Sergey Nikolaevich Maltsev
Gastroenterologist, therapist. Professional experience: 12 years
Cholestatic hepatosis of pregnancy (CHP) is a pathological condition that is caused by the sensitivity of liver cells to altered levels of hormones in a woman’s body during pregnancy.
The disease occurs in 3-5% of women bearing a child. With proper and, most importantly, timely treatment and following a diet, hepatosis can be dealt with, and all liver functions will be restored.
You can learn how to do this from this article.
What it is
Hepatosis disease belongs to the group of liver pathologies.
It occurs against the background of changes in metabolic processes in liver cells - hepatocytes. In addition, dystrophic changes at the cellular level can become a provoking factor. The disease can manifest itself in 2 forms:
- acute;
- chronic.
Acute hepatosis, as a rule, occurs against the background of severe toxic poisoning. Various chemicals and poisons act as poisoning agents.
Chronic hepatosis can be triggered by a lack of certain nutrients and long-term consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Diagnosing this disease is quite difficult. This is due to the fact that it occurs without symptoms characteristic of the inflammatory process.
Hepatosis or fatty liver responds quite well to therapy and treatment. A proper diet and medication help normalize the condition and avoid complications.
Hepatosis: features of pathology
Hepatosis is a liver disease in which its cells, under the influence of various factors, cease to perform their functions. Pregnancy may be accompanied by the following types of pathology:
- Cholestatic. A common disease that occurs due to disruption of metabolic processes, as well as dystrophic changes that occur at the cellular level. The main cause of cholestatic hepatosis is the hormonal changes that occur in a woman during pregnancy.
- Acute fatty. It is extremely rare. As the disease develops, liver cells are replaced by fatty tissues. The reason for this is a failure in the absorption of fatty acids. Women who have endocrine diseases, obesity, and an addiction to alcohol are at risk. Fatty hepatosis is a dangerous disease and poses a serious threat to the health and life of the mother and child. In emergency cases, premature delivery is performed.
In a normal state and in the absence of any pathologies, the liver remains unchanged. Its structure, blood flow and size are the same. Deviations arise against the background of the fact that during pregnancy the organ processes waste products for two people - mother and baby. Subsequently, the organ begins to produce many hormones.
An increase in load at the initial stage of pregnancy leads to toxicosis, which later develops into hepatosis of pregnant women. At this time, it is important to be under the constant supervision of specialists. If necessary, when the pathology becomes acute, the expectant mother is hospitalized.
In case of hepatosis, high sensitivity to the hormone estrogen is diagnosed. Intensive production leads to a rapid increase in its quantity. Against this background, cholestasis occurs - a violation of the formation and outflow of bile. As a result, the risk of death of the child increases.
Kinds
Hepatosis in pregnant women can be of the following types:
- fatty;
- pigmentary.
The fatty type of pathology involves the accumulation of adipose tissue in liver cells. This occurs due to excess lipid accumulation.
The following categories of women are at risk for the likelihood of developing this pathology:
- alcohol abusers;
- women who are being treated with hormone therapy or antibiotics;
- working with toxic substances;
- women who abuse fatty foods and fast food;
- expectant mothers with a sedentary lifestyle.
Pigmentary hepatosis is a hereditary pathology that is accompanied by dystrophic changes in liver cells.
As a result of its development, a violation of bilirubin metabolism occurs. This form of pathology is quite difficult to diagnose, because often resembles weakly developing hepatitis.
Dangers
The degree of danger of this disease for a woman and child directly depends on the form of its course.
The most common complications that develop are:
- severe hypoxia of the child due to oxygen starvation;
- the start of the delivery process ahead of schedule;
- a woman may develop renal failure;
- decreased blood clotting activity;
- intrauterine retardation and pathologies of child development.
In severe cases of the disease there is a risk of death. However, after the birth of the child, all negative manifestations disappear within 14 days.
Hepatosis is a complex and dangerous disease. When the first alarming symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor and undergo a comprehensive examination.
If a pathology is detected, timely and correct treatment reduces the risk of developing negative consequences for both mother and baby.
Consequences for the fetus
The baby develops serious abnormalities: too little weight, respiratory disorders. Such violations occur because:
- fetal breathing becomes difficult due to disruption of intrauterine nutrition (hypoxia);
- placental insufficiency develops, due to which the connection between mother and child is disrupted;
- During childbirth, the child suffered from suffocation.
The severe consequences of cholestatic hepatosis can be avoided if the pathology is treated in a timely manner. If a burn is detected, the child dies.
This is interesting: How to take Heptral for fatty hepatosis: how many days does the course of treatment include?
Causes
The development of a child in the uterine cavity significantly increases the load on all internal organs of a woman.
Quite often, pregnant women experience thickening of bile. As a result, the outflow of this substance slows down in the bile ducts. In turn, this negatively affects the functioning of the entire organ.
The following factors can provoke this condition:
- hereditary predisposition to the disease - the pathology is transmitted mainly through the female line;
- recurrent liver diseases that were in the latent phase;
- improper intake of vitamins and minerals, excess of certain substances;
- individual sensitivity to hormonal therapy;
- insufficient production of enzymes;
- development of pregnancy.
In addition to the above factors, the development of hepatosis can be provoked by the abuse of alcoholic beverages and work with toxic substances.
Symptoms
Hepatosis in pregnant women is manifested by the symptoms described below.
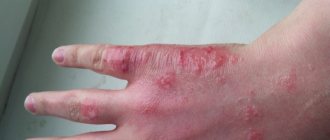
- A feeling of itching, which is caused by the entry of bile pigments into the bloodstream. As a result, skin receptors are irritated and the woman feels discomfort;
- In a blood test, the concentration of bilirubin increases, and as a result, jaundice develops. It is accompanied by the appearance of a yellow tint on a woman’s skin and on the whites of her eyes.
- Appetite decreases, taste preferences change.
- The woman may feel nauseous.
- The color of the stool becomes light. This is due to the entry of bile into the intestines.
- Darkening of the urine occurs. The color change is caused by the entry of bile masses into the excretory ducts and kidneys.
The nature of symptomatic manifestations and their intensity depend on the severity of the disease and its type.
It is impossible to diagnose your pathology yourself. If your health worsens, you should contact a specialist.
Diagnostic methods
Timely diagnosis of hepatosis helps preserve the health of the expectant mother and prevent the formation of intrauterine pathologies in the child. A number of difficulties hinder a quick diagnosis:
- Due to the fact that the clinical manifestations of the disease include common symptoms that are also inherent in other diseases to which pregnant women are susceptible, it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis based on a survey and examination of the pregnant woman. Thus, dryness and itching of the skin may indicate nervous disorders or allergic reactions, vomiting and nausea are symptoms of toxicosis, jaundice and pain in the right hypochondrium are specific to viral hepatitis.
- Laparoscopy, radionuclide liver scanning, biopsy - these studies are not prescribed during pregnancy, as they have a negative effect on the development of the fetus and its proper formation.
- Biochemical blood tests are not able to fully reflect the clinical picture of the disease, and by palpation it is impossible to palpate the affected organ.
If you suspect the development of hepatosis in pregnant women, you should contact your doctor for a more thorough examination. The specialist will prescribe a series of laboratory blood tests, ultrasound of the liver and, if indicated, other abdominal organs.
An increase in the volume of the gallbladder and an excessive concentration of bile acids in the blood indicate the development of pathology.
Diagnostics
After a woman has consulted a doctor, she will be prescribed a set of diagnostic measures that will help establish an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnostics includes:
- study of the woman’s entire medical history, analysis of past diseases;
- examining the woman to detect external signs;
- general clinical blood test;
- blood test for biochemistry;
- general clinical urine test;
- stool examination;
- Ultrasound examination of the liver and gallbladder.
In addition, a pregnant woman should definitely consult a gynecologist who monitors her during gestation.
After undergoing a detailed comprehensive examination, the doctor will be able to accurately determine what pathology is present and prescribe a course of treatment.
To get a complete picture of a woman’s condition, it is very important to go through all stages of the examination. Otherwise, the diagnosis may not be reliable.
Stages and degrees
Hepatosis in pregnant women is a disease that, as it progresses, goes through certain stages:
| Name | Description |
| Pre-icteric stage | In most cases, the disease at this stage is diagnosed in pregnant women in the third trimester. The woman complains of nausea, itching and general malaise. A burning sensation in the esophagus and heartburn also appear, and medications do not alleviate the condition. |
| Jaundice | Symptoms of the disease intensify. A woman suffers from vomiting with blood or cloudy mucous. Heartburn worries me constantly. |
| Thermal stage | Fatty liver leads to liver failure. The functioning of the organ is disrupted, pathological processes cause profuse vomiting. The esophagus and gastrointestinal tract are covered with ulcerative, erosive lesions. |
The doctor will be able to establish an accurate diagnosis after a complete examination. In emergency situations, a woman is sent for premature birth. At the initial stage, hepatosis is treated under the close supervision of a specialist in a hospital setting until labor occurs.
Treatment
Treatment of hepatosis in pregnant women consists of the following areas:
- taking medications;
- special therapeutic diet.
The choice of medications depends on the type and severity of the disease. As a rule, for hepatosis, pregnant women are prescribed the following groups of drugs:
- medications that liquefy acidity - antacids;
- folic acid;
- heptral;
- medicines from the group of sorbents;
- cholestyramine;
- membrane stabilizers.
If a woman has severe hepatosis, she is also prescribed medications to prevent bleeding.
In addition to drug therapy, a pregnant woman must adhere to a strict therapeutic diet.
- Fatty, fried, salty and spicy foods are completely excluded. The preferred methods of preparing dishes are boiling, steaming, stewing.
- The basis of the diet is porridge and vegetables.
- Meals are fractional - often and in small portions.
Consequences
In the absence of timely treatment of hepatosis, the following complications may develop:
- spontaneous miscarriage at different stages of pregnancy;
- the appearance of hidden internal bleeding and hemorrhages;
- development of chronic hepatitis;
- destruction of liver cells, cirrhosis;
- development of acute liver failure;
- hepatic coma.
To reduce the risk of complications, it is necessary to regularly consult a doctor during pregnancy, eat right, lead an active lifestyle and monitor your health.
If alarming symptoms appear, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor. Timely treatment reduces the risk of complications to almost zero.
How does hepatosis manifest during pregnancy?
Clinical manifestations of the disease have a number of features depending on the form of pathology.
Cholestatic hepatosis in pregnant women is characterized by:
- itchy and flaky formations on the surface of the epithelium, intensifying after water procedures, in the evening and at night,
- pain and a feeling of heaviness in the liver area,
- loss of appetite,
- nausea,
- vomit,
- fast fatiguability,
- change in the color of feces,
- less often – headaches and apathy.
In most cases, all symptoms of hepatosis in pregnant women go away on their own after delivery. Acute fatty hepatosis in pregnant women, in addition to the above symptoms, is characterized by special phenomena:
- jaundice,
- heartburn,
- weakness,
- drowsiness,
- hematemesis.
In the absence of proper treatment, a progressive disease can lead to the development of complications, including functional disorders in other organs (failures in kidney function are more common), as well as short-term fainting.
In advanced stages of the disease, there is a high probability of developing profuse bleeding, renal and liver failure.
How to give birth
Is it possible to give birth naturally with hepatosis only a doctor can answer after a comprehensive examination of the pregnant woman. This decision is made individually in each individual case.
To determine the method of delivery, the following criteria are considered:
- the woman's health status;
- the child's condition;
- form and type of hepatosis.
If the baby feels normal in the womb and there are no abnormalities in its indicators, then the woman can give birth on her own on time.
If the child’s condition is of concern, and the woman has a strong external manifestation of pathology, then doctors may decide on the need for early delivery by cesarean section.
In both cases, the option that maximizes the health of the woman and her baby is chosen.
Hepatosis during pregnancy is quite dangerous. It can negatively affect not only the woman’s well-being, but also the intrauterine development of the child.
Timely diagnosis and treatment of pathology significantly reduces the risk of negative consequences.
It is impossible to treat hepatosis during pregnancy on your own. This can only make the situation worse.
Following simple rules of prevention and recommendations for maintaining a healthy lifestyle reduces the risk of developing the disease.
Why is hepatosis dangerous during pregnancy?
Cholestatic hepatosis in pregnant women is not classified as a life-threatening disease, but the course of the pathology increases the emotional burden on the woman and reduces the quality of life due to the presence of clinical symptoms.
In addition, the disease negatively affects the process of gestation, causing:
- Placental insufficiency,
- Intrauterine fetal hypoxia,
- Premature birth
- Asphyxia of a child during passage through the birth canal,
- Postpartum hemorrhage.
Thus, the cholestatic form of hepatosis is not a life-threatening disease for a pregnant woman, but due to possible complications, it significantly increases the risk of irreversible pathologies in the child that develop due to oxygen starvation.
Acute fatty hepatosis is a deadly disease that poses a threat not only to the mother, but also to the unborn child due to the rapid development of the disease. There are often cases when, in order to preserve the life of women, they stimulate the onset of premature labor for medical reasons.