Pregnancy pathologies are diseases and pathological conditions that jeopardize the course of pregnancy or the health of the woman and the development of the fetus. Many expectant mothers have pregnancy pathologies of varying severity. Some of them are amenable to therapy or correction, while others require termination of pregnancy. Let's consider what pathological conditions exist during pregnancy.
Common pathologies during pregnancy
It is difficult to mention all possible pathologies during pregnancy in one article. Therefore, we will briefly consider those that occur most often:
- Toxicosis of pregnant women and gestosis (late toxicosis). Toxicosis is caused by many factors, including neuroendocrine disorders, previous illnesses, some features of pregnancy and the influence of unfavorable factors. Late toxicosis is especially dangerous, as it causes disruption of the functioning of important organs and systems.
- Anemia, most often iron deficiency . This pathology can lead to the threat of miscarriage or premature birth, gestosis, placental insufficiency.
- Miscarriage . This term refers to the expulsion from the mother's body of a fetus weighing 500 g or less.
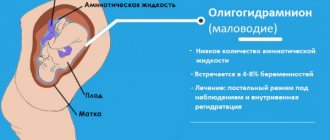
- Low water . They speak of oligohydramnios if the amount of amniotic fluid is less than 500 ml. This pathology of pregnancy often causes miscarriage, premature birth, fetal death, and weakness of labor.
- Polyhydramnios. This condition is diagnosed when there is an excessive amount of amniotic fluid. It is dangerous due to the threat of spontaneous abortion.
- Incorrect presentation of the fetus (the position of the fetus in the uterus relative to the birth canal). With this pathology of pregnancy, the child may have a pelvic, oblique or transverse presentation. In many cases of malpresentation of the fetus, delivery by cesarean section has to be used.
- Placenta previa . This pathology means partial or complete attachment of the placenta to the lower part of the uterus in the area of the internal os. It is dangerous due to the high risk of bleeding in the second half of pregnancy.
- Eclampsia . A very dangerous pathology during pregnancy, which is characterized by a seizure.
- Hypertonicity of the uterus . This term refers to uterine contractions before the expected due date. Uterine contractions can cause miscarriage or premature birth.
Non-developing pregnancy
A very serious complication is a non-developing pregnancy.
Pregnancy stops developing when the fetus dies in the womb. This occurs mainly during pregnancy up to 3 months.
The main factors causing this complication of pregnancy are: genetic (chromosomal and gene mutations of the parents), infectious (untreated chronic and acute diseases of the mother), endocrine (when the mother has impaired hormonal metabolism as a result of diseases of the endocrine glands), autoimmune (this is an immunological incompatibility between mother and fetus).
With this complication, pain in the lower abdomen and bleeding may not occur. An accurate diagnosis is made by the attending physician. This is confirmed by the absence of the baby’s heartbeat and an ultrasound examination.
If this diagnosis is confirmed, the pregnancy is terminated as an emergency. Delay can be a threat to a woman's life.
If a woman wants to get pregnant again, before that she needs to be examined at a medical institution, determine the exact cause of the undeveloped previous pregnancy and eliminate it.
Extragenital pathology and pregnancy
A special group consists of extragenital pathologies (EGP) - conditions and diseases of pregnant women that are not obstetric complications of pregnancy and gynecological diseases. What is the connection between extragenital pathologies and pregnancy? Experts note that during pregnancy the course of such diseases worsens significantly. This is due to the physiological and hormonal changes that occur in the body of a woman expecting a baby.
Doctors identify a number of diseases that can complicate the course of pregnancy. They require consultation with a specialist and observation at the stage of pregnancy planning, as well as registration of the woman with special registration during pregnancy.
Diseases included in the extragenital pathology of pregnancy include:
- Rheumatism is a systemic disease of connective tissues, which is most often localized in the circulatory organs. Prevention of rheumatism during pregnancy is not recommended due to the negative effects of drugs on the body of the mother and child.
- Arterial hypertension is dangerous due to miscarriage and the development of late toxicosis. The use of drug therapy is carried out only under the supervision of a doctor.
- Arterial hypotension increases the risk of premature birth, weakness of labor, bleeding during and after childbirth.
- Diabetes mellitus is dangerous due to the high probability of miscarriage, ovarian dysfunction, and the development of a large fetus.
- Inferior vena cava compression syndrome - leads to low blood pressure, a feeling of lack of air, and anxiety. Does not require drug therapy.
Early toxicosis: symptoms of pathology
The most common complication during pregnancy is a pathology such as toxicosis.
During the first three months, many pregnant women sometimes experience nausea and vomiting in the morning. This condition is not considered toxicosis and does not affect the course of pregnancy or the health and development of the fetus.
Toxicosis of pregnancy is considered to be uncontrollable vomiting during the day, accompanied by a sharp decrease in appetite, perversion of taste and smell, increased salivation, weakness, increased heart rate, fainting and shortness of breath.
Most experts believe that toxicosis in a pregnant woman develops as a result of a woman’s negative emotions. This condition of a woman needs to be treated, as it is harmful for both the mother and the unborn child.
There are 3 degrees of severity of toxicosis:
- Mild (vomiting occurs no more than 5 times a day, and the woman’s weight decreases slightly)
- Moderate (vomiting up to 10 times a day, the general condition of the pregnant woman worsens, weakness, apathy appear, blood pressure drops, white coating on the tongue and other symptoms)
- Severe (vomiting up to 20 times a day, constant nausea and profuse salivation, headache, dizziness, the woman loses a lot of weight: up to 2.5 kg or more per week)
Only mild toxicosis is treated on an outpatient basis, the rest are treated in a hospital.
To ease the condition of a pregnant woman, you can drink a small amount of tea with lemon balm or mint.
After a pregnancy of more than 12 weeks, toxicosis in most women goes away or becomes insignificant. A small number of pregnant women also experience late toxicosis (OPG-gestosis).
Fetal pathologies during pregnancy
The main method for determining fetal pathology during pregnancy is the triple test. It is carried out for a period of 15-20 weeks. Using the triple test, about 90% of malformations of the child’s nervous system and 60-70% of chromosomal diseases are determined.
This analysis for pathology during pregnancy is based on the determination of special markers of genetic pathology and developmental defects - AFP (alpha-fetoprotein), hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) and E3 (estriol).
AFP
An increase in AFP levels occurs with the following fetal pathologies:
- neural tube defects;
- fusion of the duodenum;
- anomalies of kidney development.
A reduced AFP level may indicate the development of Down, Shereshevsky-Turner, and Edwards syndromes.
hCG
The level of hCG in the blood of a pregnant woman may increase if the fetus has Down syndrome. A decrease in this indicator often occurs with Edwards syndrome (multiple malformations of internal organs and mental retardation).
E3
A decrease in estriol content in a triple analysis for pathology during pregnancy may indicate defects in fetal development.
If deviations from the norm are detected in the results of the triple test, the woman is prescribed a genetic consultation. Usually, a woman is recommended to conduct repeated tests to exclude errors. If the previous result is confirmed, the expectant mother undergoes additional examinations.
Pregnancy pathologies are quite common these days. However, there is no need to worry too much when diagnosing some of them. Most of these conditions and diseases can be successfully treated, which allows a woman to safely carry and give birth to a healthy baby.
Rh factor incompatibility
Incompatibility of mother and child with respect to the Rh blood factor is also called hemolytic disease of the newborn.
The blood of 85% of people on earth contains a certain antigen called the Rh factor, and such people are considered Rh positive. The remaining 15% of people do not have this antigen; such people are considered Rh negative.
If a situation arises when the mother is Rh positive and the fetus is Rh negative, the mother’s body begins to produce antibodies against the child’s Rh factor. These antibodies, having entered the baby’s blood through the placenta, cause gluing and then destruction of red blood cells.
This incompatibility is very dangerous for the child, as it causes hemolytic disease of the newborn. Such a child dies in utero or immediately after birth if he is not immediately given a blood transfusion.
If the mother’s Rh factor is negative, and the fetus’s is positive, and the woman has not had abortions or other births, that is, her first pregnancy, the child, as a rule, is born on time and absolutely healthy.
In case of repeated pregnancy, antibodies against the child's Rh factor accumulate in the mother's blood, and the child is most often born sick.
A mismatch in blood group between mother and child is also dangerous for the child, but less dangerous than a mismatch in Rh factor.
In order to avoid hemolytic disease of the newborn, a pregnant woman and the father of an unborn child need to check their blood for the Rh factor.
If a pregnant woman has a negative Rh factor, she needs to have her blood tested monthly for antibodies.
Uterine fibroids
Myoma is a benign tumor that forms in the muscular layer of the uterus - the myometrium. The disease is dangerous not only for the life and health of the child, but also for the expectant mother. Therefore, during 9 months, a pregnant woman must carefully monitor her own health.
Causes
To date, the causes of uterine fibroids are not fully understood. However, there are a number of predisposing factors, for example:
- Hormonal imbalance in the body.
- Endocrine disorders.
- Inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs.
- Late pregnancy (after 35 years).
- Weakening of the immune system.
- Nervous disorders.
- Mechanical injuries to the uterus (for example, in the case of abortion or other gynecological surgery).
- Genetic factor.
- Infectious diseases of the external and internal genital organs.
- Excess body weight.
Reference! According to medical observations, in the first 8 weeks the growth of myometrial cells increases, which provokes the appearance of a tumor in some women.
Symptoms
In most cases, the disease is asymptomatic (especially at an early stage) and is accidentally discovered during a routine ultrasound. But over time, the tumor increases in size and then it is simply impossible not to notice it. So, the following signs are characteristic of uterine fibroids:
- Pain in the pelvic organs.
- Frequent urination.
- Discharge from the genital tract.
- A sharp increase in the size of the abdomen.
- General weakness and malaise.
- Pain during intercourse.
- Intestinal dysfunction (constipation, increased gas formation, frequent urge to defecate, etc.).
Also, in some cases, signs of hemorrhoids and swelling of the legs may occur.
Possible complications
The disease threatens miscarriage, complicated childbirth and abnormalities in intrauterine development of the fetus. Possible uterine bleeding, fever and difficulty moving the fetus along the birth canal, rupture of the uterus and its cervix.
Treatment
If the disease has progressed to an advanced form (with the tumor growing steadily), the woman may be advised to have an abortion. For small tumors, conservative treatment is possible (usually in a hospital setting).
The following medications are prescribed to expectant mothers:
- Drotaverine (usually intramuscularly).
- Aspirin.
- Ginipral.
- Duphaston.
- Vitamins: A, C, E, group B, folic acid, etc.
Note! Taking medications is permitted only under the strict supervision of the attending physician, who will individually prescribe the dosage and course of therapy.
Condylomas acuminata
Genital warts are a disease of viral origin, which in most cases is sexually transmitted. The pathology is especially dangerous during pregnancy, therefore, if characteristic symptoms are detected, you should immediately contact a gynecologist or dermatologist.
Causes
Genital warts appear in women against a background of weakened immunity, when the body is more susceptible to infections. The causes of the disease include the following factors:
- Using someone else's personal hygiene items (towel, toothbrush, etc.), clothing, bed linen, etc.
- Unprotected sexual contact with a carrier of the infection.
- Frequent stressful situations.
- Avitaminosis.
- Vaginal dysbiosis.
In some cases, the incubation period lasts up to several years and occurs long before pregnancy occurs, making it difficult to determine the source of infection.
Symptoms
Unlike other gynecological diseases, genital warts are quite easy to identify. The pathology is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Growths measuring 0.5-0.6 cm appear on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes (including in the vaginal area, on the labia, near the anus, etc.).
- Itching and discomfort in the affected areas.
- Pain during bowel movements.
Important! During pregnancy, condylomas grow at an accelerated pace and appear in new areas of the skin. Therefore, delay in this situation is detrimental to the health of the mother and child.
Possible complications
If you follow all the specialist’s recommendations, there should be no complications. However, if you let the situation take its course, injury and suppuration of existing growths is possible. To avoid this, during the treatment process it is important not to peel off or scratch the drying crust that forms on the surface of condylomas. Also during this period, it is advisable to wear clothes made of soft fabrics (to avoid chafing the skin).
Treatment
In the absence of accelerated growth of condylomas, experts do not recommend therapy. But in the opposite situation, doctors often resort to the following treatment methods:
- Removal of build-up with high-frequency current.
- Use of interferon in the form of injections.
- Removal of condylomas by surgical method.
At the same time, we should not forget that no matter how effective the treatment, the virus cannot be completely destroyed (some part of it remains in the woman’s blood).
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted sexually transmitted disease that can have serious consequences for mother and child. At the same time, women with this pathology are often diagnosed with inflammation of the uterus and ovaries.
Causes
In most cases, the cause of infection is unprotected sexual intercourse, but there are rare exceptions (through personal hygiene products, underwear, etc.). The incubation period is 2-3 weeks. A weakened immune system also contributes to infection.
Symptoms
Symptoms of gonorrhea may vary depending on each specific case, but common symptoms include:
- Periodically occurring uterine bleeding.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Vaginal discharge of a purulent nature.
- Burning and itching in the external genitalia.
Attention! The acute form of the disease causes headache, fever, cutting pain when urinating and redness of the genitals.
Possible complications
Gonorrhea in pregnant women often leads to complications such as:
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Conjunctivitis.
- Nervous system disorder.
- Pathologies of the musculoskeletal system.
- Anomalies of intrauterine development of the fetus.
- Miscarriage and premature birth.
To avoid complications, it is necessary to consult a doctor in time and undergo a course of therapy (mainly in a hospital).
Treatment
After the diagnosis is confirmed, women are prescribed antibacterial drugs, for example:
- Ceftriaxone.
- Erythromycin.
- Azithromycin, etc.
The dosage and course of treatment are determined by the attending physician. Physiotherapy is used as an adjunct.
Scheduled diagnostics
Routine diagnostics consists of a set of medical procedures aimed at early detection of pathological processes in the body of a pregnant woman.
- A general urine test prescribed by a gynecologist at each scheduled visit to a pregnant woman contains important information about kidney function, the presence of infection in the genitourinary tract, and the development of diabetes.
- With the help of a biochemical blood test carried out in laboratory conditions, it is possible to evaluate the functioning of internal organs and metabolic processes in the body of a pregnant woman.
- Determining the blood type and Rh factor of both parents is required to study their compatibility, the likelihood of pathological processes (increased bilirubin, hypoxia) in the newborn and to find an effective method to prevent undesirable consequences.
- A doctor prescribes a blood test for sugar during pregnancy not only for preventive purposes, but also to assess the effectiveness of treatment in case of diabetes development.
- TORCH diagnostics involves a blood test for toxoplasmosis, herpes, cytomegalovirus, and rubella. A blood test in the first weeks of pregnancy makes it possible to prevent the occurrence of developmental abnormalities in the child with the help of timely and adequate therapy. The results of the analysis may influence the decision to continue the pregnancy. In addition to TORCH diagnostics, blood is tested for HIV, syphilis, chlamydia, ureaplasma, hepatitis B, C.
- PCR diagnostics aimed at identifying sexually transmitted infections are becoming increasingly popular. Any biological material from a pregnant woman will be required for analysis. The polymerase chain reaction has established itself as the most informative, accurate and fast type of diagnostics of infectious diseases when studying microscopic concentrations of DNA fragments. Diagnostics carried out using PCR are very effective in determining latent forms of infectious diseases.
- Collection of vaginal secretions during pregnancy is carried out in order to study the microbial landscape of the vagina, determine infectious diseases of the genital organs, and prescribe effective treatment.
- A routine ultrasound examination is carried out in each trimester to assess fetal development, compliance with physiological standards, and identify developmental anomalies. The number of ultrasound scans performed may be increased on the recommendation of the attending physician if there is a suspicion of a pathological process.
Classification of modern methods for diagnosing pregnancy:
- Biological;
- Immunological;
- Echographic (ultrasound diagnostics).
Immunological, as well as biological methods, consist of determining choriogonadotropin (CG). Any biological material is suitable for this, but most often urine. The synthesis of this hormone begins in the first days of conception and lasts until childbirth with maximum production on the 60-70th day after implantation. Afterwards, its level drops somewhat and stabilizes until childbirth.
Among the immunological methods used today, the most widely known is the method based on suppression of the hemagglutination reaction. The method consists of adding antiserum (antibodies) to the ampoule, red blood cells (antigen) with hCG and urine of the pregnant woman. The hCG present in the urine binds to the antigen (antiserum), and the red blood cells settle to the bottom, as they do not undergo agglutination.
If the urine of a non-pregnant woman is administered, that is, without hCG, an agglutination reaction takes place and the red blood cells are evenly distributed throughout the ampoule. Add 0.4 ml of phosphate buffer and two drops of morning urine, previously filtered, to the ampoule.
All components are mixed and left for 2 hours at room temperature. After the allotted time, based on the uniform distribution of red blood cells, a conclusion is made about the absence of pregnancy, and from the sediment at the bottom of the ampoule - about its presence.
The radioimmunoassay method is much more sensitive. The most common method has become the so-called double bodies. For the method, ready-made kits produced by various companies are used. The method allows you to determine hCG already 5-7 days after implantation. Determination occurs in 1.5-2.5 minutes.
Today there are also many test systems that allow the woman herself to quickly determine pregnancy at home.