How to effectively treat a disease using unconventional methods
There are a huge number of quite effective non-traditional remedies that help in the treatment of pronounced fibrosis. Treatment of the liver with folk remedies has a lot of advantages, since basically all the remedies are natural and do not cause side effects.
The fundamental goal of treatment with alternative methods is the required protection of the liver and rapid improvement of normal liver function.
To quickly cure liver fibrosis, you should use a medicinal plant called milk thistle. This product has very powerful properties, it:
- protects the liver from destruction;
- improves basic liver functions;
- restores all affected cells.
To treat the liver, you need to consume the powdered seeds of this plant; in addition, carefully ground seeds should also be added to various drinks, for example, kefir.
To stop the process of a significant increase in the size of the liver, you should eat raw chicken eggs on an empty stomach. After taking the eggs, after a certain time you need to drink fairly warm medicinal water, preferably without gas, and then lie on a heating pad for several hours.
When liver fibrosis is observed, a decoction prepared from dried birch leaves is used. This remedy significantly improves all metabolic processes, additionally cleanses the liver, as well as the blood. To prepare the medicine, you need to take dry birch leaves and pour boiling water over them, then put the mixture on low heat and heat until half of the existing liquid has boiled away.
To quickly eliminate even complex fibrosis, you need to use a variety of techniques, mainly aimed at reducing the processes that destroy liver tissue. In addition, the patient must follow a diet. Nutrition in case of liver fibrosis must be balanced. Every patient’s daily diet should contain proteins as well as fats. It is worth limiting your carbohydrate intake.
Each patient's diet should be fractional; it should contain dietary coarse fiber, fruits and vegetables.
Only a doctor can prescribe the correct treatment. Periportal fibrosis in the initial stage may not manifest itself for a long time, but in the future lead to serious irreversible consequences. That is why it is necessary to undergo preventive examinations almost regularly.
Return to contents
The main methods of treating liver fibrosis
Many people wonder whether liver fibrosis can be cured quickly and easily. If the disease is detected at the initial stage, it can be easily cured.
The main problem that faces the doctor and the patient immediately after diagnosis is how to best and quickly stop the rapid development of fibrosis and then begin restorative procedures to improve liver function.
Until recently, it was believed that the only way to treat fibrosis was surgery and organ transplantation. However, at the moment there is an effective treatment system that helps not only stop the process of rapid growth of pathological connective tissue, but also reverse it.
For the most effective treatment of liver fibrosis, medications are mainly used that:
- eliminate the main cause of the disease;
- reduce inflammatory processes in the body;
- activate the liver.
In addition to the fact that patients need to take special medications, they must give up bad habits, follow a diet and daily routine.
All this contributes to faster treatment and restoration of normal condition in the shortest possible time without much effort.
Return to contents
Complications
In the absence of timely treatment, second-degree fibrosis can lead to the development of serious complications and negative consequences.
- Complication of fibrosis and transition from early stages of the disease to later ones, development of cirrhosis.
- Accumulation of a large amount of fluid and the development of inflammation in the abdominal cavity.
- Significant dilation of the esophageal veins, venous bleeding.
- Disorders of consciousness accompanied by disturbances in muscle function.
- Development of liver tumor (carcinoma).
- Severe renal failure.
- The development of diseases of organs affected as a result of disturbances in the liver (deviations in the functioning of the stomach, intestines, anemia, infertility).
Treatment with pharmacological methods and surgical intervention
With the help of pharmacological agents, you can quickly and effectively get rid of the causes that provoke the development of fibrosis.
Patients with rapidly developing liver fibrosis must be prescribed pharmacological therapy. It is aimed primarily at eliminating the causes that provoked the occurrence of this disease. Basic liver functions are supported by various antioxidants. The patient must undergo a course of treatment with various pharmacological agents that perfectly support the basic function of all liver cells.
The use of certain drugs, which are aimed primarily at treating even the last stage of fibrosis, is quite effective in many cases, so you can completely get rid of the disease. However, all medications should be prescribed only by a doctor and the dosage should be selected individually.
Only a doctor will be able to determine the cause of fibrosis and select a drug in such a way as to completely eliminate it.
Surgical treatment is used only when other methods have not given the desired result and the disease continues to progress. If liver fibrosis was caused by the presence of parasites in the body, then it is necessary to perform surgery to remove them using special equipment. Vacuum suction is used to help remove a variety of organisms from some of the cavities in which they settle.
To achieve maximum effect in the treatment of complex fibrosis, an integrated approach should be used.
Rate this article:
Liver fibrosis is the accumulation of connective tissue in the liver in response to hepatocellular damage of any etiology. Fibrosis results from excessive formation or pathological destruction of the extracellular matrix. Fibrosis itself does not show any signs, but can lead to portal hypertension or cirrhosis. Diagnosis is based on liver biopsy. Treatment involves eliminating the underlying cause, if possible. The therapy is aimed at reversing the progression of fibrosis and is currently under investigation.
Activation of hepatic perivascular stellate cells (Ito cells, fat storage cells) causes fibrosis. These and adjacent cells proliferate, becoming contractile cells called myofibroblasts. Such cells cause degradation of the normal matrix and, in part due to changes in the metalloproteinase enzymes that regulate collagen matrix metabolism, stimulate excessive formation of defective matrix. Kupffer cells (resident macrophages), p.o.
Diseases and drugs that cause liver fibrosis
Diseases with direct liver damage
- Some hereditary diseases and inborn errors of metabolism
- α1-antitrypsin deficiency
- Wilson's disease (excess copper accumulation)
- Fructosemia
- Galactosemia
- Glycogen storage diseases (especially types III, IV, VI, IX and X)
- Iron accumulation syndromes (hemochromatosis)
- Lipid disorders (eg, Gaucher disease)
- Peroxisomal diseases (Zellweger syndrome) Tyrosinosis
- Congenital liver fibrosis
- Infections Bacterial (eg, brucellosis)
- Parasitic (for example, echinococcosis)
- Viral (for example, chronic hepatitis B or C)
Disorders affecting hepatic blood flow
- Budd-Chiari syndrome
- Heart failure
- Occlusive diseases of the liver veins
- Portal vein thrombosis
Medicines and chemicals
- Alcohol
- Amiodarone
- Chlorpromazine
- Isoniazid
- Methotrexate
- Methyldopa
- Oxyphenizatin
- Tolbutamide
- Toxins (eg iron, copper salts)
Damaged hepatocytes, platelets, and aggregated leukocytes release various reactive O2 species and inflammatory mediators (eg, platelet-derived growth factor, transformed growth factors, and connective tissue growth factor) that accelerate fibrosis.
Myofibroblasts stimulated by endothelin-1 also contribute to increased portal vein resistance, which increases the density of the altered matrix. Fiber strands separate the afferent branches of the portal vein and the vessels of the efferent hepatic veins at the confluence, bypassing hepatocytes and limiting their blood supply. Consequently, fibrosis contributes to both hepatocyte ischemia (and hepatocellular dysfunction) and the development of portal hypertension. The significance of each process depends on the nature of the liver damage. For example, congenital liver fibrosis involves branches of the portal vein, largely sparing the parenchyma. As a result, portal hypertension develops with preserved hepatocellular function.
!
Found an error? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter.
The term fibrosis is applied not only to the liver disease of the same name, it is a general medical concept that refers to the abnormal formation of connective tissue, accompanied by scarring. In this way, the body can react to an acute inflammatory process - the body tries to isolate the source of inflammation from neighboring, as yet healthy, tissues or organs.
Causes
After identifying connective tissue scars in the liver, the doctor interviews the patient to find out what the cause of fibrosis is and how to treat it. The person is asked in detail about existing diseases, bad habits and lifestyle features.
The cause of fibrous scars can be:
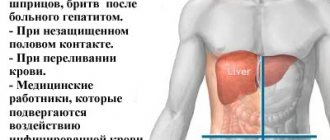
- Hepatitis. The disease caused by the C virus is especially dangerous. Fibrosis in hepatitis C is a process that occurs under the influence of a virus, as a result of which hepatocytes die, which leads to the formation of collagen scars in their place. The disease has a chronic course with periodic exacerbations.
- Parasitic infestations. Penetration of small parasites (Toxoplasma, Echinococcus) into the organ causes an inflammatory process. If the source of inflammation persists for a long time, connective tissue begins to form.
- Drug intoxication. With prolonged use of medications or an overdose of drugs, an inflammatory process develops, which is accompanied by the death of liver cells.
- Amyloidosis. When protein metabolism is disrupted, pathological deposits appear in the liver - amyloids. The accumulation of protein provokes disruption of the organ structure and the growth of connective tissue.
- Unbalanced diet. Abuse of fast food and processed foods, excess fatty foods in the diet lead to metabolic disorders in the liver and deposition of fats in the parenchyma. Inflammation of adipose tissue provokes fibrosis.
- Alcoholism. Chronic intoxication with ethyl compounds causes the organ to work under increased load. Gradually, the liver cells are destroyed, and collagen fibers appear in their place.
- Work in hazardous production. If a person at work comes into contact with toxic chemical compounds (oil refining, production of industrial poisons), then some of the toxic compounds enter the blood and gradually settle in the liver, destroying the parenchyma. Connective tissue forms at the site of liver cell death.
- Endocrine diseases. With diabetes, hypothyroidism and other hormonal diseases, metabolic disorders occur. This can lead to the appearance of pathological deposits in the parenchyma.
- Oncological formations. Malignant cells grow rapidly and put pressure on the parenchyma, causing hepatocyte atrophy. The dead liver structures are replaced by fibrous formations.
- Pathologies accompanied by stagnation of bile (dyskinesia, cholangitis, cholelithiasis). The accumulation of bile secretion in organ tissues leads to the destruction of hepatocytes and the appearance of fibrosis.
- Heart diseases. Cardiac form of disorders, when weak work of the heart muscle provokes blood stagnation, increased pressure in the portal vein and liver edema. This causes periportal fibrosis.
- Autoimmune processes. The human body perceives liver cells as foreign structures and begins to produce antibodies to hepatocytes. A fibrous scar forms in place of the destroyed tissue.
If the cause of the growth of fibrous tissue is intoxication or non-cancerous diseases, then the pathology progresses slowly. Several years pass from the formation of the first collagen scar to the appearance of the first signs of deterioration in health.
What is fibrosis?
Liver fibrosis is a pathological proliferation of connective tissue without changing the structure of the organ. Its course differs from cirrhosis in that the liver lobules do not undergo structural changes and continue to function. Fibrous tissue grows around them, which can lead to deformation of the organ and disruption of its normal functioning.
Causes of the disease:
- chronic inflammatory processes - hepatitis of any etiology;
- toxic damage from alcohol and other poisons;
- parasitic disease - schistosomiasis;
- congenital forms.
Types of fibrosis:
- reversible;
- irreversible - in severe cases it turns into cirrhosis of the liver.
It is important to understand that liver fibrosis and cirrhosis are not identical concepts. Fibrous changes can be stopped, and the affected organ can actually be restored. But without proper and timely treatment, the process of tissue change becomes irreversible.
Risk factors
The likelihood of fibrosis and the rate of its progression depend on various factors. Children, elderly people and those who have been diagnosed with hepatitis C genotype 1 are more susceptible to pathology. It much more often becomes chronic, threatening scarring of the liver.
Factors that increase the risk of fibrosis in hepatitis:
- autoimmune disorders;
- genetic predisposition;
- drug abuse;
- parasitic infestations;
- poisoning with salts of heavy metals;
- extrahepatic blockage of the bile ducts;
- portal hypertension;
- Wilson-Konovalov disease;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
All patients with hepatitis C, without exception, are prescribed a therapeutic diet. It is aimed at reducing the toxic load on the digestive and hepatobiliary system - the liver, bile ducts and bladder. If it is not followed, the load on the parenchyma increases. Activation of oxidative reactions accelerates the transformation of Ito cells into myofibroblasts.
Over time, fibrous tissue replaces the functional cells of the liver and surrounding anatomical structures - hepatic and bile ducts, blood vessels. Therefore, against the background of fibrosis, portal hypertension often occurs, which can only be treated surgically.
Systematic intake of alcohol for 7-8 years leads to massive death of hepatocytes and the formation of fibrous cords in the parenchyma. Against the background of hepatitis, fibrosis progresses 2.5-4 times faster.
Types of fibrosis
The classification of this liver pathology depends on the causes of the disease.
Doctors distinguish 3 types of fibrosis:
- primary hepatoportal sclerosis (non-cirrhotic form);
- periportal fibrosis;
- hereditary congenital form.
The first type of fibrosis - non-cirrhotic - develops due to narrowing or complete blockage of the lumen of the intrahepatic veins, as well as the portal and splenic veins. The disease develops in patients with chronic heart failure, patients with echinococcosis or brucellosis.
The following factors also contribute to the development of the disease:
- alcoholism;
- hepatitis B and C, autoimmune processes – biliary cirrhosis;
- toxic hepatitis;
- parasitic diseases;
- other viral diseases – cytomegalovirus, mononucleosis;
- the effect of arsenic, heavy metals, copper;
- the effect of certain medications - chlorpromazine, methotrexate, tolbutamide;
Periportal fibrosis is the result of the parasitic disease schistosomiasis, which is caused by helminths. It can take 10 to 15 years from the moment of infection to the first symptoms.
Hereditary diseases associated with metabolism cause a congenital form of fibrosis. Some chemicals begin to accumulate in excess in tissues and organs, primarily in the liver. These disorders are often combined with cystic kidney disease.
The second type of classification is based on the prevalence and localization of fibrosis:
- Venular and perivenular fibrosis - destroy tissue in the central lobules of the liver.
- Pericellular fibrosis – affects the membranes of hepatocytes. Impermeable membranes form around liver cells.
- Septal (zonal) fibrosis - large areas of necrotic tissue are formed. There is a disturbance in the structure of the liver lobules; the organ is enveloped in strands of connective tissue. The central veins and portal tracts of the organ are involved in the process.
- Periductal fibrosis – fibrotic areas are concentrated around the bile canaliculi.
- Mixed fibrosis – combines signs of several other types of pathology.
Therapy and prognosis for stage 1 fibrosis
Treatment of stage 1 fibrosis depends on the cause of the pathological process. There are three main areas of emphasis:
- eliminating the cause of the disease;
- adequate therapy to eliminate inflammation;
- slowing down and stopping the growth of fibrous tissue.
Treatment of stage 1 fibrosis
- If the cause of the disease is alcohol, poisons or medications, then first of all you should stop taking them, and then carry out a complete detoxification of the body.
- If fibrosis is detected at stage 1 in hepatitis C, then the most reasonable solution is to start taking direct antiviral drugs. All treatment regimens are based on a combination of Sofosbuvir and other substances, which are selected depending on the genotype.
The most universal regimen is considered to be taking Sofosbuvir and Velpatasvir or Sofosbuvir + Daclatasvir .
You can buy medicines in Russia, but pharmacies sell only American-made drugs, which cost more than a million rubles. When diagnosed with hepatitis C, most patients prefer Indian drugs , whose production is licensed by the same American pharmaceutical companies, but they cost much less. Such manufacturers include Natco, Zydus, Hetero with the drugs SoviHep, LediHep, DaciHep, Hepcinat, Natdac. The therapy provides an almost 100% guarantee of cure and no significant side effects.
- Improving the functioning of the gallbladder can be achieved with the help of choleretic drugs; if there are stones in the bile ducts, then choleretic drugs should not be used.
- To generally reduce the inflammatory process, take hormonal drugs - Prednisolone.
- As support - hepatoprotectors: Essentiale, Karsil, Ursofalk, milk thistle herb, also vitamin and mineral complexes, antioxidants.
- To suppress the progression of stage 1 fibrosis, immunomodulators are used - Virferon, Ergoferon. Additionally, drugs are used that improve microcirculation and reduce the production of connective tissue (Altevir).
The treatment also includes the nutritional principles specified in diet No. 5 - a minimum amount of salt and a healthy diet consisting of vegetables, fruits and steamed dishes with a minimum fat content.
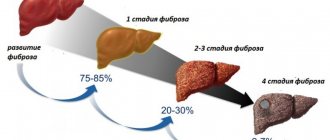
Stages of liver fibrosis
To determine the extent of organ damage, a liver biopsy is recommended. The results are interpreted using either the Metavir method or the Claudel index.
According to these methods, doctors distinguish 5 stages of the disease. A scale with values from 0 to 4 is used to indicate the degree of liver fibrosis.
- Zero degree – there is no liver fibrosis.
- Stage F1 – the organ does not fully perform its functions, the exchange process between liver and blood cells is disrupted. With proper treatment, the prognosis is favorable.
- Stage F2 – changes increase, the affected area increases. Treatment becomes more complicated, and the disease is difficult to control with medications.
- Stage F3 – compactions appear in the liver structures. If proper treatment is not carried out, the prognosis is unfavorable - the disease enters the last stage.
- Stage F4 – liver cirrhosis. It is impossible to cure this disease without organ transplantation.
Stages of disease development
The development of the disease occurs in 4 stages, each of which is characterized by the following signs and symptoms:
- Stage 1 fibrosis is characterized by the presence of a small number of dilated portal tracts, while the formation of connective tissue in the organ occurs to a very small extent or is absent altogether. With timely detection and adequate treatment, stage 1 liver fibrosis can be eliminated without serious consequences for the patient.
- At the 2nd stage of the disease, more extensive changes occur than at the previous stage of development of the disease; most of the portal tracts are expanded. When moving to stage 2 of liver fibrosis, the prognosis remains favorable only with appropriate therapy.
- With further development of the disease, the disease passes into stage 3, which is characterized by the formation of a significant amount of scar tissue. This stage is also called bridging fibrosis. A positive prognosis at stage 3 of liver fibrosis is formed based on the body’s positive reaction to the use of medications and the patient’s compliance with all recommendations.
- The final stage of the disease is stage 4 liver fibrosis. At this stage, the organ consists almost entirely of scar tissue, which in many cases forms false lobes in the liver structure. To treat the disease at this stage, only surgery is suitable, namely liver transplantation.
How quickly the transition from one stage to another will be depends on several factors. For example, if the diet prescribed by specialists for liver fibrosis is not followed, or the age of the patient at which the infection occurred is more than 30 years, then the course of the disease can be rapid. Even the gender of the sick person affects the rate of progression of the disease: in men the disease develops faster than in women. And in the presence of concomitant viral lesions, such as hepatitis C, stage 4 liver fibrosis develops in a very short time, and only a few months pass from the onset of the disease to the final stage. The reason for this is often that the disease is not recognized in time and measures are not taken to eliminate the root causes that caused extensive changes in the structure of liver tissue. Therefore, timely diagnosis plays an important role in getting rid of the disease.
Symptoms of the disease
Liver fibrosis develops slowly and only in the last stages the following symptoms begin to appear:
- fatigue;
- decreased performance;
- intolerance to physical activity and stress;
- anemia;
- bleeding from the vessels of the esophagus;
- impaired immunity;
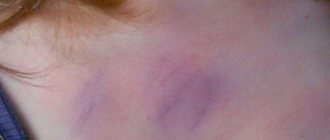
- hemorrhages under the skin, the appearance of small vascular “stars” throughout the body.
At the initial stages there are no symptoms, so a correct diagnosis can only be made using histological examination of a biopsy specimen.
Symptoms
No matter what subtype of the disease, with portal fibrosis of the liver, the symptoms in people will be the same. At stage 1, the manifestations are subtle, and at stage 4, the last, pronounced. 4 is the last stage, so the clinical picture is clear. Vivid symptoms of periportal syndrome can be felt by the patient himself.
Abdominal pain due to fibrosis
Manifestations of periportal fibrosis:
- A person complains that during the day he quickly gets tired and tired.
- Pathological changes occur in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Immunity decreases.
- The patient more often falls ill with colds and various chronic diseases (including inflammatory ones).
- Iron in the body becomes low. Outwardly, this manifests itself in bruises under the eyes, stars from blood vessels on the skin.
- When an ultrasound is performed, the specialist notes an enlargement of the liver, and with it the spleen.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of liver fibrosis includes 3 stages:
- inspection and survey;
- laboratory diagnostics;
- instrumental methods.
At the first stage, the doctor interviews the patient about his symptoms. When did the first pain appear, was there bleeding, itching, swelling of the limbs. The doctor always asks whether the patient has traveled to tropical countries.
A family history is collected. It is important to know whether there have been cases of liver disease in the patient’s family - hepatitis, stones in the bile ducts, diseases related to metabolism.
After the interview, the doctor examines the patient and palpates the abdomen and hypochondrium, notes changes in the color of the skin and sclera of the eyes.
The patient's reflexes and psychological state are assessed. In case of intoxication with decay products, hepatic encephalopathy may develop.
Laboratory diagnostics for liver fibrosis
The following series of tests are prescribed:
- Complete blood test to determine the level of hemoglobin, leukocytes, ESR. An analysis is done for blood clotting and viral hepatitis.
- Blood biochemistry - the level of microelements in the blood is determined, the functions of the liver and pancreas are checked.
- Analysis for fibrosis markers - PGA index.
- Testing for antimitochondrial, antismooth muscle and antinuclear antibodies – autoimmune processes are monitored.
- General urine analysis.
- Coprogram and stool analysis for helminthic infestation.
Instrumental methods
To confirm the diagnosis of liver fibrosis, the following procedures are used:
- Ultrasound will help detect focal areas of fibrous tissue in the liver, changes in the structure of the bile ducts, kidneys, and intestines.
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy is a minimally invasive intervention that allows you to assess the condition of the veins in the esophagus, stomach and duodenum.
- Computed tomography will help exclude tumor processes. Will give an accurate picture of the location of focal changes in the liver.
- Fine needle biopsy is performed under ultrasound guidance. This procedure will make it possible to make a final diagnosis - fibrosis, cirrhosis or liver oncology.
- Indirect elastometry is an alternative to biopsy.
Liver elastometry
This is the latest non-invasive technique for studying the liver. To carry it out, the Fibroscan device is used. The duration of the procedure is 10 minutes.
Advantages of liver elastometry:
- does not injure the skin and internal organs;
- can be carried out repeatedly;
- such a study does not require patient preparation;
- elastometry is the observation of a process in dynamics;
- inexpensive and informative procedure.
During elastometry, fibrous areas with a total volume of up to 6 cubic centimeters can be examined.
Treatment of liver fibrosis
There are several methods for treating this disease.
- Impact on the cause of changes in normal tissue - antiviral therapy for hepatitis. Complete abstinence from alcohol and medications that provoke changes in the liver.
- Stabilization of metabolic processes - removal of excess copper, reduction of stagnation of bile in the ducts.
- Symptomatic treatment of fibrotic changes.
The treatment complex includes the following groups of drugs:
- hepatoprotectors;
- glucocorticosteroids - drugs that relieve the inflammatory process;
- cytostatics - drugs that reduce the proliferation of fibrous tissue;
- immunomodulators;
- antioxidants;
- complex of vitamins;
- enzymes that help digestion.
When treating diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, you must follow a diet.
Meals should be fractional - 5-6 times a day. Eliminate fatty, salty, smoked foods, eat more vegetables and dairy products. This is not a diet, but a system of proper nutrition.
Preventive actions
Liver fibrosis is easier to prevent than to treat.
Prevention involves the following actions:
- avoid stress and physical activity when treating hepatitis;
- monitor your diet;
- play sports or do exercises, walk a lot;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- do not use potent medications without a doctor’s prescription;
- treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - ulcers, pancreatitis, cholecystitis;
- take vitamins.
Liver fibrosis is not a death sentence. With early diagnosis and systematic treatment, the prognosis of the disease is favorable.
Category: Gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary system
Liver fibrosis - main symptoms:
- Enlarged spleen
- Spider veins
- Liver enlargement
- Increased fatigue
- Malaise
- Intestinal bleeding
- Appearance of bruises
- Anemia
- Decreased performance
- Bruising
- Liver dysfunction
- Inability to cope with mental stress
- Instability to physical activity
Liver fibrosis is a pathological irreversible process, as a result of which liver cells are replaced by connective tissue. It is worth paying special attention to the fact that the cells are not restored. The replacement process is slow. For the first 5 years, the clinical picture is almost completely absent.
This has a negative impact on treatment, since liver fibrosis can only be diagnosed in the early stages by chance, when conducting research on another disease. The prognosis for this disease is disappointing, since the pathology is irreversible.
Causes, symptoms and diagnosis of stage 2 fibrosis
Briefly below is a description of the changes occurring in the liver at various stages of fibrosis:
- F1 – first stage – septa are not formed, changes affect the portal tracts;
- F2 – stage 2 liver fibrosis – against the background of fibrotic changes in the portal tracts, the formation of septa can be observed (small number);
- F3 – large number of septa;
- F4 – false lobes of the liver appear, cirrhosis begins.
Causes
There are several main causes of fibrosis:
- chronic alcohol dependence;
- viral hepatitis B, C;
- uncontrolled use of hepatotoxic drugs;
- disturbances in the functioning of the immune system - autoimmune hepatitis;
- mononucleosis of infectious nature;
- stagnation of venous blood in the liver - Budd-Chiari syndrome;
- diseases of the biliary tract - blockage, inflammation, stone formation;
- hereditary metabolic defects.
Symptoms
Symptoms of fibrosis, especially in the early stages - fibrosis 1, 2 or fibrosis at the intermediate stage 1-2, practically do not appear, but the following may occur:
- feeling of constant fatigue, physical activity is more difficult than before;
- weakened immunity;
- bruises are observed on the body, without objective reasons for their occurrence.
As the process progresses and pathological changes worsen - fibrosis of intermediate stages 2-3, 3 and 4, the symptoms become more pronounced, the following is observed:
- anemia, leukopenia, confirmed by laboratory tests;
- increase in the size of the spleen;
- pain in the liver area;
- dilation of the veins of the esophagus, as a result of internal bleeding;
- Ascites may occur - the abdomen looks like a bag of water, which complicates diagnostic procedures.
Causes of pathology formation
One of the most common causes of liver fibrosis today is excessive alcohol consumption and consumption of unhealthy foods. In addition, the following factors can be identified:
- long-term drug treatment;
- poisoning by toxins;
- congenital fibrosis;
- viral hepatitis;
- diabetes mellitus, metabolic disorder;
- deficiency of minerals and vitamins.
In some cases, the progression of liver fibrosis may be due to heredity. Also, if the patient has suffered or is suffering from group C hepatitis, liver fibrosis is practically guaranteed.
Liver fibrosis stage 2 - how long do people live with this pathology?
The prognosis for early detection of the lesion is favorable. If there are many concomitant diseases and the body’s condition is assessed as low, moderate remission can be achieved. Cases of slow progression of fibrosis have been reported in clinical practice. Without treatment, patients with organ damage live on average up to 25 years. If diagnosed in advanced stages (3, 4), the duration ranges from 5 to 12 years.
This is interesting: Stage 1 liver fibrosis: causes, symptoms, treatment and prognosis
How long patients diagnosed with stage 2 fibrosis live depends on the type of causative agent of the inflammatory disease and its susceptibility to the prescribed therapy. Hepatitis of all forms and diseases provoked by herpes viruses are successfully cured in most patients. Alcohol and toxic injuries are less treatable.
Symptoms
As mentioned above, the disease does not manifest itself in any way for the first five years. At the end of this time period, the following symptoms of liver fibrosis can be observed:
- hepatomegaly;
- enlargement of the spleen;
- bleeding from the walls of the esophagus;
- bruising and dilated blood vessels;
- malaise, increased fatigue;
- instability to stress of any type - physical, mental.
It is worth noting that the severity of symptoms largely depends on the degree of the disease. In the early stages, the symptoms of the disease may be completely absent, but in the later stages they are very pronounced, so this condition causes significant discomfort to the person.
Stages and forms of the disease
In total, there are four degrees of this pathology. If radical treatment is not started in a timely manner, liver cirrhosis may become the final stage.
The disease can begin to develop in any part of the liver lobule. Depending on this, the following degrees are distinguished in medicine:
- 1st degree – portal and periportal fibrosis (this degree is relatively mild and does not require specific treatment);
- 2nd degree – porto-portal septa;
- 3rd degree – porto-central septa;
- 4th degree – false lobules in the structure.
Stages of liver fibrosis
It is the false lobules that lead to the worst thing - cirrhosis of the liver. It is no longer possible to stop this process. This degree in most clinical situations ends in death. However, this can be prevented if you consult a doctor in time and start treatment.
Depending on how liver fibrosis spreads, the form of the disease is determined:
- venular - damage to the central part of the liver;
- pericellular – formations around the cells of an organ;
- septal - tissue necrosis;
- periductal – surrounding the bile ducts;
- mixed type.
A distinction is also made between cardiac fibrosis and periportal fibrosis. Cardiac disease can develop against the background of heart failure. As for the periportal subtype, such liver fibrosis can be caused by problems with the gastrointestinal tract and poor nutrition. Periportal fibrosis, like cardiac fibrosis, leads to liver deformation and its subsequent cirrhosis. It is quite difficult to diagnose this particular form, since the clinical picture is almost identical to venular fibrosis of the liver. Cardinal fibrosis is more common.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of liver fibrosis is one of the most difficult. To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to conduct more than one instrumental and laboratory analysis. Among the mandatory diagnostic methods are the following:
- general tests of urine, feces, blood;
- blood chemistry;
- Ultrasound of the liver;
- biopsy;
- computed tomography of the liver;
- elastography.
In addition, the doctor should pay attention to the family history and take into account the patient’s complaints. When conducting examinations and diagnostic measures, it is imperative to take into account the patient’s diet and the presence of bad habits. If liver fibrosis is diagnosed at an early stage, the prognosis is not so pessimistic. In any case, liver cirrhosis and death can be excluded.
Diagnosis of periportal fibrosis
When a person notices alarming symptoms, he may not immediately, but he goes to the clinic for an appointment with a therapist or gastroenterologist. The sooner the patient applies, the greater the chance of significantly improving the condition of the organ through medication and diet.
At the appointment, the doctor examines the patient. If the stage of development of the disease is initial, then the doctor will not find anything special. When the patient has grade 3 or 4, then by palpation the doctor will feel that the organ is greatly enlarged and has become dense.
To diagnose what stage of periportal fibrosis a patient has, the following methods are used:
- A clinical (general) blood test is performed. Bad signs are when the hemoglobin level is low, the number of red blood cells is less than normal, and the ESR is high.
- General urine analysis. Alarming indicators - excess protein, bilirubin, casts in urine sediment.
- Blood chemistry. With periportal fibrosis, all liver parameters increase: alkaline phosphatase, ALT, total bilirubin, AST, GGT.
- An abdominal ultrasound will show an enlarged liver, pathological changes in its structure: foci of periportal fibrosis, with strands of connective tissue, cysts due to parasites, dilated vessels of the organ with bile ducts.
- Elastometry (indirect). They do it with a fibroscan. This helps to find out what condition the internal structure of the tissues is in, is it broken? The technique will show how elastic the fabric is. The parenchyma is less dense than the structure of fibrous tissues.
- CT or MRI of the abdominal cavity.
The doctor prescribes a biopsy, only after which he can say for sure that the patient has periportal fibrosis of the liver.
How do they do it? Under ultrasound guidance, using a thick trepanation needle, a small amount of liver tissue is taken through a puncture for analysis.
This is interesting: What is the difference between fibrosis and cirrhosis of the liver?
To assess at what stage the disease is, use the scale:
- Grade 0 – no periportal fibrosis.
- Degree 1 – the organ is not functioning properly. The portal tracts have a stellate shape. When treatment is started at this stage, the prognosis is favorable.
- Stage 2 – there are more and more lesions. Partitions are formed in the lobes. For now they are isolated. If you start taking medications at this stage, the patient will recover.
- Degree 3 – cords consisting of connective tissue pass through the organ. It is larger than normal, with dilated bile ducts. Poor prognosis. Using medications will only provide some relief.
- Degree 4 – cirrhosis has begun, it cannot be treated. A liver transplant is required.
A biopsy is contraindicated when there is poor blood clotting, cysts with helminths, or the patient’s serious condition. In these cases, elastometry is done.
Treatment
Liver fibrosis can only be treated with medication. Conventionally, treatment of liver fibrosis can be divided into the following stages:
- eliminating the causes of pathology;
- reduction of symptoms that occur with liver fibrosis;
- elimination of processes that cause a destructive process.
At each stage of treatment, proper nutrition is required - the diet is prescribed by the doctor individually. Treatment also largely depends on the stage of the disease. If pathology is detected in the early stages of its development, then treatment will be simpler - diet and vitamin intake. In more severe situations, the doctor may prescribe other synthetic medications that will help eliminate the signs of the disease.
At the initial stage, in addition to diet, antiviral drugs are prescribed. If any medications show signs of further tissue damage, they should be stopped immediately and replaced with a similar but less aggressive drug.
It is worth noting that the diet for fibrosis is significantly different from the one prescribed for excess weight. The patient must receive the necessary complex of vitamins and minerals. In this case, the load on the liver should be kept to a minimum. During treatment, the use of:
- alcohol;
- fatty and fried foods;
- spicy, salty dishes.
It is prohibited to drink alcohol during treatment
Naturally, smoking should also be avoided. A proper diet can not only help treat fibrosis, but also cleanse the body of toxins and help lose excess weight.
Symptoms and prognosis
Signs of hepatic fibrosis may appear five years after the start of the pathological process. Often the disease already at stage 2 of the disease is accompanied by:
- increase in organ size;
- thrombocytopenia;
- bleeding from the esophagus;
- enlarged spleen.
Fibrosis, which limits the normal functioning of the liver, often causes cirrhosis, as well as liver failure and portal hypertension.
This stage cannot be treated and requires a liver transplant. The first and second stages often occur without pronounced symptoms. Therefore, at this stage the disease is difficult to diagnose. The second stage may be accompanied by inflammation and enlargement of the spleen. At the same time, the number of blood cells (leukocytes, platelets) decreases, which causes anemia and anemia. Liver tissue changes significantly. Important! If therapy is started in a timely manner at the second stage, the prognosis for recovery is favorable.
The rate of progression directly depends on the severity of inflammatory processes in the liver. Further development of the disease (stages 3 and 4) can cause cirrhosis, the occurrence of varicose veins of this organ, hemorrhage, and scar formation.
The prognosis for fibrosis of the second degree depends not only on the individual susceptibility of the body to drug treatment, but also on the normalization of lifestyle and diet.