What does low placenta mean?
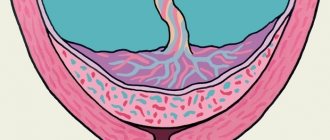
What does low location of the embryonic organ mean? The placenta begins to form in the early stages of pregnancy, completing its formation by 12-16 weeks of gestation.
When the baby's place takes the correct position - high on the anterior or posterior uterine wall, it does not interfere with the normal movement of the baby along the birth canal at birth. If it is fixed at the bottom, approaching the cervix, and the distance between the pharynx and the embryonic organ is less than 6 cm, unpleasant consequences may develop.
During pregnancy, the expectant mother must undergo an ultrasound procedure three times:
- From 11 to 14-15 weeks of gestation.
- In the second trimester from 18 to 21-22 weeks.
- At 30-34 weeks of term.
With the help of the study, the location of the embryonic organ is determined, and it is decided whether the woman herself can give birth to a child. When diagnosed with low-lying placenta, do not panic.
The baby's place is able to move upward, away from the internal os due to the enlargement of the uterus. The main migration period is considered to be up to 24 weeks. Closer to childbirth, in most pregnant women, low placentation changes to a high location - 5-6 cm from the cervix. Only 5% of patients remain diagnosed after 32 weeks of gestation.
Step-by-step instructions for checking the cervix
How to understand where the cervix is? This can be done by studying simple diagrams of the structure of the uterus. If you imagine that the vagina is a corridor, then the cervix is the door at the end. While your vagina has a sort of spongy structure that gives in to pressure, your cervix is like a hard, round dimple.
Insert your index or middle finger inside the vagina and slowly move it to the cervix. You will feel it because it is very different from the vagina. If you are not close to ovulating, you should be able to find your cervix easily. If you're ovulating, your cervix may be higher in your body and more difficult to reach.
Causes of pathology
The location of the child's place largely depends on the internal factors of the expectant mother. If a pregnant woman has any diseases or abnormalities of the reproductive system, low placentation is a common occurrence in such women.
Let us consider in detail what exactly the causes of the disease are:
- Surgical intervention on the uterus. Previous operations on the organ (curettage, cesarean section, removal of fibroids with partial resection of the myometrium) are the main cause of the disease. They lead to the fact that it is impossible to attach a child’s place to the damaged mucosa of the upper segment of the organ.
- Inflammatory diseases of the internal genital organs of a pregnant woman.
- Congenital anomalies of the uterus: bicornuate or unicornuate uterus, hypoplasia. Such defects do not allow the fertilized egg to attach correctly, so it is implanted below normal. This is where the children's place is formed.
- Gynecological pathology. Uterine fibroids develop as a node in the thickness of the myometrium, preventing the fertilized egg from implanting in this place. With endometritis, the internal functional membrane is damaged, which disrupts normal placentation. The embryo has to penetrate too low into the endometrium, where a baby's place is formed.
- Woman's age. When an expectant mother becomes pregnant for the first time after 35 years of age, uterine circulation is disrupted, which prevents normal placentation.
- Leading an incorrect lifestyle. Alcohol abuse, active smoking, poor nutrition also contribute to the deterioration of uterine blood flow, which is why the baby's place is not fixed in the fundus of the uterus, remaining below, at the internal os.
- Multiple pregnancy.
How and why is the height of the uterine fundus determined?
Data on the height of the uterus must be entered into the patient’s exchange card after each scheduled and unscheduled visit. Before the appointment, the expectant mother needs to prepare for the examination, for example, to empty the intestines in a timely manner. A full bladder can also distort the actual indicators of UMR. In addition, a pregnant patient should carefully consider her outfit. The expectant mother should choose comfortable and loose clothes. It is better for patients to avoid clothing that squeezes the stomach or is difficult to remove. Each scheduled inspection usually proceeds according to the following scheme:
- woman's acceptance of a horizontal position;
- palpation of the uterus;
- determining the length from the pubic bone to the top of the uterus using a tape meter.
Despite the fact that the procedure takes less than 1 minute, it is very informative. Usually, after fixing the height of the uterine fundus, the obstetrician measures the abdominal circumference in order to determine the estimated volume of amniotic fluid. These measurements are less accurate than the VDM, as they depend on the thickness of the fat layer on the abdominal wall and the individual characteristics of the woman’s physique. In accordance with the gestational age, the gynecologist makes conclusions about the development, position of the fetus and the amount of amniotic fluid.
A woman can independently find out where the fundus of the uterus is located at home. To do this, you need to lie down, apply a measuring tape from the pubic joint to the point at which the stomach ceases to be hard. This length is the VSDM.
Possible consequences
Low placentation is by no means a harmless condition. Under certain conditions, it can lead to serious complications, including the death of a baby or woman.
Threats to the mother
The most unfavorable consequence is placental abruption. The disease threatens a pregnant woman in several ways.
A small separation of a child's place: the pathological process may be without pain, but with the appearance of bleeding. When blood accumulates inside the uterine cavity, the woman has no spotting. Severations of a child's place are prone to recurrence: their number increases with the formation of a threat to the development of the fetus. A pregnant woman develops anemia, accompanied by a feeling of fatigue, headache, and a feeling of lack of air.
Peeling off of a large fragment of an embryonic organ entails heavy bleeding in the expectant mother, which can lead to death if medical assistance is not provided in time. Blood begins to accumulate inside the uterine cavity, its layers become saturated with contents that penetrate the peritoneum. This pathology is called Kuveler's uterus. Due to a serious threat to the life of the expectant mother, a caesarean section must be immediately performed to remove this organ.
Threats to the baby
At a period of 19-20 weeks, a low location of the placenta threatens the baby with the development of oxygen starvation. The fetus grows, increases in size, and its pressure on the uterine cavity increases, compressing the blood vessels of the placenta and disrupting blood flow. The cervix is anatomically poorly supplied with blood compared to the fundus.
Incorrect position of the child's seat leads to hypoxia in a child with intrauterine growth retardation. In addition, when the baby makes active movements, damage to the child's seat may occur. Low placentation threatens complications during childbirth: this position prevents the baby from leaving the womb.
When implantation of the embryo is disrupted, a concomitant disease appears, such as the marginal location of the placenta. With this pathology, the embryonic organ is localized less than 2 cm from the internal os. This can lead to complications during childbirth with the death of the child.
Detachment of an embryonic organ threatens disruption of intrauterine development or even death of the fetus. This is due to the fact that the separated placenta does not take part in the nutrition and protection of the child. At an early stage, the consequences are minimal, but with total detachment, acute hypoxia occurs, followed by the death of the baby.
Where is the uterine fundus located before pregnancy?
This article talks about typical ways to solve your issues, but each case is unique! If you want to find out from me how to solve your particular problem, ask your question. It's fast and free
!
Many women are interested in where the uterine fundus is located. This is the highest point protruding above the pubic joint. In a woman who has not given birth, the length of the uterus is approximately 7 cm. As soon as a fertilized egg is introduced into its mucosa, its size begins to gradually increase. In the early stages, the bottom is located slightly below the navel and rises as the organ with the child inside grows. The determination is made in two stages:
- external manual examination of the uterus;
- measuring abdominal circumference and VMR using a centimeter tape.
External palpation of the uterine fundus becomes possible only from the 16th week of pregnancy (more details in the article:). Before this period, UMD can only be determined by vaginal examination.
Features of childbirth with a low placenta
How exactly a woman with such a disease will give birth is decided by the attending physician. At 37-38 weeks of gestation, the pregnant woman is hospitalized in the pathology department so that she is under constant supervision.
Before labor begins, the baby's place can rise to an acceptable distance. In this case, natural childbirth is possible. If this does not happen, low placentation leads to overstrain of the blood vessels with their subsequent rupture with premature placental abruption. That is why its low position at 38 weeks is an indication for a cesarean section.
The doctor may choose to puncture the membranes so that the placenta is secured by the baby's head. Specialists perform this delivery in the operating room so that, if necessary, a caesarean section is performed.
Symptoms during ovulation
- Nagging pain in the lower abdomen near the ovaries (right or left). The pain is similar to that which occurs during menstruation. This may indicate that the egg has begun to mature. The duration of this process is different for everyone - from 10 minutes to 2 hours.
- Clear cervical fluid (similar to egg white) is released. Normally, this discharge is cloudy in color.
- The level of progesterone, a hormone that helps the inner layer of the uterus to secure a fertilized egg, and thereby bear a fetus, is increased.
- Most girls experience an increased craving for sex - this means the egg will mature in just a day.
- Breast enlargement occurs due to a large amount of hormones.
How to cure the disease
Having learned the diagnosis, you should not worry and try to figure out the question on your own: “What to do with a low-lying placenta?” If pathology is detected at 13 weeks, the doctor recommends following simple steps that help normalize the condition and prevent the development of complications.
What needs to be done - let's figure it out:
- Be sure to wear a bandage.
- Avoid any physical activity. Replace them with slow walks in the fresh air.
- Try not to climb stairs.
- Do not carry heavy objects under any circumstances.
- Eat nutritiously and regularly.
- Avoid sexual intercourse for a while.
- Minimize travel on public transport.
- Avoid any sudden movements.
- Do not sit cross-legged.
- Try to avoid stressful situations.
- Place a bolster or pillow under your feet so that your limbs are positioned higher than your body. This stimulates the placenta to move to its normal position.
- Do not perform any intravaginal procedures (for example, douching).
- If your doctor recommends hospitalization, be sure to follow the instructions.
Reviews on forums report that there are exercises for raising a child's seat. In fact, any physical activity threatens with adverse consequences for both mother and baby, so you should forget about gymnastics if an illness occurs .
If a low location of the placenta is detected at 21 weeks of gestation, these recommendations will also be relevant for the woman. If the rules are followed and the reaction is favorable, by the 30th week the embryonic organ rises. However, if the situation has not changed, do not panic. In most situations with this disease, pregnancy ends successfully with the birth of a healthy baby.
If a woman notices bleeding at any time, she should immediately call an ambulance: hospitalization with a course of medication will be required.
The following groups of drugs are used:
- Sedatives – valerian, motherwort.
- Hemostatic medications – Tranexam. They prevent bleeding when placental abruption occurs.
- Antibiotics – cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones. Used to prevent infection when placental hematomas appear.
- Metabolics – Actovegin. Prescribed to prevent insufficiency in the uterus-placenta system.
At the discretion of the specialist and depending on the specific situation, other medications are prescribed.
The norm of GMD depending on the stage of pregnancy
In the first trimester, the fundus of the uterus with normal indicators looks like this:
- 9 weeks – 9 centimeters. At this stage, the uterus is approximately the size of a goose egg. UMR is measured through the vagina.
- 13 weeks – 11 centimeters;
- 15 weeks – 15 centimeters;
- 17 weeks – 18 centimeters;
- 19 weeks – 20 centimeters;
- 21 weeks - 23 centimeters. At this stage, the fundus of the uterus is approximately 2 fingers below the navel;
- 23 week – 26 centimeters.
- 25 week – 27 centimeters. The fundus of the uterus is parallel to the navel;
- 28 weeks – 28 centimeters. The fundus of the uterus is located two fingers above the navel;
- 30 weeks – 31 centimeters;
- 32 weeks – 32 centimeters. The uterus is located midway between the navel and the xiphoid process of the sternum;
- 36 weeks – 37 centimeters. The fundus of the uterus is located at the junction of the costal arches;
- 38 weeks – 38 centimeters. The height of the uterine fundus begins to decrease;
- 40 weeks – 34 centimeters. The fundus of the uterus is located midway between the navel and ribs.
If the pregnancy is proceeding normally and the UMR indicators are normal, then the woman should not feel her uterus growing. The only thing is that in the first weeks of pregnancy a woman should feel some unusual sensations, but they should not be painful in any way. If the expectant mother feels pain in the uterine area, she should immediately consult a doctor.
Preventive measures
Pregnancy planning is the main measure to prevent low placentation in the expectant mother. If there are existing diseases of the organs of the reproductive system, it is necessary to treat them in a timely manner so that the pathology does not interfere with the implantation of the fertilized egg in a normal place.
Other recommendations:
- Try to avoid abortion, miscarriage and other conditions that require curettage of the uterine cavity.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle: stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
- The optimal age for the birth of your first child is no older than 35 years, so it is recommended not to delay your first pregnancy.
- Agree to have a cesarean section when there are medical indications for it.
- Make sure that all gynecological surgeries are performed by a qualified and experienced professional.
Self-examination tactics
The cervix looks like a cylinder. It connects the body of the uterus and the vagina. Its length reaches 4 cm and width - 2.5.
Monitoring the condition of the cervical uterus is not difficult if you understand the nuances of this process. Many people don’t know how to tell if the cervix is high or low, hard or soft. Carrying out a self-examination for 2-3 months makes it possible to understand all the features of the behavior of the cervix within one cycle.
Before starting the examination, you should wash your hands well with soap. Experienced women say that it is best to determine the condition of the cervix in the following poses:
- squatting;
- sitting comfortably on the toilet with your legs spread wide apart;
- standing, while one leg must be placed on a raised platform (edge of a toilet, bathtub, chair).
One examination per day is enough. They say that the cervix has risen high if it is difficult to immediately feel. The finger used for the examination has to be inserted as deeply as possible. When positioned low, many can touch it with the pad of their finger.
If the neck is hard, then its density is similar to the tip of the nose. The softened neck feels like lips. You can also evaluate the degree of opening. When closed, a small gap is felt in its center; when open, a round hole is felt.