Pyelonephritis is an infectious kidney disease that brings a lot of troubles to the child: frequent painful urination, pain in the lower back and lower abdomen, and a constant increase in body temperature. The disease affects almost all structures of the kidney. Timely diagnosed pyelonephritis in children and its effective treatment will help restore kidney function and save children from suffering.
What is pyelonephritis in children?
Children's pyelonephritis in medicine is divided into primary and secondary. The first form is characterized by the absence of any abnormalities in the urinary system. In the secondary form of the disease, pathologies of the urinary tract and kidneys are detected. Against this background, the development of obstructive (urinary function is impaired) or non-obstructive (dysmetabolic disorders) pyelonephritis is possible.
The second classification divides the disease into acute and chronic forms. Acute pyelonephritis in children lasts a couple of months and is cured without further relapses. The chronic form of the disease progresses over six months with constant exacerbations. But there are cases when this form of pathology occurs latently, that is, it does not manifest itself in any way.
Possible complications
Hemodialysis is an integral procedure for renal failure.
Lack of proper treatment for the acute form of the disease can lead to two main consequences:
- transition to a chronic form;
- development of a purulent abscess.
If we consider chronic pyelonephritis in children, then in the absence of proper treatment, this condition can cause the development of more serious health problems, in particular, lead to tissue necrosis or sclerosis.
The chronic form of the disease can provoke the development of:
- kidney failure, which will require regular dialysis and, possibly, organ transplantation;
- arterial hypertension;
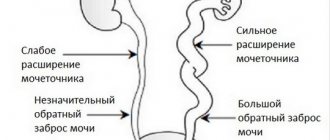
- hydronephrosis, which will lead to a deterioration in the normal function of the excretory organs.
Symptoms of the disease
Signs of pyelonephritis depend on the form in which the disease occurs.
Acute form of pathology:
- Intoxication. The child’s body temperature rises to 40 degrees, chills appear, the heartbeat quickens, nausea and vomiting begin, and, as a result, weakening and dehydration of the body, and lack of appetite.
- Painful and frequent bowel movements . The baby often asks to go to the potty, grunts for a long time and only then pees, while writhing in pain and screaming. The urine begins to smell specific. Children under 3 years old often complain of pain in the lower abdomen.
- Regurgitation and bad stool . Symptoms of pyelonephritis in children often resemble gastrointestinal disorders. The baby is losing a fair amount of weight. This is especially dangerous for premature babies.
- Laboratory indicators . In children with pyelonephritis, leukocytes are increased in the urine and erythrocyturia occurs. Blood hemoglobin is low, neutrophils are high (this indicates the development of a bacterial infection).
Treatment of acute pyelonephritis
Treatment of acute kidney inflammation should be carried out in a hospital, especially if we are talking about an infant or one-year-old child. Children with suspected pyelonephritis are usually hospitalized in the nephrology or urology department. Many parents refuse to stay in the hospital, but this is really necessary to monitor the dynamics of the results of clinical and instrumental diagnostic methods.
Therapy of pyelonephritis in pediatrics requires complexity. The components of the treatment of kidney inflammation in children are the following components.
Drug therapy
Treatment of pyelonephritis, first of all, requires taking antibacterial drugs, such as:
How does the disease manifest itself in newborns?
The causes of the disease in infants are congenital pathologies of the kidneys and urinary tract. Also, signs of pyelonephritis in a child under one year of age appear as a result of acute respiratory viral infection, bacterial or viral infection.
Symptoms of the disease in an infant:
- The temperature rises sharply to 39-40 degrees, convulsions are possible.
- Urination becomes either too frequent or, conversely, very rare.
- Urine smells bad, changes color, and becomes cloudy. Sometimes blood streaks are observed.
- Diarrhea and vomiting begin.
- The newborn does not sleep well, especially at night.
- During bowel movements, the baby cries or screams.
The pathology occurs in a latent form without manifesting itself in any way. In this form, the disease is recognized by doctors only through tests.
How does the disease affect a child's body?
The causes of pyelonephritis in children are bacteria, viruses, fungi. Their entry into the body and progression leads to inflammation. The main causative agent of the disease in babies is E. coli. Influenza viruses, Staphylococcus aureus, and Proteus are in second place in the activity of damaging children's organisms. The sources of infection in the body are: in girls – the vagina, in boys – the foreskin. The conducted route is often the large intestine.
Microorganisms enter the kidneys in the following ways:
- By blood. This path is typical for infants. The pathogen moves to the kidneys from foci of infection in other organs.
- Through the lymphatic pathways. This type of entry of microorganisms occurs in the case of constipation, diarrhea, dysbacteriosis and intestinal infections.
- Ascending path. Such kidney damage is typical for children older than one year. Bacteria enter the organ through the urethra, anus, and genitals.
Causes of pathology
Pyelonephritis is often recognized in a preschool child. After identifying this disease, the cause must be urgently found.
The main causes of the disease are:
- Kidney tissue can be affected by various pathogenic microorganisms; bacteriological culture of urine reveals: Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and other viruses. Pathogenic microorganisms and viruses can enter the kidneys in all sorts of ways: through blood vessels, through the walls of the ureter, from the bladder through the lumen of the ureter. If several pathogens enter a child’s body at the same time, chronic pyelonephritis may develop.
- Diseases suffered in childhood such as pneumonia or otitis may be the cause of this pathology.
- Bacterial endocarditis or sepsis causes the symptoms of this disease to occur in adolescents; the pathogenic microorganism penetrates from the intestine to the kidney through the lymphatic system. This occurs with intestinal infections, diarrhea in a child suffering from chronic constipation and dysbacteriosis.
- Infection often occurs through the genital area, anus, urethra or bladder. Such infection actively manifests itself in girls 3–5 years of age. Microorganisms can penetrate the urethra, but in healthy children the immune system does not allow such an inflammatory process to develop. However, any acute or chronic illness reduces the body's immune strength.
- Foci of infections that remain in the body for a long time, hypothermia, worms, diabetes, quite often give rise to this insidious disease.
- A disease of the genitourinary area, as well as poor hygiene, can provoke pyelonephritis.
- After a long inflammatory process in the area of the external genital organs, a symptom of this disease often appears.
Diagnosing the disease in children
The doctor listens to all the patient’s complaints and prescribes a series of special tests to confirm the diagnosis. Diagnosis of pyelonephritis in children includes the following studies:
- general and chemical tests of urine and blood;
- urine testing using Nichiporenko, Zimnitsky and other methods;
- tank culture, sediment analysis, urine enzymes;
- antibiogram;
- diuresis study;
- ultrasound of the urinary tract;
- analysis of fluid excreted by the kidneys for fungi and viruses;
- urine cytology;
- CT (computed tomography);
- study of bladder functions;
- cystography and urography.
After conducting a full examination and creating a complete picture of the disease, the doctor prescribes treatment for the baby and, if necessary, hospitalization.
How is the disease treated in children?
Treatment of pyelonephritis in children is carried out only after an accurate diagnosis of the disease. After all, the symptoms of the pathology are sometimes confused with intestinal infection, chronic cystitis and other diseases. Infancy or an acute form of the disease causes the child to be hospitalized, and immediately.
Treatment of acute pyelonephritis in children is represented by the following measures:
- Sticking to a diet. It is recommended to eat according to table No. 5 according to Pevzner. Salt is allowed to be consumed in moderation, while increasing the daily dose of water by 50%. It is necessary to exclude from the diet all spices, fatty, spicy, smoked foods. The consumption of protein and plant foods is encouraged. The diet is part of a large set of procedures used to treat dysmetabolic pyelonephritis.
- Strict bed rest is indicated for a child with pyelonephritis who has a fever and complains of pain in the abdomen and lower back. If there is no fever or pain, the baby is allowed to move around the ward. Next, doctors will allow short walks around the hospital premises.
- Antibacterial therapy. This procedure is the most important point in the treatment of pathology. It is carried out in stages. Before receiving the results of the study, the most effective drug against the most common pathogens is prescribed. After a urine test, a drug is prescribed that can defeat the identified virus or bacteria.
- Uroantiseptics. Pyelonephritis in children is also treated with drugs that kill microbes, stop their growth, thereby disinfecting the urinary tract. The product is not an antibiotic.
- They also get rid of acute pyelonephritis in children by treating them with antispasmodics, antipyretics, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Preventive measures for pyelonephritis
If kidney function is restored and there are no causes of pathology, pyelonephritis will no longer bother the baby. But for this it is necessary to observe a number of preventive measures:
- do not let the child become hypothermic;
- watch your urination - it should be frequent;
- the baby needs proper nutrition, healthy sleep, sufficient fluids and vitamins;
- strengthen children's immunity: walk more, get stronger, play sports;
- Make sure your child follows the rules of intimate hygiene;
- Follow all doctor’s recommendations, conduct examinations and take all control tests in a timely manner.
Pyelonephritis in children, symptoms and treatment shows how serious and dangerous this disease is.
A well-chosen clinic with professional doctors will help the baby get rid of the disease without complications and without harm to health.
Prevention
Remember that the disease can be prevented by following simple rules.
- Make sure that your baby goes to the toilet regularly and does not experience urine retention in the body.
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules.
- Regular bowel movements.
- Prevention of dysbacteriosis.
- Maintaining proper drinking regime.
- Timely and adequate treatment of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Conducting an ultrasound examination of organs in children under one year of age in order to identify anomalies in the anatomical structure.
Now you know what the signs of pyelonephritis in children are, as well as methods of treating this disease. Remember that you can prevent illness by taking proper precautions. Do not self-medicate, do not forget about the possible consequences. Contact a specialist in a timely manner at the slightest suspicion of any deviation.