Classification
There are several types of tachycardia in the fetus during pregnancy. There are many forms, but among them the main ones have been identified, in which the heart beats more than two hundred times per minute. Pathology can be:
- Reciprocal supraventricular type. In this case, the development of unnecessary contractions occurs in the area of the atria. This diagnosis can be made at the thirtieth week of pregnancy, and is sometimes accepted as a normal heartbeat.
- Ectopic. The development of excitation is observed above the sinus node. The formation of extrasystoles occurs in a disorderly manner in different parts of the heart.
- Atrial flutter is considered a separate type. In this state, the heart rate increases to four hundred beats. Flutter is characterized by regular contractions and occurs due to blockade of conduction of the atrioventricular node.
General characteristics of pathology, forms
The primary treatment is to change your own lifestyle. In particular, experts advise:
- change mode. Pregnant women need to spend more time in the fresh air and spend less time at the computer;
- diversify your diet. Tachycardia can occur if the diet lacks essential microelements, especially magnesium, potassium and calcium. You need to eat more plant foods, whole grain cereals, dried fruits, etc.;
- To calm and bring the body back to normal after stress, tea with lemon balm and mint helps.
To relieve an attack, the expectant mother is advised to sit down or lie down to relax. You need to breathe deeply. Antiarrhythmic drugs in this case are not used until the last minute, because they can harm the baby. As for the fight against tachycardia in the fetus, they also try to avoid drug treatment. Normalize your routine, change your diet, and everything should be fine.
If the cause of tachycardia is the formation of heart pathology, the use of antiarrhythmic medications is mandatory. The selection of drugs is based on the form of the disease. If inflammation of the heart wall is detected, steroid drugs are used. Application is carried out in courses - about a week and a half. Medicines can be in the form of tablets, or in the form of injection solutions or droppers.
Treatment is carried out in a hospital setting, under the constant supervision of a cardiologist and obstetrician-gynecologist. The unauthorized use of any medications is strictly prohibited! Violation of the dosage can lead to the most unpleasant consequences.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Drugs for hypertension with tachycardia
With correct drug treatment, in combination with the correct daily routine, fetal tachycardia can be overcome in 90% of cases. If the disease cannot be treated, transplacental administration of special drugs is used. Normalization of heart rate occurs after birth, in the first year of life.
Tachycardia is diagnosed when the heart rate exceeds 90 beats per minute. For the fetus, the norms are different, so exceeding the parameter of 180 beats per minute is considered pathological.
Tachycardia is considered to be not an independent disease, but a symptom that accompanies various diseases. Palpitations need to be dealt with as they reduce the efficiency of the heart. Because of this, blood pressure increases and blood flow to the organs decreases. The heart has to work harder, so it needs more oxygen.
Differential diagnosis allows you to find out the specific form of tachycardia:
- Atrial flutter. This phenomenon is observed in every 3-4 cases of fetal tachycardia. This form of pathology is characterized by a consistently high heart rate. It can reach up to 400 beats per minute, when in other cases the upper limit is 220-240 beats per minute.
- Reciprocal tachycardia (supraventricular type). Pathology of this form is usually detected at 24-33 weeks. Often it accompanies atrial extrasystole, that is, a type of arrhythmia. In some cases, a combination of reciprocal tachycardia and bradycardia (sinus rhythm disturbance) is detected. Such a tandem is dangerous due to the accompanying inflammatory process, and therefore requires urgent treatment.
- Ectopic tachycardia. This form of tachycardia is characterized by ectopic foci. They can be localized in one or different parts of the atrium. This form of pathology is characterized by a chaotic heart rhythm.
A possible manifestation of tachycardia in the fetus was first identified about 90 years ago. Today, diagnosing such a pathology is not difficult. Violations can be suspected even during a standard examination.
Treatment of fetal tachycardia depends on a number of features. This includes the general condition of the mother’s body, the form of tachyarrhythmia, the presence of concomitant pathologies and, of course, the timing of detection. A larger percentage of cases are temporary manifestations of the disease, and therefore serious treatment may not be required. Monitoring a woman’s condition in a hospital setting can be carried out if the pathology does not manifest itself constantly.
Drug therapy is often prescribed if it is associated with dysfunction of the heart muscle or its valve.
- The polymorphic ventricular type of disease entails taking the drugs propranolol, lidocaine and magnesium.
- When the fetal heart rate is above 220, Amiodarone and Sotalol are used. Flecainide may also be prescribed under the special supervision of doctors. In case of ventricular dysfunction, it can cause the death of a child, and therefore the dosage is observed very strictly.
- If during pregnancy tachycardia occurs due to a syndrome associated with a long QT interval, then treatment is possible only under conditions of constant monitoring, that is, in a hospital. In the process, an appropriate drug is selected that provokes arrhythmia, lengthening the interval.
- Dexamethasone is prescribed in a course if a specialist suspects myocarditis.
Beta blockers also often help reduce heart rate, but the therapy is considered not very effective compared to other treatment methods, since they penetrate the placenta less well.
Why does pathology develop?
Typically, an increase in heart rate in the fetus occurs due to:
- Taking certain medications.
- Infection of the embryo with infection.
- Insufficient oxygen supply to the fetus.
- Increased production of hormones.
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
- Disturbances in the balance of electrolytes in the body with severe toxicosis.
- Insufficient intake of vitamins and microelements into the child’s body.
The development of tachycardia during pregnancy occurs due to:
- Increased load on the heart muscle due to insufficient blood flow to the embryo.
- Pathological processes in the cardiovascular system and compression of the organ.
- Enhanced metabolism and rapid fetal development.
Doctors say that mild tachycardia in pregnant women is normal.
The development of attacks occurs abruptly, and they last a short time. A woman should be in a calm state and not worry about high heart activity, since it is associated with the need to provide blood not only to the woman, but also to the fetus.
The heart beats faster and as a result of increased gas exchange in the child. Therefore, most pregnant women suffer from rhythm disturbances.
Symptoms
The main sign of tachycardia is an increased heart rate, which can be determined by measuring the pulse. If a value of more than 100 heart beats per minute was recorded in combination with characteristic symptoms, then you urgently need to seek medical help. So, a pregnant woman should definitely be wary of the following manifestations:
- weakness in the body;
- fast fatiguability;
- chest pain;
- attacks of nausea followed by vomiting;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- dizziness, fainting;
- numbness of the limbs;
- increased anxiety and irritability.
If any of these signs appear, you should reduce your activity and try to calm down. At the same time, it is necessary to open a window or door in the room to ensure the flow of fresh air. If the attack drags on, you should not ignore it and let the situation take its course. Only qualified medical assistance will minimize the risks for the expectant mother and her baby.
Main signs of a problem
Fetal tachycardia during pregnancy manifests itself as an increase in rhythm in a woman. In this case, the heart beats at a frequency of more than 120 beats per minute - this happens to the mother. As for the fetal body, its heart rate reaches 200 beats.
Tachycardia may indicate that the child is suffering from hypoxia. In the initial stages, the problem manifests itself as ectopic tachycardia. The development of pathological foci is observed in the area of the atria or pulmonary veins.
This is usually accompanied by severe nausea and cardiac dysfunction. The problem can manifest itself in prolonged attacks that occur regularly.
Therefore, expectant mothers are advised to avoid stress and also monitor moderation of physical activity. If you suddenly feel a strong heartbeat, you should visit a doctor.
The development of sinus tachycardia is considered a separate pathology, which indicates abnormalities in the functioning of the heart. If left unaddressed, this problem can cause birth defects.
Increased heart rate in the fetus sometimes manifests itself as chest pain and anxiety in the woman, as well as numbness in certain areas of the body.
Sometimes a pregnant woman notices general weakness and loss of strength.
Tachycardia and pathological disorders
The appearance of tachycardia during pregnancy may indicate the development of pathological disorders in a woman’s body. The heart rate may become very intense: 120 beats or more. This is accompanied by the appearance of severe weakness, characteristic pain in the chest area, numbness of the limbs, dizziness, nausea and single vomiting.
In severe cases, the skin turns blue. Such symptoms require immediate medical correction. In this case, the pregnant woman should remain under the constant supervision of specialists until childbirth or until the body is completely restored.
If tachycardia develops during pregnancy, childbirth is not carried out naturally. A caesarean section is used to deliver a baby.
Diagnostic methods used
If there are signs of increased heart rate in the fetus, then a number of research measures are prescribed, including:
- Echocardiography of the embryo. With its help, abnormalities in fetal development are detected.
- Radiographic examination.
- Dopplerography. This procedure is considered the most informative method for identifying such abnormalities in the fetus. During the examination, the contractility of the ventricles and atria and the movement of blood in the heart are assessed.
To determine the type of tachycardia, differential diagnosis is performed.
Prognosis of tachycardia in the fetus
With timely diagnosis of pathology associated with heart rhythm abnormalities, it is possible to get rid of tachycardia in nine out of ten cases, which is considered a good indicator.
The prognosis regarding the results of treatment of fetal tachycardia in the fetus depends on a combination of factors: the form of the pathology, the time of occurrence (diagnosis), the characteristics of the fetus’s body and, of course, the mother.
Fetal sinus tachycardia in most cases normalizes during the first year of the baby’s life.
If there are indications for drug treatment of fetal tachyarrhythmia, antiarrhythmic drugs are administered by the transplacental method. Course therapy in a hospital is accompanied by constant monitoring of the concentration of medications in the umbilical cord.
There are high-risk medications that, if dosed incorrectly, can lead to cardiac arrest of the embryo, so the prognosis depends on the medications used, and on strict adherence to the dosage and frequency of taking them.
How is the treatment carried out?
How to eliminate the disease is decided depending on the individual characteristics of the body of the woman and child, the form and severity of tachycardia. Usually the condition normalizes on its own. The doctor monitors the fetus and the expectant mother, regularly measuring the heart rate using a Doppler monitor. You need to check your pulse at least twice a day.
Also read: Possible causes of nocturnal tachycardia If there are complications in the form of valve or myocardial dysfunction, a woman should take medications to stabilize the child’s heart rhythm. A doctor should select the drug, since antiarrhythmic drugs are quite dangerous.
If used incorrectly, they increase the load on the heart and can cause fetal death.
Depending on the type of pathological condition, the following treatment options are used:
- To cure polymorphic tachycardia, lidocaine, magnesium preparations, and propranolol are prescribed. They are injected into a vein or taken orally.
- If ventricular-type tachycardia with a prolonged QT interval is observed, the pregnant woman is hospitalized. Treatment should be carried out with extreme caution, as some drugs prolong the interval and aggravate the course of the arrhythmia.
- If the heart beats at a rate above two hundred beats, the condition is stabilized with Sotalol or Amiodarone. Flecainide is sometimes used. But this drug, if the ventricular functions are impaired, can cause cardiac arrest and embryo death.
- If there are signs of myocarditis, a woman is prescribed a course of Dexamethasone lasting one or two weeks.
Good results can be achieved with the help of drug treatment when an ectopic focus forms above the ventricles. A correctly designed regimen in most cases ensures complete recovery.
Beta blockers are also used to normalize the heartbeat. But their effectiveness in treating the embryo is low, since the active components have difficulty crossing the placental barrier.
Fetal tachycardia in later stages occurs quite often, which is associated with an increase in its size and an increase in the load on the body.
Seizures can bother any woman during pregnancy. Therefore, it is necessary to know how to deal with pathology.
The basic methods are selected by the doctor, but some rules help make you feel better:
- If an attack begins, you need to sit down or take a horizontal position. The load on the heart will decrease and it will begin to contract more slowly.
- Deep inhalation and slow exhalation helps stabilize the condition. These steps must be repeated several times. Breathing exercises are good for eliminating attacks.
- Avoid emotional stress and worries. In case of prolonged attacks of the disease, it is necessary to do a cardiogram.
Tachycardia during pregnancy
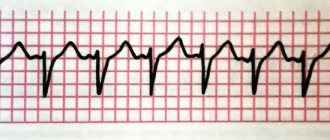
Normally, the heart rate is calculated using the formula 72 plus or minus 12, which means it ranges from 60 to 94 beats per minute. If the contraction rate is below 60, this is called bradycardia. and above 95 – tachycardia. The easiest way to determine the frequency of contractions is by the human pulse: contractions of the heart muscle are transmitted along the walls of the arteries and can be felt under the fingers on the wrist.
Tachycardia in pregnant women - causes
In pregnant women, the heart rate (HR) at rest does not differ from normal values, and during physical activity it increases by 10-15 beats per minute. Tachycardia during pregnancy is an acceleration of the heart rate (acceleration of the pulse) above 100 beats per minute at rest. Tachycardia can be caused by:
- excess body weight and excessive growth during pregnancy;
- altered position of the heart due to the growth of the uterus, pressure on the vessels (reflex effect), displacement of the abdominal organs and pressure on the diaphragm;
- diseases of the thyroid gland, which are accompanied by excessive production of its hormones;
- anemia of pregnant women;
- increase in body temperature (heart rate increases by 10 beats per one degree increase in temperature);
- bronchial asthma ;
- inflammatory lung diseases;
- dehydration of the body (with toxicosis accompanied by repeated vomiting);
- severe bleeding (especially with ectopic pregnancy, premature placental abruption, severe injuries);
- severe infections, sepsis;
- reactions to medications (allergies, overdose of vitamins, side effects of medications);
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- increased excitability of the nervous system;
- bad habits (nicotine, coffee, etc.)
Sinus and paroxysmal tachycardia in pregnant women
Sinus tachycardia during pregnancy is accompanied by a constant increase in heart rate while maintaining its normal rhythm. Paroxysmal (attack-like) tachycardia is characterized by attacks of accelerated heart rate from 140 to 220 per minute with a normal rhythm, sudden appearance and disappearance, between which the heart rate usually returns to normal.
Tachycardia during pregnancy - symptoms
The main symptom of tachycardia is increased heart rate of the mother. But often it is accompanied by pain in the heart area, nausea and vomiting, dizziness, numbness of body parts, fainting, excessive fatigue, and anxiety.
Treatment of tachycardia during pregnancy
Sinus tachycardia, which is accompanied by an increase in heart rate by 20-30 beats per minute during exercise, disappears with rest or after rest, and usually does not require treatment. Rare attacks of paroxysmal therapy are also common in overly suspicious, anxious women; usually it is enough to simply calm down and even sedative therapy is not required.
Many women are worried whether tachycardia is dangerous during pregnancy, but speeding up the heart improves blood supply to the fetus, access to oxygen and nutrients. But if tachycardia does not go away or is accompanied by other symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
Pathological tachycardia can be distinguished from physiological by excluding all diseases and causes that could cause pathological tachycardia. For this purpose, an ECG and EchoCG, a general blood test, examination by a cardiologist, endocrinologist, etc. are prescribed.
Why is tachycardia dangerous during pregnancy?
Often, tachycardia only worsens the quality of life of a pregnant woman and disappears without a trace after childbirth. If tachycardia during pregnancy is associated with other diseases, especially with defects and heart diseases of the pregnant woman, then this can become a threat to the life of not only the unborn fetus, but also the mother, causing premature birth and complications during childbirth. Therefore, in case of tachycardia, it is necessary to examine the woman in order to take into account any possible risks for the mother and child in the future.
Possible consequences
What complications the problem will have depends on many factors, including the form of tachycardia, gestational age, the nature of the embryo development process, and the individual characteristics of the fetus and mother.
Usually the outcome of the disease is positive. If a child has sinus tachycardia, the rhythm returns to normal during the first year after birth.
If there is a need for treatment, transplacental administration of antiarrhythmic drugs will eliminate the disorder.
The prognosis for tachycardia is favorable if treatment is started on time and the use of medications is carefully monitored.
Prevention
- As soon as you notice an increase in the beat rhythm, try to rest. Relax, take a nap, or at least just lie down.
- If you have experienced a strong outburst of emotions, calm down. Do light breathing exercises, breathe slowly, drink a soothing decoction.
- Excitement and panic can provoke a serious attack, so try to distract yourself.
- A nutritious diet does not always compensate for the lack of various microelements, so talk to your doctor about choosing a suitable vitamin complex.
Don’t overload your body, but don’t forget that movement is necessary. Take short walks, attend sports recommended during pregnancy, and completely remove negative habits from your life.
Doctors promote planned pregnancy after checking the parents and treating all their chronic diseases. Such preparation gives confidence that the mother is healthy enough to bear and give birth to a baby, and an individual management plan is outlined taking into account preliminary data.
If the pregnancy is not expected, then responsibility for the child’s health falls on the parents. A woman needs support, good nutrition and routine. Regular visits to your obstetrician-gynecologist for examination are necessary for timely diagnosis of abnormalities.
Inpatient treatment of maternal and fetal arrhythmia according to optimally selected regimens gives a high chance of preventing hypoxia of the child’s organs and systems.
Compliance with working and rest conditions, the absence of overwork and intoxication allow us to hope for a good pregnancy and healthy offspring.
Specific prevention of this disorder simply does not exist, and cannot exist. Since the list of pathological conditions is quite large, it would be completely wrong to give comprehensive recommendations to a wide audience without relying on an individual approach.
Therefore, the main thesis of preventive work should be the painstaking and conscientious work of local obstetric and gynecological services. If there are changes in the child's movements, immediately carry out additional diagnostics.
Tachycardia during pregnancy
Sinus tachycardia during pregnancy
How to give oxygen to a baby? | Prevention of fetal hypoxia in pregnant women | "Before and After Childbirth"
The expectant mother must take care of herself and her child, long before the moment of conception. Any negative impact on a woman’s reproductive system leaves an imprint for her entire life and, unfortunately, can affect her future children.
Proper nutrition, an active lifestyle, a rational regime of work and rest - these are the few things that any girl and woman can do to ensure the health of their children.
Do not forget about the possibility of chromosomal pathology; modern medical and genetic consultations will help to understand many issues of interest to young couples.
How to avoid the problem
Prevention of tachycardia should begin while planning pregnancy. Long before conception, you should not drink alcohol or smoke; you need to be examined and, if possible, get rid of all diseases.
To prevent the problem from bothering you during pregnancy, the woman is prescribed sedatives based on medicinal plants. They help normalize heart rate. The expectant mother should avoid stress, walk regularly and do gymnastics.
To carry and give birth to a healthy baby, it is important to adhere to the principles of proper nutrition. To keep your heart rate from rising, you must:
- Avoid sweets and fatty foods. Failure to follow a diet can lead to rapid weight gain and increased stress on the heart.
- Eat enough fruits, vegetables and greens every day. Dairy products with a low fat content are beneficial.
- Eliminate caffeine, nicotine, and alcoholic beverages from your diet. These substances can adversely affect pregnancy and cause developmental abnormalities or even fetal death.
- Ensure adequate intake of vitamins and minerals. During pregnancy, the body needs more nutrition, so multivitamin complexes may be prescribed.
- If there are no contraindications, light physical activity is allowed in the form of visits to the pool, walking.
Carrying a child is a very important period. A woman must follow all the doctor’s instructions so that the baby is safely formed and born without complications.
Heart problems during pregnancy
Sinus tachycardia is a sinus rhythm of the heart with a frequency of up to 160 per minute, and sometimes more. Normally, such a condition can occur after active physical activity, as well as during a strong emotional outburst. Such tachycardia is called physiological and does not pose a danger to the vital functions of the body. There are quite a few reasons for the occurrence of pathological tachycardia. Very often, sinus tachycardia occurs during pregnancy. There are many factors contributing to development. This includes naturally increasing body weight and changes in the functioning of all systems as a whole. The load on the heart and circulatory system, all this leads to an increase in heart rate. Such tachycardia can occur in the early stages of pregnancy, but in most cases a woman begins to notice an increase in rhythm at the end of the second or even in the third trimester of pregnancy.
Signs
Sinus tachycardia during pregnancy is expressed by:
- increased heart rate;
- pain in the heart;
- dizziness;
- increased fatigue.
These signs may be presented in aggregate or partially presented.
Diagnostic tests for fetal heartbeat
If there are signs of increased heart rate in the fetus, then a number of research measures are prescribed, including:
- Echocardiography of the embryo. With its help, abnormalities in fetal development are detected.
- Radiographic examination.
- Dopplerography. This procedure is considered the most informative method for identifying such abnormalities in the fetus. During the examination, the contractility of the ventricles and atria and the movement of blood in the heart are assessed.
To determine the type of tachycardia, differential diagnosis is performed.
Unfortunately, using a stethoscope (this diagnostic method is scientifically called auscultation) it is not always possible to establish deviations of this kind. This may be hampered by the inconvenient position of the fetus or the physiological characteristics of the pregnant woman.
But an experienced gynecologist may suspect abnormalities at the examination and listening stage, based on heart rate, the general condition of the mother and the duration of pregnancy.
The most accurate and informative methods for establishing tachycardia, its form and possible causes include:
- Ultrasound. There are still a lot of rumors and speculations about the dangers of ultrasound examination during pregnancy. But experts (including the famous pediatrician Komarovsky) claim that sound waves and vibrations do not pose any danger to either the child or the mother. On the contrary, this is one of the safest and most painless hardware procedures. In the early stages of pregnancy, a regular, two-dimensional ultrasound is performed, which allows you to study the anatomy of the heart structures and listen to the heart rhythm.
- Echocardiography. This diagnostic method combines ultrasound scanning with an electrocardiogram. As a rule, it is prescribed no earlier than the 2nd trimester. The study helps determine the frequency and nature of contractions of the heart muscle.
- Doppler examination. It records the movements of red blood cells, which allows you to evaluate the speed and direction of blood flow, the volume of blood that leaves and returns to the heart.
- X-ray. This study will not establish arrhythmia, but will exclude (or confirm) heart defects and pathologies of the pericardium (heart sac). Therefore, x-ray is a concomitant, but not the main examination for suspected fetal tachycardia and for identifying its causes.
- CHT (cardiotocography). This is a relatively young technique (it appeared in the 60s and is still being improved). With its help, fetal heart rate and uterine tone are recorded. This is done using ultrasonic and strain gauge sensors. As a result, the cardiotocogram represents 2 graphs, where the tachogram reflects changes in heart rate, and the hysterogram reflects uterine contractions.
A modern cardiac monitor is a device that takes into account the motor activity of the embryo, sleep period and other important details when drawing up charts.
The decision on the need for diagnosis is made by the doctor based on the complaints of the pregnant patient. After analyzing them, the specialist prescribes a series of diagnostic procedures for the expectant mother in labor. Information about the methods used to study the work of a child’s heart is presented in the table.
| Diagnostic methods | abbreviated name | Description | At what stage of gestation is it performed? |
| Ultrasound examination of the heart | Ultrasound | Diagnosis of tachycardia and identification of associated pathological processes | After 6 weeks |
| Echocardiography | ECG | Diagnosis of heart defects | From 5-6 weeks |
| Cardiotocography | CTG | Analysis of the contractile activity of the uterus and the frequency of contractions of the fetal heart muscle | From 30 weeks |
| Auscultation | Absent | A study of the heart, which consists of listening to the patient’s abdomen using a stethoscope | After 18-20 weeks |
| Doppler study | Doppler | Assessment of the nature of atrial contractions in the fetus, as well as the state of blood circulation in the myocardium | Starting from 21-22 weeks |