Hepatitis B is a fairly stable virus that survives well in the external environment. Due to its “endurance,” the type B virus is highly infectious, remaining in a viable state even in dried blood stains. Since the virus has a high prevalence, a significant proportion of people are its carriers, and every fourth carrier dies. In countries with developed economies, mortality is significantly lower than in regions with poor quality of medical care. And here the question of whether it is treated or not depends more on the quality of medical care that patients receive.
Routes of infection
Through microtraumas on the skin, the hepatitis B virus penetrates the human body and reaches the liver through the bloodstream, where it begins to actively multiply in its cells, provoking their pathological changes. The human immune system reacts to this process - lymphocytes attack the changed cells, but at the same time they also attack the organ’s own tissues.
The main source is the blood of an infected person. It can be transmitted to a healthy person through:
- use of personal hygiene items;
- hemodialysis machines;
- poorly processed instruments in beauty salons;
- transfusion of contaminated donor blood;
- through instruments used in dentistry, in operating rooms, manipulation rooms, etc.;
- through unsterile needles.
The virus is also transmitted sexually and transplacentally - from an infected mother to a child during fetal development. It is worth noting that shaking hands, using the same utensils, and breastfeeding do not transmit the infectious agent. Other routes of transmission have not been recorded.
Risk group
Risk factors for hepatitis B infection
Now, at the state level, a list of people who are at risk of contracting this disease has been approved, so they need to be given a vaccine against hepatitis B:
- students of schools and institutes;
- drug addicts;
- patients who regularly require intravenous administration of drugs;
- people who need regular hemodialysis;
- children who go to kindergartens;
- workers of medical institutions;
- people who are promiscuous.
Forms
This dangerous disease has several forms of development:
- lightning fast. In this case, the symptoms of the pathology develop rapidly, accompanied by severe cerebral edema and a coma. The treatment is not effective. The entire pathological process takes only a few hours and ends with the death of the patient;
- acute hepatitis B. This form has several stages of development: the stage of manifestation of general symptoms, icteric and the stage of resolution or further progression of the pathology;
- chronic viral hepatitis B.
Symptoms
The incubation period of the disease is quite long - from two months to six months, but sometimes this period can be shortened to 30 days or extended to 225 days. During the progression of the incubation period, symptoms of the pathology are completely absent.
Symptoms of hepatitis B depend on which form of the disease affects the person.
Lightning form
The most dangerous type of pathology, as the clinical picture develops rapidly. A person experiences an attack, which is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- vomit;
- severe weakness;
- a person cannot get out of bed on his own;
- dizziness;
- bruises appear on a person’s skin during this period;
- swelling occurs in the legs;
- fainting;
- blackouts;
- gums bleed;
- Nosebleeds often occur.
As a rule, this period ends in a coma and death is also possible.
Anicteric period
During this period, there are no specific manifestations of pathology yet. Symptoms that are characteristic of most viral diseases come to the fore:
- headache;
- the person’s well-being gradually deteriorates;
- there is a loss of appetite;
- lethargy;
- weakness;
- muscle and joint pain;
- the appearance of respiratory manifestations (cough, runny nose) is observed.
Jaundice period
During the icteric period, the manifestation of symptoms characteristic of this disease is observed. They appear in the following sequence:
- at the beginning of the period, urine changes its color - it becomes the color of dark beer;
- further yellowing of the sclera and oral mucosa is observed;
- The palms and skin acquire a yellow tint.
As soon as jaundice appears during this period, the patient’s condition gradually stabilizes. Of the main symptoms, he may be bothered by heaviness in the right hypochondrium (at the location of the liver). There are no other symptoms. Possible lightening of the stool due to blockage of the bile ducts.
The severity of jaundice is directly related to the severity of the pathology, as well as the progression of cholestasis syndrome. Stabilization of jaundice is observed on the 10th day, after which it decreases. In severe cases, hemorrhagic syndrome may also appear - pinpoint hemorrhages into the skin are observed. Hepatitis B is more severe in children. Symptoms persist for a long time and there is a high risk of developing dangerous complications.
Recovery period
After jaundice, a convalescence period begins. The jaundice disappears. The patient has no complaints - his appetite is restored, weakness disappears. If the disease is benign, then liver functionality is restored after 4 weeks. If treatment of the pathology was not carried out in a timely manner or was incomplete, then there is a risk of the acute form of viral hepatitis turning into chronic.
Chronic form
Chronic hepatitis B is manifested by the following symptoms:
- increased fatigue;
- weakness;
- drowsiness;
- decreased appetite;
- nausea, vomiting;
- bloating;
- characteristic symptoms of chronic hepatitis B, such as darkening of urine and jaundice, appear much later than in the acute form.
Symptoms of hepatitis B
Hepatitis C incubation period
The incubation period of infectious diseases is the period of time between a person becoming infected and the appearance of the first symptoms. The incubation period is one of the most important criteria for the disease, which reflects the body’s response to the virus and their interaction.
The incubation period of viral hepatitis C can be short (about 14 days), or it can reach more than 20-30 weeks, that is, more than 1 year can pass from the moment of infection to the first signs of the disease.
In this respect, hepatitis C is similar to hepatitis B, the incubation period of which can last from 2 months to six months. On average, the incubation period for HCV is thought to be 59 days. During the incubation period of hepatitis B and C, the virus multiplies in the human body, which leads to an increase in its number. After this, it spreads throughout the body and reaches the organs to which it shows typicality, that is, the liver. Then the virus enters the active stage and begins to have a pathological effect on liver cells and tissues. At first, liver cells resist harmful bodies, but over time their protective properties decrease, which leads to clinical changes. In 45% of cases, hepatitis C occurs in an acute form. The incubation period lasts about 14-20 days, after which the first symptoms of the disease appear. This allows you to diagnose pathology in the early stages and provide high-quality treatment, with the help of which a person will be healthy within a few months. In the remaining 55% of cases, the incubation period is quite long, and the disease immediately becomes chronic without any obvious symptoms. In this case, the person does not even suspect that he is a passive carrier of a virus that is gradually destroying his liver. Considering the fact that identifying hepatitis C is extremely difficult, and treatment of the disease is expensive and time-consuming, for prevention purposes, try to do the following:
- under no circumstances use other people’s personal hygiene items that may contain the blood of an infected person (razors, toothbrushes, etc.);
- go only to trusted beauty salons;
- try to control all medical procedures to which you undergo;
- If you are sexually active, give preference only to protected sex.
Compliance with these simple requirements will protect you from possible health problems.
Hepatitis B is an acute or chronic viral infectious disease that damages hepatocytes (liver cells). The disease is caused by a DNA virus.
Diagnostics
As a rule, during the incubation period, almost none of the patients seek help from a doctor, since there are no symptoms of pathology. A doctor is consulted when an acute form of pathology develops, when the clinical picture is more than pronounced.
Diagnosis of hepatitis B in children and adults is carried out by an infectious disease specialist. For this purpose, the patient is interviewed, thoroughly examined, and clinical and laboratory tests are prescribed.
It is mandatory to take a blood test for:
- determination of the biochemical composition of blood;
- detection of hepatitis B virus;
- detection of IgM and IgG antibodies.
Which hepatitis can be cured and which cannot?
The group of viral hepatitis consists of five viruses, which are designated by the letters A, B, C, D and E. Previously, scientists had isolated hepatitis G, but they quickly realized that this virus causes a completely different disease.
What are hepatitis A and E viruses?
The dangers of a hangover
Russian allergists are demanding a ban on hangover medications containing the substance unithiol. The idea of the ban arose due to the fact that doctors often... →
Hepatitis viruses A and E belong to the group of viruses with an enteral mechanism of infection. It implies infection “through the mouth.” They are the least dangerous from the patient's point of view. These viruses always cause an acute disease that never becomes chronic.
Hepatitis A is Botkin's disease, or "dirty hands disease", it occurs when eating dirty food or water.
A patient with hepatitis A or E almost always recovers and has lifelong immunity to the infection. However, fulminant hepatitis, which is acute liver necrosis, can become a complication. In this case, liver failure occurs, often leading to the death of the patient.
There is no specific treatment for hepatitis A and E. However, there are effective and safe preventative vaccines. The hepatitis A vaccine was invented a long time ago, however, it is not included in the vaccination calendar in our country. It is known that during outbreaks of hepatitis A, virtually no infection occurs among those who are vaccinated against this infection. And I, for example, am vaccinated.
Hepatitis E is a rarer hepatitis in developed countries with a similar route of infection. A vaccine against this virus was created in China several years ago, but so far it has only been approved in this country.
Hepatitis B and C
Homeopathy: how to dilute correctly
On April 10, Samuel Hahnemann, the father of homeopathy, an alternative medicine that involves the use of highly diluted drugs, was born... →
There are also hepatitis B and C viruses, which belong to the group of parenteral infections. Infection with them occurs through the blood: through intravenous drug use, medical procedures using poorly sterilized instruments, infected blood during transfusions, and so on. Hepatitis B and C viruses cause chronic liver disease in most cases.
According to current estimates, there are about 240 million people in the world with chronic hepatitis B.
The risk of chronic infection when infected with the hepatitis B virus varies depending on the age of the patient: in children under one year of age it is more than 90%, while in adults it does not exceed 5%. The danger of chronic hepatitis B is that almost a third of patients develop cirrhosis and/or liver cancer.
Scientists have developed a prophylactic vaccine against the hepatitis B virus, which is safe and protects very well against infection. It is protein based rather than infectious material and is well tolerated by humans. Interestingly, there is now a combined vaccine against hepatitis A and B.
The hepatitis C virus was discovered the latest - in 1989, when I was in second grade. This virus is extremely difficult for laboratory research. With other viruses, scientists usually take a cell line and try to infect it. And the hepatitis C virus, as it turns out, is unable to develop in almost any standard cell line. In general, research into the hepatitis C virus has been severely hampered.
An incomplete cellular model was obtained only in 1999.
“I ate homemade mushrooms - and aha”
What forms of botulism exist, what is the most common poisoning in Russia and the USA, what first aid should be provided to the victim and why during the first... →
And the complete infectious model appeared only in 2005 - quite recently. But by now, scientists know all the key mechanisms of infection development in a cell: from infection to the assembly of new viral particles.
We know that this is a very common virus. Why? Most likely, because in most cases the disease begins asymptomatically. Now, according to various sources, 130–150 million people have chronic hepatitis C. In Russia, according to some data, up to 3% of the population suffers from it. In 4/5 cases, hepatitis C becomes chronic. And even in the chronic stage, this virus can be asymptomatic - and can only be diagnosed using special tests.
Like hepatitis B, hepatitis C is extremely dangerous: it often leads to fibrosis and cirrhosis of the liver. And in a number of patients, it ultimately leads to cancer. As far as I know, treatment for liver cancer is not very effective and can only be cured by transplantation. It is believed that up to 80% of all patients with cirrhosis and liver cancer are patients with chronic hepatitis B and C. There is evidence that even patients who have recovered from hepatitis C have an increased risk of developing cirrhosis or liver cancer.
How to treat hepatitis B and C?
Hepatitis B is treated quite poorly. That is, it is easy to suppress, but almost impossible to cure, because it has so-called cccDNA - double-stranded circular DNA. And it is still unknown how to remove it from already infected cells. Several types of substances are used to suppress infection: nucleoside analogues and interferon alpha and its pegylated forms. However, they do not always work.
Pseudodiagnosis: how to avoid becoming a victim of a medical scam
How to understand that you are being deliberately misdiagnosed, whether detox programs are effective and why we are so fond of “treating tests”, the department of science... →
Recently, a drug was developed against hepatitis B based on inhibition of the cell receptor with which the virus interacts. In the early 2000s, scientists first found a cell line that reproduces the full cycle of the hepatitis B virus and identified the NTCP receptor, a bile acid receptor. And it turned out that when interacting with this receptor, the hepatitis B virus enters the body. Then the researchers took peptides that imitate a fragment of the viral protein that is responsible for binding to it, and developed a drug that is now undergoing clinical trials.
However, all these drugs cannot cure patients with chronic hepatitis B.
Unlike hepatitis B, hepatitis C can be cured. He is responding very well to treatment now. Patients are considered cured if viral RNA is not detected by sensitive test systems 24 weeks after the end of therapy. In the 2000s, therapy was based on interferon alpha - treatment lasted up to 48 weeks, was very difficult for the patient and ineffective. After six months, the patient was checked, if he did not have the virus, the patient was considered completely healthy. Then scientists developed direct-acting antiviral drugs, that is, those not aimed at the virus proteins.
Thanks to them, the number of people recovered (percentage of cure / effectiveness of therapy) increased.
Is it possible to beat Parkinson's disease?
Almost two centuries have passed since the first description of Parkinson's disease, but there is still not a single recovered patient in the entire world.
Why... → And what is important, the treatment time has been reduced. Currently, there are combinations of direct-acting drugs that can cure up to 99% of patients with a virus of any genotype, without the use of interferon. It has become possible to treat also HIV-infected people, who previously represented a separate cohort of patients. Now doctors treat them simply by taking into account the interactions of anti-hepatitis drugs with antiretroviral drugs. It has become possible to treat patients with cirrhosis of the liver, as well as patients before liver transplantation. And this is a huge breakthrough in science.
By the way, I personally work in a laboratory that studies metabolic processes during infection with the hepatitis C virus. Although patients can be cured, it is impossible to completely eliminate the risk of cirrhosis, fibrosis and liver cancer. These risks remain. We are studying metabolic pathways and finding out how the virus affects them and whether it is possible to make a substance that can suppress the pathogenicity of the virus.
Hepatitis D virus, or Parasite on a parasite
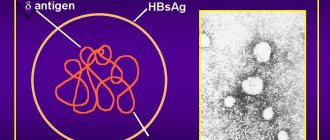
Hepatitis D virus (or delta virus) is a satellite virus. It was discovered a long time ago by an Italian group of scientists who tried to find out why in the north and south of Italy patients with chronic hepatitis B have different courses and severity of the disease. And the Italians discovered that patients with severe disease have some additional delta antigen. Then scientists realized that it was a satellite virus, that is, an incomplete virus. If an ordinary virus is a parasite within a cell, then it is a parasite within a parasite. It carries a short circular RNA and encodes only one antigen (protein). This antigen can be in two different forms - but still it is encoded by a single gene.
This protein can form the virus capsid - the inner shell of the viral particle, but it is not enough to form a full-fledged virion of its own. To form a viral particle, this virus uses the envelope proteins of the hepatitis B virus. The delta virus protein does not have enzymatic activity, and it uses the host cell apparatus to replicate its genome.
“Liver cleansing is a dangerous misconception”
The science department of Gazeta.Ru told about how to remove fat from the liver, how to prevent the formation of cirrhosis and whether one should be afraid of viral hepatitis... →
The number of people infected with hepatitis delta in the world is estimated at 15 million people. There are two different types of infection - coinfection and superinfection.
Coinfection is the simultaneous infection of hepatitis B and delta viruses, and superinfection is the infection of hepatitis D in patients with established chronic hepatitis B.
In each case, the course of the disease will be different. With coinfection, acute hepatitis will develop in 95% of cases, but there will be no chronic disease. But at the same time, there is a fairly high probability of developing the already mentioned fulminant hepatitis. And that's bad.
In the case of superinfection, as a rule, chronic hepatitis will occur, in which the development of liver fibrosis is sharply accelerated - the proliferation of connective tissue with the appearance of scar changes, as well as an increased risk of cirrhosis and liver cancer.
In conclusion, it is important to note that hepatitis D can be prevented by vaccination against the hepatitis B virus. This is especially important for certain regions where the spread of this virus is quite high: in the Mediterranean countries, in parts of Africa, in the Middle East. In Russia, such a region is, for example, Tuva. About ten years ago, the number of infected people in some age groups reached 20%. However, in younger people who were vaccinated against hepatitis B according to the vaccination schedule, no infections were detected.
Therapy
Treatment of a mild form of pathology can be carried out at home, but only after examination by a qualified specialist and obtaining permission from him. The treatment plan includes:
- carrying out detoxification. The patient needs to drink as much mineral water as possible to reduce the severity of symptoms and also restore water balance in the body;
- moderate physical activity;
- complete cessation of alcohol consumption;
- It is prohibited to take any medications without a doctor’s recommendation;
- dieting. Fatty, fried and smoked foods are excluded from the diet;
- Antiviral drugs are not prescribed for this form of the disease.
Treatment of acute forms of pathology:
- for the treatment of this form, antiviral drugs are already prescribed: interferons, nucleide analogues;
- maintenance therapy. The basic treatment plan is supplemented with hepatoprotectors and immunomodulators;
- detoxification. In this case, taking oral fluids is no longer enough, so doctors prescribe sterile solutions to be administered intravenously to reduce the level of toxins contained in the body;
- vitamin therapy;
- dieting.
Surgical treatment is indicated only in cases of liver cirrhosis. It is allowed to be carried out only in the inactive stage. This treatment method involves transplanting a donor liver to a sick person.
Treatment of the disease
In mild cases, the patient is prescribed bed rest and a diet with fractional meals. With good immunity, 90% of patients recover on their own.
Pharmaceuticals are traditionally and widely used in complex therapy.
In order to alleviate the condition and reduce intoxication, it is recommended to take sorbents, normalize water-salt balance, vitamins and hepatoprotectors, which prevent the resolution of liver cells. Taking antiviral medications is important to stop the virus from multiplying and prevent reactivation. This is achieved by prescribing Adenofir, Lamivudine, Tenofovir, Entecavir. If the liver is in good condition, Interferon injections are given. UDCS is necessary for complications such as cholestasis. Particularly severe cases require intensive treatment. A diet without fatty, salty, spicy foods is required, that is, with the most gentle diet possible.