Neurologists call polyneuropathy a group of diseases in which several peripheral nerves are affected under the influence of various factors. Doctors at the Neurology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital identify the cause and type of disease using the latest diagnostic equipment from the world's leading manufacturers. Laboratory technicians conduct research on biological fluids using ultra-sensitive reagents that allow them to obtain accurate research results.
Neurologists take an individual approach to choosing a treatment method for each patient. Doctors at the Neurology Clinic provide complex therapy for polyneuropathies using modern pharmacological agents that have a minimal range of side effects. Rehabilitation specialists use innovative methods of physical therapy, modern physiotherapeutic procedures, and conduct reflexology to restore impaired nervous functions.
Causes
There are several causes of polyneuropathy:
- diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2;
- infection with the immunodeficiency virus and AIDS;
- prolonged exposure to toxins on the body;
- drug use;
- poor environmental conditions;
- burdened heredity;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse.
The development of polyneuropathy is caused by a long-term deficiency in the body of B vitamins, which are vital for the proper functioning of the nervous system. Peripheral nerves may be affected due to deformation of their processes or insufficient blood supply to the nerve trunks.
Expert opinion
Author: Irina Gennadievna Smolentseva
Head of the Research Center for Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson's Disease, Professor, Associate Professor of Medical Sciences
Polyneuropathy of the upper and lower extremities is a fairly common disease caused by dysfunction of the peripheral nervous system. The disease is classified according to the location of the source of symptoms into upper and lower polyneuropathy and into primary and secondary.
The causes of primary polyneuropathy are difficult to establish; it is mainly a hereditary pathology, while secondary polyneuropathy develops due to various factors. These include diabetes mellitus, deficiency of B vitamins, consequences of serious injuries, chemical intoxication, alcohol, drug and tobacco addiction, severe hypothermia of the extremities, hormonal imbalance, toxicosis of pregnant women, systemic and chronic complex diseases of the kidneys and liver.
Treatment of polyneuropathy requires an integrated approach; the tactics of therapy and recovery procedures are selected in accordance with the severity and neglect of the disease, the presence of side effects and concomitant diseases. Doctors at the Yusupov Clinic will conduct a full examination of the patient and, based on the diagnosis, prescribe comprehensive treatment.
Treatment with folk remedies - fiction or help?
There are many methods of treating neuropathy of the lower extremities with folk remedies. Before using them, you should consult a specialist.
Below are the most effective recipes.
- Egg and honey drink. To prepare it you will need a raw egg yolk and 4 teaspoons of olive oil. These products need to be mixed and beaten with a blender or whisk. Then add 100 ml to the resulting mixture. Freshly prepared carrot juice and 2 teaspoons of honey. Mix everything and drink twice a day before meals.
- Fenugreek infusion with bay leaves. To prepare it, you need to mix 6 teaspoons of fenugreek seeds with 2 teaspoons of crushed bay leaves, pour everything with a liter of boiling water and leave to infuse in a thermos for 2 hours. Afterwards, the infusion should be strained and consumed in small portions throughout the day.
- Saline solution. The recipe for its preparation: pour hot water into a bucket, filling it halfway, add 200 grams of salt and 2/3 cup of 9% vinegar. Keep your feet in this solution every day for 20 minutes for one month.
- Clay compress. To prepare it, you need to dilute 100-150 grams of green or blue clay to a thick sour cream. Then apply the resulting mixture to the affected area and keep until completely dry. Always use a freshly prepared compress before use.
- Treatment with camphor oil. Camphor oil should be massaged onto the affected area and left for 10-15 minutes. Once the oil has been absorbed, you need to rub the area with alcohol and wrap it in a warm cloth. Do it daily, preferably before bed, for a month.
- Calendula infusion. To prepare it, you need to brew 2 tablespoons of marigolds in a glass of boiling water. Let it brew for 25-30 minutes. Take 100 ml daily for a month.
- Baths based on red pepper and pine needles. To prepare such a bath you need 500 g. Boil the needles in 3 liters of water for 30 minutes. Once the broth has cooled, add 2 tbsp. spoons of red pepper, having previously crushed it. Then add not too hot water to this solution, and steam your feet in it for about 20-30 minutes. This procedure can be performed daily.
Another method of folk treatment: you need to trample young nettles with your bare feet.
All these methods of treatment with traditional medicine will lead to results if they are used as an addition to the main therapy.
Kinds
Depending on which mechanism of nerve damage predominates, neurologists distinguish the following forms of polyneuropathy:
- axonal: the disease develops due to dysfunction of the axon - the central core of the nerve, which provides its nutrition;
- demyelinating: the disease is caused by the breakdown of myelin, a special protein that envelops nerve fibers and ensures rapid transmission of impulses along the nerves;
- neuropathic – occurs when nerve cell bodies are damaged.
Based on the predominance of damage to the nerves that perform a particular function, the following types of polyneuropathy are distinguished:
- sensory – characterized by a predominance of signs of involvement of sensory nerves in the pathological process (pain, numbness, burning);
- motor – manifested by the dominance of symptoms of damage to motor nerve fibers (muscle weakness, muscle thinning);
- sensorimotor – signs of simultaneous damage to sensory and motor fibers are determined;
- vegetative – autonomic nerves are involved in the pathological process, which is manifested by increased sweating, rapid heartbeat, dry skin, a tendency to constipation, erectile dysfunction;
- mixed - the clinical picture of the disease contains signs of damage to all types of nerves.
Depending on the reason why the peripheral nerves were damaged, the following types of polyneuropathy are distinguished:
- hereditary - transmitted to children from parents;
- dismetabolic – arise as a result of metabolic disorders;
- toxic – develops when exposed to toxic substances (salts of heavy metals, organic solvents);
- post-infectious - occurs due to damage to the nerves by infectious agents - human immunodeficiency virus, diphtheria bacillus;
- paraneoplastic – there is compression of the nerve by a neoplasm or metastases of a malignant tumor;
- post-traumatic – resulting from mechanical damage to peripheral nerves.
If the nature of the damage to the peripheral nerves cannot be identified, neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital make a diagnosis of “idiopathic polyneuropathy.”
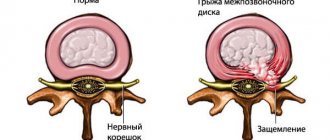
What is spinal discosis
It is important to learn what discosis of the intervertebral disc (or spine) is. This pathology means the development of a degenerative process in this area. The underlying mechanism of the disease is a metabolic disorder in the area of one or more discs.
With the development of discosis, the normal structure of the nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus is transformed, and the tissues that form them gradually become thinner and dry out. As a result, the nucleus pulposus extends beyond its location, and the same thing happens with the intervertebral disc. A protrusion, or protrusion of the disc, is formed, which provokes clinical symptoms. To summarize, protrusion is also discosis.
In advanced cases, this pathological process can lead to a herniated disc, which provokes compression of nerve trunks, blood vessels, and sometimes the spinal cord, which, in turn, causes severe pain and other complications.
It is important to note that discosis most often affects the lumbosacral spine, which is associated with its high mobility and high load. Pathology is also diagnosed in the cervical spine. This is also due to the fact that this area is characterized by the highest mobility in the body, but it is affected less frequently than the lower back, since the load on the neck is significantly lower.
Symptoms
At the onset of the disease, patients are bothered by tingling and numbness in the fingers of the upper and lower extremities. Then pain appears. In most cases, symptoms of polyneuropathy first appear on the feet, move up the legs to the knee joint, and then appear in the upper extremities. Most often, neurologists identify the following signs of polyneuropathy:
- sharp pain;
- increased sensitivity of the affected areas;
- burning;
- itching
Due to the lack of tactile sensitivity on the limbs, patients are easily injured - burned or hypothermic without noticing the damage. In rare cases, patients with polyneuropathy lose coordination and balance. For this reason, they cannot move independently. In the late stage of the disease, the patient suffers from constant pain, which disrupts the quality of sleep, develops a depressive state, and disrupts psychological balance.
Neurologists distinguish between signs of irritation and loss in polyneuropathy. Signs of irritation include the following:
- tremors of the limbs (tremor);
- painful muscle cramps (Crumpy syndrome);
- involuntary, visible to the naked eye, contractions of individual muscle groups (fasciculations);
- rapid heartbeat (tachycardia);
- crawling sensation on the skin (paresthesia);
- increased blood pressure (arterial hypertension).
Signs of prolapse include several symptoms: muscle weakness, muscle atrophy (thinning), hypoesthesia (decreased sensitivity of the limbs). Patients initially develop weakness in the muscles located distally - away from the body. If the patient's anterior group of leg muscles is affected, it is difficult for him to walk on his heels. When the pathological process spreads to the posterior group of leg muscles, he cannot walk on tiptoe.
With polyneuropathy, the following signs of prolapse can be detected:
- fixed pulse - the heart contracts at a constant frequency due to loss of function of the nerves that regulate the functioning of the heart;
- tendency to constipation - develops when the function of the nerves that ensure the functioning of the digestive organs is impaired;
- hypohidrosis – due to insufficient sweating, the skin becomes dry.
Due to damage to the nerves that provide information to the brain about the relative position of the limbs in space, unsteadiness of gait occurs when walking with eyes closed. The patient, having closed his eyes, completely loses information about the position of the arms and legs, as a result of which balance is disturbed. Due to dysfunction of the nerves that provide changes in the tone of the veins of the lower extremities, patients, when moving from a horizontal to a vertical position, experience a feeling of lightheadedness, dizziness, and flickering of spots before the eyes. Due to the fact that blood continues to remain in the venous vessels of the legs, oxygen starvation of the brain occurs and orthostatic collapse develops.
Lumbar osteochondrosis: symptoms of the disease and treatment methods
Have you been struggling with JOINT PAIN for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure your joints by taking the product every day for 147 rubles...
Read more "
Lumbar osteochondrosis is one of the most common types of osteochondrosis, in which degenerative changes occur in the ligaments, intervertebral discs and vertebral bodies of the lumbar spine.
This widespread occurrence of the disease is explained by the fact that the main load of body weight falls on the lumbar region. The intervertebral discs of this part of the spine are especially susceptible to stress when bending, lifting heavy objects and in a sitting position.
Contents of the article: Causes of lumbar osteochondrosis Stages of lumbar osteochondrosis Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis Treatment methods
Therefore, the treatment of the disease must be taken very seriously. Moreover, complications such as protrusion and herniated intervertebral disc may occur, which can cause paralysis of the lower extremities.
Causes of the disease
The main reasons for the development of lumbar osteochondrosis of the spine are considered to be injuries and a sedentary lifestyle.
In addition, heredity plays an important role, in particular, the individual characteristics of the body, its hormonal, biochemical and psychogenic constitution.
If parents suffered from osteochondrosis, most likely their children will also encounter this problem, having inherited predisposing features of the body structure.
The risk group for developing lumbar osteochondrosis includes everyone whose activities involve stress on the back. These are movers, builders, waiters, etc. In addition, people with sedentary work - office workers, drivers - are also more likely to develop lumbar osteochondrosis.
In addition, some diseases of other organs and systems of the body can contribute to the development of osteochondrosis. This:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and liver;
- metabolic disease;
- diseases of the pelvic organs;
- diseases of the nervous system.
Factors contributing to the onset of the disease also include:
- decreased physical activity;
- stress;
- prolonged stay in uncomfortable positions;
- hypothermia;
- incorrect posture;
- congenital changes of the spine;
- hormonal disorders.
Stages of the disease
- At the first stage of the disease, pain in the lower back is mild. The patient feels discomfort and pain, which intensifies with physical activity. The rest of the time there is no pain. At this stage, the intervertebral discs begin to deteriorate.
- At the second stage of the disease, the fibrous ring is destroyed and the distance between the vertebrae decreases, which leads to pinched nerve endings. This leads to severe pain, spreading not only in the lumbar region, but also covering the outer surface of the thighs, buttocks, and sometimes lower legs.
- At the third stage of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, the destruction of the fibrous rings and the formation of intervertebral hernias begin. In this case, a noticeable deformation of the spine occurs. The patient at this stage experiences constant severe pain.
- At stage 4 of the disease, such changes occur in the spine that it becomes difficult for the patient to move. This may lead to disability.
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
All symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis are divided into 4 groups:
- pain;
- ischemic syndrome;
- radicular syndrome;
- spinal syndrome.
Lumbar osteochondrosis can have pain of varying degrees of severity, localization, origin, nature and intensity. Highlight:
- Lumbodynia is a constant aching pain in the lower back, which intensifies after physical exertion, heavy lifting, hypothermia, and bending. It decreases significantly when lying down.
- Lumbago is a sudden pain like a lumbago. It is acute and intense in nature and radiates to the pelvic organs, the anterior abdominal wall, and to the sacral region. With the slightest movement or even coughing, the pain intensifies significantly, forcing the patient to lie in bed. Often the cause of such pain is a sharp turn, heavy lifting, or injury.
- Lumboischalgia is pain that spreads to the buttocks, one or both legs, which may lose sensation.
Radicular syndrome
If osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is not treated, it progresses. In this case, the vertebrae lose their real estate and become mobile.
This leads to the fact that when lifting heavy objects and sudden movements, the vertebrae are compressed and irritate the nerve endings and blood vessels. In such cases, lower back pain subsides slightly, but appears in the area of innervation of the damaged nerve.
The pain may appear in the thigh, lower leg, buttock or foot and is unilateral, severe, and boring in nature. At the same time, the body tries to protect the damaged root, which causes muscle tension and a change in gait. It becomes gentle with a bias towards the healthy side.
If the necessary treatment is not carried out at this stage, then after irritation of the roots, their inflammation appears. It is accompanied by swelling, blood stagnation, and intoxication. In this case, after rest, pain occurs in the joints and muscles, which disappear after warming up. The pain may be accompanied by a feeling of heat, chills and sweating.
In addition, as a result of radicular syndrome, tingling, numbness, and a sensation of “goosebumps” in the lumbar region may occur. This also causes a decrease in muscle tone, atrophy and thinning.
It becomes difficult for patients to walk, climb up and down stairs. In particularly difficult cases, when compression of the spinal cord occurs, paralysis may develop.
Ischemic syndrome
This group of symptoms is associated with poor circulation due to compression of blood vessels. At first, the narrowing of the arteries is not constant, but over time a constant spasm occurs. In this case, pain occurs while walking, which goes away after stopping the movement and short rest.
As a result of the lack of treatment and prolonged spasm of blood vessels, the nutrition of the pelvic organs occurs and, as a result, their activity is disrupted.
Pain also appears in the buttocks and inner thighs. In advanced cases, paralysis of the buttocks may occur.
Spinal syndrome
Due to the syndromes described above, a gradual change in the skeleton occurs. Due to severe pain and muscle weakness, the spine and pelvis become distorted, stooping occurs, posture changes, and gait becomes uncertain and tense.
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis
Treatment of the disease must be comprehensive and timely. Very rarely, osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine ends only in an acute period. Much more often it becomes chronic, which requires treatment to prevent relapses.
Main goals of treatment:
- Elimination of the causes that caused compression and irritation of the nerve roots and blood vessels in the spine.
- Suppression of pathological processes and elimination of pain.
- Stimulation of the body's regenerative reactions.
- Strengthening the musculoskeletal system.
Non-drug treatment
If you experience pain in the spine, you should definitely consult a doctor. At home, the patient should be provided with rest and bed rest. In this case, the bed must have a hard or orthopedic mattress.
Drug treatment
Treatment with pharmaceutical drugs will be slightly different in the acute phase and the remission period.
The people were taken aback! Joints will recover in 3 days! Attach...
Few people know, but this is exactly what heals joints in 7 days!
In the acute phase, it is very important to relieve pain, reduce the inflammatory process and release the roots of pinched nerves. For these purposes, NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, glucocorticoids, and blockades are used.
NSAIDs
This group of drugs has analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects. The drugs relieve swelling in the tissues, due to which inflammation goes away and pain decreases. Preparations for internal use, rectal preparations and injections can be used.
The most widely used:
- Diclofenac (Diclak, Dicloberl, Voltaren, Diclobene, Feloran, Diclonat P, Ortofen, Diclovit);
- Ibuprofen (Nurofen, Pedea, Brufen, Advil, Cefekon, Ibufen);
- Piroxicam (Revmador, Sanikam);
- Naproxen (Apranax, Nalgesin, Sanaprox, Naprobene, Aleve);
- Aceclofenac (Aertal, Asinak);
- Nimesulide (Nise, Aulin, Nimesil, Sulaydin);
- Dexketoprofen (Dexalgin, Flamadex);
- Meloxicam (Movalis, Mataren, Oxycamox, Melox, Meoflam).
Muscle relaxants
The products in this group are designed to relieve muscle spasms, while eliminating pain and relieving stiffness of the vertebrae and joints. The drugs Mydocalm and Sirdalut are prescribed.
Glucocorticoids
These drugs are prescribed only in cases of ineffectiveness of other groups of pharmaceuticals, as they have serious contraindications and adverse reactions. Treatment with these drugs is carried out strictly under the supervision of a doctor.
Blockades
Most often they do a novocaine blockade, or a novocaine blockade with a glucocorticoid (for example, hydrocortisone). The essence of the blockade is that the medicine is injected directly into the area of pain and quickly eliminates it.
Blockades are used only for temporary relief of pain, since they do not exhibit healing properties. Often it is impossible to take such measures, since the body gets used to it and reacts much less. In addition, muscle atrophy may occur at the injection site.
When an acute attack of lumbar osteochondrosis is removed, remedies are prescribed to restore damaged body tissues, improve blood circulation and conductivity of nerve fibers and restore muscle function.
For these purposes the following are used:
- Chondroprotectors. Prescribed to strengthen bone tissue and normalize metabolic processes in cartilage. Used: Alflutop, Mukosat, Teraflex, Dona, Rumalon, Structum, etc.
- Vitamin preparations, in particular group B, which improves nerve patency. Milgama, Neurobex, Neuromultivit, etc. may be prescribed.
- Vascular agents that are designed to improve blood microcirculation and tissue nutrition (Cavinton, Eufilin, Pentoxifylin, Trental).
- Biogenic preparations that stimulate restoration processes in the body.
In addition, both during the period of exacerbation of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine and during the period of remission, local agents in the form of ointments, gels and creams that have an analgesic, warming, anti-inflammatory or distracting effect can be used.
Widely used: Deep Relief, Fastum gel, Dolobene, Capsicam, Apizartron, Traumeel S, Chondroxide, Voltaren gel, Finalgon, Nicoflex, Dolobene, etc.
Massage
Lumbar osteochondrosis is treated with massage. Thanks to its competent implementation, the nutrition of damaged tissues improves, muscle spasms are relieved, pain is reduced and the muscle frame is strengthened. It is very important that the massage is performed by a qualified specialist, especially in the acute phase of the disease, since any incorrect movements can aggravate the patient’s condition.
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy exercises are selected individually in each case and are performed only when osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is in remission.
Physiotherapy
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is also treated with physiotherapy methods both in the acute period and in the period of remission. The most commonly used are electrophoresis, UV irradiation, phonophoresis, darsonvalization, acupuncture, etc.
ethnoscience
There are many traditional medicines to alleviate the condition of lumbar osteochondrosis, but it is not recommended to use them on your own. You definitely need to consult a doctor.
To reduce pain and relax muscles, take pine baths. Compresses made from a decoction of burdock leaves are also widely used.
Cure arthrosis without drugs? It's possible!
Get the free book “Step-by-step plan for restoring mobility of the knee and hip joints with arthrosis” and start recovering without expensive treatment and surgery!
Get the book
Consequences
If the function of the nerves that regulate the functioning of the heart is impaired, the rhythm of cardiac activity is disrupted, which can result in sudden death. In cases of severe muscle weakness, patients cannot move without assistance. In some polyneuropathies (Guillain-Barré syndrome), the function of the nerves that provide movement of the respiratory muscles is impaired.
The consequences of polyneuropathy can be different. In some patients, the symptoms of the disease reverse under the influence of medications. In others, despite timely initiation of adequate complex therapy, the disease progresses. The clinic's neurologists make every effort to stabilize the patient's condition.
Make an appointment
Diagnostics
To determine the cause of polyneuropathy, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital Neurology Clinic conduct a comprehensive examination, which includes toxicological tests, determining the level of thyroid hormones and blood glucose. Neurologists use American and European recommendations, algorithms, and scales to assess the severity of polyneuropathy.
The patient's examination begins with a neurological examination. Quite often, the only diagnostic method that allows one to identify polyneuropathy at the initial stage of the disease is to determine vibration sensitivity. Neurologists assess the vibration sensitivity threshold using a neurological calibrated tuning fork with a frequency of 128 Hz. To determine tactile sensitivity, a 10 g monofilament is used. The sensitivity of this method ranges from 86 to 100%.
In order to determine the threshold of pain sensitivity, doctors perform an injection with a blunt neurological needle. Temperature sensitivity is assessed using a tip-therma device. This is a thermal cylinder, one end of which is made of metal and the other of plastic. Normally, people feel the touch of different materials differently.
At the Yusupov Hospital, neurologists use an electrophysiological method for assessing peripheral nerves - stimulation electroneuromyography. This objective, minimally invasive and fairly reliable method for diagnosing polyneuropathy allows you to assess the severity, dynamics and progression of the disease, and identify the subclinical stage of the disease.
The use of electrophysiological research methods allows neurologists to obtain information not only about the function of the nerve fiber, but also about its structure. Doctors at the neurology clinic determine which fibers are predominantly damaged - motor or sensory, and also evaluate the nature of nerve damage - demyelinating or axonal.
Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital use electrophysiological research methods for the differential diagnosis of polyneuropathies. They are informative in cases of rapid progression and atypical course of the disease.
Doctors at the Neurology Clinic use invasive research methods, in particular punch biopsy of the skin of the feet, to very early detect damage to thin unmyelinated nerve fibers. Subsequently, laboratory technicians perform an immunohistochemical analysis of nerve fiber density using the nerve tissue marker PGP 9.5. Non-invasive diagnostic methods include studying the density of thin nerve fibers in the cornea using a confocal microscope. Such a detailed study of the condition of thin nerve fibers is necessary so that doctors are able to begin adequate therapy for polyneuropathy at the earliest stages of damage to nerve fibers.
Doctors use a biopsy of the sural nerve to detect peripheral neuropathy. This diagnostic procedure is useful if the cause of the disease is unknown or the disease is atypical.
Diagnostic methods
Since neuropathy has a number of symptoms similar to other diseases, it is necessary to carefully approach the diagnosis of the patient and exclude the most common diseases. The specialist must carefully listen to the patient’s complaints, use an examination to identify external manifestations of symptoms, and study the medical record and history of chronic diseases. It may be necessary to ask about hereditary pathologies that also occur.
In addition, instrumental diagnostic methods are used to accurately identify deviations:
- study of reflexes and their sensitivity;
- General and biochemical analysis of blood serum;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and kidneys;
- Electroneuromyography - to identify deviations in the speed of impulse delivery from the central nervous system to the fibers;
- spinal puncture;
- x-ray of the spine;
- if necessary, tissue biopsy.
A preliminary examination and research data will help to create a complete clinical picture, make the correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
Treatment
Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital begin complex therapy for polyneuropathy by eliminating the cause of the disease. Endocrinologists use diet and medication to stabilize blood glucose levels. If nerve damage is caused by an infectious agent, antibacterial or antiviral therapy is carried out. In case of deficiency of B vitamins, they compensate for their deficiency in the body. Nutrition of nerve fibers improves with the prescription of drugs that improve blood microcirculation.
To restore nervous functions, specialists at the rehabilitation clinic use various types of therapeutic massage, which has the following effects:
- improving elasticity and tone of muscle tissue;
- voltage reduction;
- increased degree of joint mobility;
- improvement of metabolic processes and lymph circulation;
- reducing stress levels;
- increasing immunity.
Physiotherapeutic methods have a good effect. They improve microcirculation, reduce pain, and restore muscle cells. An occupational therapist works with patients who have serious nerve and muscle damage. It helps the patient adapt to the new condition, develop a new movement algorithm for performing everyday activities. The scheme of rehabilitation measures is developed individually for each patient.
For patients who have developed bedsores as a result of acute polyneuropathy, it is important to maintain joint mobility. The exercise therapy instructor conducts passive or active therapeutic exercises with the patient several times a day, aimed at increasing the range of motion. In the acute period of polyneuropathy, doctors control the patient’s pain and relieve it with analgesic drugs. For patients suffering from Guillain-Barré syndrome, doctors in the intensive care unit provide respiratory support if necessary.
How to treat neuropathy
It is impossible to cure polyneuropathy without addressing the root cause of the disease – diabetes mellitus. Blood sugar levels need to be carefully controlled. Moreover, both its sharp increase and its sharp fall are equally harmful. The patient is prescribed insulin injections or tablets. The dosage of both drugs should be selected strictly individually. In practice this is not an easy task. The type of drug and its dose are almost constantly adjusted, because Sugar levels may change frequently.
Also used to treat neuropathy are:
- means for strengthening blood vessels;
- drugs that regulate metabolic processes in tissues;
- antioxidants with lipoic acid;
- group vitamins – B1, B6, B12;
- vitamin E;
- painkillers - analgesics, opioids, anticonvulsants, and antidepressants;
- Additionally, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed: electrophoresis, electrical stimulation, magnetic therapy. Special exercise classes, massage, acupuncture are shown.
If the therapy does not produce the desired effect, special stimulator implants are implanted into the patient’s spinal cord, which relieve severe pain.
Symptomatic treatment is carried out taking into account the manifestations of the disease, which depend on which organs suffer from dysfunction of the nervous system.
Treatment with folk remedies
Traditional medicine offers a number of recipes to alleviate the condition of a patient with plineuropathy. These measures can be taken, but only as additional treatments.
- Blue clay compress: dilute the clay with water in a 1:1 ratio, apply to the sore spot and let dry. Repeat for 2 weeks.
- A decoction of herbs - chamomile and nettle in a 1:1 ratio - in 200 g of water. To infuse, keep it in a water bath for 15 minutes. Drink 3 times a day for about 2 months.
Forecast
Polyneuropathy is a dangerous disease for humans. In the absence of adequate therapy, the disease progresses and leads to serious consequences. Patients may develop muscle weakness, decreased muscle tone, and then complete muscle atrophy.
Patients are forced to change their usual lifestyle. They lose the ability to move independently and take care of themselves in everyday life. As a result, the level of anxiety increases and chronic depressive syndrome develops. To avoid undesirable consequences and improve your quality of life, if you have signs of polyneuropathy, make an appointment with a neurologist at the Yusupov Hospital by calling. Contact center specialists will offer a convenient time for consultation with a doctor specializing in the treatment of polyneuropathies.
Make an appointment
Author
Svetlana Vladimirovna Shcherbakova
Anesthesiologist-resuscitator, cardiologist
Possible consequences and complications of lower extremity neuropathy
The disease can have a serious impact on your health.
Bad consequences and complications include:
- Sensory disorders. They occur if sensitive (sensory) nerve fibers are damaged. Manifest in the form:
- The presence of severe pain in the area of the affected nerve, which is shooting in nature;
- The appearance of unpleasant sensations reminiscent of the presence of a foreign body under the skin, which bother you constantly, both at rest and in motion;
- Loss of certain types of sensitivity, for example, the inability to distinguish between hot and cold, or to feel the surface under your feet.
- Vegetative-trophic changes. Appear due to damage to the autonomic fibers that are part of the nerve. These damages lead to the following consequences:
- Dryness and thinning of the skin;
- Hair loss;
- Formation of pigment spots on the skin;
- Disruption of the sweat glands;
- Failure to heal injuries, cuts, with further suppuration and gangrene of the limbs.
- Motor disorders. Appear due to damage to motor fibers. The changes lead to the following consequences:
- Decreased knee and Achilles reflex;
- The appearance of cramps and muscle spasms;
- Muscle weakness and muscle atrophy leading to disability.
Bibliography
- ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases)
- Yusupov Hospital
- Batueva E.A., Kaygorodova N.B., Karakulova Yu.V. The influence of neurotrophic therapy on neuropathic pain and the psycho-vegetative status of patients with diabetic neuropathy // Russian Journal of Pain. 2011. No. 2. P. 46.
- Boyko A.N., Batysheva T.T., Kostenko E.V., Pivovarchik E.M., Ganzhula P.A., Ismailov A.M., Lisinker L.N., Khozova A.A., Otcheskaya O .V., Kamchatnov P.R. Neurodiclovit: possibility of use in patients with back pain // Farmateka. 2010. No. 7. pp. 63–68.
- Morozova O.G. Polyneuropathy in somatic practice // Internal medicine. 2007. No. 4 (4). pp. 37–39.