The beginning is half the battle. This rule applies to almost any field of activity, and even to software testing.
Often at the beginning of a project, testers exude enthusiasm by writing documentation (test strategy, test plan, or test cases).
But in the future, difficulties often arise. After completing the first round of testing, testers usually find a bunch of bugs, and then approach the second round somewhat relaxed. There is a so-called the human factor and the universal human tendency when it becomes boring to perform repeated operations.
In such situations, many people feel that they are doing monotonous work, and, as a result, they lose interest in continuing testing of already familiar software. And during approximately the third round, the question inexorably hangs over the tester: “When should you stop testing?”
Every tester has asked this question at least once, the extended version of which would look like this:
What is meningitis and why is it dangerous?
Meningitis is a disease of infectious or non-infectious origin. The pathology is characterized by inflammation of the meninges. Non-infectious forms of meningitis develop as a result of complications, injuries, and abnormalities in the development of the head. The causative agents of the infectious type of disease are:
- Pneumococcus;
- meningococcus;
- hemophilus influenzae;
- Klebsiella;
- enterococcus and other microorganisms.
Children of the first year of life are especially vulnerable to pathogens because they have not yet formed immunity. Vaccination begins a few months after birth, and periodic boosters are required throughout life.
Meningitis is dangerous due to its complications and difficulty of diagnosis. The disease is often confused with ARVI, losing precious time for treatment. If assistance is not provided in a timely manner, the child develops blindness and deafness in a short time, and the sad consequence of inflammation of the meninges is death.
Meningitis in a child – Doctor Komarovsky School
How often do adults need
Adults should undergo a tuberculin test for medical reasons in the following cases:
- suspicion of extrapulmonary tuberculosis;
- treatment with certain drugs (glucocorticoids, immunosuppressants);
- unwanted additional radiation exposure (recently performed x-rays, radiotherapy).
After 16-18 years, the Mantoux test is rarely done - once every few years, unless there are medical indications. And after 35 years it can only be done upon request. Mantu can often be given to those who spend a long time (business trips, residence) in areas unfavorable for tuberculosis, come into contact with people with tuberculosis, due to the specifics of the profession or in a burdened epidemiological environment.
Normally, in adults, the reaction to the test should be negative or the papule with a diameter not exceeding 4 mm. The characteristics of an adult’s body and its immune status make the test less informative than in children, so preference is given to fluorography.
Who needs immunization
The meningitis vaccine is not included in routine vaccinations. Parents will not be able to find this name on the immunization schedule. However, some vaccines contain sera against specific pathogens, such as pneumococcus and Haemophilus influenzae.
Emergency vaccination is carried out in areas with outbreaks of this disease. Pediatricians and immunologists recommend vaccination:
- babies and older children who have immunodeficiency;
- children who attend preschool and school educational institutions or sections;
- children who live in epidemically unfavorable areas;
- if the child has been in contact with an infected person.
If parents wish, immunization is performed without indications. You can purchase the vaccine from public and private medical institutions and supply it at your own expense.
Emergency vaccination of the population is carried out during an epidemic. An epidemic is recognized when 20 cases of meningitis are detected among 100 thousand children.
Testing can be completed when:
- All 100% of the requirements are taken into account.
- Defects identified/expected number of defects detected.
- All defects classified as Show Stopper or Blocker have been fixed; none of the critical defects have the “open” status.
- All high priority defects have been identified and corrected.
- Defect Rate is below the established acceptable level.
- A very small number of medium-criticality defects have been “opened” and have been analyzed.
- The number of "open" mid-level defects that do not affect the use of the system is very small.
- All high priority defects have been closed and the corresponding regression scenarios have been successfully completed.
How does the vaccine work and how long does it protect?
Vaccinations against meningitis are single-component and multi-component. The first contain the serum of one pathogen, while others form protection against several at once. After the vaccine is administered, immunity is formed already on the 5th day, so emergency immunization is considered quite effective against certain pathogens. The formation of antibodies is completed by the second week.
After the introduction of serum, active biological and chemical processes begin in the body. The immune system detects the causative agent of meningitis, recognizes it and produces antibodies. Immunoglobulins remain in the body for a long time. The duration of action of vaccines for different pathogens differs. Some vaccinations provide lifelong immunity.
If, after immunization, a child encounters a meningitis pathogen, the probability of infection will not exceed 0.1%. If infection does occur, the risk of complications and negative consequences will be 0.
Expert opinion
Irina Katykova
Pediatrician, pediatric neurologist
Ask a Question
Do you still have questions about your child's health? Ask them right here on the website and we will definitely answer!
How to take a pregnancy test correctly?
General rules
- Make sure your hands are clean and dry before the procedure.
- Check the expiration date of the test.
- Buy products only in pharmacies.
- Adhere to the rules of storage and use described in the instructions for the purchased product.
- Keep the area where the test will be kept clean while the results are being displayed.
Stripes
They are the cheapest and easiest to use. To begin with, morning urine is collected in a dry, clean container. It is desirable that it be small, but with high walls. The strip is dipped into the liquid to the marked mark for 20 seconds. After this, it is better to place the test on a flat horizontal plane and wait a few minutes.
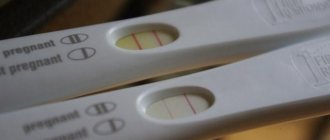
Results:
- one strip - not pregnant;
- two stripes - pregnant.
Tablet
Similar to the previous view. The difference is that the product comes with a pipette, and the indicator line is located in the body itself.
A small amount of urine is collected with a pipette. It is better to take it again from the container. Then a few drops from the pipette are left on the indicator located in a small hole on the body. All that remains is to wait.
Results:
- one strip - not pregnant;
- two stripes - pregnant.
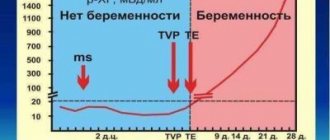
Electronic
Its main advantage is that it can show the approximate date of conception. Procedure:
- remove the cap from the dough. Proceed to the second step immediately
- place the object under the stream of urine for 5 seconds or lower its tip into a container with urine for 20 seconds;
- close the cap and place the product on a horizontal surface. You can also hold it in your hands, but make sure that the tip is pointing down and not up;
- wait until the final image appears on the screen.
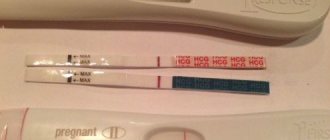
Results:
- “not pregnant”, “no” or “-” - absence of pregnancy;
- “pregnant”, “yes” or “+” and numbers - pregnancy and the approximate period from the moment of implantation of the embryo.
Jet
It is valued for its accuracy, good response to hCG, and ease of use. After removing the cap, the tip is placed under a stream of urine. It is recommended that it be tilted downwards. Often the result appears right before your eyes in just half a minute. However, to be completely sure, it is better to postpone the test for 3-10 minutes.
Results:
- one strip - not pregnant;
- two stripes - pregnant.
Vaccination schedule
Without emergency indications, the vaccine is given to children from 3 months. After the introduction of the first vaccine, a break of 1.5 months is required for the formation of immunity. At 4.5 months the vaccination is repeated. The next vaccine is administered at six months. It is the final step in the immunization program.
Revaccination is required for all patients who have received 3 vaccinations against meningitis. This procedure is prescribed one year after the administration of the last portion of serum.
Recommended immunization schedule:
- 3 months;
- 5 months;
- six months;
- one and half year.
If vaccination began between 6 and 12 months, then two vaccines are administered with an interval of 45 days. Revaccination is carried out every other year. People with immunodeficiency and adult children are vaccinated once.
Types of vaccines against meningitis with drug names
There are many microorganisms that provoke inflammation of the meninges. However, vaccination is performed only against a few. Meningitis is most often caused by meningococci, pneumococci and Haemophilus influenzae. Serums have been developed based on these microorganisms, which provide lasting immunity.
Against meningococcal infection
Vaccination against meningococcal infection is well tolerated by children and almost never causes adverse reactions. It is used in unfavorable areas, as well as during an epidemic. The vaccine is recommended for children living in these areas.
The serum is administered as a stand-alone vaccine or combined with other vaccines. By the 14th day after use, the level of antibodies in the child’s body reaches its maximum. The vaccination requires a single application.
Titles:
- Meningo A+C is a French-made drug. Recommended for use for children over 2 years old.
- Meningococcal A+C or A is a domestic vaccination. It is prescribed after one and a half years, and in case of an outbreak - from 6 months.
- Meningo ASW is suitable for use in children over one and a half years old.
- Mencevax is a Belgian serum. Applicable from 9 months.
- Menactra is an American vaccine. Suitable for use in 9-month-old babies.
Against pneumococcus
The Prevenar 13 vaccine is used against pneumococcal infection in pediatrics . Immunization is prescribed for babies from 2 months. Vaccination is carried out for children under 5 years of age. The serum is administered 4 times, which allows the formation of stable immunity. The protective functions of the body are preserved for life.
Pneumo 23 serum . This drug is prescribed to children only after 2 years of age. It provides protection against pathogens of meningitis and pneumonia for 10 years.
Against Haemophilus influenzae
Vaccination against hemophilus influenzae is available free of charge. This vaccine was included in the national childhood immunization schedule. The serum is administered together with the DPT vaccine in a clinic at the place of residence.
Titles:
- Hiberix is a monovaccine that provides protection only against Haemophilus influenzae infection.
- Infanrix Hexa is a combined serum against whooping cough, diphtheria, tetanus, Haemophilus influenzae, hepatitis and polio.
- Pentaxim is a complex injection that forms immunity to Haemophilus influenzae, tetanus, whooping cough, diphtheria, and polio.
Test coverage:
- Test coverage should be 95%.
- The Pass Rate of the text case should also be 95%. To calculate this percentage, the formula is used:
(Total number of successful text cases / total number of test cases) * 100.
- All critical test cases were successful
- 5% of test cases may fail, but this applies to low-priority cases.
- Full functionality coverage has been achieved.
- All major functional defects have been successfully eliminated.
Side effects and possible consequences
Most children tolerate vaccination against meningitis calmly. In rare cases, a child develops an allergic reaction. Side effects usually occur within half an hour, so after administering the serum it is better to remain under medical supervision for 10-20 minutes.
The reason to consult a doctor are adverse reactions that may appear several hours or days after vaccination:
- high body temperature;
- allergic rash;
- swelling at the injection site;
- painful sensations;
- increased heart rate;
- labored breathing;
- weakness in the limbs;
- headache.
What does the exit criterion include?
Ideally, it is a combination of several factors unique to all projects. It all depends on the requirements of a specific project. Therefore, during planning, it is advisable to calculate as many parameters as possible.
Below are some things to consider during functional or system testing. You can make a specific combination or use all of these factors to determine exactly when to complete testing.
Pros and cons of childhood vaccinations
Many modern parents refuse immunization because they consider infections outdated and irrelevant for today's children. However, the absence of outbreaks of meningitis and other diseases is a merit of vaccinations.
Pediatricians, immunologists and other specialists recommend vaccinations for children. Doctors justify their opinion with the following arguments:
- Immunization is the only reliable way to prevent meningitis. No other methods of protecting the body can compare with it.
- It can be difficult to recognize meningitis from the first days, which leads to progression of the disease and complications. Vaccination allows you to immediately eliminate this disease.
- After vaccination, you don’t have to be afraid to travel to dangerous regions. The risk of becoming infected from carriers of pneumococcus and meningococcus is negligible.
- The effectiveness of the vaccine reaches 99%. The risk of contracting an infection is reduced to 0.1%. The vaccination is well tolerated and does not cause complications.
- Immunization not only provides protection against meningitis. After vaccination, the risk of infection of the upper and lower respiratory tract is reduced.
When should a developer stop testing and ship the product?
The decision may be based on measuring error rates. However, the key decision will always be based on the resources available. If there is a certain amount of time before the product is released, testing could be expanded at each stage. However, if the software was promised 6 months ago, the tester might go out on a limb and say that the software works without major bugs, even if he or she is aware of some minor bugs. It all comes down to assessing the degree of risk and being able to determine when it is more or less safe to ship the product to the customer. If a defective product is shipped, a new version of it may still be released, but this involves a whole new set of risk assessments.
What Doctor Komarovsky says
Dr. Komarovsky in his opinion expresses the position of many modern pediatricians and immunologists. The doctor believes that children should be vaccinated. The only exceptions are those groups of patients who have contraindications to immunization. Vaccination provides lasting protection against meningitis pathogens. The risk of contracting the disease is minimal. If infection does occur, the disease will proceed in a mild form. The child will not develop serious complications and will not die.
In his programs, the doctor says that there is no “vaccination against meningitis.” The disease may not only have an infectious nature of origin. It is possible that a child will be vaccinated against meningitis, but he will still get it. When talking about vaccination against meningitis, it should be understood that we are talking about a vaccine that protects against some pathogens of this disease, and not against pathology in general.
Is it possible to prevent meningitis? — Dr. Komarovsky
Parents must weigh the pros and cons when deciding whether to immunize. You should not listen to the propaganda of anti-vaxxers, since many of them do not realize the seriousness of the situation. We must understand that refusal to vaccinate is a direct path to outbreaks of epidemics and pandemics.
Who is involved in the software testing process?
The buyer and/or user of the software should play a major role in the software testing process. The client must work with the developer during the planning and design process so that all parties reach agreement on what the final product will consist of and how it should look and perform. Joel Gilman, in the "Law Report" column of Systems Integration magazine in February 1991, suggested that a test criteria document be compiled and included in the initial product requirements or contract. Programmers should be responsible for basic software testing. A good programmer should never hand over a program to a tester or testing department without first running test scripts that determine whether the program meets certain requirements. It should be noted, however, that testers and programmers have different goals when they test software. Boris Beizer in Software Testing Techniques, an excellent book on testing fundamentals, said that a tester is “one who writes and/or performs software testing with the intent of demonstrating that a program does not work, while a programmer is one whose testing (if any) is intended to show that the program actually works."