
- dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors,
- glucagon-like peptide 1 agonists.
The mechanism of action of sulfonylurea derivatives is to stimulate the secretion of the hormone insulin.
To a lesser extent, these drugs:
- Increases the specific sensitivity of tissues,
- Reduces glucose production in the body.
Table: Sulfonylurea derivatives:
| Generation | Representatives | Peculiarities | How to use | Contraindications |
| I |
| Currently almost never used. They have a short duration of action and require high doses. |
| |
| II |
| They last longer and have less side effects. There is a risk of developing hypoglycemia | 1-2 times a day 30 minutes before meals |
The mechanism of action of these drugs
These blood sugar-lowering tablets have a number of advantages:
- rapid achievement of pharmacological effects,
- reducing the risk of developing microangiopathies,
- available in combinations with metformin,
- low price.
Don't forget about the negative points:
- when taking them there is a risk of developing hypoglycemia,
- effect on body weight (weight gain is possible),
- with long-term use - a decrease in effectiveness due to the development of resistance.
The doctor must warn about the side effects of medications
. Attention! According to recent data, over time, sulfonylurea drugs lead to the depletion of pancreas and the transformation of CD-2 into CD-1.
Meglitinides, or benzoic acid derivatives, are another class of drugs that increase insulin production.
Main representatives:
- Nateglinide,
- Repaglinide.
They are fast-acting and have good glycemic control, however, like sulfonylureas, they can lead to a sharp drop in sugar levels. Negative points, according to patient reviews, also include the need for frequent administration and a fairly high price.
Episodes of hypoglycemia may occur when taking these medications.
The group of drugs that affect the release of insulin by pancreatic cells also includes fundamentally new drugs for reducing blood sugar. They are characterized by a glucose-dependent mechanism of action.
This means that these drugs have a hypoglycemic effect only in hyperglycemia syndrome. If the glucose concentration reaches 4-5 mmol/l, they stop working.
Table: New generation drugs:
| Pharmacological group | Representatives | Trade names |
| Glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists (injectable forms) | Exenatide |
|
| Liraglutide |
| |
| Lixisenatide |
| |
| Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (blood sugar pills) | Saxagliptin |
|
| Sitagliptin |
| |
| Vildagliptin |
|
Positive aspects of treatment with these drugs include maintaining a stable glycemic level and a low risk of low blood sugar. In addition, modern medications do not affect the patient’s body weight, rarely cause side effects and are absolutely safe for elderly patients and people with cardiovascular diseases. The only “but” for using these drugs is the high cost.
Agents that reduce insulin resistance in peripheral tissues
This group includes biguanides:
- Metformin (Glucophage, Siofor),
- Pioglitazone (Pioglar, Actos).
The most popular group of drugs
These drugs improve the uptake of glucose by cells without affecting the production of the hormone insulin. The advantages of this therapy include:
- low risk of hypoglycemia,
- no effect on the patient's weight,
- concomitant improvement in lipid profile, reduction in cholesterol and “bad” HDL levels,
- reducing the likelihood of developing macroangiopathies,
- the possibility of combination therapy (strictly according to the doctor’s indications),
- affordable price.
Note! Biguanides today are the most popular drugs for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. In addition to increasing tissue sensitivity to insulin, they significantly reduce the absorption of carbohydrates in the digestive tract.
Drugs that block glucose absorption
You can reduce the concentration of glucose in the blood with the help of drugs that interfere with its absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. A typical representative of the group of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors is Acarbose.
Mechanism of action of Acarbose
A drug:
- does not affect the patient's weight,
- has a low risk of side effects and hypoglycemia.
- may cause gastrointestinal discomfort.
Note! Many patients find it inconvenient that tablets containing Acarbose must be taken three times a day.
So, what drugs are best for lowering blood sugar?
Based on the information obtained above, two basic rules can be identified when drawing up a treatment plan for patients with T2DM:
- Preference is given to drugs that increase cell sensitivity to insulin rather than stimulating hormone production. According to the latest data, long-term use of metformin (Siofor, Glucophage) is considered more effective and safe than sulfonylurea derivatives.
- If there are indications for transferring the patient to insulin therapy, it should be started immediately. It is not advisable to try to replace injections with tablets, herbs, traditional medicine, etc.
Correctly selected treatment will allow you to achieve excellent results.
Thus, the most effective drug treatment for T2DM can be considered taking pills that increase insulin resistance of receptors. This is due to the fact that in patients with this form of diabetes, the cells almost do not respond to this hormone, which is released in normal or even increased quantities.
In addition, we should not forget that more than half of the success in treating the disease belongs to a low-carbohydrate diet and physical exercise with pleasure. Only in this case will the patient feel good and avoid the risk of developing severe complications.
List of hypoglycemic active ingredients
Classification of sugar-lowering drugs, consisting of the most common effective components:
The medicine may be based on levothyroxine sodium.
- tolbutamide;
- carbutamide;
- chlorpropamide;
- glibenclamide;
- glipizide;
- gliclazide;
- glimepiride;
- levothyroxine sodium;
- metformin hydrochloride;
- thiamazole;
- gliquidone;
- repaglinide.
Drugs on the market with the same composition may have different names.
Return to contents
Gliclazide
A new generation sulfonylurea derivative. Participates in enhancing the early production of its own insulin by beta cells of the pancreas. It effectively smoothes out peaks in blood sugar by constantly maintaining its level at the same values. In addition, a drug based on it can prevent blood clots and reduce the number of complications of diabetes.
Return to contents
Glimepiride
The drug belongs to the short-acting group.
Also a type of sulfonylurea, it can be used for type 1 diabetes. Enhances insulin release by affecting beta cell potassium channels. The effect of the drug does not last long, and therefore it is necessary to take it again after 5-8 hours. The drug is not used for liver or kidney dysfunction or severe diabetic ketoacidosis.
Return to contents
Levothyroxine sodium
A hypoglycemic drug that is identical to the hormone thyroxine produced by the thyroid gland. It is used in combination with drugs of a different composition and promotes better absorption of insulin along with glucose by target cells. Thus, the amount of sugar in the blood drops quickly. It is often used for hyperglycemic coma, as it has a rapid and significant effect.
Return to contents
Metformin hydrochloride
It belongs to the list of drugs from the biguanide group and impairs the absorption of glucose in the intestine and inhibits the formation of glucagon in the liver. This helps reduce the need for insulin production. Well suited for patients suffering from obesity due to overeating. The substance normalizes the balance of blood lipoproteins, preventing the development of atherosclerosis and vascular wall disorders.
Prescription Thiamazole
It is an inhibitor of thyroid hormone, and is used in case of overdose of hypoglycemic drugs, especially the increased consumption of levothyroxine sodium. To purchase a drug based on this substance, you definitely need a prescription, because it is a potent drug that, if used incorrectly, can lead to allergic reactions or even death of the patient.