Importance of urine testing
The fluid secreted by the kidneys, that is, urine (urine), is a waste product of the body.
Having gone through all the stages of filtration, during which it undergoes many transformations, it descends through the ureters into a special natural storage reservoir - the bladder. After it is filled, urine is removed from the body through the urethra (urethra), thereby making room for the next filtered portions. A significant portion of the final products formed during the metabolic process is released into the urine, and therefore, if the activity of functional systems or individual organs is disrupted, changes will also be noted in it.
Therefore, when diagnosing certain diseases, several types of urine tests are often performed, which make it possible to evaluate its organoleptic, biochemical, physicochemical, microbiological and microscopic properties. The need to take a urine test arises not only in critical situations when the child has pathological symptoms.
Examinations of this type of biological material are often prescribed for preventive purposes in order to be able to monitor the correspondence of the development of the child’s functional organs to his age. Based on this, OAM (general urinalysis) in children, as well as other methods for studying fluid filtered by the kidneys, are prescribed in the following situations:
- After an illness, control diagnostics of blood and urine parameters are carried out to assess the dynamics of recovery and identify possible complications.
- If there are suspicions of hidden diseases of internal organs (diabetes mellitus, liver disease, pancreas disease, etc.)
- After illnesses characterized by a high probability of developing renal complications (viral infections, scarlet fever, tonsillitis, etc.)
- Before planned or urgent hospitalization in a hospital.
- For preventive purposes to assess the general condition of the child.
- To check the effectiveness of the therapy.
All of the above emphasizes how important urine tests are in children. Considering that children are most susceptible to various colds, infectious diseases, as well as injuries, these procedures become indispensable when carrying out any diagnostics.
What do the increased indicators indicate?
Increased relative density of urine is called “hypersthenuria”. Hypersthenuria is said to occur when the specific gravity of urine exceeds 1030 g/l.
This condition physiologically occurs with insufficient consumption of drinking water, in the hot season due to profuse sweating and large fluid losses in diseases accompanied by profuse vomiting and diarrhea. The urine becomes concentrated, dark, and the smell is pungent and unpleasant.
Pathological hypersthenuria is observed in diseases of the cardiovascular system with severe edematous syndrome, and in diabetes mellitus due to the presence of glucose in the urine. Increased density of urine is always observed with glomerulonephritis, nephrotic syndrome due to the loss of large amounts of protein through the kidneys.
Taking antibacterial drugs, infusion of high-osmotic intravenous solutions, and radiocontrast agents also increases the specific gravity of urine. Hypersthenuria as a symptom may be the onset of renal failure (stage of oligoanuria).
During what periods of a small child’s life is urine collected for analysis?
The developed scheme for examining infants primarily pursues preventive objectives. After all, it is much easier to prevent the development of serious pathology from the internal organs by detecting its initial manifestations than to engage in long-term treatment later. In addition, diagnosing some diseases at an early stage can greatly improve the prognosis for the health and even life of the baby.
A comprehensive examination of the newborn’s health status begins already in the maternity hospital and continues throughout the subsequent months.
If we consider the period of a child’s life up to 1 year, then at certain moments blood and urine are drawn, feces are examined, instrumental examination is carried out (ultrasound of internal organs, hip joints, brain), and the newborn baby is also consulted by doctors of narrow specialties.
A child's urine can tell you a lot about his health.
According to the accepted observation scheme, pediatricians prescribe a general urine test at certain periods of the child’s life:
- 1 month, during which the doctor receives information about the state of the urinary system and the presence of sugar, which allows one to judge the health of the pancreas;
- 3 months;
- 6 months;
- 12 months.
Urine examination during these periods is planned, that is, it is performed in the absence of any complaints from parents about the condition of their baby’s urinary organs. Naturally, if pathological abnormalities appear in an infant (frequent and painful urination, very rare urination, impurities in the urine, abdominal pain, symptoms of intoxication and other signs of ill health), it is necessary to take a general urine test more often for timely diagnosis and monitoring the effectiveness of therapy.
This method of studying urine allows you to evaluate the physical properties of urine (color, acidity, transparency, smell, specific gravity), as well as learn about the content of leukocytes, erythrocytes, epithelial cells in the resulting sediment, determine the presence of microorganisms and some chemicals. Cell counting is carried out using the “field of view” method, when a laboratory technician examines the components of urine under a microscope, so the normal content of, for example, epithelium looks like 5-10 in each field of view.
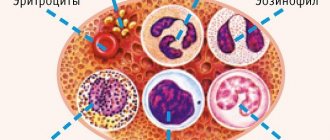
Under a microscope, different types of cells are counted in urine
But a general analysis does not allow one to find out the content of red blood cells or white blood cells per unit volume of urine; it can only be used to determine the excess of their number in the visual fields. Therefore, the doctor often orders the collection of urine from the child for analysis according to Nechiporenko, during which the exact number of these cells in 1 ml of urine becomes known.
Acquaintance
Leukocytes are the formed elements of blood. You can see them under a microscope; they are white bodies with clearly defined boundaries. The counting is carried out by a laboratory assistant or a special device (automatic counter). White blood cells in a child’s urine are normally absent or present in small quantities. Their main task is to protect the body from various infections and parasites. The growth of leukocytes is inflammatory in the body, or indicates an infectious disease. Mainly for pathologies of the kidneys, ureter and bladder.
Preparing for the study
Your child will not need any special preparation to undergo a urine test. However, there are a few things parents should consider. This is necessary to obtain reliable results. These include the following recommendations:
- protect the baby from physical fatigue and emotional turmoil;
- do not change your usual daily routine, nutrition and drinking regime on the eve of collecting biomaterial;
- Fatty and spicy foods, as well as fast food and carbonated drinks should be excluded from the child’s diet;
- make sure that the food does not include foods that can change the color of urine (beets, carrots, rhubarb, etc.);
- If your baby is taking any medications, you must notify the doctor about this.
Attention! It is very important to follow all the rules regarding the collection of biomaterial, since neglecting them may lead to errors during laboratory study, and, consequently, it will be difficult or impossible to decipher the obtained materials.
Sterile container for urine sample collection
How to properly collect urine from a child
It is permissible to collect the analysis only in a sterile container (sold in pharmacies and costs 12-20 rubles). Do not use mayonnaise jars for this - containers that are poorly rinsed from food and soap will distort the final result.
Do not collect material for analysis in the evening: urine should be delivered to the laboratory no later than 2 hours from the moment the container is filled.
If the material is left for a longer period of time, the analysis may be unreliable due to sedimentation.
Ideally, more than 5 hours should have passed since the last urination. However, for a baby who may urinate more than 15 times per day, it is impossible to fulfill this requirement. Therefore, try to collect urine immediately after your baby wakes up.
Features and preparation:
- Transport urine carefully - frost or heat can distort the results. If you are not sure about the weather, use a thermal bag.
- The day before, do not give your child unfamiliar foods (and do not eat them yourself if the child is breastfed), and do not feed vegetables and fruits that can color the urine.
- Try to keep your baby from overheating, sweating and freezing before donating urine - all this can negatively affect the final result.
- Try to make sure that the child does not cry - the emotional state also affects the performance.
Important: you must give urine on an empty stomach. You should collect an average portion of the very first morning urination!
Needless to say, how valuable the results of all these tests are for diagnosis. Therefore, to properly collect urine from newborns, parents must know some requirements and strictly follow them:
- the collected urine sample should not contain any foreign matter;
- the minimum amount of urine is 15-25 ml, which is quite enough to determine all the necessary parameters;
- the portion of urine should be medium, collected in the middle of urination (this rule can only be observed in boys);
- the sample must be fresh, urine can be stored for no more than 2 hours (to ensure maximum reliability of the results), therefore it is necessary to collect urine for analysis from an infant not in the evening, but in the morning;
- Urine collection should be carried out in a sterile container.
Special containers are very convenient to use
At first glance, it is not easy to fulfill all these requirements, and many parents find it very difficult and do not know how to collect urine from a baby without hassle, quickly and on time. Meanwhile, all the necessary instruments and devices are now on sale for this purpose, with the help of which correctly collecting morning urine will not be a problem for either boys or girls.
General collection rules
Considering that there are quite a lot of methods for studying urine, after receiving a referral for analysis, parents must definitely clarify all the details of collecting biomaterial. This list includes:
- Where to collect urine, where to buy a sterile container, and how to sterilize the existing container if necessary?
- How to toilet a child’s external genitalia without getting foreign impurities into the sample?
- How many ml of urine is needed to perform a specific test ordered?
- How to properly collect biomaterial so that the analysis does not need to be repeated?
The very first study of secreted fluid, which is prescribed during a visit to the hospital, is OAM. With its help, it is possible to evaluate a large number of indicators, which provides the doctor with the opportunity to adjust further examinations of a small patient.
Urine collection for general analysis is carried out in the morning, after a carefully performed toilet of the genital organs. It is necessary to wash your child without using products containing various fragrances and antibacterial components. Regular baby soap is best, and it is recommended to use it the rest of the time. It is hypoallergenic and does not pose a threat to sensitive children's bodies.
It is best to use a special sterile container purchased from a pharmacy as the container in which you plan to collect the urine test. Although you can also use ordinary small glass or plastic dishes for these purposes, after holding them in boiling water for several minutes.
To take an analysis from newborn babies and children up to one year old, it is recommended to purchase a special urine bag that is glued to the pubis and perineum, preventing spillage of the required biomaterial.
To conduct the study, you will need a portion of morning urine collected immediately after waking up. For older children, parents should explain in detail the collection rules and how much urine is needed for analysis, so that they can do it themselves.
The collection procedure itself has a clear sequence, namely:
- the first portion of urine (approximately 2-3 seconds after the start of urination) is released into the toilet;
- subsequent liquid is collected in a prepared container (approximately 20-30 milligrams);
- urination ends again into the toilet, since the last portion of urine is not suitable for diagnosis.
Thus, to carry out OAM, the middle portion of morning urine is taken, and the remaining two are poured into the toilet. There is a technique in which all three portions are studied (three-glass sample), which allows one to determine a more specific localization of pathologies of the urinary tract.
Taking urine for analysis from a newborn is not an entirely simple procedure. It must be remembered that unscrewing the diaper or squeezing out the diaper is strictly prohibited, as foreign impurities may get into the container, which will prevent you from obtaining a reliable result. You can collect urine from a baby in the following way - “watch for” the first morning urination, and support it over a container prepared in advance.
When using a special urinal, it should be taken into account that when children stick it on, they feel some discomfort and try to throw it off. Therefore, you need to make sure that the urinal is in its place before urinating.
The resulting urine should be sent to the laboratory as quickly as possible, since it is suitable for analysis in the first 2 hours after collection if stored at room temperature, and up to 6 hours if stored in the refrigerator at 4-6º C.
In addition to the average portion of morning urine, a study of daily diuresis may be prescribed, which involves collecting all the fluid excreted during the day. This analysis shows the performance of the kidneys and other features of their activity. In pediatric nephrology, assessment of daily diuresis is no less important than TAM.
Before collecting urine, the child must be washed well with regular baby soap under running water and dried with a soft towel. The girl needs to be washed from front to back to avoid water from the perianal area getting into the urethra and causing infection. Boys need to carefully open and wash the head of the penis; this is contraindicated if the baby has physiological phimosis.
Urine squeezed out of diapers, onesies or diapers is not suitable for analysis. You also can't use it from a pot. These results will initially be distorted and may lead to additional unnecessary studies. It is necessary to collect material for analysis in the morning, and only in newborns is it permissible to examine the night portion. This procedure is quite troublesome - you need to undress the baby and wait until urination begins, and have time to substitute a container or jar.
For boys, it is quite convenient to collect urine in a dry, sterile jar by placing it near the penis. For girls, you can place a sterile disposable warm plate or saucer under the bottom, and then pour it into a sterile container.
To simplify the task, you can buy a disposable urine bag at the pharmacy. This is a special transparent sterile bag, which is attached to the perineum using adhesive tape. In girls, fixation is carried out in the area of the labia majora, in boys - at the base of the penis and testicles. Using a urine bag makes urine collection much easier.
You can try collecting urine in a sterile bag, which must be cut on the sides and secured in the perineum. Many mothers have successfully adapted to collecting urine from boys in a condom.
It must be remembered that newborns and infants pee well during feeding, when they are unwrapped and the diaper is removed, it is at these moments that tests can be collected quickly and without problems. You can open the tap in the bathroom; the sound of flowing water stimulates urination. Some babies pee faster if you give them clean water to drink.
Tables with norms for general urine analysis in children and interpretation of results
A general urine test (UCA) is a basic test that is almost always prescribed when seeking medical help - from a preventive examination to hospitalization in a medical facility. Urine testing is the simplest non-invasive way to identify abnormalities in the urinary system, as well as assess the patient’s health status. The parents’ task is to correctly collect and timely deliver the biological material to the laboratory; the doctor must decipher the results and prescribe additional examination.
Indications for a general urine test
Urine testing is prescribed not only if there are complaints from the patient, but also for preventive purposes. The doctor will write a referral for OAM if:
- preventive medical examination of the child to assess the general state of health and early detection of pathologies of the genitourinary system;
- hospitalization;
- diseases of the kidneys, bladder and urethra;
- suspected of developing diabetes mellitus in a child, problems with the pancreas and liver (we recommend reading: how to identify and diagnose diabetes mellitus in a child?);
- recent diseases that can cause complications on the kidneys (sore throat, scarlet fever, influenza, etc.);
- assessing the effectiveness of the completed course of treatment.
How to properly collect urine for analysis?
In order for a child’s urine test to show a reliable result, a number of conditions must be met when collecting and storing biological material. The container in which urine will be collected must be sterile; it is advisable to purchase a container from a pharmacy. The urine collected in the morning must be delivered to the laboratory within two hours. Frozen or prepared urine the night before is not suitable for research, as the analysis data will be distorted. Also, you should not drain urine from the pot, squeeze it out of a diaper or gauze (even sterile) (see also: how to properly sew gauze diapers for newborns?).
READ ALSO: Oxalates in the urine of a child: what is it?
On the eve of the study, you should limit the child’s physical activity, exclude from the diet excess sweets and foods that can color urine (beets, carrots), as well as mineral water. Before collecting urine, it is necessary to thoroughly wash the child using baby soap; this will ensure a neutral alkaline environment for the external genitalia and prevent bacteria from entering the biological material.
Rules for collecting biomaterial for infants
At an early age, when the baby is not yet able to control the process of urination, the simplest solution would be to collect urine using a special urinal bag sold in a pharmacy. It is a sterile plastic bag that is glued to the external genitalia of the child using an adhesive layer (suitable for both boys and girls). All the mother needs to do is secure the urine bag and wait until the baby empties the bladder, then drain the urine into a sterile jar.
If for some reason it is impossible to use a urine bag, you should resort to other methods. For boys, place the penis in a small bottle or test tube and secure it with an adhesive plaster on the stomach, or simply wait for the moment of urination and place the jar under a stream of urine.
To collect urine from a girl under 1 year old, you need to put her on a diaper, place a clean (boiled) plate under her buttocks, or hold the baby over the tray (plate) until urination occurs. This process requires patience from parents, but it is worth working hard for a truthful result of the analysis.
Disposable pediatric sterile urine bags
Collecting urine from a child over one year old
For children older than one year, you should try to collect a medium portion of urine. To do this, you need the baby to first start peeing in the potty or toilet, then collect the urine in a sterile container, and add the rest to the potty. Children over 1-2 years old, when they can already control the process of urination, should not have problems with this. 10-20 ml of urine is quite enough for a general analysis, so it is not necessary to collect a full jar.
READ ALSO: How often should a newborn baby write?
Normal urine values for children with a table
A child's urine test shows enough information for the doctor to determine the condition of the child's genitourinary system. If, when reading the urine test, the doctor sees deviations from the norm, he will prescribe an additional examination for the child (ultrasound, blood tests, etc.). The table shows the normal indicators of a general urine test for children:
READ ALSO: RBC blood test in children: interpretation and norm
| Index | Designation | Norm |
| Color | Color | Light yellow, almost transparent in a newborn; straw, yellow in children over one year old |
| Transparency | Clarity | Transparent |
| Smell | — | Absent |
| Specific gravity (density) | sg | Up to 4 years 1007-1016, up to 10 years 1011–1021, teenagers 1013-1024 |
| Acid-base environment | pH | 4.5-8 (slightly acidic) |
| Red blood cells | BLD | No or 0-1 in p/z |
| Leukocytes | LEU | No or for boys 0-2 in the field, for girls from 0-2 to 8-10 in the field |
| Epithelium | VTC | 1-2 |
| Protein | PRO | Absent |
| Glucose | G.L.U. | Absent |
| Salts | SAL | Small quantities allowed |
| Bacteria | NIT | None |
| Urobilinogen | UBG | Less than 17 µmol/l |
The parameters of a general urine test for children are similar to those for adults, but there are slight differences in the normal variants
Are all OAM indicators stable?
In urine analysis, some data may vary. The indicators presented below are physical and are measured “by eye”:
- The color may vary from light yellow to a yellow tint depending on the concentration. The first morning urine is darker, the next portion is lighter.
- The density of physiological fluid varies in the range of 1009-1049. The parameter depends on the time of day.
Deciphering a child's general urine test - what do deviations from the norm indicate?
It should be understood that it is impossible to determine pathology based only on the interpretation of the analysis. The doctor will compare the patient’s complaints, clinical symptoms of the disease, and data from other examinations and make a diagnosis based on this. A deviation from the norm of any indicator does not always mean the presence of a disease. This can happen while taking medications or vitamins; the composition of urine is also affected by the diet of children.
Organoleptic indicators
The urine of children older than one year has a specific odor, but it should not be pungent. The color can vary from light to bright yellow. Deviations from the norm, as well as possible diseases when indicators change, are indicated in the table.
| Index | Meaning | Deviations from the norm |
| Color | Depends on the amount of pigment; the color can be affected by medications and dietary habits. |
|
| Smell | Depends on the amount of essential oils. The smell can be affected by taking certain medications or eating foods with a strong aroma. |
|
| Transparency | The value indicates possible cloudiness of the urine. If the sample has been standing for a long time before delivery, the urine darkens due to salt deposits. | Turbidity is associated with an increased content of red blood cells, leukocytes, uric acid, in the presence of epithelium. White or cloudy urine indicates kidney pathologies. If urine is opaque, you need to look at other data. |
Physico-chemical data
An experienced laboratory technician should be involved in conducting tests of children's urine.
During the study, the laboratory technician determines the physicochemical values of urine, which include the density and reaction of the pH of the environment. Relative density indicates the ability of the kidneys to dissolve various substances. If the normal values of 1006 – 1026 g/l are increased, this may indicate the following conditions:
- nephrotic syndrome;
- liver diseases;
- diabetes;
- decreased urine production;
- heart failure.
The pH reaction in an infant changes in an acidic direction during the height of rickets, as well as with an increase in body temperature; if the pH is constantly above the norm, renal acidosis should be excluded. An alkaline reaction is also obtained as a result of the presence of a large amount of fruits and juices in the baby’s diet, and a lack of proteins.
If the environmental reaction indicators are underestimated, additional examination of the kidneys will be required. This value is typical when eating exclusively protein foods; the patient needs to add more vegetables and fruits to the menu. Low values may indicate diseases:
- tumors of the urinary system;
- food poisoning;
- excess potassium levels in the body.
Specific gravity (sg) below normal may be a consequence of impaired kidney function; high urine density occurs with diabetes mellitus, infection, during treatment with antibacterial drugs, and also with dehydration (for example, in the heat).
Biochemistry
Protein in the urine is unacceptable, even a small amount indicates a violation of the kidneys, and this phenomenon is also possible against the background of elevated body temperature and in children actively involved in sports. High protein content in urine is observed in diseases:
READ ALSO: Protein was detected in a child’s urine: what does this mean?
- pyelonephritis;
- allergy;
- heart failure;
- tumors.
An increase in glucose levels in the urine may indicate diabetes mellitus or galactosemia, and may also occur in premature babies due to immature renal tubules. In some children, an increase in the rate is observed due to excessive consumption of sweets and vitamins. Urobilinogen (UBG) exceeds the norm in case of problems with the digestive tract (enterocolitis) or liver (hepatitis, jaundice).
When analyzed, ketone bodies, toxic substances formed as a result of fat and carbohydrate metabolism, can be detected in urine. Ketonuria is observed in children suffering from acute pancreatitis or diabetes mellitus. Substances may also appear in the sample through repeated vomiting.
Microscopic examination
In this case, physiological fluid is examined under a microscope. The material may contain red blood cells, leukocytes, epithelial cells, salts, and casts. The disease is determined depending on their quantitative content:
| Index | Disease | Peculiarity |
| The appearance of red blood cells in the urine (we recommend reading: normal red blood cells in urine in children) | Viral infection, kidney and bile duct diseases, cystitis. It is found when the body is poisoned by toxins. | A small number of red blood cells may be the result of physical overexertion. |
| Detection of leukocytes | A sign of pyelonephritis, cystitis or urethritis. Normally, the epithelium should not be detected in the urine, but during the inflammatory process, the cells of the upper layer of the mucous membrane of the kidneys or bladder are exfoliated and excreted with urine. A very high level is observed during a purulent process. | In girls, leukocytes can enter the urine from the vagina and external genitalia (we recommend reading: leukocytes in the urine of a child: normal by age). |
| Detection of bacteria | If bacteria are found in the urine, it is necessary to exclude a bacterial infection of the urinary organs. | Sometimes the detection of bacteria may be due to improper urine collection or poor hygiene. |
| Presence of salt | The presence of salt in urine sediment directly depends on nutrition. If salt is constantly determined in a child’s urine, it is necessary to exclude urolithiasis. | If detected in a baby, you need to review the menu of the nursing mother. The indicator is often indicated in the analysis of infants and in children when introducing complementary foods. The reason for the presence of salts may be excessive consumption of meat products, cocoa, and chocolate. |
READ ALSO: table of leukocyte norms in children by age
You can take a general urine test both in a city hospital and in a private laboratory. It is carried out not only according to indications, but also on the initiative of the patient if he wants to check his health.
vseprorebenka.ru
What methods of collecting urine from newborns exist?
Urine tank test. sowing
Grandma's method is gradually becoming a thing of the past: using a clean plate. But still, sometimes it is used, especially if parents are unable to use modern methods. To do this, the baby is placed with his bottom on a cleanly washed, boiled and dried plate, preferably warm, and then begins to wait for the act of urination.
It is necessary to take into account the fact that babies pee often and regularly, approximately every 10-20-30 minutes depending on age. Therefore, it is not difficult to “stay in the way” of urine excretion; it will not take much time even in the morning, when the baby’s urine needs to be taken to the laboratory for analysis quickly, without allowing it to be stored at home.
With a urinal you can collect urine quickly and comfortably
Collecting urine from an infant can be made faster and more accurately. To do this, you should use special devices called urinals, available in every pharmacy. These are a kind of transparent bags made of polyethylene, in the upper part of which there is a slot, decorated with adhesive tape. The urinal bag is applied to the child’s perineum with this slit so that the genitals are inside the pouch.
Urination will occur only into the receiver, but in this case it becomes impossible to collect an average portion of urine (but the urine will definitely be free of impurities and will not be able to wet the baby’s underwear).
At the pharmacy you can buy a urine bag for a boy who has recesses for the testicles. Universal models can be used for both boys and girls. The collected urine is quickly poured into a jar or plastic container with a screw cap, also available at the pharmacy, and taken to the laboratory for testing.
A homemade urinal bag made from a bag is also easy to use.
If such devices for collecting urine cannot be purchased, then you can use ordinary plastic bags taken from the factory packaging. It is important that such a package has not been used previously. Its edges are partially cut through, the child’s legs are inserted into the holes, and the top is tied with two knots on the sides.
You can collect urine in a very simple way, for which you need a plastic container from a pharmacy or a glass jar. This method is suitable only for boys, and of any age. Parents take the baby in their arms and hold the container at the ready. As soon as urination begins, the container is placed under the stream. This method is good because it is possible to collect an average portion of urine in the required amount, 15-25 ml.
All these methods should be used so that the child does not experience negative emotions and behaves calmly. Collecting urine from newborns sometimes requires some creativity. To speed up urination, you can give your baby something to drink, massage his tummy, or turn on the water tap. If the urine is collected correctly, in compliance with all the above rules, then the research results obtained will be reliable and it will not be necessary to take it again.
Interpretation of indicators
Deciphering a urine test in children should be carried out exclusively by a specialist, since many diseases in young patients develop rapidly, and any delay can result in a serious complication.
The most extensive information about the state of the body is provided by general and biochemical tests, which are often prescribed first in pairs together with a blood test. As mentioned above, when they are carried out, five properties of the released liquid can be assessed.
Color – Children's urine is usually a lighter shade of yellow than that of an adult. If a child is breastfed, then his urine is almost transparent. When you introduce foods containing bright pigment (beets, carrots) into your baby’s diet, the shade becomes more pronounced.
Odor – a child’s urine, as a rule, does not have a strong specific odor. If a child's diet is oversaturated with protein, and, in particular, meat food, then the smell of the secreted liquid intensifies.
Foaming – in healthy people, both adults and children, the fluid secreted by the kidneys should not foam. The appearance of foam may be due to dehydration. However, if, when the drinking regime is brought back to normal, foaminess remains, then this indicates the presence of pathological changes.
Transparency – normally, children’s urine is transparent. Turbidity is often a signal of the development of an infectious disease or a disruption of metabolic processes, expressed, for example, by accumulations of a large number of salt formations.
Density (specific gravity) (SG) - the norm for this coefficient in a newborn baby is 1.002-1.004. If the diet of a nursing mother consists to a greater extent of fatty and meat foods, then the density increases, and if plant foods predominate, then, on the contrary, it decreases. The same applies to the nutrition of children whose breastfeeding has already been completed, and whose density also decreases with heavy drinking.
By six months, this parameter in a child increases to 1.006-1.016, and remains this way until the baby is one year old. In children 3-5 years old, the specific gravity values vary in the range of 1.010-1.020, 7-8 years old - 1.008-1.022, and at 10-12 years old they gradually approach adults, that is, 1.011-1.025. Using this indicator, the laboratory technician determines the presence of salts and other decomposition products.
What does acetone mean in a child's urine?
An increase in the coefficient is noted:
- for diabetes mellitus;
- pyelonephritis, cystitis;
- high dosage of drugs excreted in the urine;
- dehydration due to vomiting, diarrhea, intense sweating.
A decrease in the specific gravity of urine is observed:
- with heavy drinking;
- diabetes insipidus;
- taking diuretics;
- renal failure.
Acidity (Ph) – the normal urine reaction in children is neutral (7) or slightly acidic (5-7). If urine is collected shortly after eating food, then its reaction is close to alkaline (above 7).
In addition, an alkaline reaction is observed with excessive consumption of vegetables, fruits and rye bread. Ph increases with an increase in protein and fatty foods in the diet, baked goods made from wheat flour, and also after physical exercise.
Attention! If, when the drinking and eating regimen is normalized, and physical activity is reduced, the density and reaction of urine do not return to reference values, then this may indicate the development of renal failure.
Norm and deviations of the acidic environment of urine
Protein (PRO) - protein molecules in the urine of infants should not exceed 5 g/l. The appearance of protein is also noted during the period when children begin to walk. An increased content of this substance is observed after intense physical activity, but normally there should be no protein in the morning urine.
Sugar (GLU) – the appearance of sugar in a child’s urine can be caused by eating large amounts of carbohydrate foods. Another reason is a temporary disorder of digestive function (flatulence, heartburn, diarrhea). If the increase in the indicator is not associated with the factors described above, then perhaps we are talking about an endocrine disorder, which should be a reason for additional diagnosis.
Ketone bodies (KET), or so-called acetone, appear in the urine when children's diets contain low amounts of carbohydrates. If the child consumes enough of them, then perhaps there is a problem with absorption, which is observed in diabetes mellitus.
Bilirubin (BIL), urobilinogen (URO), indican and bile acids - normally, all of these substances should not be detected in the fluid excreted by the kidneys in a child. Their presence indicates pathologies such as liver dysfunction, urolithiasis, inflammatory processes in various parts of the intestine, and therefore mandatory further examination is required.
The fluid filtered by the kidneys may contain various microscopic elements, which precipitate when the urine settles. In turn, it is divided into organic and inorganic.
Sediment is sometimes observed if urine is delivered to the laboratory later than expected, but if the biomaterial was delivered on time, then its presence indicates the presence of pathology. This is often evidence of a high content of crystals of mineral salts of various compositions (phosphates, urates, oxalates).
Urine analysis in children: norm and interpretation according to the table / Mama66.ru
A urine test in a child is carried out quite often and in most cases this is not associated with the determination of any pathological processes or deviations from the norm in the baby, but is, in combination with a clinical blood test, an indicator of the normal growth and development of the child at different age periods.
Laboratory tests help the doctor timely identify minimal functional deviations in the maturation of the baby’s organs and systems and correct them in time or prescribe correct and timely treatment for the pathology.
Correct interpretation of a child's urine test is of great diagnostic importance. Only a doctor can do it, but parents also need to be familiar with the norms of a general urine test in a child and know under what pathological conditions deviations may occur.
The table with a transcript of the urine test will clearly demonstrate how the main indicators of the general urine test differ in children in normal conditions and in pathological conditions. The transcript shows the values of indicators for infants and newborns.
Analysis indicators Norm in a general urine analysis of a child Possible deviations
| General physical properties | ||
| Urine color | From straw yellow to amber yellow. In newborns, the urine is almost colorless, and in breast-fed infants, the urine is light lemon or soft straw color. | Dark yellow color - for diseases that are accompanied by dehydration with diarrhea and vomiting, and heart failure. Very dark urine (the color of tea or dark beer) can be observed with liver pathology - the color is due to the presence of bile pigments or urobilinogen, with diseases of the gallbladder or some infectious diseases. Red color (“meat slop”) can occur with glomerulonephritis, kidney injuries, hemorrhagic cystitis, and urolithiasis. |
| Urine clarity | Completely clear urine | Turbid urine is an indicator of inflammatory diseases of the urinary system, dysmetabolic nephropathy, amyloidosis or the presence of lymphostasis in the kidneys |
| Relative density |
| A decrease in this indicator can occur with heavy drinking, diabetes insipidus, chronic pyelonephritis, while taking diuretics, or when eating a large amount of plant products (vegetables and fruits). An increase in the specific gravity of urine can be observed with dehydration, diabetes mellitus, kidney disease with impaired concentration function, with profuse sweating and the predominance of meat in the baby’s diet. |
| pH (acidity) of urine | From 4.5 to 8.0 This indicator depends on the time of collection of the analysis:
| The acidity of urine can change:
|
| Presence of biological substances | ||
| Protein in urine | Absent (traces of protein not exceeding 0.033 g/l are allowed). In newborns, the level of protein in the urine is normally allowed to increase to 5 g/l. | Proteinuria (the presence of protein in the urine) can be observed in inflammatory or infectious-allergic diseases of the kidneys (glomerulonephritis, nephrotic syndrome, renal sclerosis or amyloidosis), in diseases that are accompanied by febrile conditions. In children during the period when they begin to walk and stand for long periods of time, an increase in protein in the urine is considered physiological and is defined by the term “orthostatic proteinuria.” |
| Sugar urine | Absent or allowed no more than 0.8 mmol/l. In newborns, urine sugar can normally be elevated and this is not a pathological condition. | Glucosuria (sugar in the urine) can occur at a certain stage of diabetes mellitus, acute pancreatitis, nephrotic syndrome, pheochromocytoma, as well as when there is a large amount of sweet or starchy foods in the baby’s diet |
| Bilirubin, urobilinogen or bile pigments | Absent | The presence of bilirubin, urobilinogen or bile pigments in the urine is an indicator of the development of pathology of the liver or gall bladder (hepatitis, cholelithiasis, cirrhosis), hemolytic anemia, some infectious diseases, severe colitis. |
| Ketone bodies | Not defined | Ketone bodies include acetone, acetoacetic and hydroxybutyric acids. They can be detected in urine in dysmetabolic disorders, which are accompanied by acetonemic vomiting and in diabetes mellitus. |
| Sediment microscopy | ||
| Leukocytes | Up to 6 leukocytes per field of view | An increase in leukocytes in the urine occurs with acute and chronic diseases of the urinary tract and/or with infections of the external genitalia. |
| Red blood cells | Absence or presence of single red blood cells (no more than three elements). In newborns: the normal indicator is up to 7 elements in the field of view. | Inflammatory or non-inflammatory diseases of the kidneys (most often glomerulonephritis) and urinary tract, reactive hematuria in severe diseases of other organs and systems, prolonged stress. |
| Cylinders | None | The cylinders are specific casts of various protein cells and pigments. Cylindruria develops in various inflammatory kidney diseases. |
| Epithelium | The presence of squamous and transitional epithelium in small quantities | Flat or transitional epithelium is found in large quantities during inflammation of the urethra, bladder and ureters, dysmetabolic nephropathy, and urinary stagnation. The presence of renal epithelium during sediment microscopy indicates renal pathology. |
| Salt crystals | Absent, small amounts of urates and oxalates are acceptable. The presence of a large amount of salts during the adaptation period of a newborn (up to a month) is “uric acid diathesis.” | Dysmetabolic nephropathy, urolithiasis |
| Slime | Absent or found in small quantities | A large amount of mucus can be observed with inflammation of the lower urinary tract and kidneys, dysmetabolic nephropathy, inflammation of the genital organs (phimosis, vulvovaginitis), with prolonged stagnation of urine, and improper analysis. |
| Bacteria | None | Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urinary system or external genitalia, failure to comply with hygiene standards |
How to take a child's urine test
To obtain objective results, it is important to correctly collect the child’s urine for analysis. To do this, parents must follow the following rules.
- A morning portion of urine is collected with an interval between urinations of no more than 6 hours.
- Before urinating, it is necessary to wash the baby's genitals with warm water.
- Urine is collected in a urine collector or a special sterile container.
- Collected urine should be stored in a closed container and in a cool place for no more than three hours.
Don't panic if you find any abnormalities in your child's urine test. Contact your doctor for clarification. only a specialist can determine the severity of deviations in relation to other factors.
Author: Olga Ivanovna Sazonova, pediatrician
Educational program on the topic
We recommend reading: Original ideas for organizing discharge from the maternity hospital
You are here: Home » Child » Child’s urine analysis: interpretation and explanation
mama66.ru
Hygiene before urine test collection
Remember that cleanliness of the external genitalia is the key to an accurate urine test result.
Bacteria that accumulate on the skin with the material end up in the container, causing the laboratory technician to write an unreliable result.
However, a large number of bacteria in the urine, while other indicators are normal, almost always indicates poor hygiene before the test, and the doctor requires a urine retake.
Both girls and boys should be washed from front to back to prevent bacteria from the external opening of the rectum from reaching the external genitalia:
- We wash with warm water and a small amount of baby soap, which we then rinse well.
- We do not use herbal decoctions - they can cause allergic reactions.
Usually there are no problems with an older child:
- If the child already understands that he needs to go to the toilet, we simply ask him to do it. It is advisable to carry out the procedure in a bathtub so that an average portion of urine can be collected in a container.
- We put the baby in the bath and turn on the water. The baby will react to the pouring liquid by urinating.
- You can give water during the process so that the child urinates faster.
- If possible, turn on the sounds of running water on your computer or phone.
- You can provoke urination by placing the child’s palm in a bowl of warm water.
You can buy special urine bags at the pharmacy - they are glued to the skin around the external genitalia, and urine is collected in a sterile container:
- If you don’t have a urinal, you can patiently wait with a jar in your hands for the next urination, but this method only works with babies 1-2 months old: more active children will not lie still!
- Another option is a thick, sterile disposable bag, but this method is only suitable for boys.
- For girls, the option for collecting urine is a shallow plate or saucer, but if possible, you should still use a sterile disposable urine bag.
The minimum amount of material is 50 ml.
For newborns, at least 20 ml is usually sufficient.
A smaller amount of urine will not allow you to determine all the parameters that a general urine test usually requires.
Errors
What not to do when collecting urine:
- You cannot take urine for analysis from a potty, from an oilcloth, and even more so from squeezing it out of a diaper. The results of such analyzes will be distorted.
- You cannot take urine for analysis from the second, third and subsequent “trips to the toilet”.
- Do not keep urine in the refrigerator for a long time or freeze it.
- Use a dirty container for urine or fail to wash the baby.
- Donate urine after the child’s intense stress - physical or emotional.
- It is also not worth giving urine immediately after vaccination.
Why do you need a general urine test?
- This study is prescribed to children during medical examination. Usually it is carried out in the maternity hospital, then at 1, 3, 6, 12 months, 2 years. Further - according to indications.
- Examinations before admission to kindergarten and school.
- OAM must be taken after treatment of various diseases, for example, ARVI. It will display the functioning of the kidneys, digestive system and other organs. It is important to know how the infection has affected the body, as well as the medications prescribed (especially antibiotics).
- A urine test shows how the kidneys and the urinary system in general are working.
- It is important to donate urine after a child has had bacterial infections, which often impair kidney function.
- OAM is prescribed before vaccination to make sure that the baby is healthy.
- For the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus as a screening.
What do leukocytes in a child's urine indicate?
Leukocytes, or white blood cells, are the basic functioning units of human immunity. Thanks to them, the body is protected in the event of pathogenic bacteria, viruses or toxic substances, so the level of leukocytes increases to carry out its activities.
This allows white cells to fight the invading infection. They rush towards the pathogen or toxin and concentrate in the affected area. Most pathologies are accompanied by an increase in leukocytes in the blood or lymph.
But since the urinary system is connected to another biological fluid, which is also easily taken for analysis, and is almost the first to respond to the occurrence of pathology, it is this fluid that is used to diagnose these organs. That is why, if a child has an increased number of leukocytes in his urine, the first thing the doctor needs to do is conduct a detailed examination of the urinary tract.