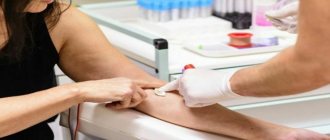
Good afternoon or evening, dear readers! From time to time, we are all forced to take a general blood test so that the doctor can determine whether there are any problems in the patient’s body.
One of the most important indicators of this analysis is the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, since it may differ from the norm and indicate the presence of pathological processes in the body. In medicine, there is a special table that shows the ESR norm for women , men and children of different ages.
Reasons for deviation from the norm
The very first factor by which the norm of ESR in the blood of men is determined is compliance with all the rules for taking the test. If the patient ate food before the procedure, or the body was exposed to sudden temperature changes, then it is better to re-donate blood, because there is a high chance that the results will be inaccurate.
Although the analysis itself will not show anything special, and it is impossible to say exactly what disease a man has, some data still helps determine the list of suspected diseases. Of course, when making a diagnosis, the patient’s symptoms and complaints matter. The following diseases can cause an increase in ESR:
- Arthritis (as is known, there are several types), rheumatism;
- Diseases of the endocrine system;
- Tuberculosis;
- Infections of various (including unknown) origins;
- Autoimmune diseases;
- Burns;
- Malignant formations. A significant increase in the level of ESR in the presence of cancer indicates that stage 3 or 4 of the disease has been reached and metastases are already spreading throughout the body.
The ESR may also increase when the patient is not eating properly, or is allergic to foods or medications.
A reduced male ESR is observed in the following cases:
- The patient is interested in vegetarianism or fasting;
- Neuroses, epilepsy;
- Kidney and liver diseases;
- Corticosteroids are present in the body;
- Polycythemia;
- Increased blood viscosity;
- The period after surgery;
- Oncological diseases of the blood.
A decrease in the norm occurs under the influence of certain medications that reduce the weight of red blood cells, which is why they settle to the bottom more slowly.
Of course, there are no medications to restore normal ESR levels. It is necessary to find out the causes of deviations and eliminate them. This can be either a disease or the consequences of using certain pharmacological drugs, as well as a change in diet. It is necessary to accurately establish the reason for the increase or decrease in ESR through an interview with the patient, as well as additional examination.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that a general blood test is a simple procedure that does not take much time, but requires compliance with all the rules for donating blood. The value of all indicators of the general analysis, including ROE, directly depends on competent preparation for laboratory research, as well as on the choice of clinic and medical personnel working in this clinic.
What is ESR analysis?
Using this indicator, the presence of inflammation in the body or its absence is determined.
A general blood test (clinical) includes a test for the normal ESR, and is a test with high sensitivity.
It is important to understand that the ESR rate does not indicate the cause of inflammation, but only indicates its presence in the body.
Blood is drawn from a vein, after which it is placed in a reservoir, and a substance (anticoagulants) is added that prevents the blood from clotting.
The blood is stratified, plasma (transparent color) goes up, and red blood cells (dark red color) settle to the bottom.
In the middle of the tank there is a scale, which helps to determine at what speed red blood cells settle (mm/hour).
The analysis takes place on an empty stomach, in the morning. But if inflammation is detected, blood can be drawn after eating during the day. This is done in order to track the dynamics of subsidence.
Options for detecting ESR or ROE
A detailed blood test for ESR is carried out in several ways:
Panchenkova. The method consists of filling the capillary with a five percent composition of trisodium citrate to the “P” mark, followed by transferring it to a special glass. Next, the same graduated Panchenkov capillary is filled twice with the patient’s blood to about 0, followed by blowing onto a watch glass in both cases. Then the blood mixed with sodium citrate is again placed in the capillary up to the “K” mark and placed on a tripod in a vertical position for an hour. Then the result is assessed in millimeters.
Westergren and his variations. This approach is used throughout the world as recommended by the International Union for Standardization in Hematology, ESR analysis. Nowadays, the method is automated, which gives it an undoubted advantage over other methods. The technology is carried out using test tubes and calibration of the result scale.
The Westergren method is more susceptible to increasing ESR levels, and the results are more accurate compared to the Panchenkov method. To obtain a blood test for ROE, you will need venous blood taken with trisodium citrate in the required combination. Venous blood can also be used in combination with ethylenediaminetetraacetate and then diluted with saline or sodium citrate in the required ratio.
Calculation of the movement of erythrocyte aggregation. Measurement of red blood cell aggregation is carried out automatically, thanks to a special device from Alifax that simulates the microcapillary of a blood vessel. The object of study can be venous or capillary blood.
Detection of ESR using analyzers. Alifax ESR meters are used to determine the erythrocyte sedimentation rate by measuring optical density. The latest model in this area, TEST1 THL, is equipped with modern software that allows the use of advanced latex controls.
How is ESR determined?
Determination of ESR using the Panchenkov method
The analysis is carried out using one of two methods. Which one will be used is determined by the equipment of the laboratory. The accuracy of both methods is the same.
- Panchenkov's method. This method uses a capillary with 100 divisions. A 5% sodium citrate solution is poured into it up to the P mark. Up to the K mark, the container is filled with blood. After complete mixing of the blood with the solution, the container is fixed in a vertical position on a special tripod. The result is assessed after 60 minutes.
- Westergren method. The analysis is carried out in vitro. For the study, blood taken from a vein is used with sodium citrate at a concentration of 3.8% in a ratio of 4:1. Special test tubes with a scale having a lumen of 2.5 mm are used. The scale on the test tube is 200 mm. The container is left in a vertical position for an hour and then the results are calculated.
The indicator obtained using any of the two methods is correlated with the norm and evaluated. If necessary, ESR can be re-determined.
How to lower ESR in the blood of women and is it worth lowering?
Obviously, to normalize ESR, it is necessary to determine the source of dysproteinemia and eliminate it (i.e., detect and cure the disease or optimize nutrition and lifestyle). After eliminating the factor that accelerates ESR, blood counts will return to normal on their own.
Most often, the cause of an increase in ESR is diagnosed according to the plan described above. But sometimes, to clarify the nature of the disease and at the same time bring the elevated ESR back to normal, the treatment and diagnostic tactics “ex juvantibus” are used.
Algorithm for bringing ESR back to normal using ex juvantibus therapy
The principle of the method: verification of the alleged diagnosis by trial treatment.
1. First, the patient is prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics. If the ESR does not decrease, then the reason for its acceleration is not an infection.
2. Then steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used (glucocorticoids: prednisolone, dexamethasone, etc.). If there is no positive result, then the reason for the acceleration of ESR is not inflammation (immune, autoimmune).
3. Having ruled out infection and inflammation, the patient is examined for oncology (malignant neoplasm).
This primitive-simplified approach in some cases helps to determine a controversial diagnosis.
How to return ESR to normal?
When something in the body goes beyond a healthy state, any person has a natural desire to return everything to normal.
And how to do this? Only cure the cause, that is, the disease that caused the increase in ESR. Of course, self-medication will not lead to anything good. Instead of looking for the necessary antibiotics and other drugs on your own on the Internet, it is better to immediately contact a specialist. It is he who will prescribe the necessary course of treatment after determining the diagnosis. After successful treatment of the disease, the ESR will return to normal after some time (2-4 weeks in adults and up to 6 weeks in children).
In case of anemia, iron-containing foods, proteins and some traditional methods will help restore the indicator, but in this case it is also better to consult a doctor.
If you are simply dieting, fasting, or experiencing a special physiological state (pregnancy, lactation, menstruation), the indicator will return to the desired level as soon as your normal physical condition is established. In this case, there is nothing to worry about.
Elevated ESR requires examination
The main factor accelerating ESR is rightfully considered to be a change in the physicochemical properties and composition of the blood: a shift in the protein A/G (albumin-globulin) coefficient towards a decrease, an increase in the pH value, active saturation of red blood cells (erythrocytes) with hemoglobin. Plasma proteins that carry out the process of erythrocyte sedimentation are called agglomerins
.
An increase in the level of the globulin fraction, fibrinogen, cholesterol, and an increase in the aggregation abilities of red blood cells occurs in many pathological conditions, which are considered the causes of high ESR in a general blood test:
- Acute and chronic inflammatory processes of infectious origin (pneumonia, rheumatism, syphilis, tuberculosis, sepsis). Using this laboratory test, one can judge the stage of the disease, the subsidence of the process, and the effectiveness of therapy. The synthesis of “acute phase” proteins in the acute period and the enhanced production of immunoglobulins at the height of “military operations” significantly increase the aggregation abilities of erythrocytes and the formation of coin columns by them. It should be noted that bacterial infections give higher numbers compared to viral lesions.
- Collagenosis (rheumatoid polyarthritis).
- Heart damage (myocardial infarction - damage to the heart muscle, inflammation, synthesis of “acute phase” proteins, including fibrinogen, increased aggregation of red blood cells, formation of coin columns - increased ESR).
- Diseases of the liver (hepatitis), pancreas (destructive pancreatitis), intestines (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis), kidneys (nephrotic syndrome).
- Endocrine pathology (diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis).
- Hematological diseases (anemia, lymphogranulomatosis, myeloma).
- Injury to organs and tissues (surgeries, wounds and bone fractures) - any damage increases the ability of red blood cells to aggregate.
- Lead or arsenic poisoning.
- Conditions accompanied by severe intoxication.
- Malignant neoplasms. Of course, it is unlikely that the test can claim to be the main diagnostic sign for oncology, but its increase will one way or another create many questions that will have to be answered.
- Monoclonal gammopathies (Waldenström's macroglobulinemia, immunoproliferative processes).
- High cholesterol levels (hypercholesterolemia).
- Exposure to certain medications (morphine, dextran, vitamin D, methyldopa).
However, at different periods of the same process or under different pathological conditions, ESR does not change the same:
- A very sharp increase in ESR to 60-80 mm/hour is typical for myeloma, lymphosarcoma and other tumors.
- Tuberculosis in the initial stages does not change the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, but if it is not stopped or a complication occurs, the rate will quickly creep up.
- In the acute period of infection, the ESR will begin to increase only from 2-3 days, but may not decrease for quite a long time, for example, with lobar pneumonia - the crisis has passed, the disease recedes, but the ESR persists.
- It is unlikely that this laboratory test will be able to help on the first day of acute appendicitis, since it will be within normal limits.
- Active rheumatism can last for a long time with an increase in ESR, but without frightening numbers, but its decrease should alert you to the development of heart failure (blood thickening, acidosis).
- Usually, when the infectious process subsides, the total number of leukocytes returns to normal first (eosinophils and lymphocytes remain to complete the reaction), ESR is somewhat delayed and decreases later.
ESR level for women
As you know, taking a general blood test, first of all, makes it possible to assess the general condition of the body, as well as the presence of an acute or chronic inflammatory process in it.
Any clinical blood test consists of a fairly large number of different indicators (leukocytes, red blood cells, hemoglobin, platelets, etc.), one of the most important elements of which, of course, is ESR.
ESR (ROE) - the erythrocyte sedimentation rate in women, can fluctuate quite often, which is influenced by a fairly large number of different reasons and factors.
For many women, the ESR level constantly jumps (increases or decreases) due to the period of menstruation (menstrual cycle), pregnancy, menopause, menopause, as well as various hormonal changes in the body.
A normal ESR rate for an adult, healthy woman is considered to be from 2 to 15 mm/hour.
Quite often, a slight increase or decrease in ESR in the blood is an absolutely normal physiological phenomenon for the body that does not require additional examination.
As a rule, the ESR level almost always increases during a common respiratory viral infection (ARVI) or influenza, while immediately after the woman recovers, the ESR quickly returns to its previous normal.
Attention: you need to take a general blood test early in the morning and only on an empty stomach, since any consumption of food will lead to an incorrect result.
The ESR indicator is very important for the timely detection of a fairly serious disease of the body in its early stages, since it is one of the first to respond to any penetration of an infectious pathogen into the body.
As a rule, it is the ESR indicator in a general blood test that indicates the dynamics of the treatment of various diseases in women.
Normal ESR values for women of different age categories:
- 18 – 29 years – 2 – 15 mm/hour;
- 30 – 39 years – 3 – 14 mm/h;
- 40 – 49 years – 4 – 15 mm/h;
- 50 – 59 years – 6 – 18 mm/h;
- 60 – 69 years – 8 – 19 mm/h;
- 70 – 80 years and older – 12 – 30 mm/h.
In old age, the ESR level increases significantly, which is absolutely normal for the female body, while an ESR value of 20 is considered a completely normal laboratory test for a woman aged 65-70 years.
Remember: if the ESR level remains elevated for a long time, it is recommended to consult with a general practitioner to conduct a comprehensive examination of the whole body.
What does ESR mean?
In fact, this is not a term, but an abbreviation. Full explanation of ESR is the erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
The study of this indicator began in 1918, when the Swedish scientist Robin Fareus discovered that at different ages and during pregnancy, as well as during various illnesses, red blood cells behave differently. Later, other scientists, Westergren and Winthrop, began working on developing methods for studying their behavior.
Even now, this parameter is measured during a general blood test. However, when the ESR is elevated, few people understand what this means. But you shouldn’t mindlessly panic about such news; too many factors can increase the level of red blood cells. And even if you have some kind of inflammation or disease, it is likely that now you can cure them without difficulty. The main thing is to urgently contact a specialist.
What does ESR show in a blood test?
The ESR reacts to any inflammatory process unfolding in the body, and the extent to which the ESR will deviate from the permissible value depends on the severity of the disease.
Based on the results of ESR, one can also predict the onset or development of cancer.
If the change in ESR is not large, this may not be suspicious for the disease. For example, during a strict diet, psychological stress and excessive physical activity, the ESR changes. It must be said that even if you take a general blood test not on an empty stomach, as is customary, but after having a hearty breakfast, the ESR value will have an inaccurate result.
In general, ESR shows how quickly cells in the blood settle to the bottom of a specially graduated test tube in one hour. Their movement can be influenced by:
- number and size of red blood cells;
- the appearance of proteins that respond to inflammation;
- increase in the number of fibrinogen;
- an increase in the number of immunoglobulins in the blood;
- increased cholesterol;
- other reasons;
What is the normal level of ESR in the blood in adults?
The ESR indicator may depend on age, gender, physiological and mental state. It happens that a completely healthy person has a standard ESR value that differs from those generally accepted.
Norm for children:
- 0-several days: 1 mm/h;
- 0-6 months: 2-4 mm/h;
- 6-12 months: 4-9 mm/h;
- 1-10 years: 4-12 mm/h;
- up to 18 years: 2-12 mm/h.
Norm for women:
- 2-16 mm/h;
- during pregnancy up to 45 mm/h;
Norm for men:
1-12 mm/h.
ESR is higher than normal: what does it mean?
Often it is the increase in blood sedimentation rate that is of interest to the doctor. If a blood test shows an elevated ESR that is significantly different from the norm, the doctor should prescribe further examination that will help determine the cause of this deviation.
If the ESR value is slightly increased, a repeat blood test can solve this problem. The fact is that the speed at which blood cells move increases with increasing temperature. And factors such as increased temperature in the laboratory, temporary overheating or cooling of the body can significantly affect the result.
ESR increases with:
inflammatory process.
Moreover, ESR can be affected by both serious illnesses (pneumonia) and minor colds (ESR with allergies, by the way, also changes its indicator).
- with pneumonia;
- for sinusitis
- heart attacks and strokes.
This can also be associated with inflammation, since damage to the heart tissue that occurs during a heart attack causes an inflammatory impulse in the body, which is detected by the ESR analysis.
tumors.
Often, by analyzing the ESR, it is possible to preliminarily determine whether there are neoplasms in the body. If the result differs from how much ESR should be in a healthy person by 60-80 units or more, but there are no noticeable viral, infectious and bacteriological diseases, then the probability of detecting tumors during further examination is very high.
for any viral and infectious disease
since in this case the body produces a large amount of immunoglobulins, which slow down the movement of red blood cells.
for certain conditions in women
In general, the ESR rate in women is higher than in men of the same age. However, during menstruation, ESR tends to increase even more. During pregnancy, ESR increases by several dozen, and this figure is considered normal. ESR also changes during menopause, before menstruation and after childbirth; the norm in the latter case can vary over several days. In particular, blood loss, and as a consequence a decrease in hemoglobin levels, can cause an increase in ESR.
- for tuberculosis;
- for diabetes;
- after operation;
When a person loses any significant amount of blood or suffers an injury, the ESR level may increase. This is due to the fact that in an emergency dangerous situation the body slightly changes the composition of the blood, which, of course, affects the rate of its deposition. It is difficult to judge how long it takes for ESR to recover after an illness, because everything depends on the severity of the disease, the individual characteristics of the person and the damage caused to the body. In some cases, recovery may take several months.
- with HIV infection;
- with anemia;
- with cirrhosis of the liver;
- with cirrhosis;
If you have received the result of your blood test and are worried about your condition, ask your doctor what the ESR indicator in the general blood test means in your case. You shouldn’t push yourself if the result differs from the norm; to make or refute a diagnosis, you need to completely examine the body.
Be healthy!
Normal ESR in humans
When examining, you must be guided by the fact that the analysis examines red blood cells. Norm for women by age (table):
| In women under 30 years of age | norm 8-15 mm/h |
| In women over 30 years old | norm up to 20 mm/h |
Based on the table, it can be seen that there are always maximum indicators. You need to know that the rate of pregnant women is growing significantly, it can reach 45 mm/h.
During pregnancy, additional studies are not required.
Norm
Increased ESR in the blood, what does this mean? This indicates a change in the electrochemical properties of the blood. Proteins secreted by pathological cells lead to the gluing of red blood cells, the appearance of “columns” of cells similar in appearance to coin cells. The more coins there are, the heavier they are, therefore, the ESR increases. The units of measurement for erythrocyte sedimentation rate are millimeters per hour. When normalizing ESR, the gender and age of patients are taken into account. In clinically healthy newborns (four weeks of age), ESR ranges from 1.0-2.0. This is explained by the high concentration of red blood cells in the blood, in other words, high hematocrit.
The ESR rate depends on gender and age
Age-related changes up to six months are manifested in an increase in ESR to values of 12.0-17.0. The process of growing up gradually brings the ESR norm to a state characteristic of adult males; it ranges from 1.0-8.0.
The normal ESR level in the blood of men varies widely, from 1.0 to 10.0 mm. Women, who are more susceptible to the influence of various hormones than men, have a slightly different ESR norm than men. The normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate ranges from 2.0 to 15.0 mm.
The ESR rate during pregnancy can fluctuate sharply. So, in the fifth month of gestation, 55.0 mm is considered normal. This is probably due to an increase in plasma volume, increased production of globulins and sterols with a lack of calcium in the blood. After childbirth, a woman’s ESR is in no hurry to return to the usual 15 mm or less. This happens about three weeks after the successful delivery of the pregnancy.
Some therapeutic and prophylactic effects can cause an increase in ESR in the body. Starvation diets and limited drinking predictably lead to the degradation of tissue proteins. Additional amounts of globulins and fibrinogen glycoprotein are released into the blood, which agglutinate red blood cells, which increases the sedimentation rate. Eating before taking blood for analysis can increase ESR to a level of 25.0 mm, therefore, to clarify the tests, an incontinent patient will have to donate blood again. Some drugs from the dextran group, as well as contraceptives, have a similar effect.
The average normal values of ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) depending on age and gender, as well as the limits of fluctuations, are presented in the table.
Table of normal ESR in blood depending on age and gender, mm/h:
| Age, gender | Norm |
| Newborns (up to four weeks) | 1±1 |
| Babies up to six months | 14,5±2,5 |
| Children | 5±3 |
| Women | 7±5 |
| Pregnancy, second half | 45±5 |
| Women >60 | 10±10 |
| Men | 4,5±3,5 |
| Men > 60 | 7,5±7,5 |
ESR increases mainly due to an increase in the concentration of globulins and fibrinogen glycoprotein. Such a protein shift can occur for various reasons, but, most often, such a process indicates the development of inflammatory pathologies and destructive phenomena in connective tissue formations. The consequences of such pathological disorders can be foci of necrosis, the development of malignant neoplasms, and disruptions in the functioning of the immune system.
In the case of a prolonged increase in ESR to values exceeding 4 cm, which does not have a rational explanation, we are talking about differential diagnosis of specific diseases. This requires additional hematological studies.
The ESR rate depends on gender and age
The normal ESR level in the blood (where else could it be?) primarily depends on gender and age, but is not particularly diverse:
- In children under one month old (newborn healthy babies), ESR is 1 or 2 mm/hour; other values are rare. Most likely, this is due to high hematocrit, low protein concentration, in particular its globulin fraction, hypercholesterolemia, and acidosis. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate in infants up to six months begins to differ sharply - 12-17 mm/hour.
- In older children, the ESR levels out somewhat and is 1-8 mm/h, corresponding approximately to the ESR norm of an adult male.
- In men, ESR should not exceed 1-10 mm/hour.
- The norm for women is 2-15 mm/hour, its wider range of values is due to the influence of androgenic hormones. In addition, at different periods of life, the ESR in women tends to change, for example, during pregnancy, from the beginning of the 2nd trimester (4th month), it begins to grow steadily and reaches a maximum by childbirth (up to 55 mm/h, which is considered absolutely normal). The erythrocyte sedimentation rate returns to its previous values after childbirth in about three weeks. Probably, the increased ESR in this case is explained by an increase in plasma volume during pregnancy, an increase in the content of globulins, cholesterol, and a decrease in the level of Ca2++ (calcium).
An accelerated ESR is not always a consequence of pathological changes; among the reasons for an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, other factors that are not related to pathology can be noted:
- Starvation diets and limited fluid intake will likely lead to the breakdown of tissue proteins, and, consequently, an increase in fibrinogen, globulin fractions and, accordingly, ESR in the blood. However, it should be noted that eating will also speed up ESR physiologically (up to 25 mm/hour), so it is better to go for analysis on an empty stomach, so as not to worry in vain and not donate blood again.
- Some medications (high molecular weight dextrans, contraceptives) can accelerate the erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
- Intense physical activity, which increases all metabolic processes in the body, will most likely increase the ESR.
This is approximately what the change in ESR looks like depending on age and gender:
| Age (months, years) | Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (mm/hour) |
| Newborns (up to a month of life) | 0-2 |
| Babies up to 6 months | 12-17 |
| Children and teenagers | 2-8 |
| Women under 60 years old | 2-12 |
| During pregnancy (2nd half) | 40-50 |
| Women over 60 | up to 20 |
| Men under 60 | 1-8 |
| Men over 60 | up to 15 |
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate accelerates, first of all, due to an increase in the level of fibrinogen and globulins, that is, the main reason for the increase is considered to be a protein shift in the body, which, however, may indicate the development of inflammatory processes, destructive changes in connective tissue, the formation of necrosis, and the onset of a malignant neoplasm , immune disorders. A long-term unreasonable increase in ESR to 40 mm/hour or more acquires not only diagnostic, but also differential diagnostic significance, since in combination with other hematological indicators it helps to find the true cause of high ESR.
Reasons for increasing and decreasing ROE
When taking a general blood test, which is used to determine the norm of ESR in the blood of women, you can often observe its breakdown into two halves: the lower one is platelets, and the upper one is red blood cells. The latter gradually go down over the course of an hour.
The amount that has settled over a certain period of time is measured in millimeters. It is the rate at which red blood cells fall that shows whether the ESR is normal or not.
However, its value only gives an approximate idea of the state of health.
Depending on how old a woman is, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate also changes. Below is a table of ESR norms and norms for women by age.
| Age | ESR norm |
| From 14 to 18 years old | 3 – 17 mm per hour |
| From 18 to 30 years old | 3 – 20 mm per hour |
| From 30 years to 60 | 9 – 26 mm per hour |
| 60 and older | 11 – 55 mm per hour |
| During pregnancy | 19 – 56 mm per hour |
Why may the erythrocyte sedimentation rate be disrupted in the blood of women aged 14 to 30 years? There may be several reasons for an increase or decrease in the subsidence rate. An increase in the norm may be due to diseases and abnormalities such as:
- previous cold or viral infection;
- recent fractures;
- taking birth control pills;
- time of day (in the morning there is an increased rate, and in the evening - a decrease).
As for a slight decrease in ESR, this may be due to overeating or stress. However, if the value is less than two, then this indicates a lack of nutrients.
This happens when a woman fasts for a long time or is on a strict diet.
At the age of 30 to 50 years, the blood test ESR norm in women will differ slightly in indicators. However, the reasons for a significant increase may be different circumstances. These include:
- postpartum period;
- the onset of menopause - menopause;
- pneumonia;
- previous heart attack;
- condition after shock or surgery.
When the ESR norm decreases for women after 50 years of age, the reasons may be: lack of meat in the diet, taking certain medications, lack of bilirubin in the blood.
At 60 years of age and older, the main causes of deviations will be:
- menopause;
- pressure changes;
- diabetes;
- arthritis.
If the indicator is greatly reduced, this may be due to:
- cancerous or malignant tumors;
- heart problems;
- liver disease.
The category of pregnant women is considered by doctors separately from other female representatives. The thing is that the ESR rate during pregnancy varies due to:
- Physique. Thus, in thin women in the first trimester, values from 20 to 62 are observed, and in the second – 40 – 90 mm per hour.
- Restructuring of the body. What level of normal ESR in the blood of women will be observed with this factor depends on the individual characteristics of each.
- Inflammatory processes in the body.
- Anemia. This disease is most common in pregnant women. This is due to a decrease in hemoglobin.
As for a slight decrease in ESR, there is nothing wrong with this - this is a common case in practice.
Regardless of age, there are a number of diseases and abnormalities in which an increase in the norm will be observed. These include:
- liver diseases;
- discharge of pus or sepsis;
- destruction and necrosis of body tissues;
- obesity or emaciation;
- bone marrow disease: leukemia, myelonoma;
- diarrhea, constipation;
- nausea and vomiting;
- Lupus erythematosus is a red rash on the bridge of the nose and cheeks.
There are deviations in which the increased ESR rate in the blood of women is not pathological:
- Treatment of allergic reactions (if the drug is correctly selected, the ESR will decrease, otherwise the indicator will increase).
- Eating before analysis.
- Menstrual cycle or postpartum period.
An increase or decrease in erythrocyte sedimentation rate is safe and due to natural causes. Also, we should not forget that a change in the ESR norm is not a disease or infection. To confirm or deny the pathology, it is necessary to undergo a number of additional tests, which are prescribed by the attending physician.
✔ How to donate blood
In order for a woman to display ESR 14 at every test (if she is truly healthy), then she should properly prepare for it. Before donating blood, it is recommended to monitor your diet. In particular, you should avoid fatty, fried and spicy foods and alcohol 48 hours before the test. The last meal should be 9 hours before visiting the laboratory. That is why the analysis is prescribed in the morning, on an empty stomach. Pregnant women are advised to take a sandwich with them so that after donating blood they can refresh themselves and restore strength in the body.
You should also not be nervous before the analysis or expose yourself to stress. After all, it has been proven that after 30, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate depends on stress and even on the room temperature. If you have your period or ARVI (influenza and other inflammatory diseases) on the day of the test, you should refuse to take it. In any case, the result will not be objective.