What foods can you eat if you have liver pain?
There are so-called permitted foods that you can eat if you have liver disease. This is the kind of food the patient’s diet should consist of. So, foods that are good for the liver include:
- pasta and some types of cereals;
- vegetables and herbs;
- sweet soft fruits (dried fruits are also possible), berries;
- dairy products with minimal fat content;
- meat, fish and seafood;
- eggs.
From the above products it is easy to create various tasty and healthy dishes that will benefit the body. So, you can prepare salads, vegetable lean soups, cereals and pasta. Meat and fish should first be finely chopped or minced and then baked. Food should be soft and warm.
Nutrition tips
Doctors give all patients some advice on nutrition and dietary principles. The main ones are:
- First meal. They need to be used in the diet every day. It is recommended to cook soups using vegetable broth, preferably second broth. Other types of rich broths on meat and other products are prohibited. First courses may include vegetables, cereals, dietary meat, and egg whites. Cold soup in the form of okroshka is excluded.
- Bread and baked goods. It is allowed to eat only 1-2-day-old wheat bread and bread crackers made at home. It is prohibited to use fresh bread, yeast dough, or baked goods. You can have very little rye bread.
- Cereals and pasta. The diet for the liver and gall does not prohibit such products; almost all types can be consumed. Cereals need to be boiled in water, making them slimy and boiled. It is allowed to season with a small amount of vegetable oil; pasta can only be made from hard varieties.
- Vegetables. Only those that do not contain oxalic acid are recommended. Pickled and salted vegetables are also prohibited.
- Mushrooms. Such a plant product is strictly prohibited during the diet.
- Fruits. A diet for kidney or gallstone inflammation allows you to eat almost all types of fruits, the main requirement is that they should not be sour. It is recommended to eat them raw, bake or use them to make compotes and jelly.
- Meat. It is best to use dietary varieties; skinless chicken is suitable, beef, lamb, rabbit, and turkey are fine. Such products for the liver and gall should be cooked boiled, steamed or baked. It is allowed to use meat for preparing cutlets and other dishes. By-products are excluded.
- Eggs. It is better to eat them not often. A diet for the gallbladder and liver involves eating only 1 egg per day. It is very useful to make a steamed omelette from protein.
- Fish. Use dietary varieties; hake and pollock work well. It is prepared like meat.
- Milk products. Almost all fermented milk and dairy products are allowed for consumption; in addition, they improve the functioning of the digestive system; the main thing is to monitor the fat content and it is better to use low-fat types.
- Beverages. Dietary table No. 5 does not set strict limits; you can even use coffee and weak tea, but coffee must be diluted with milk. Compotes, fresh juices, and jelly are useful.
- Dessert. One must refuse such food; all that is allowed is honey, jam, jelly.
The course of therapeutic nutrition is determined by the doctor and can last up to 1 year; in some cases, the diet of table No. 5 must be used throughout life.
Prohibited foods for liver disorders
Any food that can irritate liver tissue should be excluded from the menu. List of prohibited foods for liver problems:
- Yeast-based pastries, fried pies, pasties, puff pastry, pancakes, cream-filled products, fresh bread.
- Corn porridge, beans, lentils, barley and pearl barley porridge, pumpkin and sunflower seeds.
- Various sweets.
- Halva, sherbet, kozinaki, popcorn, waffles, chocolate products, products with nuts or sesame seeds, ice cream.
- Mushrooms, spinach, radishes, asparagus, radishes, olives, greens in large quantities, corn, sorrel, pickled cucumbers, garlic, tomato-based products, white cabbage.
- Sour fruits and berries.
- Oranges, grapes, lemon, figs, raspberries, melon, persimmons, dates, pears, hazelnuts, walnuts, peanuts, almonds.
- Strong teas (black, green, hibiscus), cocoa, chocolate-based drinks. Vegetable and fruit juices containing preservatives or colorings. All drinks that contain alcohol. Coffee, sparkling water, stevia, knotweed decoction.
- Fatty dairy products.
- Lamb and beef fat, tongue, pork, liver, kidneys, canned food, various types of smoked foods (lard, balyk, sausages).
- Fatty fish and seafood (carp, salmon, trout, sturgeon, stellate sturgeon, catfish, mackerel, beluga), as well as derivatives of these products - crab sticks, caviar, sushi.
- Fried eggs.
- Spicy foods, sauces, seasonings for meat, ground black pepper, ketchup, mustard, mayonnaise, spices, adjika, unrefined oils.
Diseases of the liver and gall bladder. Basic principles of nutrition
You will have to give up alcohol!
The liver is one of those organs in the human body that endures enormous loads every day. And in order for it to work as it should, it is necessary to “pity” it, that is, to lead the right lifestyle. Unfortunately, 90 percent of the world's inhabitants begin to monitor their diet only when problems have already begun to manifest themselves. This is especially true for the liver. There are several basic principles of nutrition if a person has one or another liver disease:
- In total, up to 2,500 calories should be consumed per day, especially if a person suffers from hepatitis
- You need to eat several times a day and in small portions. This is approximately four to six times a day, depending on your daily routine and opportunity. But 4 is the minimum number of techniques
- You can only eat boiled and steamed foods, because they do not put much strain on the gastrointestinal tract
- It is necessary to completely avoid fried foods. Such prepared dishes are quite heavy, and a diseased liver simply cannot cope with them
- You should only eat warm foods. Under no circumstances should you eat cold or hot, as such changes negatively affect the mucous membranes.
- You need to eat more foods containing fiber, as it stimulates the excretion of bile in the body
As for the gall bladder, the principles of nutrition are the same, because these two organs are closely interconnected, and what is good for the liver will be good for the gall bladder.
Sample menu for the week
A special diet for liver diseases allows you to eat tasty, healthy and varied. The menu for may be as follows:
Monday:
- Breakfast - oatmeal, steamed rabbit cutlets, grated fresh apple, still water.
- 2nd breakfast - cookies, yogurt.
- Lunch - beet soup, fish soufflé, bread, carrot juice, jelly.
- Afternoon snack - fermented baked milk, a piece of biscuit.
- Dinner - boiled fish, green tea, semolina porridge.
Tuesday:
- Breakfast - beet cutlets, boiled rice, jelly.
- 2nd breakfast - crackers, still water, apple-banana soufflé.
- Lunch - vegetable broth, stewed peppers stuffed with rice and meat, cottage cheese casserole, compote.
- Afternoon snack - fruit salad (pineapple, banana and peach), seasoned with low-fat sour cream.
- Dinner - boiled beet salad, dressed with olive oil, kefir.
Wednesday:
- Breakfast - semolina porridge, apple baked in the oven, green tea (with honey), biscuits.
- 2nd breakfast - apple pie, carrot juice.
- Lunch – tomato juice, dumplings with minced chicken, oatmeal cookies.
- Afternoon snack - compote, marshmallows.
- Dinner - boiled chicken fillet, low-fat milk, bread, buckwheat porridge, crackers.
Thursday:
- Breakfast - jelly, muesli with dried fruits, cookies.
- 2nd breakfast - yogurt, a portion of biscuit
- Lunch - vegetable pilaf, seaweed and boiled shrimp salad, bread, carrot juice, marmalade.
- Afternoon snack - potato dumplings, tomato juice.
- Dinner - oatmeal, steamed meatballs, rosehip broth, crackers.
Friday:
- Breakfast - beet and zucchini soup, cabbage cutlets, bread, carrot juice.
- 2nd breakfast - baked apples with low-fat cottage cheese, non-hot chamomile infusion.
- Lunch - fish bits with sour cream, buckwheat porridge, kefir.
- Afternoon snack - banana, cookies, honey drink (stir 2 tsp honey in 200 ml warm water)
- Dinner - fish soufflé, vegetable pilaf, fermented baked milk, crackers.
Saturday:
- Breakfast - meatless soup with pasta, beet cutlets, tomato juice.
- 2nd breakfast - marmalade, banana, jelly.
- Lunch - buckwheat porridge, beef cutlets, bread, compote, cookies.
- Afternoon snack - dumplings with strawberries, tea with mint.
- Dinner - semolina porridge, soup with dumplings, raspberry compote.
Sunday:
- Breakfast - oatmeal, boiled chicken breast fillet, fruit mousse.
- 2nd breakfast - dry biscuits, fermented baked milk.
- Lunch - mussel soup, rice, seaweed, carrot juice.
- Afternoon snack - rosehip decoction, lazy dumplings.
- Dinner - vegetable soup, bread, beet cutlets, still water.
The energy value of the diet should be 2300-2850 kcal (in the case of acute liver inflammation - up to 2450 kcal). Proteins make up the bulk of the diet - from 80 to 130 g per day.
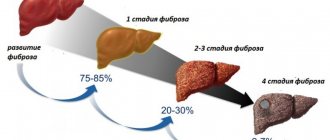
In case of decompensated cirrhosis or absence of positive dynamics, a protein-free diet is prescribed.
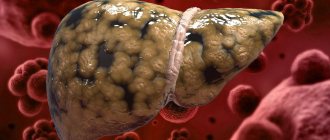
Causes and symptoms of liver pathology
Recognizing a disease of a particular organ can be difficult. But there are a number of symptoms that indicate problems with the gallbladder or liver. These include:
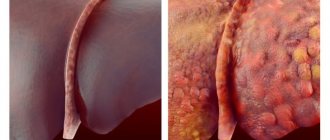
- Aching dull pain in the right hypochondrium. Patients often complain of paroxysmal or prolonged pain. Gallbladder pathology is indicated by attacks of severe pain that radiate to the back, heart or right shoulder blade. Dull painful sensations occur with cirrhosis or hepatitis. When prescribing treatment, the doctor will select the optimal diet for liver pain.
- Heaviness in the right hypochondrium. This symptom indicates overflow of the bile ducts or an increase in the size of the organ. A diet for an enlarged liver should be selected taking into account concomitant diseases.
- The appearance of bitterness in the mouth, decreased or lack of appetite, vomiting/nausea. These symptoms inform about the pathology of the organ. With liver disease, relief does not come after vomiting.
- Changes in emotional state – irritability, fatigue, lack of mood. The doctor will prescribe a set of medications and recommend a gentle diet for the gallbladder and liver.
- An increase in the size of the abdomen, resulting from the accumulation of fluid between the layers of the peritoneum. A properly selected diet for liver diseases will quickly cure cirrhosis and other pathologies.
- Bleeding. If blood begins to flow from the nose frequently for no apparent reason, then you need to visit a doctor. Bleeding that occurs when brushing your teeth also indicates pathology of the liver and other organs. The presence of blood in the stool may be a symptom of varicose veins in the esophagus. It is necessary to adhere to a balanced diet if you have a diseased liver, this will replenish the supply of vitamins and microelements and restore the body’s defenses.
- The appearance characteristic of a sick person is a large belly, thin arms, putrid breath, yellow skin, redness of the palms, changes in the structure of the nail plates.
Pathological processes can be triggered by metabolic disorders in the body, toxins, parasites or viral infections. A properly selected diet for a diseased liver should not contain spicy and fatty foods, alcohol, or an abundance of spices. To quickly restore the functions of the organ, it is necessary to stop taking narcotic substances and a huge number of medications.
How to eat with liver diseases
The diet for liver disease is prepared in accordance with some basic rules:
- Food should be sufficiently high in calories - on average up to 2500 kcal per day.
- You can’t eat a large amount of food at once: split meals in small portions are optimal.
- The best way to prepare food is boiling and pureeing. Such food will not burden the diseased organ.
- Fried foods should be avoided.
- Dishes can be eaten warm: hot and very cold food has an irritating effect.
- The menu should contain fiber-rich foods that help remove bile from the body.
- It is necessary to provide a sufficient amount of light protein (approximately 85-90 g). Its deficiency can provoke degeneration of liver tissue and the development of cirrhosis. Dairy products, in particular cottage cheese, are rich in easily digestible proteins.
- Carbohydrates should not be reduced: they should be consumed from 400 to 450 g daily. The restriction applies to the so-called fast (simple) carbohydrates, found in large quantities in sugar, baked goods, honey, and white flour products. These products provoke stagnation of bile and lead to the deposition of fat in the liver.
- As for fats, many experts believe that when consumed in moderation they are not dangerous for the liver. In case of mild illness, you can eat up to 90 g per day. Fats help normalize the metabolism of fat-soluble vitamins, which is very important for a diseased organ.
Therapeutic diet No. 5 is indicated:
- at the stage of recovery after acute hepatitis and cholecystitis;
- outside of exacerbation of chronic hepatitis;
- with cirrhosis of the liver, not accompanied by liver failure;
- outside of exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis and cholelithiasis.
Therapeutic diet No. 5 is prescribed only in the absence of severe gastric and intestinal diseases.
Therapeutic diet No. 5 is prescribed for the purpose of:
- chemical sparing of the liver with adequate nutrition;
- promoting the normalization of the liver and bile ducts;
- improving bile secretion.
Diet No. 5 is based on a physiologically normal content of proteins and carbohydrates with a slight limitation in the amount of fats, mainly refractory. Products rich in lipotropic substances, fiber, pectin, liquid, as well as products with low cholesterol content, nitrogenous extractives, purines, and oxalic acid are recommended. Dishes are boiled, baked, and rarely stewed. Stringy meat and vegetables with a lot of fiber are consumed pureed. Flour and vegetables should never be sautéed. A 5-6 meals a day diet is recommended.
Chemical composition of therapeutic diet No. 5
- 80 g of proteins, 55% of which are of animal origin;
- 80 g fats, 30% of which are vegetable;
- 350-400 g of carbohydrates, 70-80 g of which is sugar;
- 10 g salt;
- 1.5-2 liters of liquid.
If desired, you can consume 25-40 g of xylitol and sorbitol.
The energy value of diet No. 5 is 2400-2600 calories.