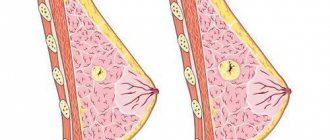
Mammologists and gynecologists strongly recommend regular self-examinations of the mammary glands to timely detect changes in their structure. Detecting lumps at an early stage of development will help prevent transformation or begin timely treatment of malignant tumors. Often, when visiting a doctor, benign neoplasms are detected. In this article we will talk about one of them. Lipofibrosis of the mammary gland, what is it?
What is a lipoma and its signs
Lipoma is a benign tumor expressed by the proliferation of fat cells. Usually it does not degenerate into a malignant tumor, and occurs in different areas except the feet and palms.
A lipoma that forms superficially under the skin is called a wen. Almost all types of lipomas occur specifically in the wen, and only a small proportion (about 5%) extends to the spinal region, peritoneum, chest cavity, muscles and bones. When the disease spreads multiple times, the patient is diagnosed with lipomatosis. Read about what a wen is and how to treat it here.
Hibernoma is a subtype of lipoma, practically no different in appearance from the classic one, and is differentiated using a histological research method. Symptoms, causes and therapy are also similar to classic lipoma.
The mechanism of their development is of 2 types:
- Tumor-like growth. The cambial cell is duplicated by new fat cell clones, and mitotic activity is significantly enhanced.
- Superficial subcutaneous lipomas resulting from malfunction of the sebaceous glands. These lipomas do not have a lobular structure. Often occur in the area of the sebaceous glands.
What is breast lipofibrosis
A lipoma is a benign formation in the fatty tissues of the breast. Such neoplasms can appear in various organs containing adipose tissue.
Lipofibrosis is a common occurrence in women over 40 years of age. If such a benign tumor is found in young girls, then, as a rule, it is a hereditary disease.
There are both single and multiple neoplasms. The latter are extremely rare, but their development should not be ruled out. This disease is complicated by the appearance of similar formations in the limbs, neck, abdomen and many other organs of the human body. Sometimes the size of tumors in the chest reaches more than 10 cm. The reason why such lumps appear has not been fully identified by medicine. But there are certain assumptions. Let's talk about how to diagnose and treat lipoma and whether its development can be prevented.
Symptoms of lipoma in various parts of the body
Depending on the area where the lipoma formed, the clinical picture may be different:
- When palpating the lipoma, a thickened area of skin is determined. The patient does not experience pain. Often the formations are not welded together and do not contribute to inflammatory processes. Lipomas range in size from 1 to 20 cm. They most often spread to the facial, cervical, thoracic, abdominal, dorsal and lateral areas, as well as to the hips and forearms. It is worth noting that lipomas are characterized by symmetry, and therefore often when formed on one forearm, a lipoma also forms on the second in a similar location.
- Lipoma of the trunk is characterized by growth in the thoracic, dorsal or abdominal region. In old age, lipomas often appear on the anterior abdominal wall and interfere with palpation of internal organs. They can grow up to 20 cm, but the patient does not experience any inconvenience (except for lack of aesthetics). If the lipoma has spread to the spine, an MRI is required to differentiate from a hernia.
- Lipomas of the thighs and forearms can be painful, depending on their location. Pain occurs when nearby nerves are compressed. The protective shell is destroyed, axons are exposed and pain occurs.
The tumor can also compress the vessels of the veins, but only a large fatty formation that compresses several veins at the same time can contribute to the appearance of the clinical picture. The arteries are not compressed due to their thickened walls. It is worth noting that the pain from squeezing blood vessels or veins is significantly different from squeezing a nerve.
Next, adhesions form and thicken, the vascular lumen decreases, and aching pain occurs, which intensifies with physical activity. Small vessels can also grow into the tumor. Then the lipoma turns into an angiolipoma, but even with severe pain, angiolipoma is not malignant. The more vessels have grown into the vessel, the more intense the pain syndrome.
- With lipoma of parenchymal organs, pain occurs due to enlargement of the capsule. More often it is formed in the kidneys or liver, much less often in the spleen or adrenal glands. Most rarely - in the ovaries. People cannot diagnose lipomas on their own, and believe that the pain is characterized by other pathologies of the organ. Lipomas grow slowly, the capsules are periodically rearranged, and the pain is dull and inconsistent. This symptom is required to differentiate lipoma from other diseases diagnosed using CT or MRI.
Here we have already covered the issue of basal cell carcinoma of the face and its treatment.
Is it possible to do a puncture for lipofibroma during pregnancy?
There are suspicions that it is a lipofibroma. Is it worth doing a puncture during pregnancy? A puncture is one of many research methods and is an invasion into the mammary gland to take a sample of tumor tissue. After which the material is sent for diagnostics. This is the most current method for identifying or excluding the presence of cancer cells in a pathological breast formation. The result of a cytological analysis of fluid removed with a thin long needle may depend on the professionalism of the specialist who conducts it. The accuracy of the research is close to 90%.
There are contraindications to carrying out this method of studying the material taken: these are allergies to painkillers, the period of breastfeeding and pregnancy.
Other symptoms of lipoma on different parts of the body
A lipoma of the head can be visualized in the area of hair growth (these are the cheeks, chin and main scalp). The skin in the area of lipomas on the head is colder than in normal skin areas, this is easily determined by palpation.
Due to more frequent hypothermia of the head, lipomas are more often diagnosed in women than in men. Lipomas of the head are characterized by intracranial growth.
Their insidiousness lies in disguising themselves as various diseases and presenting positive symptoms or signs of loss of any functions.
If the lipoma has grown into one of the meninges, positive symptoms occur : impaired vision, hearing, smell, hallucinations, involuntary vibrations or body movements, bad behavior, schizophrenia-like thinking, etc.
With symptoms of loss of functions associated with compression of a certain nerve or chiasm, for example, loss of the visual field may occur.
A tumor in the pituitary gland provokes a decrease in the production of tropic hormones, and clinical signs of endocrine disease arise.
If a lipoma has formed in the lumen of the ventricles , the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid is disrupted, which can lead to hydrocephalus, expressed by increased intracranial pressure, bursting headaches and other related symptoms, and carry an unfavorable prognosis. With a neck lipoma, swallowing functions may be impaired. If compression occurs in the larynx area, changes in vocal timbre are noticed, including hoarseness.
A compressed phrenic nerve contributes to frequent and prolonged hiccups.
If the reverse laryngeal nerve is compressed , the vocal cords weaken. When the jugular vein is compressed by a large lipoma, the blood flow to the brain worsens, which contributes to frequent attacks of pain and dizziness. Lipomas on the back of the neck have no symptoms.
For breast lipoma, consultation with a mammologist is required. They are formed during the growth of the fatty layer located near the mammary gland, which is not much denser than the surrounding tissues, but the lipoma is motionless on the side of the gland. If there is rapid growth, pain, an increase in tumor density, or the occurrence of inflammatory processes, a consultation with an oncologist may be required in conjunction with a mammologist.
With lipomas of the heart, depending on the location, the following occur:
- arrhythmia;
- impulse blockades;
- its prominence in the atrial region;
- decrease in diastolic and systolic volume;
- worsening contraction of the atrium or ventricles;
- heart failure in combination with pulmonary edema.
Alternative medicine recipes
Despite the ban from doctors, folk remedies are popular. The following are considered the most effective:
- Pathology can be treated with viburnum-based tincture. To do this, you need to grind 100 g of berries, add 100 ml of honey and 50 g of cognac
.
Infuse the composition for 3 weeks
.
After this, take the medicine morning and evening, one tablespoon at a time
. Continue therapy for 2 weeks. - A baked onion compress is considered an effective remedy. To prepare it, you need to bake several onions in the oven and chop them into a paste
. Apply the resulting mass to the sore spot for 20 minutes. Repeat the procedures daily for 2 weeks. - A decoction of celandine helps to cope with the disease. To prepare it, you need to boil 2 tablespoons of the herb in a glass of water for 20 minutes, cool
.
Moisten a cloth in the solution and apply to the sore spot for 15 minutes
. Repeat every evening for 10 days. The recipe must be used with caution, since celandine can cause burns to the epidermis.
Lipoma is a pathological condition that in most cases does not require treatment. If symptoms of the disease are detected, it is recommended to consult a specialist. The use of folk remedies is permitted only after the approval of the attending physician.
Fibrolipoma is a benign neoplasm that consists of mature adipose tissue with connective tissue layers. The combination of these components varies
.
The size of fibrolipoma varies from 2 to 10 cm
.
The tumor can be single or multiple. Appears at any age of a person, with the same frequency in both women and men
. Most often painless.
The consistency of fibrolipoma, compared to lipoma, is denser due to the high content of connective tissue. Sometimes a fibrolipoma can consist of a different number of segments surrounded by an independent membrane.
Localization is observed in areas of the body where there is connective tissue and many sebaceous glands: in the subcutaneous tissue, skin and mucous membranes. This is always the neck, abdomen, buttocks, back and mammary glands
.
Its density and shape depend on the location of fibrolipoma
.
A tumor may also appear on the surface of internal organs. Fibrolipoma does not develop into a malignant neoplasm
. But with injury, severe pain and tissue necrosis may occur.
Diagnostics
If you have a superficial subcutaneous lipoma, you should contact an oncologist or surgeon. If the formation causes pain and discomfort due to compression on organs, you need to consult a therapist, gastrologist, nephrologist, hepatologist or surgeon.
Blood tests may be prescribed as part of the diagnosis.
And most likely there is a lipoma if the blood contains above normal levels:
- cholesterol;
- LDL;
- beta lipoproteins;
- triacylglycerols.
Instrumental diagnosis is necessary if the disease is disguised as other ailments with similar symptoms. Using ultrasound, you can find out the depth of germination, structure, geometric data, and even establish the degree of connection with nearby organs.
In the abdominal cavity, a lipoma is diagnosed only if it is completely excluded from other diseases. It must be differentiated from aortic aneurysm, parasitic cysts, malignant neoplasms and other serious illnesses.
Hepatocarcinoma and clear cell cancer may have similar symptoms to lipoma, and therefore tests are necessary to identify tumor markers.
To exclude an hydatid cyst, a CT or MRI , and contrast may be required.
Using CT and MRI, the size of the fatty growth, the effect on nearby organs, density and content, as well as the presence of blood vessels are determined. They are not present in lipoma, but are present in angiolipoma and malignant tumors.
It is worth noting that when lipid metabolism is normalized, the entire body loses weight, but the size of the lipoma remains unchanged. MRI differs from CT in visually increased clarity of soft tissues and the absence of harm to the patient.
In the presence of a malignant neoplasm, a biopsy is required, after which a morphological study is carried out in the biopath to accurately determine the nature of the formation . The purpose of the morphological study is the final confirmation of the diagnosis.
Therapy ends here if the neoplasm is benign. In case of malignancy, chemotherapy is required to get rid of the remaining cells of the tumor. If this method of therapy is not carried out, a biopsy will be required, on which the future state of health will seriously depend.
Moreover, oncology surgeons determine how necessary this procedure is, because the organization of fast work of laboratory technicians plays a huge role. The result of the biopsy must be received within 24 hours from the moment it was taken. After the tumor is removed, a wound remains at the site of the operation, the cells of the removed tumor penetrate into it, and then spread throughout the body through the bloodstream. In this case, the risk of increasing the number of metastases increases even after surgery on the main lesion.
Therefore, in clinics with a serious organizational level, a biopsy is performed before surgery, and the result of the tests is reported to the oncologist within not a day, but several hours, on the basis of which he determines the need for surgery.
In other hospitals, biopaths are sent to medical centers, and the doctor receives the result after 1.5-2 weeks.
Such a diagnosis reduces the chances of recovery to zero, and surgeons are forced to remove more tissue, which leads to increased trauma. But there are practically no residual cells. Next, the removed tumors are sent for histological analysis to adjust treatment tactics.
Diagnosis of lipomas
When located subcutaneously, diagnosing a lipoma does not cause difficulties even when examining and palpating the formation by a doctor. The diagnosis can be clarified using ultrasound.
The presence of a lipoma located in a parenchymal organ or body cavity or retroperitoneal space requires a more serious approach and the use of additional examination methods to clarify the location, size of the tumor and its relationship with surrounding tissues. Patients undergo:
- Ultrasound;
- MRI;
- CT, which can be combined with contrasting of blood vessels;
A thorough examination of the patient not only clarifies the characteristics of the lipoma, but also excludes more dangerous pathological processes (vascular aneurysm, parasitic invasion), including malignant tumors. Sometimes the diagnosis of lipoma is established by excluding other diseases and tumor-like changes.
A biochemical blood test often does not have any features, but in some patients changes in cholesterol and lipid fractions are possible.
The most accurate diagnostic method is considered to be a morphological examination of the tumor, which is usually performed after removal of the entire lipoma. Puncture or intraoperative examination are ineffective due to the complexity of such studies for adipose tissue. The attending physician and the patient receive an accurate diagnosis after surgery to remove the lipoma, unless minimally invasive methods were used, in which the tumor is destroyed immediately without leaving its fragments.
Causes of lipomas on the skin
The reasons for the appearance of lipomas have not been fully elucidated, but numerous genetic and physiological studies suggest several reasons for the formation of these tumors. However, scientists have not yet been able to fully prove the theory; accordingly, there is no main reason for fatty growth.
Theoretically, the reasons could be:
- Genetic factor. Moreover, this is not only an inherited disease. When diagnosing lipomatosis in 1 monozygotic twin, it can be confidently stated that the second may undergo lipomatosis. The gender of the child does not play any role in the transmission of the disease from parents.
- Poor metabolism. Diagnosed in obese and thin patients. Clinically, impaired fat metabolism is determined by large amounts of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) in the blood. These fats do not pass into the endothelium, and therefore vascular blockage occurs from the inside, after which the amount of fats in the blood increases, and atherosclerotic plaques form on the vessels. Fatty liver disease may develop in the liver. Causes of impaired metabolism: sedentary lifestyle and hereditary diseases.
- Disorders of the feedback regulation of fat formation . Mediators of the fat layer are located inside the cells. An increase in the number of cells is equivalent to an increase in the number of mediators. The higher their concentration, the lower the rate of membrane processes. The body does not process glucose, cholesterol and triglycerides back into fat. To restore, it triggers a mechanism aimed at regulating the fat layer. With excellent functioning of the body, a person can overeat repeatedly and not gain weight - the excess is excreted through the bile and urinary tract. In case of failures caused by burns, stress, radiation exposure, etc. Neurogenic obesity occurs throughout the body or in some areas, and then lipomas form.
- Failure to comply with hygiene standards. Those. The cause may be boils or pimples that do not go away for a long time. It is not recommended to remove such wen on your own due to improper execution of the procedure. Patients do not squeeze out all the pus, as a result of which the sebaceous glands actively produce a thick secretion. As a result, the pores and sebaceous accumulation in the gland become clogged, and a capsule-shaped lipoma is formed. Read more about blocked sebaceous glands and its treatment.
- Demodecosis. A small number of people in the general population have microscopic mites in the meibomian glands, visualized at 40x microscopic magnification. With weak immunity (or if it fails), these parasites are not suppressed, but multiply significantly, provoking blockage of the glandular lumen with their own bodies. The sebaceous glands become inflamed and a boil or carbuncle is formed. In the absence of an inflammatory process, a fat accumulation forms, which subsequently forms a lipoma.
Reasons for the formation of lipomas
There is no consensus regarding the causes of lipoma, but the role of several factors is assumed:
- Heredity;
- Changes in fat metabolism;
- Injury;
- Concomitant pathologies – diabetes mellitus, dysfunction of the thyroid and pancreas, liver disease, alcoholism, etc.;
- Old age and decreased natural immunity.
A hereditary predisposition to tumors from adipose tissue can be traced in lipomatosis, when multiple nodes form throughout the body in family members. Most likely, the cause of this phenomenon will be a genetic defect transmitted from parents to offspring, regardless of their gender.
Disorders of lipid metabolism, with a certain degree of probability, can also contribute to the growth of lipomas. However, this does not mean that a tumor will necessarily occur in obese people suffering from excess adipose tissue. In thin people, lipoma is also found quite often and can reach significant sizes.
In the human body, there are mechanisms that regulate the deposition of subcutaneous fat in varying quantities in its different parts. Under stress and unfavorable external factors, disruptions in the functioning of such regulation are possible, then locally there is an increase in the formation of adipose tissue and tumor growth.
Injuries in the regeneration stage may be accompanied by increased cell proliferation, which is likely to cause the appearance of a lipoma at the site of damage to the subcutaneous fat.
Lipoma treatment
Lipoma therapy involves surgery. Many lipomas do not cause serious discomfort or pain to patients, and do not put pressure on surrounding structures, and therefore there is no need for surgical treatment.
There is no medicine to completely eliminate lipoma. It has been proven that side effects often occur during drug treatment, which is why surgical treatment is required. If it is not malignant, the patient has the right to delay the operation or refuse it. But if it threatens the patient’s life, surgical intervention is mandatory.
What does a lipoma look like?
Lipoma is a benign tumor in humans that develops from adipose tissue. At the initial stage it is difficult to detect, it grows slowly and does not cause concern. This formation is mobile, elastic and soft to the touch, looks like a spherical bulge on the body, and has sizes from a small pea to several tens of centimeters. Most often they form in the subcutaneous tissue and affect the neck, forearms, arms, back, head, but since there is also an accumulation of adipose tissue in the internal organs, lipomas appear there too.
Indications for lipoma removal
There are 2 types of indications for lipoma removal:
- Relative. This is a pain syndrome when a nerve is compressed, localized in the kidney or liver, permanent damage to the formation during movements and limited blood flow or outflow.
- Absolute. This is for intracranial or intracardiac lipoma, with a formation that contributes to poor circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, and in case of a risk of rupture of the peritoneum or beyond it.
Treatment
Treatment of lipoma involves removing the entire tumor along with the capsule. Since this is a tumor process, self-medication is unacceptable in any form. Firstly, a patient who does not have special knowledge cannot accurately determine what exactly a tumor is on the body. Secondly, no non-surgical methods have yet been invented to combat this tumor, so if you discover a suspicious formation in yourself, it is better to immediately go to the doctor.
Of course, if the lipoma is small and does not cause any subjective or aesthetic concern, then a wait-and-see approach is fully justified, because the risk of surgery may be higher than the expected benefit. The tumor grows very slowly and is not prone to malignancy, so observation by a doctor can be limited. Naturally, it is the doctor who should offer this option, so you should not postpone a visit to him. At the request of the patient, he can also be relieved of a small asymptomatic lipoma, if for some reason the patient definitely wants to have it removed.
Indications for lipoma removal may include:
- Pain, compression of blood vessels and nerves at the site of the tumor;
- The appearance of signs of inflammation in the growth area of the tumor;
- Fast growth;
- Cosmetic defect;
- Impaired function of surrounding tissues or organs;
- Patient's wishes.
Intracranial, intracardiac lipomas, as well as a tumor that threatens to rupture if localized in the abdominal cavity or retroperitoneal space, are absolute indications for surgery, which should not be postponed due to possible dangerous complications.
The choice of pain relief method and method of lipoma removal is determined by its location, size, and patient’s condition. For small superficial formations, preference is given to local anesthesia, but if the tumor is located inside the body, general anesthesia is indispensable.
It is important to remove the lipoma radically, that is, not only the source of adipose tissue growth itself, but also the surrounding capsule, otherwise a relapse is almost inevitable, and the patient will have to see a doctor again and undergo unpleasant treatment procedures. It is important to entrust the treatment to a competent specialist and avoid any manipulation of the tumor in beauty salons, and in this case it is better to avoid witch doctors and traditional healers.
Today, the most common methods of treating lipomas are:
- Surgical removal.
- Radio wave therapy.
- Laser treatment.
- Puncture-aspiration method.
Surgical treatment involves removing the tumor using a scalpel. This approach is justified when the tumor is large and located in tissues inaccessible to physical methods of influencing cells. The doctor chooses an adequate method of pain relief in accordance with the location of the tumor and the patient’s condition. In most cases, lipoma removal can be performed on an outpatient basis, but for large tumors and especially those growing inside the body, the patient will be offered hospitalization.
The operation to remove a lipoma usually consists of enucleating the node, that is, the doctor excises the adipose tissue along with the capsule, after which the tissue is sutured in layers. The course of the postoperative period is usually favorable, and the sutures are removed on days 7-10. It is clear that lipomas located inside the cranial cavity or in the heart can only be removed with the participation of highly qualified cardiac and neurosurgeons, because such localization requires not only appropriate preparation of the patient for surgery, but can also cause complications (bleeding, infection, etc.). d.).
If the tumor has a pronounced lobular structure, “entwining” vessels, nerves or tendons, then removing it can be significant difficulties, and the surgeon will need precise and precise movements, since crossing a nerve or vessel through negligence can lead to serious complications.
“Open” surgery to remove a lipoma carries a risk of relapse that is several times lower than some more gentle methods, since the surgeon has the opportunity to examine the formation and completely remove it within healthy tissue.
Among the gentle methods of treating lipomas, the use of laser has proven itself. Without this method of influencing pathologically altered tissues, it is difficult to imagine modern medicine, and oncology is no exception. Thanks to the targeted action of the laser beam on the tumor tissue, it is removed, while the surrounding cells remain unaffected. After laser removal, there are no scars left, healing occurs quickly, and relapses are extremely rare. Laser therapy is considered the treatment of choice for small superficial lipomas.
Radio wave treatment is low-traumatic, leaves no marks on the body, and tumor cells die due to heating. The method requires local anesthesia, complete healing takes several days. Since no tissue incision is made, there is no need for sutures, which means there will be no scar. The radioknife removes the entire tumor, along with the capsule, which minimizes the risk of recurrence. Radio wave treatment causes virtually no complications, but is usually used for small tumors.
Puncture-aspiration removal of a lipoma involves suctioning out its contents using a thick needle. The patient can go home within 15-20 minutes after the procedure. The tumor capsule, especially a well-defined one, cannot always be removed, so the risk of relapse is quite high, and the effectiveness depends on the skill and qualifications of the surgeon. The method does not require sutures and has a good cosmetic result.
Minimally invasive methods of treating lipoma are indicated for small tumors, as well as when they are located on the face, neck, head and other open areas of the body.
Complications during the removal of lipomas occur rarely and are most often associated with infection of the postoperative wound or the appearance of a hematoma, although the formation of a keloid scar and tumor recurrence are possible. Usually the postoperative period proceeds well, and if gentle techniques are used, the patient can immediately go home.
Treatment with folk remedies does not lose popularity for tumor pathology. There are a lot of recipes on the Internet on how to get rid of lipoma using lotions, compresses, etc. At best, such treatment will not harm, but it is quite likely that not only further growth of the tumor, but also damage to the skin at its location, which is fraught with inflammatory process, suppuration. In addition, even if you manage to get rid of the contents of the wen, you will not be able to remove the capsule yourself, so a relapse is inevitable. It is also worth keeping in mind that a tumor that seems benign may actually be something more dangerous, so self-medication with alternative medicine should not be carried out.
The true causes of lipoma growth are unknown, so there is no way to prevent these tumors. If you suspect a lipoma, you should go to the doctor, and if there is a hereditary predisposition to this kind of neoplasm, then you should carefully monitor changes in the body and visit a specialist as necessary.
Methods for removing lipomas in the clinic
Lipoma is operated on under general or local anesthesia. The method of anesthesia is chosen depending on the size, concomitant ailments and location of the lipoma. Next, surgery is performed.
Advanced clinics practice:
- laser removal;
- radio wave;
- plasma;
- cryotherapy (removal with liquid nitrogen).
These 3 types of operations are known for the fact that postoperative sutures are not required, and the operated area heals in 3-4 days.
If the lipoma is large, a minimal incision is made, removed, the wound is treated with antiseptics and a cosmetic suture is applied while maintaining the tissue topography.
Sometimes it is necessary to leave a drainage in the wound to separate the ichor, and as soon as the wound has healed, the drainage is removed. Sutures are removed after 1.5-2 weeks. Read more about how a wound heals here.
Methods of treatment and removal of breast lipofibrosis
The approach to treating a lipoma depends on its size, growth rate, the condition of the pathological cells, the appearance of the skin of the breast, the presence of pain and discomfort in the patient. There are four ways to get rid of wen:
- complete removal through surgery;
- destruction of the formation by radio waves or laser (this method is quite expensive and requires special medical equipment, which not all institutions can afford);
- liposuction of the tumor (with this method, the pathological contents are pumped out through a small puncture in the skin. But repeated appearances of the tumor often occur, since after this operation it is impossible to check whether the wen has been completely removed);
- administration of a resolving drug.
Doctors do not recommend intervening in any way with the disease if the size of the formations is insignificant and there are no tangible and visible changes in the patient’s mammary gland. If there is no cause for concern about the development of cancer cells in the tumor, then the woman needs to register with a specialist and undergo an ultrasound examination every three months, a mammogram every six months and regular tests to detect pathological cells.
If the lipoma is not deep, it is possible to operate under local anesthesia, which leaves a neat cosmetic suture. After the intervention and removal of the wen, the patient is ready for discharge in 7-14 days. During the postoperative recovery period, antibiotics are prescribed to avoid inflammation in the wound. At the same time, it is necessary to take vitamins and medications that support the immune system.
Often in medical practice, medication is used to dissolve small formations no larger than 3 cm in size. One of the effective drugs is “diprospan”. This treatment method takes about four weeks, including breaks.
Surgical treatment is followed by a rehabilitation period and mandatory regular examinations and tests.
Removal at home, precautions
There are also methods for removal at home, but they are not recommended in a contaminated room, and if the wen has penetrated into the inner layers and its size is no more than a centimeter.
To remove you will need:
- cotton swab;
- disinfectant solution or vodka;
- needle from a sterile syringe.
First, hands are washed and disinfected and then, having taken a comfortable position, they begin.
They treat the sponge, needle and hands soaked in a disinfectant, stretch the skin in the area of the lipoma, pierce it, pick up the fat in the capsule with a needle and pull it out. If the actions are unsuccessful, make a second skin puncture or expand the existing one, and try again.
It is worth noting that these actions may be painful, and the wound may bleed. After completing the operation at home, the procedure site is disinfected. Wound healing time ranges from 3 days to a week, depending on the regenerative functions of the skin.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis is not difficult, since the disease is asymptomatic, which is rare in medical practice. To confirm the diagnosis, it is recommended to conduct a laboratory blood test.
An ultrasound examination is performed to determine the structure of the tumor. If a specialist has doubts, an instrumental examination of education is indicated.
To clarify the diagnosis and size of the tumor, it is necessary to conduct computer diagnostics and magnetic resonance imaging. During the procedure, the patient undergoes a complete examination to determine the presence of other lipomas.
Possible complications
Some complications may occur during the operation.
Thus, a previously deformed capsule and rupture of adipose tissue into the space around it leads to infiltration of nearby tendons or muscles. As a result, 1 large knot is formed from tendons, nerves, blood vessels and muscles, welded together in many places.
Such a lipoma is difficult to visualize during surgery, and the risk of crossing a blood vessel or a certain nerve increases. This will lead to appropriate complications.
There is also a risk of repeated development (relapse) of lipoma in an area that has already been operated on and thoroughly cleaned. This is facilitated by residual cells between muscle or tendon fibers.
Causes
Lipomas are formed primarily due to the proliferation of adipose tissue.
What is the reason for its growth? Often this is caused by poor nutrition and, as a result, metabolic disorders. This applies not only to obese people, but also to those who have a thin physique. Often the reasons for the development of wen are:
- Hereditary factor . It is transmitted genetically, without dependence on gender;
- Endocrine system dysfunction (including diabetes mellitus and thyroid disease);
- Development of the inflammatory process of acne . The duct of the sebaceous gland is blocked by a scar after removal of the acne;
- Insufficient hygiene contributes to the appearance of acne and boils. And as a result of chronic inflammation, the sebaceous glands are injured, and sebum accumulates in their cavity;
- Demodicosis (reproduction of subcutaneous parasites). Microscopic mites that feed on subcutaneous fat clog the lumen of the sebaceous gland with their vital activity;
- Violation of the mechanism for regulating the level of fat metabolism . This mechanism prevents the deposition of excess fat and removes it from the body. Failure of this process can occur due to stress or injury.
Lipoma in a child
In children, just like in adults, lipomas form for unknown reasons. They may lie in a genetic factor or in the impaired activity of lipolytic enzymes that promote the breakdown of fats. Often, a lipoma does not cause concern to a child.
It is not fused, lobed, mobile, the skin around it is not inflamed and pain does not occur on palpation.
If the lipoma does not cause any inconvenience, it is enough to show the child to the pediatrician. In other situations, consultation with a surgeon, oncologist or relevant related specialist is appropriate (depending on the location of the tumor in the area of certain organs). During the diagnosis, a visual and instrumental examination is carried out; if necessary, a puncture of the lipoma is prescribed for the purpose of its morphological examination.
Treatment for lipoma in a child is identical to treatment in an adult – surgery. Limitations may include a very young age (up to 3 years) and concomitant diseases.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that in order to prevent lipomas in children and adults, one should promptly get rid of demodicosis, avoid injuries and hypothermia, and observe basic hygiene standards. Only then will such neoplasms not arise and, possibly, degenerate into a malignant form.
Types of lipoma
Lipomas are divided into types based on cell composition.
- Lipofibroma is a tumor consisting of lipid tissue. Has a soft structure.
- Angiolipoma is a type of lipoma that differs in that it grows between blood vessels.
- Fibrolipoma - this neoplasm has a dense structure, and also includes connective tissue.
- Myelolipoma is a rare wen that forms in the tissue of the pelvis and in the area of the adrenal glands. Consists of blood vessels and adipose tissue.
- Myolipoma is a lipoma consisting of muscle tissue.
Causes
The exact cause of the development of fibrolipoma has not been established. A number of experts are inclined to believe that the development of pathogenic anomalies occurs during the period of “birth” and formation of fat cells; others argue that neoplasms progress against the background of a general weakening of the body’s immune system. There is a group of factors contributing to the development of pathology:
Genetic failure (the disease is inherited, manifests itself in young people aged 15-25 years).- Metabolic disorders (use of food additives, use of potent medications).
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Pituitary gland diseases, liver failure.
- Diabetes.
- Inflammatory processes progressing in the genitourinary system.
- Chronic diseases of the nervous system (long-term stress leads to depletion of the central nervous system).
- Living in unfavorable ecological areas (heavy industries, oil developments, processing platforms).
- Abuse of alcoholic beverages and narcotic substances.
- Neglect of the rules of a healthy lifestyle.
The development of fibrolipoma is promoted by hormonal imbalance and a general weakening of the body's defenses. Women over 40 years of age are at potential risk; changes in hormonal levels during menopause lead to pathological changes in the functioning of the body. As the tumor grows, it penetrates into neighboring tissues, filling the resulting space. The development of the tumor occurs painlessly, which makes it difficult to detect fibrolipoma in the early stages of development. The formation is extremely mobile, easily identified by palpation, the lobar parts are pronounced.
Fibrolip treatment
For lipomas, only surgical treatment is prescribed. The operation is performed for the following indications:
- large lipoma size;
- rapid increase in size;
- compression of nearby organs or tissues; painful formation; cosmetic effect.
For small-sized fibrolipomas, operations are performed under local anesthesia on an outpatient basis. For fibrolipomas of large size, as well as those located in difficult places, treatment is carried out in a surgical hospital
. One suitable method is used:
- Excision of fibrolipoma simultaneously with the capsule. The advantage of this operation is the absence of relapses, and the disadvantage of this operation is considered to be a cosmetic defect.
- Endoscopic removal through a small incision. The operation provides a good cosmetic effect.
- Liposuction of fibrolipoma. The procedure is performed using a lipoaspirator
. This surgical intervention is fraught with the possibility of relapse, but has a good cosmetic effect.
Complications from fibrolipomas are very rare. But it may happen:
- inflammatory process. The fatty tissue increases in volume, turns red, and becomes very painful. Even with slight pressure, the presence of liquid in the capsule is felt;
- degeneration of the formation into liposarcoma (malignant tumor);
- displacement of surrounding tissues with a significant size of fibrolipoma.
There are no preventive measures that can affect the causes of fibrolipoma. This tumor is benign and low-risk . But with constant irritation of the tumor, its further development may occur
. Therefore, removing the formation is the only correct solution.
Treatment for breast fibrolipoma depends on many factors. This includes the main symptoms of the disease, the size of the seals, as well as associated complications and individual characteristics of the body.
. The tumor is considered a benign formation; it does not resolve on its own and is often removed through surgery.
Characteristic signs of lipoma
If a tumor is detected, you must consult a doctor who will conduct an examination and refer you for tests to exclude the risk of developing cancer and confirm the benign nature of the growth. If it is not possible to consult with an oncologist, visit a physician or surgeon. To clarify the conclusion, the following are carried out: MRI, ultrasound, CT, which makes it possible to study the structure of the subcutaneous tumor and timely detect a wen located on the internal organs. The characteristic signs of a lipoma help to distinguish the disease from other formations.
Outdoor
Symptoms: the skin at the site of localization does not change in color and texture, remains smooth and is small in size (3-5 cm). Active growth can cause stretching of the skin and the formation of a pouch. If the lump is not removed in time, the risk of ulcerative lesions and further tissue necrosis increases, which is caused by insufficient blood and oxygen supply. Large seals cause compression of surrounding muscles and blood vessels and slow down regenerative processes.