When carrying a child, many women's tests may be unstable and have elevated values, which also applies to blood sugar levels in pregnant women. Careful monitoring of the condition contributes to the successful development of the baby and minimizing health problems for the expectant mother. In this regard, a woman should monitor the level of glucose concentration and carry out analysis each time on the recommendation of a doctor.
How is diabetes diagnosed during pregnancy?
Most women don't know they have it until they get tested. Almost all nondiabetic pregnant women are screened for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. At this time, glucose screening is performed. For the test, you drink a glucose drink and check your blood glucose levels after 2 hours.
How is diabetes treated during pregnancy?
If this test shows high blood glucose levels, a 3-hour glucose tolerance test will be performed. If the results of the second test are not normal, gestational diabetes is diagnosed. Treatment will depend on your symptoms, your age, and your overall health. This will also depend on how severe the condition is.
What is blood sugar
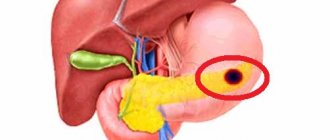
Glucose is one of the essential components of human blood and has certain normal limits and indicators.
After taking carbohydrates, which provide energy to cellular tissue, it enters the body. If a large number of them come with food, then they are accumulated by the liver in reserve, the blood sugar level during pregnancy increases, which changes the level of hemoglobin and insulin content.
What are the possible complications of diabetes during pregnancy?
Treatment focuses on maintaining blood glucose levels within a normal range and may include.
A careful diet of low carbohydrate foods and drinks Exercise Blood glucose monitoring Insulin injections Oral medications for hypoglycemia. Most complications occur in women who already have diabetes before they become pregnant. Possible complications include. Very low blood glucose levels, which can be life-threatening if untreated, ketoacidosis due to high blood glucose levels, which can also be life-threatening if untreated.
The need for insulin injections is more frequent. . Women with gestational diabetes are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes later in life. They are also more likely to have gestational diabetes with another pregnancy. If you have gestational diabetes, you should get tested a few months after your baby is born and every 3 years thereafter.
Analysis for hidden diabetes mellitus during pregnancy
Latent diabetes mellitus is characterized by the absence of typical symptoms of the disease. In most cases, gestational diabetes occurs between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. If the fact of hyperglycemia (excess sugars) has been established, then repeated tests are prescribed throughout pregnancy and within 2-3 months after birth. Such an approach is necessary for timely control and tracking of any changes. Because elevated glucose levels during pregnancy pose a threat to mother and baby.
Important: the manifestation of gestational diabetes indicates a high probability of manifestation of type 2 diabetes in the future, even if the disease disappeared on its own after childbirth.
There are cases where bearing a child became a decisive factor for the onset of diabetes mellitus and its manifestation in the future.
Typically, type 2 diabetes develops when tissues no longer respond to the effects of insulin, despite its normal levels in the blood. To treat the early stage, a competent diet, lifestyle correction and dosed physical activity are sufficient. If necessary, treatment is supplemented with sugar-lowering drugs.
Why monitor your blood sugar levels during pregnancy?
Glucose is the main indicator of the level of carbohydrate metabolism. In healthy pregnant women, its meaning changes. Glucose promotes energy, with its help the body is enriched with nutritional components. It is synthesized in the correctly forming cells of the mother and the growing fetus. Deviations can cause serious consequences - for example, the development of diabetes, which is why it is so important to take a blood test to detect sugar.
Can diabetes be prevented during pregnancy?
Possible complications for the baby include: The baby may be growing slowly in the uterus due to poor circulation or other conditions such as high blood pressure or damaged small blood vessels. The risk of stillbirth increases in women with low blood glucose levels and changes in the blood vessels. Birth defects. Birth defects are more common in children with diabetes. Some birth defects are serious enough to cause stillbirth. Birth defects usually occur in the first trimester of pregnancy. Babies of diabetic mothers may have serious birth defects in the heart and blood vessels, brain and spine, urinary system and kidneys, and digestive system. Macrosomia. This is a term for a child who is much larger than normal. All the nutrients the baby receives come directly from the mother's blood. If there is too much sugar in the mother's blood, the baby's pancreas makes more insulin to use this glucose. This leads to fat formation and the baby becomes very large. Sooner or later. Birth trauma can occur due to the large size and severity of the baby's birth. Hypoglycemia. The baby may have low blood glucose levels immediately after birth. This problem occurs if the mother's blood glucose levels have been very high for a long time. This leads to a large amount of insulin in the baby's blood. After birth, the baby still has high insulin levels, but no longer has glucose from the mother. This causes blood glucose levels in newborns to become very low. The baby's blood glucose levels are checked after birth. This can cause breathing problems in infants. This is more likely in babies born before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
- Stillbirths.
- Dead bodies are more likely to occur in pregnant women with diabetes.
- The exact cause of stillbirth in diabetes is unknown.
Not all types of diabetes can be prevented.
Consequences of high sugar during pregnancy for a child
The state of hyperglycemia is dangerous for mother and child, as it can lead to:
- an increase in fetal weight to 4.5-6 kg, which leads to the need for cesarean section. In the future, the child is prone to obesity and early onset of diabetes;
- abnormalities in fetal development: pathologies of the nervous system and heart, abnormal development of internal organs;
- increase in the volume of amniotic fluid, which can subsequently cause termination of pregnancy;
- failure in the process of placental exchange;
- not carrying a child;
- injuries to the child and maternal birth canal during childbirth (due to the large mass of the fetus);
- asphyxia of the newborn;
- development of respiratory distress syndrome in a newborn;
- cerebrovascular accident in a newborn;
- development of severe gestosis in the mother;
- severe hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinism in a newborn;
- development of polycythemia in a newborn;
- manifestations of chronic diabetes mellitus, more often type 2, etc.
The degree of risk of developmental defects in the child or postpartum complications is directly proportional to the level of hyperglycemia in the expectant mother.
During sugar surges, the likelihood of a missed pregnancy or postpartum complications increases significantly. Therefore, it is important not only to monitor the value of the indicator, but also to follow all the doctor’s recommendations for correcting your diet or daily routine. In some cases, hospitalization in a hospital is required for round-the-clock monitoring.
Why is the rate increasing?
After conceiving a child, a woman’s functional activity of the pancreas to produce insulin is inhibited. The hormone regulates carbohydrate metabolism, increasing the activity of proteins transporting glucose into cells. A decrease in insulin proportionally leads to an increase in sugar levels.
In parallel with this process, placental hormones are produced. Somatomammotropin is the main antagonist of insulin. This means the ability of somatomammotropin to weaken the effect of insulin on tissue. It is necessary for the normal metabolism of the pregnant woman and the regulation of the supply of glucose to the developing fetus.
What kind of sugar should a pregnant woman have?
The permissible blood sugar level during pregnancy should not exceed 6 mmol/l. Normal values: from 3.3 to 5.5 mmol/l. When the level is higher, this indicates the presence of hypoglycemia and minimal levels of the hormone insulin. In this case, adjustment (or intervention) by specialists may be necessary. When such indicators appear in the third trimester of pregnancy, they can be considered the norm. Below are tables of what the sugar intake should be for pregnant women.
How is diabetes managed during pregnancy?
Type 1 diabetes usually begins when a person is young.
Type 2 slump can be avoided by losing weight. Healthy food choices and exercise may also help prevent type 2 diabetes. Special testing and monitoring of the baby may be required for pregnant diabetics, especially those taking insulin. This is associated with an increased risk of stillbirth. This means counting the number of movements or strokes in a certain period of time and observing the change in activity. This is an imaging test that uses sound waves and a computer to create images of blood vessels, tissues and organs. Ultrasounds are used to view internal organs as they function and to analyze blood flow through blood vessels. Non-constructive testing. This is a test that measures the baby's heart rate in response to movement. Biophysical profile. This is a measurement that combines tests such as the no-stress test and ultrasound to check the baby's movements, heart rate and amniotic fluid. Doppler flow studies. This is a type of ultrasound that uses sound waves to measure blood flow.
- Counting fetal movements.
- Ultrasound.
The baby from a diabetic mother can be delivered vaginally or by caesarean section.
The norm of sugar during pregnancy from a vein
The test must be taken strictly on an empty stomach, but in some cases this is impossible or the expectant mother cannot do it. Then the specialist takes into account the intake of food or sugar-containing drinks. Thanks to this, it is possible to create the correct picture, obtain accurate indicators and prescribe the correct therapeutic measures for the expectant mother.
This will depend on your health and how much your pregnant doctor thinks the baby weighs. Your maternity care provider may recommend a test called amniocentesis in the last weeks of pregnancy. This test removes some of the liquid from a bag of water. Fluid testing can determine whether a baby's lungs are mature. The lungs mature more slowly in children whose mothers have diabetes. If the lungs mature, the healthcare provider may recommend induced labor or cesarean section.
Key points about diabetes during pregnancy
Diabetes is a condition in which the body cannot produce enough insulin or it cannot use it. Almost all pregnant women without diabetes are screened for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. Treatment for diabetes focuses on keeping blood sugar levels within a normal range. Follow-up testing is important. There are 3 types of diabetes: type 1, type 2 and gestational diabetes. . Tips to help you get the most out of your visit to your healthcare provider.
Sugar norm during pregnancy from a finger
Blood from a fingerstick is taken from pregnant women 2 times a month. Thanks to the analysis, the first violations of the glucose norm are revealed, which can be high or low, which is almost equally harmful for the expectant mother. The procedure requires refusing food before the procedure, but if this is unacceptable, it is necessary to warn the specialist about eating: this will allow you to get an accurate result.
Bring someone with you to help you ask questions and remember what your provider tells you. During the visit, write down the name of the new diagnosis and any new medications, procedures, or tests. Know why a new medicine or treatment is being prescribed and how it will help you. Also know what side effects are. Ask if your condition can be treated in other ways. Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what results may matter. Know what to expect if you do not take your medicine or have a test or procedure. If you have a follow-up appointment, write down the date, time, and purpose of that visit. Know how you can contact your provider if you have questions.
- Know the reason for your visit and what you want.
- Before your visit, write down the questions you want answered.
- Also write down any new instructions your provider gives you.
What is self-monitoring of blood glucose?
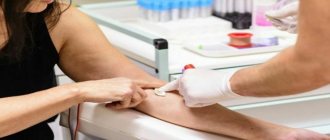
How to donate blood to determine glucose?
A blood sugar test is carried out twice - at a period of 8 to 12 weeks and then repeated at 30 weeks. If, during the first test, the expectant mother's sugar level was found to be above normal, she will need to retake the test. Such an increase (if it is insignificant) may be temporary, and therefore, in order to monitor the stability of sugar levels, it is recommended to repeat the diagnosis.
Blood for analysis can be taken either from the ulnar vein or from a finger (the second method is more common).
To give birth to a healthy baby, it is imperative to control glucose in the body. A high concentration of glucose, especially in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy, can provoke increased weight gain in the fetus, not due to muscle or bone tissue, but due to fat.
Macrosomia, as this phenomenon is called, leads to the fact that the baby becomes too large at the time of birth. Natural childbirth is difficult, both mother and baby are injured.
The risk group for hyperglycemia in women during pregnancy, when blood glucose exceeds the norm, includes persons:
- those suffering from obesity, polycystic ovary syndrome;
- over 30 years old;
- who gave birth in previous pregnancies to a child weighing more than 4 kg;
- with a family history of diabetes;
- not carrying previous pregnancies.
Symptoms of the formation of gestational diabetes are:
- increased appetite;
- increased thirst;
- dry mouth;
- blurred vision;
- frequent urination;
- blood pressure surges;
- drowsiness during the day;
- fast fatiguability.
Gestational diabetes may be asymptomatic. In such a case, excess sugar in the blood is detected in a pregnant woman only with the help of a glucose tolerance test.
A manifestation of gestational diabetes can be polyhydramnios, a condition characterized by an abundance of amniotic fluid.
Exceeding the glucose norm in a pregnant woman contributes to the development of:
- Diabetic fetopathy
- Impaired lung development due to lack of synthesis of surfactant, a substance that prevents the collapse of the walls of the pulmonary alveoli
- Conditions of hyperinsulinism
- Decreased muscle tone
- Inhibition of a number of innate reflexes
Diabetic fetopathy is a condition of a fetus that develops when a pregnant woman has excess sugar. With gestational diabetes, diabetic fetopathy does not always develop, but only in 25% of cases.
By controlling glucose during pregnancy, a woman will be able to avoid the troubles caused by diabetic fetopathy in the fetus.
The consequences of exceeding the norm of glucose in the mother’s blood can be for the child after birth:
- Metabolic disorders in the first hours of life - hypoglycemia, below normal levels of calcium, magnesium, iron, albumin protein
- Respiratory dysfunction
- Cardiovascular diseases
Children who have had diabetic fetopathy need control over their blood sugar from birth.
In principle, when registering at the antenatal clinic regarding pregnancy, all women, along with other examinations, are prescribed a blood sugar test (standard biochemical analysis). Usually for workers this occurs for up to 12 weeks. In general, this parameter must be assessed in a woman up to 24 weeks without fail. No special consultation with an endocrinologist is required for examination or detection of abnormalities.
A gynecologist or therapist is quite capable of administering the study and assessing its results. According to the standard, blood plasma from a vein is examined (although quite often laboratories give conclusions on serum analysis, which may lead to discrepancies in the interpretation of the sugar indicator). Ideally, blood sampling is on an empty stomach. But it is also possible to study during the day without connection with food intake (it will most likely require monitoring of fasting glucose).
All screening for hyperglycemia in pregnant women can be divided into two stages. At the first, the following studies can be performed:
- For all women in an interesting situation, during the initial visit to a gynecologist or therapist, fasting venous plasma sugar is determined during the first 24 weeks.
- Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) may be measured instead. An alternative option is to determine plasma sugar in venous blood throughout the day. The last indicator is only indicative and requires monitoring of fasting sugar levels.
The second stage is performed if glycemia was not previously determined or if pathological abnormalities in the tests did not appear at the first stage. To do this, glucose sensitivity is monitored between 24 and 28 gestational weeks. In some situations (high risk of diabetes in a pregnant woman, signs of diabetic fetopathy in the fetus), the test can be performed before the end of 32 weeks.
To determine blood sugar levels, a finger prick test is performed in the morning on an empty stomach. To get reliable results, prepare properly for the study:
- in the morning, do not drink anything, do not eat, do not brush your teeth with toothpaste, do not rinse your mouth;
- limit food intake 8 hours before the test;
- give up fast carbohydrates one day before;
- 24 hours before the test, stop taking medications, and if it is impossible to stop them, notify your doctor.
A biochemical blood test from a vein will determine the sugar concentration. However, the norm is slightly different; the acceptable value in decoding is 6 mmol/l.
If previous test results indicate hyperglycemia, a glucose tolerance test is performed:
- In the morning on an empty stomach, blood is taken from a finger or vein.
- A pregnant woman drinks 100 ml of glucose solution.
- After 60 and 120 minutes, blood is drawn again. During this period you should not consume anything.
- The results of the analysis are checked against the table of norms. If the indicators are exceeded, a consultation with an endocrinologist is prescribed.
DETAILS: Leukocytosis after childbirth in women: reasons for the increase in leukocytes in the blood of a woman in labor after cesarean section
Increased blood sugar in pregnant women
An analysis done on an empty stomach and exceeding 6 mmol/l is a deviation. The reasons for this problem may vary. The indicators exceed the permissible limit due to polyhydramnios, overweight of the expectant mother, and unstable hormone levels. The problem can also arise in first-time mothers, as well as in women whose previous births were accompanied by the appearance of a large child, a miscarriage or a stillborn fetus.
Once you are diagnosed with gestational diabetes, you and your healthcare providers will want to know more about your daily blood sugar levels. It's important to know how your physical and eating habits affect your blood sugars. Additionally, as your pregnancy progresses, the placenta releases more hormones that act against insulin. Testing your blood sugar levels at important points throughout the day will help determine if healthy diets and weight gain are being followed, your blood sugar levels are normal, or if extra insulin is needed to help protect the fetus.
Acceptable plasma glucose levels for gestational diabetes during pregnancy
When cells begin to perceive the effect of insulin worse, then gestational diabetes develops.
In 3% of cases, this pathological condition leads after delivery to the development of diabetes of the second or first form.
If you have prediabetes before pregnancy during the period of gestation, the likelihood of the appearance of a gestational type of pathology increases.
After delivery, glucose levels usually return to normal.
Capillary blood
The sugar standard in capillary serum for women with the gestational form of pathology is given in the table below:
| Normal on an empty stomach | Normal after a couple of hours of food |
| from 5.2 to 7.1 mmol/l | up to 8.6 mmol/l |
In women with gestational diabetes, the presence of sugar in urine is allowed in a concentration of up to 1.72 mmol/l.
Deoxygenated blood
The standard venous blood glucose concentration for pregnant women is given in the table below:
| Normal on an empty stomach | Normal value one hour after eating |
| up to 7.5 mmol/l | up to 8.8 mmol/l |
Low sugar
This problem occurs when the pancreas produces a large amount of insulin, but little sugar enters the body. This is indicated by readings below 3.3 mmol/l. This condition can be caused by many reasons. These include long breaks between meals with little consumption, and exhausting diets. The reasons may be the following:
Blood glucose monitoring is done by using a special device to take a drop of blood and test it for blood sugar levels. Your doctor or other health care provider will explain this procedure to you. Make sure you are shown how to test before attempting it yourself. Some items you can use to control your blood sugar levels.
The laser device is a spring device for attaching fingers. A test strip is a chemically treated strip to which a drop of blood is applied. A glucose meter is a device that “reads” the test strip and gives you a digital number. Your doctor can tell you where to get self-monitoring equipment in your area. You may want to ask if any places have rental or credit blood glucose meters, since you likely won't need one after your baby is born.
- Intense physical activity, accompanied by serious energy consumption. If it is not possible to give up exercise completely, then you need to take additional carbohydrates (for example, regularly consume ascorbic acid).
- Frequent intake of sweet foods. Because of this, sugar levels rise rapidly. In this case, there is a rapid increase in insulin levels, which drop over a short period. This glucose content leads to drowsiness, fatigue, weakness and the desire to eat more candy or cake. Because of this condition, a constant need to consume sweets is formed and there are serious consequences and a threat to bearing the baby.
- Taking carbonated and alcoholic drinks causes a rapid increase and then a sharp decrease in glucose. Based on this sign, one can judge the occurrence of dangerous pathologies, due to which serious consequences develop not only for the mother, but also for the baby.
You may need to have your blood checked several times a day. As a rule, this time is fasting and 2 hours after each meal. Sometimes you may be asked to get tested more frequently during the day or night. Because each person is an individual, your healthcare provider can advise the schedule that is best for you. How do I record my test results? Most manufacturers of glucose testing products provide a record diary, although some healthcare providers may have their own version.
Preparing for the study
Sometimes a blood glucose test gives a false positive or false negative result. To obtain accurate glucose test data, a pregnant woman should prepare for the examination.
Experts advise adhering to the following rules:
- do not have breakfast before going to the clinic. In the morning you can only drink still water;
- if a day before the examination a pregnant woman begins to feel unwell, then you need to inform the laboratory assistant or doctor about this;
- Before the analysis you should get a good night's sleep;
- on the eve of the examination, there is no need to overload the stomach with heavy carbohydrate foods;
- one hour before the test it is necessary to avoid physical activity;
- There is no need to worry during the blood collection period;
- On the day of the study, you should stop drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking.
How to normalize blood sugar levels
Doctors prescribe following a certain diet and eliminating certain foods, which helps restore normal blood sugar levels in pregnant women. During consultations, the specialist will tell you that it is recommended to limit the intake of sweet, fatty, fried foods, milk (whole and condensed), chocolate products, mayonnaise, sausage, cheese, ice cream, juices, fruits, carbonated drinks. Foods that promote slow absorption of carbohydrates are useful: buckwheat, baked potatoes, wheat.
A blood glucose monitoring diary is included at the end of this book. You should write down any test results immediately because it is easy to forget what you read during a busy day. You should always have this diary with you when you visit or contact your doctor or other health care provider. These results are very important when making decisions about your health care.
In addition to a blood test, you may be asked to test your urine for ketones. Ketones are byproducts of fat breakdown and can be found in the blood and urine as a result of inadequate insulin or not enough calories in your diet. Although it is unknown whether small amounts of ketones can harm the fetus, when large amounts of ketones are present they are accompanied by a blood condition, acidosis, which is known to harm the fetus.
Experts advise eating beef, fresh vegetables, and legumes. If the expectant mother has not taken prenatal vitamins before, it is best to do so now. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and regular routine examinations can help prevent gestational diabetes. In some cases, insulin therapy is required to treat the disease. The doctor will conduct examinations and, in case of certain disorders, recommend the use of this drug, with the help of which the normal blood sugar level in pregnant women will be restored.
Reasons for changes in glucose levels
To answer why the concentration of glucose in the blood of pregnant women increases, you need to understand what is happening in the female body. During gestation (pregnancy), the endogenous steroid and progestogenic sex hormone progesterone reaches high concentrations. Its main function is to maintain pregnancy and ensure the successful development of the fetus. Active production of progesterone partially or completely blocks insulin production.
In the second half of the perinatal period, the synthesis of placental hormones increases. The provisional (temporary) organ begins to perform its endocrine function. Hormonal imbalance has a negative impact on metabolic processes, in particular carbohydrate metabolism. Pregnant women have an increased need for glucose, since two organisms need to be provided with energy and nutrition (one of which requires permanent sugar replenishment, since it is in a state of growth).
The expectant mother begins to eat more foods containing simple carbohydrates (confectionery, chocolate, etc.). With such a glucose attack, the pancreas tries to compensate for the situation by increasing the production of insulin. Considering that in the 2-3 trimester, a woman’s physical activity decreases, cells and tissues lose sensitivity to the hormone, and the pancreas wears out greatly.
Insulin resistance occurs (insulin synthesis is maintained, but the ability to realize it is lost). As a result, glucose accumulates in the blood, sugar levels rise, and body tissues are left without the necessary nutrition. Both mother and child are “starving.” Additional causes of unstable glycemia (blood sugar) during gestation may include the following:
- chronic pathologies of the pancreas and hepatobiliary system (usually diagnosed before pregnancy);
- unstable functioning of the renal apparatus;
- a woman’s genetic predisposition to diabetes mellitus (hereditary predisposition);
- distress (constant stay in a state of neuropsychological discomfort);
- high BMI (body mass index), indicating obesity.
Clinical manifestations of hyperglycemia are moderate, therefore, women are not inclined to pay due attention to them
Measuring sugar levels at home
To help those suffering from diabetes, there is a special device, thanks to which you can get your own sugar levels. It's called a glucometer (a small device with a small display). It is necessary to correctly measure the indicator, before which you need to follow the same rules as before the analysis (take it on an empty stomach). It is important to monitor the quality of test strips, which must be stored correctly and have an acceptable expiration date. Then the blood glucose level in pregnant women will be determined accurately.
- A test strip is inserted into the device and it is activated.
- The scarifier pen is placed at the site of the future puncture.
- A drop of blood is squeezed out and the device is brought to it.
- After a few seconds, the result will appear (time is calculated depending on the type of device and its functionality).
What should be the normal sugar level on an empty stomach and after meals during lactation?
During the lactation period, the fasting sugar standard is within the range of 3.5-5.5 mmol/l for capillary serum and up to 6.1 mmol/l for venous serum.
When feeding, it happens that the glucose concentration decreases. A couple of hours after lunch (dinner), the glycemic level can reach 6.5-7 mmol/l.
Video
During pregnancy, a woman’s blood sugar may increase (this test is mandatory for pregnant women, especially if the woman is gaining excess weight at an accelerated pace). If, according to the results of a blood test, blood sugar has increased, then in this case there is a suspicion that the pregnant woman has developed gestational diabetes. But there is no need to be scared or worried about this form of diabetes, since it goes away completely after the birth of the child (unlike standard diabetes).
Even though gestational diabetes does not mean diabetes, the condition can harm both the baby and the pregnant woman. If a pregnant woman has high sugar levels, there is a risk that the fetus will end up being very large and this will significantly complicate the course of labor. In addition, such children may begin to experience hypoxia by the age of 9 months, that is, oxygen deficiency. What to do in this case? How can such complications be avoided?
To avoid complications of gestational diabetes during pregnancy, it is recommended not to miss appointments with your gynecologist, get tested and, if necessary, undergo appropriate medical treatment.
According to medical statistics, women who had high blood sugar levels during pregnancy, leading to the onset of diabetes, were exposed to the pathological course of diabetes mellitus a few years later.
You can reduce the risk of diabetes after childbirth through constant monitoring of body weight, physical activity, and a nutritious healthy diet.
Dangers and consequences of gestational diabetes
Hyperglycemia in the first stages goes unnoticed, and the woman attributes the initial symptoms to physiological changes associated with pregnancy. Pathological signs appear clearly from the third trimester of gestation. This is due to the active synthesis of hormones by the adrenal glands, placenta, hypothalamus, as well as increased load on the pancreas. During this period, the pregnant woman notes the following signs of diabetes:
- constant thirst, dry mouth;
- increased appetite, rapid weight gain;
- dry skin, itching in the genital area;
- decreased visual acuity;
- increased volume of urine excreted;
- fatigue, lethargy, drowsiness.
- for the mother: risks of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus, obesity, cardiovascular pathologies, gestosis during this and subsequent pregnancies;
- for the fetus: diabetic fetopathy, asphyxia and hypoxia during childbirth, skeletal and central nervous system injuries during childbirth, postpartum drop in sugar levels and jump in insulin, hyperbilirubinemia, respiratory distress syndrome, death in childbirth.
DETAILS: High bilirubin in the blood in adults: causes and signs, bilirubin norm. Ways to reduce the amount of a substance in the blood
The meager external manifestations of gestational diabetes in pregnant women turn it into a problem that is very important to be identified in a timely manner using laboratory indicators and separated from full-blown diabetes mellitus that first appeared during pregnancy.
- fasting glucose equal to or greater than 7.0 mmol per liter,
- venous blood plasma sugar at any time of day is equal to or more than 11.1 mmol per liter,
- glycated hemoglobin is equal to or greater than 6.5%,
- venous plasma sugar 2 hours after a carbohydrate load (during a glucose tolerance test) is equal to or more than 11.1 mmol per liter.
If there are no characteristic diabetic signs (dry mouth, thirst, increased urination), glycemic control is carried out twice to verify the diagnosis.
Causes of high blood sugar during pregnancy
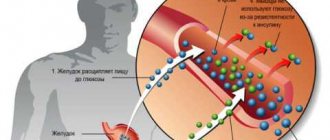
In order to understand the reasons for the increase in blood sugar during pregnancy, it is necessary to turn to our physiology. The level of sugar in our blood (both men and women) is maintained thanks to the hormone insulin. The hormone insulin in our body is produced by the pancreas.
Glucose is produced from food that enters our gastrointestinal tract and is naturally digested there. Insulin suppresses excess blood glucose levels, as a result of which our health remains stable and does not deteriorate due to excess blood sugar.
During pregnancy, a woman’s body’s functioning is completely restructured. In particular, the placenta, which provides life support to the fetus, produces a number of hormones that, on the contrary, increase the level. This leads to increased stress on the pancreas. And sometimes this organ can malfunction. Only one thing follows - the level of glucose in the blood begins to significantly exceed the norm.
So, the reason for the increase in blood sugar levels in a pregnant woman is the production of hormones by the placenta, which lead to an increase in sugar and a malfunction of the pancreas.
Clinical signs of hyperglycemia
Normal blood sugar levels in pregnant women can be combined with characteristic symptoms of diabetes, which include thirst, frequent urination, hunger, and decreased visual acuity. However, if tests indicate the absence of pathology, then, most likely, this is an absolutely normal pregnancy. Simply, during the entire period of bearing a child, you should be more attentive to your health and regularly monitor laboratory indicators.
If we talk about the normal physiological process, it occurs as follows. The amount of glucose in the blood is regulated by the pancreatic hormone insulin. Under its influence, the substance is transported into the cells of the body, and there is less of it in the blood.
But placental pregnancy hormones act on the opposite principle. The load on the pancreas increases, and it cannot cope with its work. As a result, the blood sugar level of the mother, and as a result, the child, increases.
In terms of risk factors, these include:
- Age over 35 years;
- Obesity, overweight, tendency to be overweight;
- Gestational diabetes in previous pregnancies;
- Polycystic ovary syndrome;
- Polyhydramnios;
- Unsuccessful pregnancies in the past (miscarriage, frozen pregnancy);
- The birth of large children or children with congenital developmental anomalies;
- Hereditary predisposition.
According to statistics, diabetes in pregnant women occurs in 3-10% of women, so it can be considered a fairly common and relatively safe disease. It is much more dangerous if diabetes is permanent and associated with diseases of the internal organs, endocrine system and other problems.
Sometimes the cause of an increase in blood sugar levels is poor nutrition, when the expectant mother is more concerned about the desire to eat something sweet or salty than about the need to supply the body with all the vitamins and nutrients.
Low blood sugar during pregnancy is associated with long breaks between meals, significant physical activity, and frequent consumption of sweets. The latter is due to the fact that in people with a sweet tooth, their blood sugar levels rise very quickly, but drop just as quickly.
Diabetes in pregnant women is common, but not entirely safe. Blood sugar levels are closely related to the endocrine system, which is also responsible for the production of sex hormones. Expectant mothers are required to undergo a test, which is carried out at the beginning of pregnancy and in the third trimester, and if there is a tendency to increase blood sugar levels, additional tests may be prescribed.
There is no need to be afraid of gestational diabetes: it can be successfully eliminated with the help of nutritional correction, acceptable exercise, and even the simple elimination of nervous experiences and stress.
Especially for beremennost.net – Elena Kichak
Constantly elevated sugar during pregnancy is fraught with consequences for both the mother and the fetus.
- Spontaneous abortion. Due to a violation of the trophism of the placenta, it becomes inferior: glucose is not absorbed, which means there is no energy substrate. Plus, glycosylated proteins destroy blood vessels. As a result, the fetus does not receive an adequate amount of nutrients and dies.
- Gestosis (also known as late toxicosis). Again, the pathology is associated with damage to the blood vessels of the placenta. The incidence of gestosis in pregnant women with diabetes increases at least 10 times!
- Polyhydramnios. This is a compensatory reaction in response to increased glucose. Can lead to fetal hypoxia, umbilical cord torsion with compression of the neck organs and malpresentation.
Polyhydramnios during pregnancy is very dangerous
We also recommend studying this topic:
High blood sugar - how to treat and quickly lower it
An increase in blood sugar is medically called hyperglycemia. This problem is quite serious and can affect anyone. Its symptoms and causes of development should be known in order to recognize the development of pathology in time.
- Diabetic fetopathy. With this disease, the internal organs of the child are affected, but the main problem during delivery is the weight of the fetus - more than 4 kg. This causes difficulties in passing the birth canal, which can lead to birth trauma in the child (dislocation of the cervical vertebrae) and rupture of the mother’s birth canal with bleeding.
- Fetal malformations: abnormalities of the heart, kidneys, brain, problems with the musculoskeletal system.
The effect of diabetes mellitus on the fetus
So what should a woman do if she experiences diabetes during pregnancy? More on this later.
Hyperglycemia during pregnancy is caused by the inability of the pancreas to synthesize sufficient amounts of insulin. Due to a lack of the hormone, sugar is not distributed to cells and tissues, but remains in the blood.
An increase in glucose levels is also caused by hormones synthesized by the placenta. Somatomammotropin acts as an insulin antagonist and helps ensure that the fetus receives enough glucose. It ensures an increase in blood sugar and reduces the sensitivity of cells to the pancreatic hormone.
Risk factors for hyperglycemia:
- the age of the pregnant woman is over 30 years;
- genetic predisposition to diabetes;
- diagnosed preeclampsia or gestational diabetes in previous pregnancies;
- a history of miscarriages and missed pregnancies;
- polyhydramnios;
- obesity or underweight.
In some cases, test results give false positive results. Factors that contribute to a short-term increase in glucose levels above normal:
- stress, emotional experience;
- past infectious disease;
- non-compliance with recommendations for preparation for analysis;
- excessive physical activity the day before;
- taking certain groups of medications.
Complications during pregnancy
Excessive blood sugar levels lead to metabolic disorders in both the fetus and the pregnant woman. If excess glucose is observed in a pregnant woman, then the same changes occur in the fetus’s body. As a result, the pancreas of the pregnant woman and the child suffers.
In the fetus, the pancreas begins to work with double the load, increasing the amount of insulin produced. Under the influence of hormonal imbalance, all excess glucose in the fetus passes into fat mass. As a result, the fetus gains more weight than is normal for it. Such changes in the fetus’ body provoke excessive oxygen consumption. If there is not enough oxygen supplied, then hypoxia occurs.
Why does sugar rise?
Glycemic levels increase during pregnancy due to the body's loss of ability to synthesize the required amount of insulin (a pancreatic hormone). This hormonally active substance is necessary for the proper distribution of sugar and its entry into cells and tissues. Without enough insulin, the body's glucose numbers rise.
In addition, hyperglycemia is caused by placental hormones, which are characteristic of pregnancy. Placental somatomammotropin is considered the main antagonist of insulin. This hormone is similar to growth hormone, takes an active part in the mother’s metabolic processes, and promotes the synthesis of protein substances. Somatomammotropin helps ensure that the baby receives enough glucose.
Important! The hormone not only increases sugar levels, but also reduces the sensitivity of a pregnant woman’s body cells to insulin.
Risk group
It occurs in approximately 10 women out of 100 during pregnancy. Moreover, the risk group includes women who entered pregnancy with such pathological conditions as:
- Excess body weight leading to obesity 2, 3 degrees;
- Gestational diabetes recorded in previous pregnancies;
- The presence of sugar in the urine;
- Ovarian wasting syndrome or polycystic ovary syndrome;
- Diabetes mellitus in direct relatives.
If a woman enters into pregnancy before the age of 25 and has never had any prerequisites for excess weight or gestational diabetes, then in this case there should be no pregnancy complications.
Signs
A woman should immediately consult a specialist if she has a pathological thirst, the number of trips to the toilet has increased, or she has a feeling of dry mouth. A rash may appear periodically, which does not go away for a long time, and visual acuity decreases.
Important! Pregnant women often do not pay attention to the symptoms of hyperglycemia, because they consider them to be manifestations of an “interesting situation.”
To confirm that sugar is really elevated, the patient’s complaints will be few. The doctor will definitely prescribe laboratory diagnostic methods, including the following methods:
- capillary blood test for sugar;
- biochemistry;
- glucose tolerance test (sugar load test);
- determination of glycosylated hemoglobin indicators.
In addition, the woman is advised by a neurologist, ophthalmologist, surgeon, and cardiologist.
Fundus examination is one of the stages of ophthalmological examination during pregnancy.
Pregnant women often attribute symptoms of high glucose to a change in the general condition of the body. At a routine appointment with a doctor managing a pregnancy, expectant mothers rarely complain about the manifestation of primary signs of hyperglycemia. A high glucose level is detected only during routine screening.
If your blood sugar has increased, the following symptoms should attract your attention:
- Polydipsia (permanent thirst). The desire to drink water arises regardless of the consumption of salty foods. Increased amounts of glucose in the blood require additional fluid, and the body tries to prevent dehydration (dehydration).
- Pollakiuria (frequent urination). It occurs, firstly, due to impaired absorption of free fluid by the kidneys, characteristic of hyperglycemia. Secondly, because of the growing baby (the enlarged uterus puts pressure on the bladder). Thirdly, due to the constant replenishment of water supplies (quenching thirst).
- Polyphagia (increased appetite) or anorexia (lack of appetite). Impaired insulin perception negatively affects the functioning of the hypothalamus, an area of the brain that regulates homeostasis and hunger. Eating behavior is out of control.
- Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS). Fatigue and weakness are caused by a lack of energy and tissue nutrition, since the delivery of glucose is stopped (or the cells refuse to absorb it).
External signs of high glucose levels: loss of elasticity and dryness of the skin, slow skin regeneration after damage, swelling, brittle hair and nails, telangiectasia (spider veins on the legs). If sugar increases by 2 or more mmol/l, manifestations of hyperhidrosis (increased sweating), cephalgic syndrome (headache), and increased heart rate (tachycardia) are possible.
Important! You should tell your doctor about all your sensations. A seemingly insignificant change in condition may be a sign of hyperglycemia.
Symptoms of gestational diabetes mellitus
As a rule, pregnant women do not in any way feel that they have gestational diabetes mellitus. This condition does not have characteristic symptoms that worsen the well-being of the pregnant woman.
The fact that a woman has gestational diabetes mellitus can only be determined by a timely blood sugar test. Even with a slight increase in blood sugar levels in a pregnant woman, the patient will be recommended to undergo additional tests that will confirm or refute the diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus. Additional studies in this case are a glucose tolerance test, as well as a sugar curve.
When conducting a glucose tolerance test, the pregnant woman will first need to give fasting blood from a vein to determine her blood sugar level. Then, immediately after this study, the patient should drink 1 glass of water with glucose dissolved in it (the ratio of water and glucose should be indicated by the doctor). After the pregnant woman drinks the sugar solution, she will need to take a blood test again.
How is gestational diabetes diagnosed?
It is determined based on a test with a load of 75 g of glucose - the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). And you shouldn't be afraid of him. It is absolutely safe for both the mother and the unborn baby.
How to properly self-monitor glycemia
Self-monitoring of glycemia is possible using a glucometer. At the pharmacy you can choose a glucometer that will suit you specifically. Simple and fast or more complex that saves measurement values and helps you build a glycemic curve. But whatever the glucometer, it is best to start keeping a diary of self-monitoring of glycemia and a food diary.
Difference between gestational diabetes and other types
Abnormal blood sugar levels always indicate diabetes.
It is only important to determine the type of this disease. If type 1 is mainly a disease of the young, and type 2 is the result of an unhealthy diet and lifestyle, then type 3 of the disease can only appear in a woman, and only during pregnancy. More precisely, it can be diagnosed in this piquant position. The specificity of gestational diabetes is that glucose surges occur until the baby is born.
In the future, the woman can live as usual and not fear for her health. But there is no complete guarantee of a positive outcome if the expectant mother does not follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Diabetes in pregnant women occurs due to hormonal changes, which are normal in most cases. The mechanism of the natural process is as follows:
- After fertilization of the egg, progesterone, a hormone that guards the safety of the fetus and its successful development, increases the activity. This hormone partially blocks insulin production. But the pancreas, receiving a signal about a deficiency of the substance, begins to produce it in larger quantities and can overexert itself. Hence the signs of diabetes.
- The placenta does its work, rebuilding the internal life of the expectant mother so that the baby is formed correctly, gains the required weight and is born safely.
- During pregnancy, elevated levels of cholesterol and glucose are acceptable, because it is necessary to provide energy and nutrition to two organisms - mother and baby.
But gynecologists have a medical scale that determines what can be considered normal during pregnancy and what should be called pathology.
And also the situation with the sugar content and the amount of insulin in a pregnant woman.
In a certain period, increased numbers in the analysis do not cause alarm, but if the level of sugar or insulin in the blood is higher than permissible, then there is reason to assume the development of diabetes during pregnancy. Due to the increased production of hormones, a failure occurs in the absorption of glucose or insufficient production of pancreatic insulin.
The effect of hyperglycemia on pregnancy
This phenomenon occurs when carrying a baby, because poor tissue sensitivity to insulin occurs. But diabetes mellitus can also precede pregnancy. Be that as it may, high sugar levels pose a danger to the expectant mother and her child, because excessive glucose concentration increases the risk of miscarriage, gestosis, pyelonephritis, and complications during childbirth (there may be a need to carry them out by cesarean section). All these risks depend on the adequacy of diabetes treatment.
Pregnant women have their own standards for carbohydrate metabolism. Thus, fasting blood sugar should not exceed 5.1 mmol/l. If it is above 7.0 mmol/l, then a diagnosis of “manifest diabetes” is made. It means that after the birth of the baby, the woman’s disease will remain, and treatment will need to be continued.
When the fasting blood sugar level of the expectant mother is in the range from 5.1 mmol/l to 7.0 mmol/l, a diagnosis of “gestational diabetes mellitus” is made. In such a situation, one can hope for normalization of carbohydrate metabolism after childbirth.
If we rely on medical statistics, then in diabetes mellitus spontaneous abortions occur in every third pregnancy. And the reason for this is premature aging of the placenta. After all, its blood vessels are damaged due to excess glucose in the blood. As a result of this negative phenomenon, the full supply of oxygen and nutrients to the fetus ceases.
The negative tendency of the influence of diabetes mellitus is also manifested in the risk of developing late toxicosis. This occurs after 20-22 weeks of pregnancy in half of pregnant women. Late toxicosis is usually associated with low estrogen levels. Since sugar also damages the ovaries, they cannot provide the female body with estrogen.
Toxicosis in such cases is manifested by obvious or hidden edema, weight gain, the appearance of protein in the urine, and increased blood pressure. Also, women with high glucose levels may develop polyhydramnios. This pathology develops in 60% of pregnancies.
Twisting of the umbilical cord, fetal hypoxia, and breech presentation are also possible.
For an expectant mother, an increase in sugar levels can threaten vision impairment, retinal detachment, and the development of heart failure. Against the background of elevated sugar, infectious diseases sometimes develop, for example, pyelonephritis.
High blood glucose poses a danger not only to the mother's body, but also to the fetus. High sugar levels increase the risk of developing preeclampsia, pyelonephritis, premature delivery, complications during pregnancy and the birth of the baby.
Diabetes mellitus in pregnancy
Medical statistics show that hyperglycemia causes spontaneous abortions, premature aging of the placenta, and late toxicosis. Elevated glucose levels lead to disruption of blood vessels, which alters the sufficient supply of blood and vital nutrients and trace elements to the fetus.
Late toxicosis is one of the severe complications of high blood glucose levels in pregnant women. This condition is manifested by significant swelling, the appearance of protein in the urine, weight gain, and an increase in blood pressure. In addition, hyperglycemia provokes the development of polyhydramnios (in 65% of clinical cases).
On the part of the baby’s body, an increase in sugar manifests itself as follows:
- macrosomia - a child is born with a pathologically increased body weight, which causes the development of complications during the period of his birth;
- retardation in physical development;
- mental development disorder - possible in the absence of correction of hyperglycemia in a mother who has diabetes even before conception;
- a small amount of surfactant - a substance that is responsible for the proper functioning of the lungs and the implementation of breathing acts;
- jaundice of newborns;
- hypoglycemia of a child - occurs due to the fact that the baby’s pancreas gets used to producing large amounts of insulin during intrauterine life, which continues after birth.
Weight more than 4 kg in combination with maternal hyperglycemia may indicate fetal macrosomia
Gestational diabetes does not cause malformations in the fetus, as is typical for type 1 diabetes, since the formation of organs and systems occurs in the first trimester, and the onset of the gestational form of pathology occurs from the 20th to 24th week.
Failure to correct glucose levels can lead to diabetic fetopathy. The disease is manifested by disruption of the pancreas, kidneys and blood vessels in the baby. Such a child is born with a large body weight (up to 6 kg), his skin has a red-burgundy tint, and pinpoint hemorrhages are visible.
Children with macrosomia differ markedly from healthy children
The skin is richly flavored with white grease and swollen. Upon examination, the large size of the abdomen and relatively short limbs are clearly visible. The baby may have difficulty breathing due to insufficient surfactant (the substance responsible for preventing the alveoli in the lungs from sticking together).
Important! In the first hours after birth, low muscle tone, suppression of the sucking reflex, and the absence of some physiological reflexes are noticeable.
Such complications can be prevented by correcting glycemic levels in the mother’s body with diet therapy and medications (usually insulin).
Methods of glycemic control during pregnancy
Standard studies are considered to be capillary blood analysis, biochemistry and determination of glucose tolerance.
Blood sampling from a finger occurs according to generally accepted rules. A woman takes it in the morning before food enters the body. You should not brush your teeth with toothpaste, as it may contain sugar, or use chewing gum. The blood sugar levels for pregnant women are indicated above.
Important! Venous blood indicators are slightly different, as, indeed, for all other people. A woman should not worry if she sees numbers up to 6 mmol/l as a result. This is acceptable when collecting material from a vein.
A glucose tolerance test is carried out in cases where the results of previous tests are outside the acceptable range. However, recently it was decided to prescribe this diagnostic method to all pregnant women upon reaching the 24th – 25th weeks.
The test does not require special preparation. For 48 hours before collecting the material, the woman should behave naturally; there is no need to reduce the amount of carbohydrates in the diet. In the morning you need to give up breakfast and tea, you can only drink water.
A blood or vein sample is taken in the laboratory. Next, the pregnant woman drinks a special sweet solution based on glucose powder. After 2 hours, an additional blood sample is taken in the same way as the first time. During the waiting period, the subject should not eat or drink anything except water. Explanation of the results in the table.
Interpretation of OGTT results in healthy pregnant women and against the background of gestational diabetes
Another important study is a urine test to determine glycosuria. There is no need to collect the first urine in the morning; it is poured out. Subsequent urination processes should be accompanied by collection of the analysis into one large container, which is stored in a cool place. The next morning, shake the container and pour about 200 ml of urine into a separate container. Deliver to the laboratory within 2 hours.
There are some criteria by which a gynecologist understands that a pregnant patient is at risk; increased monitoring of the general condition of the woman and fetus is required. Ladies preparing for pregnancy or already expecting a baby would do well to pay attention to this.
- The presence of a diagnosis of diabetes in someone along the family line.
- The expectant mother is overweight even before conception. If the body mass index exceeds the permissible norm by 20%, then it is better to pay attention to diet and physical activity to reduce the likelihood of failure in the absorption of glucose by cells.
- Age of the expectant mother. It is believed that after 30 years, processes occur in a woman’s body that can affect the course of pregnancy. By this age, cell tolerance to insulin may be impaired. Having such a problem before conception, a woman runs the risk of getting even greater cell insensitivity.
- The previous pregnancy ended in miscarriage, fetal death and stillbirth.
- The woman's weight at birth was 4 kg or more.
- Previous children were born weighing more than 4 kg.
- Polyhydramnios throughout the entire pregnancy cycle.
- A urine examination revealed elevated sugar levels.
- Gestational diabetes had already been diagnosed in previous pregnancies, but did not develop into a serious disease after childbirth.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with How to remove a large nail using traditional and folk remedies?
If at least one of the listed factors is present in a woman’s medical history, monitoring of the patient’s health and the development of pregnancy should be enhanced.
But you shouldn’t think that only those ladies who have warning signs of gestational diabetes are at risk. Cases are often diagnosed when the expectant mother is 100% healthy. The birth and development of a new life is a complex process that can violate any rules of medicine and nature.