About cytomegalovirus
Cytomegaly is a common viral infection that is transmitted through blood transfusions, household, sexual and intrauterine routes.
They first learned about the disease in the mid-50s. Its peculiarity lies in its affinity for the tissues of the salivary glands, in which the virus can be detected. CMV is present in the human body until the end of life. The low level of infectiousness makes it safe for family, friends and friends. Once you know how cytomegalovirus is transmitted, you can relax. To become infected, you need prolonged, close and frequent contact with someone infected. Infection occurs even when the parasitic bacteria are passive. A strong immune system is able to cope with the threat, eliminating symptoms. In this case, the viral cells remain in the body.
Important! The striking symptoms of cytomegalovirus should never be ignored by three groups of people: pregnant women, people with a dysfunctional immune system, and those who often experience recurrent herpes.
CMV is found in urine, vaginal mucus, semen, blood cells, and tears. They determine the ways in which a healthy person becomes infected. But not all people who carry the virus are sick. There are many cases when it does not manifest itself in any way, even in the human body for many years. Often, the manifestation of cytomegalovirus in men, women and children occurs when the immune system is weakened. Serious complications occur in people who take immunosuppressive drugs, have bone marrow transplants, or are infected with the human immunodeficiency virus.
Attention! Half of adults and 15% of teenagers develop antibodies to cytomegalovirus during adolescence. Approximately 80% of women of childbearing age become infected with the infection, which is asymptomatic.
Even if cytomegalovirus is detected in a smear of a human carrier, he cannot be called sick. The infection can remain in an inert state for years and not manifest itself in any way. Symptoms appear in rare cases and in a certain group of people.
Prevention
According to the Women's Forum, the spread of cytomegalovirus is often preventable because it is most often transmitted through contaminated body fluids that come into contact with the hands and then ingested through the nose or mouth of a susceptible person; its microorganisms are present in urine, blood, lymph, secretions vaginas, etc. People who interact with children should use safe hygiene practices including sanitizing hand washing and using gloves when changing diapers. Hand washing with soap and water is effective in preventing the spread of CMV. In any case, the main carrier of the disease is humans.
Climate change also has a good result; recently, clinical studies have shown that women from large cities are more susceptible to CMV than from small towns. You can reduce CMV rates by taking herbal teas and infusions (consult with specialists first).
Transfer methods
In developed countries, they know well what kind of infection cytomegalovirus is. According to statistics, 95% of the world's population are carriers of the virus. In the USA and other economically and socially developed countries, approximately half of the residents have antibodies to CMV. In rural areas of third world countries, almost everyone is infected.
Methods of transmission of the CMV virus:
- When receiving blood transfusions or using contaminated instruments. There are cases when the virus infected the body during organ and tissue transplantation, transfusion of infected donor blood, or the use of infected eggs and sperm. Sometimes doctors (dentists, surgeons, gynecologists) become infected with CMV, spreading the infection to their patients.
- During sexual intercourse. Infection occurs not only during classic sex, but also during oral or anal sex.
- Contact during touching, kissing. Cytomegalovirus is not transmitted from cats, so you can safely play with your pet.
- From mother to child during breastfeeding.
- By airborne droplets (during kissing, using shared dishes, the same toothbrush).
- Infection of the fetus in utero.
Despite the fact that the contagiousness of the virus is low, it spreads easily in villages with poor hygiene. Due to its widespread occurrence, it is difficult to protect yourself from it.
Symptoms
For the first two months, CMV is in the incubation period, when no symptoms are visible. The person is not even aware of the infection, leading his usual way of life.
Important! The acute phase of cytomegalovirus lasts 2-6 weeks. It goes into a calm form if the body has no strength. In this case, symptoms of VSD appear; in rare cases, damage to internal organs is detected.
If symptoms of VSD appear, it is necessary to donate blood for cytomegalovirus. This is especially important for pregnant women, as they are at risk.
The most common and common symptoms of CMF infection:
- General weakness, malaise.
- Increased body temperature.
- Muscle pain.
- Cough, bronchitis.
- Severe headaches.
- Chills, sweating.
Due to general intoxication, the immune system is rebuilt and prepared for protection. But if the strength is not enough, the acute phase turns into a calm one. At this stage the following appear:
- Lesions of the urinary and genitourinary systems. They are poorly treated with traditional methods using antibiotics. Specific drug therapy is required. Lesions manifest themselves in the form of periodic atypical inflammations.
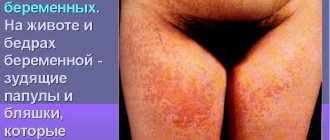
- Damage to internal organs: gallbladder, spleen, kidneys, adrenal glands, etc. If not treated in a timely manner, patients develop pneumonia and bronchitis, which further aggravate the situation and suppress the body’s immune system. In parallel with these diseases, damage to the intestinal walls, a decrease in the number of platelets, and dysfunction of the central nervous system, brain, and blood vessels are observed. Many photos of cytomegalovirus show a skin rash, which is one of the symptoms of damage to internal organs.
- ARVI. With an acute respiratory viral infection, classic symptoms appear: a sharp decline in performance, weakness, muscle pain, elevated body temperature, runny nose, inflamed tonsils (rarely), inflammation of the salivary glands. In severe cases, problems with coordination of movement, vision and hearing are observed.
In the latent form, cytomegalovirus does not manifest itself in any way, but as soon as a person gets sick, symptoms are immediately visible. Pregnant women should beware, because the consequences for children can be very serious. The doctor will tell you what cytomegalovirus affects and what tests need to be taken to determine infection. Symptoms in pregnant women are the same as in ordinary people: headaches, enlarged lymph nodes, fever, body aches.
What kind of disease
Cytomegalovirus infection occurs when a viral pathogen belonging to the category of herpes viruses, which is considered conditionally pathogenic, enters the body. The virus is included in the list of TORCH infections, as are infectious pathologies such as rubella, herpes or toxoplasmosis. These TORCH infections are especially dangerous for gestation and fetal development; even after the baby is born, they can have a long-term negative impact.
Cytomegalovirus, according to statistics, is present in approximately half of the world's population (no more than 60%) and can be acquired or congenital in origin. Pathology can occur in various forms:
- The mononucleosis-like cytomegalovirus form is typical for patients with a weak immune status. Symptoms can be similar to a common cold infection. Usually this form does not pose a danger, because the body often copes with such an infection on its own. At the same time, the virus does not disappear from the body; it simply falls asleep temporarily and lives hidden.
- Asymptomatic CMV or a latent form of pathology is detected in patients with a strong immune status. It manifests itself for a long time without any clinical symptoms. Such forms are called carriage. When immunity decreases, the virus is reactivated. In pregnant women, as a rule, the immune status decreases after conception, thereby provoking the development of CMV infection.
- The generalized form of CMV is very severe, affecting most systems and organs of the patient. It is often detected in newborns up to 3 months of age who were infected with cytomegalovirus infection in utero during pregnancy. A similar form also occurs in patients with HIV. Sometimes it occurs during transfusions of donor blood and its components, during tissue or organ transplants.
- The cytomegalovirus hepatitis form is considered a very rare variety. The symptoms are very similar to hepatitis of viral origin, occurring with jaundice, hyperthermic reactions, change in the color of stool and a general deterioration in health. Approximately a week after the onset of acute symptoms, the signs subside, indicating chronicity of the infectious process.
If ordinary patients, with proper therapy, can still cope with a viral infection, then when carrying a child, CMV infection can provoke various kinds of complications.
Cytomegalovirus in women
Expectant mothers whose immunity weakens during pregnancy are at high risk. In women, the “initial acquaintance” with the virus is asymptomatic. Then a clinic like ARVI appears. The acute period is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Weakness, lethargy, apathy.
- Low-grade fever for a week or longer.
- Throat irritation.
- Pain in joints and muscles.
Once the virus enters the body, it remains there for life. Treatment of CMV infection in adults consists of eliminating symptoms and diseases caused by cytomegalovirus. The immune system produces special IgG antibodies, which, in the event of an exacerbation of infection, quickly immobilize pathogens. Relapses are most often observed in people with weak immune systems.
Important! In most cases, CMV occurs without symptoms and the body is able to cope with the infection on its own. But women have complications when the ovaries, vagina, inner layer and cervix are affected. Among the consequences, doctors highlight loss of vision and internal bleeding of the affected organs. In the most severe cases, death is possible.
Knowing how dangerous cytomegalovirus is, women should get tested. To determine infection, the PCR method and immunological testing are used. In the first case, the doctor detects the DNA of the virus in biological fluids, in the second, the presence of antibodies to the virus is determined. PCR research allows you to determine active forms of infection in specific places. For this, a swab from the mouth, nose, anus, urethra, vaginal and cervical secretions, and mother's breast milk can be used.
Cytomegalovirus during pregnancy
When planning a pregnancy, it is important for a woman to be screened for TORCH infection. The information obtained makes it possible to develop tactics in the event of detection of high titers of Ig M or Ig G. If a woman is already carrying a child, she still needs to be diagnosed for the presence of CMV. The further picture will develop depending on the results obtained:
- Negative Ig titers detected for cytomegalovirus indicate the need to monitor the pregnant woman at 20, 30, 31 and 32 weeks in order to exclude primary infection during gestation.
- If cytomegalovirus Ig G is positive, another examination will be needed only according to the doctor’s indications, for example, if there is a suspicion of intrauterine infection of the fetus.
- Positive ig M of cytomegalovirus is the reason for additional diagnosis. It allows you to clarify the prognosis, prescribe the correct treatment or the need to terminate the pregnancy.
In rare cases, an examination is prescribed for the entire TORCH complex. It is necessary in cases of impaired blood flow in the umbilical cord, fetal death, dysfunction of the placenta, suspected intrauterine infection, polyhydramnios and other dangerous diagnoses.
High-quality diagnostics and competent interpretation of the results make it possible to avoid fetal malformations, serious complications during pregnancy and neonatal losses.
Why is CMV infection especially dangerous in pregnant women? This is due to 3 factors:
- Permeability of membranes.
- The virus easily passes through the placenta.
- Weak immune system.
The most dangerous situation occurs when the expectant mother becomes infected with CMV infection for the first time. There are no antibodies in the body that would fight the threat. Because of this, a large portion of pathogens reaches the fetus. The consequences of cytomegalovirus during pregnancy are unpredictable. In the early stages there is a threat of miscarriage, frozen pregnancy, and developmental defects. Infection in the last months of pregnancy is no less dangerous: congenital CMV viral infection, premature birth, fetal death.
Symptoms of cytomegalovirus in a newborn may not appear immediately. Symptoms such as hemorrhages on the skin and mucous membranes, enlarged spleen and liver, jaundice, pathology of dental development, visual and hearing impairment, encephalitis are typical. Children born with the CMV virus are always complex and weak. They are often premature due to placental abruption or premature release of water. As practice shows, a high mortality rate remains.
How is cytomegalovirus infection dangerous for the fetus?
Cytomegalovirus infection is the leading disease among congenital viral infections of newborns. Approximately 1-2% of children are born with the CMV virus in their body. But infection does not always mean illness! However, CMV infection can cause profound pathologies in children. Both primary infection with the virus during pregnancy and reactivation of an infection already living in the body are dangerous.
The concept of “immunity to CMV” does not exist!
Carriers of the CMV virus aged 30 to 40 years are 50% of the population, and in developing countries - up to 90%.
Primary infection occurs in 0.7-4% of all pregnant women. Return infection (reactivation) can occur in 13% of previously infected pregnant women.
An active cytomegalovirus infection that has penetrated the fetus leads to:
- intrauterine fetal death (miscarriage, spontaneous abortion, stillbirth - up to 15%),
- the birth of a child with congenital CMV infection, which is manifested by developmental defects (microcephaly, hydrocele, jaundice, enlarged liver, spleen, hepatitis, heart defects, inguinal hernia, congenital deformities),
- the birth of a child with congenital CMV infection, which does not appear immediately, but in 2-5 years of life (blindness, deafness, speech inhibition, mental retardation, psychomotor impairment).
- the birth of a child with disorders caused by insufficiency of the function of the feto-placental complex.
But a healthy child can be born without any problems.
Clinical manifestations of primary CMV infection resemble ARVI.
Clinical manifestations of CMV reactivation:
Basically, cytomegalovirus worsens asymptomatically. However, it also happens differently.
- If a person has both the herpes simplex virus and CMV in the body at the same time, they often become aggravated at the same time. Therefore, a “cold” on the lip is a reason to be examined for CMV.
- White-bluish discharge from the vagina.
- Any rash on the skin (even isolated ones). They differ from pimples in that they appear simultaneously and do not have a purulent head - just red dots.
- The appearance of small hard subcutaneous formations on the labia minora or majora.
- In some cases, the only sign of the disease is inflammation of the salivary glands, where the cytomegalovirus feels most comfortable.
If you have at least one of these symptoms during pregnancy, you should urgently start testing for cytomegalovirus!
The risk of transmitting cytomegalovirus to the fetus can be reduced if both partners who are CMV carriers undergo treatment before conceiving a child.
The duration of pregnancy has a significant impact on the incidence of infection in the mother's body. In the early stages of pregnancy, the production of cytomegalovirus is suppressed, but this suppression decreases as pregnancy progresses, and by the third trimester the likelihood of reactivation of the infection increases.
Taking drugs that suppress the production of antibodies in the body (metipred, for example) also increases the likelihood and degree of intrauterine damage to the fetus.
Cytomegalovirus in children
The choice of treatment method depends on the age of the child. In children under 6 years of age, the immune system is not yet well developed, so symptoms that appear are treated with conservative methods. To reduce the activity of CMV infection in older children, antiviral drugs and immunoglobulins are used. The first ones are toxic and are prescribed by the local pediatrician. They are given to the child only when absolutely necessary.
Symptoms and treatment of cytomegalovirus in older children are almost the same as in adults. The acute stage is characterized by fever, pain in the joints and muscles, general weakness, lethargy, and swollen lymph nodes.
Cytomegalovirus in men
The virus can remain in the incubation period for up to 60 days. Then manifestations characteristic of ARVI symptoms are possible: fever, loss of strength, low physical activity. High avidity for cytomegalovirus excludes infection acquired within the last four months. Genital cytomegalovirus may not manifest itself for a long time and will make itself felt only when the immune system is weakened.
CMV manifests itself with different symptoms, which are divided into 3 groups:
- Clinical: headaches, body weakness, stuffy nose, enlarged lymph nodes, skin rash.
- Minor: dysfunction of the urinary system.
- Main: intoxication of the body, increased body temperature.
Often, men become infected after intimate intercourse with a female carrier of the virus. In severe cases of the disease, serious diseases such as pancreatitis, pneumonia, encephalitis, and hepatitis may appear.
Cytomegalovirus is second in strength after the human immunodeficiency virus. After an episode of illness, CMF infection does not lead to the formation of stable immunity. If a man is once infected, the parasitic bacteria will remain in the body all his life and will be “activated” when the immune system is weakened.
Complications and consequences of the disease: termination of pregnancy, fetal anomalies
Cytomegalovirus infection is often the cause of recurrent miscarriage. A woman may not be aware of the presence of the virus in her body and suffer from infertility.
With the development of intrauterine cytomegaly, the born child has:
- abnormalities of brain development (hydro- or microcephaly);
- increased bilirubin levels, enlarged liver and spleen at 2–3 weeks of life;
- deafness, blindness, kidney and intestinal diseases.
About 10% of children who have symptoms of congenital cytomegalovirus infection die in the first months of life. Mental retardation and deafness are observed in 60–85% of children with clinical manifestations of the disease from birth and in 20% with asymptomatic pathology.
Diagnostics
There are several methods to determine the presence of CMF in the body:
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Aimed at calculating the DNA of the virus and confirming its presence in the test sample.
- An enzyme immunoassay for cytomegalovirus is performed to detect antibodies in the blood serum.
- A cytological examination is carried out to look for large cells characteristic of a given virus.
- Cell culture culture is a method that provides information about the activity (aggressiveness) of CMF infection.
The most common diagnostic method is cell culture. It does not require special equipment; it allows you to determine the type of virus and its degree of danger. The diagnosis is confirmed by detecting the infection itself or a pattern of increasing IgG antibodies. For this purpose, the analysis is done a couple of times every ten days.
Laboratory and instrumental examinations for cytomegalovirus
Prevention of infection with cytomegalovirus when planning pregnancy is carried out through laboratory diagnostics for TORCH infection. Serological analysis includes the study of peripheral blood for the content of antibodies - IgM and IgG to infections that are dangerous for intrauterine infection of the fetus. These include cytomegalovirus, herpes, rubella, and toxoplasmosis.
Laboratory tests for cytomegalovirus
It is important to undergo a diagnosis before conceiving a child to determine the risk of developing an intrauterine infection during pregnancy. If there is a high risk of infection, preventive and therapeutic measures are taken to preserve the life and health of the unborn baby. If a woman has not been tested for TORCH infections before pregnancy, then laboratory diagnostics are prescribed by a gynecologist when registering with a antenatal clinic.
The level of specific immunoglobulins in the blood helps to establish early previous disease, primary infection or exacerbation of CMV. On the serological test form, a “positive” or “negative” result will be indicated next to each type of antibody. In controversial diagnostic cases, an additional test is prescribed to identify immunoglobulin avidity - the ability of antibodies to bind to an antigen (cytomegalovirus). Let's consider several options for serological diagnostic results.
Result: IgM and IgG negative
The absence of immunoglobulins class M and G in the blood indicates that there was no infection with CMV, and therefore there is no stable immunity to infection. A woman with this test result is at risk for intrauterine infection of the fetus. To prevent infection during pregnancy, doctors recommend adhering to nonspecific preventive measures:
- every 4-6 weeks, take tests to detect IgM and IgG to CMV;
- use individual utensils and hygiene products (toothbrush, washcloth, towel);
- minimize the time spent visiting public places with large crowds of people;
- avoid close contact with small children, who can be a source of infection;
- Avoid contact with people with acute respiratory infections and colds.
For specific prevention, human immunoglobulin "Octagam" is injected every month during pregnancy.
Result: IgM negative, IgG positive
IgG antibodies to cytomegalovirus indicate a previous infection and the presence of stable immunity. During pregnancy, a woman needs to protect herself from colds, acute respiratory infections, stressful situations, eat right and maintain a healthy lifestyle. These measures are enough to prevent relapse of the disease.
Result: IgM positive, IgG negative
The detection of class M immunoglobulins in the blood indicates the acute phase of the infection - primary infection. This is a dangerous situation for intrauterine infection of a child. To establish infection of the fetus and the negative effect of the virus on the body, ultrasound and amniocentesis are prescribed. Fetal ultrasound is performed from the 21st week of pregnancy, no earlier than 7 weeks from the onset of infection. The examination helps to identify malformations and external deformities.
Amniocentesis allows you to collect amniotic fluid and conduct a laboratory analysis to detect the genetic material of the virus - PCR. If the DNA of the virus and severe malformations are detected, the woman is offered termination of pregnancy.
Result: IgM and IgG positive
The detection of immunoglobulins class M and G in the blood indicates either a relapse of the disease or a primary infection in the recovery stage. To clarify the time of infection of the woman and the fact of infection of the fetus, a laboratory test for IgG avidity is prescribed.
If the immunoglobulin avidity is high, with an indicator of more than 60%, then the infection occurred no earlier than 20 weeks ago and the risk of infection of the fetus in the first trimester is minimal. If the indicator is intermediate or low, the risk is high. To confirm the diagnosis, fetal ultrasound and amniocentesis are prescribed. A positive PCR result and developmental defects on ultrasound indicate in favor of intrauterine infection of the fetus. The doctor decides on further management of pregnancy after agreeing on the tactics with the patient.
Treatment
It is aimed at reducing symptoms after infection. Those at high risk include infants, people living with HIV, people with weak immune systems, and pregnant women.
CMV infection in children and adults often occurs without symptoms. The body is able to get rid of the threat on its own without medical help. But if symptoms appear, treatment is necessary.
All drugs used in the fight against CMV virus are divided into 5 groups:
- Drugs to bind or eliminate infection cells.
- Means for the restoration of damaged tissues.
- Medicines to strengthen and restore a weakened immune system.
- Blockers of the proliferation of viral bacteria.
- Medicines to alleviate symptoms, all kinds of anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
Treatment of cytomegalovirus in people with HIV and infants should be carried out in a hospital setting under the supervision of a physician. For a quick recovery, those infected are advised to have a light diet, drink plenty of fluids, and rest in bed.