The replacement of healthy liver cells with degenerated fatty cells—liver hepatosis (ICD code 10)—develops as a result of the chronic proliferation of pathological tissues. The impetus for the manifestation of symptoms is systematic violation of diet and lifestyle, negative processes in the body. If you seek medical help in a timely manner, the disease can be inhibited and corrected.
Causes
Liver steatosis develops gradually under the influence of diseases of the body or independently as a reaction to regular exposure to unfavorable factors.
The main causes of pathology:
- genetic predisposition;
- metabolic failure, lack of enzymes;
- endocrinological diseases, diabetic process;
- infectious and inflammatory pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- parasitic infection of the body;
- exposure to toxins;
- surgical intervention on the peritoneal organs;
- overweight and obesity;
- influence of drugs.
Lack of a healthy diet disrupts the complex process of digestion.
The following factors can cause liver disease with damage to hepatocytes:
- unhealthy diet, overeating, eating food that is difficult to digest;
- low mobility;
- high blood pressure;
- strict dietary restrictions;
- radiation exposure;
- sudden and rapid weight loss;
- pregnancy and hormonal changes;
- age-related changes after 45 years;
- injury to the abdominal area;
- cystic formations;
- being female.
Preventive actions
Prevention of fatty hepatosis includes compliance with a whole range of specific measures, including:
- maintaining proper nutrition;
- performing physical exercises;
- reduce alcohol consumption to a minimum.
It is necessary to take medications strictly according to the instructions and after a doctor’s prescription. Before using the medicine, be sure to read the instructions for this medicine, taking into account the rules for its use, as well as compatibility with other therapies.
In order not to worry about whether fatty liver disease can be cured, it is important to undergo regular preventive examinations and tests. If you experience unpleasant symptoms associated with impaired functioning of the intestines and stomach, you need to visit a doctor and begin timely treatment.
Classification of liver changes
Long-term use of medications poisons the liver.
Fatty liver hepatosis is classified as a diagnosis according to the nature of the disease, the causes of development and the type of cellular damage. Main forms of the disease:
- Spicy. Develops in response to strong toxic effects (mushrooms, drugs, chemicals). Symptoms rapidly increase along with liver enlargement.
- Chronic. It appears against the background of diseases of the body with a dim clinical picture and an undulating course.
Fatty liver degeneration due to development reasons is:
- Primary (hereditary). Formed during intrauterine development.
- Secondary (acquired). It occurs as a result of lifestyle and associated diseases of the body.
Depending on the damage at the cellular level, steatohepatosis of the following nature is distinguished:
- Fine droplet. Development of pathological processes without changes in liver cells.
- Large droplet. Significant diffuse change and damage to cells with further decay and death.
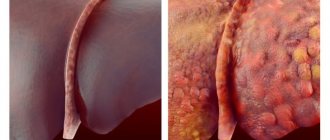
Fat cells replace healthy organ cells.
Fatty liver and differences in modifications and nature of the course:
- Fatty hepatosis (steanosis). The chronic course of the disease with structural changes in liver tissue, a complication is focal cirrhosis.
- Pigmented (benign hyperbilirubinemia). Genetic disorders of liver function with chronic manifestations of jaundice without changes in the structure of the organ.
- Cholestatic. Impaired outflow and excretion of bile with liver intoxication. If not treated promptly, this form can develop into fatty hepatitis.
Causes and factors for the development of fatty liver
Most often, fatty liver develops in people who abuse alcoholic beverages, but this is not the only cause of the pathological process.
The reasons for the development of steatosis may be fasting with rapid loss of body weight, exposure to toxic and poisonous compounds on the body, and disruption of metabolic processes.
In addition, the liver reacts to fatty foods by accumulating lipids in its own parenchyma. Abuse of fatty foods, especially when leading a sedentary lifestyle, leads to obesity of the liver parenchyma.
In addition to toxic and poisonous compounds, steatosis can be provoked by long-term use of drugs with pronounced hepatotoxic properties during therapeutic measures.
Such medications are:
Disorders of metabolic and metabolic processes that contribute to the development of fatty hepatosis can be triggered by conditions in the body such as:
- Diabetes.
- Pregnancy.
- Reye's syndrome.
- Konovalov-Wilson disease.
- Weber-Christian disease.
Smoking tobacco in the presence of other factors for the development of liver dysfunction worsens the situation, which increases the likelihood of obesity of the gland.
In some cases, the cause of fatty degeneration of the liver parenchyma is the development of severe enteritis and pancreatitis in the body.
In addition to these reasons, the occurrence of the disease can be caused by a lack of proteins and vitamins in the body, the presence of chronic intoxication, general obesity of the body, as well as excess iron.
Symptoms
Liver hepatosis is characterized by slow development and a mild clinical picture. Manifestations increase gradually as organ damage progresses. The main initial signs of fatty liver hepatosis:
- decreased and lack of appetite;
- discomfort and heaviness in the liver area;
- nausea, vomiting;
- the liver pulls and hurts, tingling in the side;
- bloating, flatulence;
- weakness, increased fatigue;
- bowel disorders.
The skin and eyes take on a yellowish tint.
Severe hepatic hepatosteatosis causes the following symptoms:
- decreased immune strength of the body;
- deterioration of skin and hair condition;
- frequent colds;
- yellowing of the skin, sclera and mucous membranes;
- allergic reactions;
- night itching of the skin;
- elevated temperature;
- disorders and disruptions of the menstrual cycle in women;
- worsening blood clotting;
- rashes of varying intensity on the body;
- decreased visual acuity and clarity;
- reproductive dysfunction;
- swelling of varying degrees;
- exhaustion of the body;
- seizures;
- presyncope, fainting;
- coma.
Degrees of the disease
Lack of treatment provokes complete destruction of the organ.
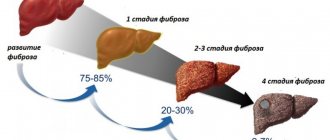
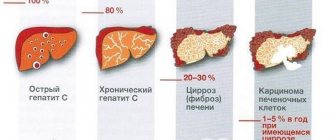
Depending on the development of damage to the liver structures and the severity of pathological changes, fatty liver hepatosis is divided into 3 degrees of course:
- Liver steatosis grade 1. Initial accumulation of individual fatty areas, no symptoms.
- 2 degrees. Increased accumulation of fat with the formation of focal fibrosis in liver cells.
- 3 degrees. The growth of fat deposits and connective tissue, the disease causes severe symptoms.
Diagnostics
To determine the causes of the disease and the stage of the pathological process, you must consult a gastroenterologist. Diagnostics includes:
- Medical history - information about lifestyle, concomitant diseases, habits, patient complaints.
- External examination - study of the condition of the mucous membranes and skin. Next, the doctor determines the boundaries of the liver and the presence of pain.
- Laboratory research.
- Instrumental diagnostics.
Basic laboratory examination methods
Carrying out the analysis requires preliminary preparation.
- General blood analysis. Assessment of the general condition of the body.
- Urine analysis for bile pigments. Definition of violation of excretory functions.
- Liver tests. Biochemical blood test for liver function and enzyme activity.
- Corpogram. Analysis of stool for the presence of parasites and abnormalities in the digestive processes.
- Coagulogram. Determination of blood clotting.
- Infection panel. Detection of viral activity.
Instrumental diagnostics
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound). Determines the boundaries, size and structure of the organ. Echo signs of pathological changes are detected.
- Computed tomography (CT). Sectional radiography of the liver.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Detailed three-dimensional image of structures with determination of pathological changes and the condition of the bile ducts.
- Fibroelastography. Scanning the liver using a special device that determines the degree of fibrous damage and the density of the organ.
- Biopsy with histological examination. Removing a section of tissue with a needle for laboratory analysis.
Symptoms of fatty liver
Symptoms of fatty liver are usually pain in the upper right side of the abdomen, malaise, chronic fatigue, and a feeling of heaviness, especially after eating. Although it is also true that there are patients who do not have symptoms.
Although a few years ago fatty liver was associated with heavy alcohol consumption, experts now associate it with high levels of obesity, cholesterol and triglycerides.
There are several symptoms of fatty liver , although it is also true that not all patients have symptoms. Generally, the most common are the following:
- Pain in the upper right abdomen
- General malaise
- Fatigue
- Chronic fatigue
- Weight loss
- Feeling of heaviness
- In some cases, jaundice
In severe cases, where the degree of involvement of the fatty liver is much more severe, symptoms such as severe pain in the upper abdomen and the development of acute liver failure may be observed.
However, the absence of associated symptoms does not mean that you cannot suffer from fatty liver. In fact, it is estimated that about 30% of patients have little to no symptoms.
While asymptomatic, it is often the case that fatty liver is discovered by chance, such as after performing an abdominal ultrasound or when examining the abdomen if the doctor can feel that the liver has become enlarged.
Given that some patients may have no symptoms, the best way to confirm whether or not steatosis exists is through an abdominal ultrasound, immediately after checking for high transaminases in a blood test. Not in vain, in some cases high bilirubin can also appear.
Evolution of fatty liver
Fatty liver is a benign disease that usually does not progress to more serious stages of the disease.
Once the appearance of fatty liver is detected (through abdominal ultrasound), necessary measures must be taken to eliminate the fat in the liver and thus avoid the development of fatty liver in steatohepatitis (inflammation of the liver, enlargement, in this case caused by the accumulation of excess and excess fat), and from there to possible cirrhosis and/or cancer.
In fact, when fatty liver is left untreated, it can be present with cirrhosis and therefore increase the risk of developing liver cancer.
Treatment for fatty liver
Although there is no definitive cure for fatty liver, the main recommendations given in this regard are through weight loss and following a healthy and healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
Doing any exercise helps in all cases, as we help our body get rid of excess fat. Moreover, when we also choose to consume foods like artichoke or milk thistle capsules, which help the liver perform its functions and also renew the liver cells.
A good option is to consult a nutritionist who tells us about the right diet for fatty liver and monitor the weight we lose as rapid weight loss is associated with more liver damage. Of course, don't forget to stop drinking alcohol.
Fatty liver is a condition that is usually easy to treat and most cases are benign. In fact, controlling the underlying causes makes it easier to heal.
Treatment of pathology
A timely visit to a doctor will help avoid unwanted consequences.
Liver hepatosis requires a complex effect on the patient’s body. Therapeutic methods are aimed at achieving the following effect:
- elimination of external provoking factors;
- complete abstinence from alcoholic beverages;
- liver regeneration;
- restoration of digestive functions;
- restoration of disrupted processes in the body;
- treat concomitant diseases.
Treatment of liver hepatosis is carried out by a gastroenterologist, who selects an individual treatment regimen for each specific patient. Depending on the severity of fatty liver damage, the following methods of treatment are used:
- changing lifestyle and habits;
- dietary nutrition;
- acceptable physical activity;
- medications;
- treatment with folk remedies and homeopathy;
- physiotherapy.
Medications
Drug treatment is aimed at improving the patient’s general well-being, regenerating damaged liver cells and tissues, restoring digestion and metabolism. Liver steatosis is treated with the use of medications, which are given in the table:
| Group of drugs | Overall Impact | Subgroup of drugs | Therapeutic effect | Tradename |
| Hepatoprotectors | Cell regeneration and protection | Essential phospholipids | Tissue preservation | "Essentiale" |
| "Lecithin" | ||||
| Plant flavonoids | Choleretic and antioxidant effect | "Gepabene" | ||
| "Karsil" | ||||
| Amino acid derivatives | Detoxification | "Heptral" | ||
| Improved blood circulation | "Remaxol" | |||
| Ursodeoxycholic acid preparations | Immunomodulatory effect | "Ursofalk" | ||
| Bile removal | "Ursodez" | |||
| Dietary supplements (BAS) | Acceleration of fat breakdown | "Hepafor" | ||
| "Pumpkin" | ||||
| Hypolipidemic | Regulate the amount of fat | Bile acid sequestrants | Stimulates the natural elimination of bile acids | "Cholestipol" |
| "Cholesteed" | ||||
| Statins | Block cholesterol production | "Lovastatin" | ||
| "Fluvastatin" | ||||
| Fibrates | Activate enzyme activity | "Clofibrat" | ||
| "Bezofibrate" | ||||
| Niacins | Reduce fat production | A nicotinic acid | ||
| "Niacin" | ||||
| Antioxidants | Stop destructive processes | Vitamins | Protect the body | Ascorbic acid |
| B vitamins | ||||
| Bioflavonoids | Suppress free radicals | "Ascorutin" | ||
| "Venarus" | ||||
| Enzymes | Stimulates metabolic processes | Catalase | ||
| Peroxidase | ||||
| Minerals | Improve metabolism | Zinc | ||
| Manganese | ||||
| Antihypoxants | Improve oxygen saturation of cells | Straight type | Act in cells | "Mexidol" |
| "Tiatriazolin" | ||||
| Indirect action | Improves overall oxygen absorption | Lipoic acid | ||
| "Probucol" |
Therapy with folk remedies
Herbal medicine is used as an adjuvant therapy.
To eliminate symptomatic manifestations and as an auxiliary effect, homemade recipes and medicinal herbs are used. Before use in children, you should consult your doctor to prevent allergic reactions and complications. Treatment of fatty liver hepatosis with folk remedies at home is controlled by a gastroenterologist - the timing, composition and regimen of therapy are established. The main folk recipes are described in the table:
| Means | Components | Impact |
| Herbal treatment | Peppermint | Choleretic |
| Dog-rose fruit | Detoxification | |
| Saturation with vitamins | ||
| Calendula flowers | Anti-inflammatory | |
| Choleretic | ||
| St. John's wort herb | Strengthening vascular walls | |
| Antibacterial | ||
| Chamomile flowers | Recovery and relief of spasms | |
| Crushed lemon fruit | Eliminate fat | |
| Warm drinks | Mint+melissa | Removes nausea |
| Milk thistle treatment | Antioxidant | |
| carrot juice | Restorative | |
| Nutritional supplements | Turmeric, cinnamon, pine nuts, bran | Reduce cholesterol |
| Apricot kernels | Regenerate | |
| Mixture | Sugar with blue onion | Antibacterial and cleansing |
| Honey with pumpkin | Cleaning and restoration | |
| ASD fraction 2 | Cleansing, relieving inflammation |
Additional Methods
Proper nutrition and physical activity will help speed up your recovery.
Steatohepatosis must be treated with mandatory lifestyle and dietary modifications. The diet is aimed at normalizing digestive processes, removing excess load from liver cells and improving the health of the body. Basic recommendations:
- Preparation is carried out by boiling, baking, stewing and steaming.
- Stick to fractional meals in small portions (5-6 times a day).
- Limit or eliminate table salt.
- Avoid fasting and overeating.
- Maintain sufficient drinking regime.
- Completely eliminate the consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Specially designed exercises will help the patient lose weight, maintain good physical shape, heal and restore the body. You can get rid of excess weight by swimming, fitness, walking and running. Physical activity can be combined with ozone therapy, pressure chamber and ultrasound. The level of permissible voltage must be agreed with the attending physician.
Prevention and prognosis
It is possible to cure non-alcoholic liver hepatosis if detected in a timely manner. The patient will get rid of the pathology if he takes medications, adheres to the rules of a healthy lifestyle, follows dietary recommendations, maintains a normal body weight and practices acceptable physical activity. With poor nutrition, consumption of alcoholic beverages and refusal of treatment, the pathology leads to irreversible changes. Hepatoma develops with localization of metastasis in the liver, complete intoxication of the body and death occur.
Therapeutic diet for fatty liver hepatosis
How to treat fatty liver disease with diet?
Features of nutrition for this disease:
- refusal of harmful products;
- inclusion of natural healthy foods in the diet.
Compliance with the following recommendations will have a beneficial effect on both the liver and overall health.
It is necessary to exclude:
- prepared meat products (sausages, sausages, pates, canned food):
- fats (palm oil, margarine, rapeseed oil, corn oil);
- caffeine;
- carbonated drinks;
- sugar:
- white pastries;
- fast food;
- alcoholic drinks;
- cigarettes.
Products indicated for use:
- vegetables;
- fruit menu;
- seafood;
- beef;
- brown rice;
- eggs, chicken (not from a poultry farm);
- legumes;
- mutton;
- garlic;
- soy sauce, apple cider vinegar;
- nuts;
- spices (curry, cinnamon, cumin, ginger, turmeric).
Therapeutic dietary menu for fatty liver hepatosis
Developed specifically for people suffering from this disease, the therapeutic dietary menu is suitable for anyone who watches their diet.
How to treat fatty liver hepatosis using ordinary foods and dishes?
Both the quality of the selected products and their quantity are important. Overeating is unacceptable with hepatosis.
Breakfast. In the morning on an empty stomach, drink two glasses of clean water with the addition of freshly squeezed lemon juice. After 15–20 minutes, provide your body with vitamins and microelements by drinking juice from carrots, parsley or fresh celery.
Important!
If you have liver diseases, you should refrain from excessively frequent consumption of fresh carrots or their juice.
List of dishes as a main breakfast:
- yogurt with fruit (pieces);
- muesli with nuts;
- eggs (boiled, poached, omelette);
- fruit salad with nuts (yogurt as a dressing);
- if you are not hungry, drink vegetable juice and eat a handful of nuts;
- any breakfast option should additionally contain raw vegetables or fruits.
Dinner and supper. Choose any two dishes from the menu below for lunch and one for dinner:
- vegetable salad (dressing - olive oil, lemon juice, apple cider vinegar);
- fish salad (fresh or canned fish in brine);
- boiled vegetables;
- lamb or beef (boiled or stewed only);
- chicken breast, served with vegetable salad and avocado;
- as a sandwich: bread with avocado, tomato, herbs, red onion, olive oil;
- chicken soup;
- salad: feta cheese, cherry tomatoes, herbs, avocado;
- mixture: nuts, cheese (low-fat), fruits, vegetables, hummus;
- berries to taste.