Rating: No rating
The level of amniotic fluid within the normal range does not always mean a normal pregnancy. In this regard, it is not surprising that many expectant mothers are often concerned about this issue. Sometimes gynecologists diagnose polyhydramnios. There is a lot of conflicting information on the Internet. So let's figure it out: what is polyhydramnios actually called?
To begin with, this statement: the question of the amount of amniotic fluid should be decided by the doctor for each pregnant woman individually, without resorting to hasty treatment and premature conclusions. However, in our country, intimidation of pregnant women with such a diagnosis is actively practiced.
The position of the World Health Organization is quite definite: slight and moderate polyhydramnios during pregnancy is not a direct indication for treatment, but an incentive for active monitoring of a pregnant woman.
Causes of manifestation at different times
The occurrence of polyhydramnios at different stages of gestation occurs for various reasons. But it is worth noting that the causes of this pathology have not been fully identified. In 30% of cases, polyhydramnios of “unexplained origin” is diagnosed.
1st trimester
Reasons for the development of polyhydramnios in the 1st trimester:
- the presence of infectious diseases (rubella, ureaplasmosis, chlamydia) – in 60% of cases;
- dysfunction of the membranes;
- multiple pregnancy, in particular in the presence of identical twins.
2nd trimester
The most common causes of polyhydramnios in the second trimester include the following:
- gastrointestinal obstruction;
- congenital neuromuscular diseases;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- diabetes;
- syphilis.
3rd trimester
In the third trimester, the described pathology may develop due to the reasons already indicated, but the following are also added to their list:
- placental disorders;
- the presence of Rh conflict between the expectant mother and the baby – provokes polyhydramnios in 95% of cases;
- kidney disease;
- large size of the fruit;
- pathologies in the development of the baby.
What is the danger of polyhydramnios for a baby?
Having received this diagnosis, a woman inevitably begins to wonder what the dangers of polyhydramnios are for her and her baby. The most common consequence of this complication is considered to be deterioration in the condition of the fetus. The child may experience oxygen starvation and lack nutrients, which affects his intrauterine development and growth. If polyhydramnios is caused by an infection, the baby may become infected with it in utero. Such an infection threatens the baby’s organ function and increases the risk of death in the first week of life. A child may be born with inflammation of the lungs, intestines, or meninges.
Polyhydramnios also disrupts the process of labor. Particularly dangerous are placental abruption and heavy bleeding during childbirth; the risk of premature birth is high. Acute polyhydramnios in the later stages can provoke rupture of membranes and fetal death.
To understand why polyhydramnios is dangerous, you should look at the statistics:
- the threat of miscarriage is present in 69% of pregnant women with polyhydramnios;
- a third of pregnancies end in miscarriage or early birth;
- gestosis begins in 50%, it is often severe and leads to a serious deterioration in the well-being of the expectant mother;
- fetal nutritional disorders are diagnosed in 53% of cases;
- 49% of women require caesarean section;
- in 7% of pregnant women the fetus is positioned incorrectly;
- a third of births occur with various complications;
- with infectious polyhydramnios, 61% of children are born with signs of intrauterine infection;
- In half of the cases, placental abruption occurs during pregnancy, and bleeding occurs during childbirth.
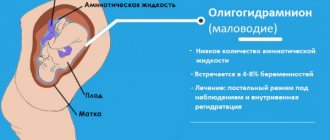
Degrees of polyhydramnios
Today, there are several degrees of development of polyhydramnios, characterized by the presence of their own symptoms.
Lightweight
It is characterized by the presence of amniotic fluid, up to 3 liters in volume. The general condition of the woman is satisfactory, heaviness may be felt, and there is minor pain in the abdominal area. There is weakness.
Average
The volume of amniotic fluid ranges from 3 to 5 liters. The woman feels weak all the time, even with the slightest physical exertion, shortness of breath develops, the pulse increases sharply, and there is swelling in the lower extremities and labia.
Heavy
The volume of amniotic fluid exceeds 5 liters, most often observed in the 3rd trimester. There is “gurgling” or “squelching” in the abdomen, many rough stretch marks are formed, the uterus is greatly enlarged, and the amount of urine released per day is reduced.
Relative polyhydramnios
Relative polyhydramnios is a condition that is not dangerous to the health of the expectant mother and fetus, but this is only in the absence of any infections. In most cases, it occurs in the presence of a large fetus.
Border
This type of pathology is quite often called a tendency to polyhydramnios. The volume of amniotic fluid is on the border between normal and increased.
Marked polyhydramnios and large fetus
It is characterized by a rapid increase in the size of the pregnant belly. The woman feels the activity of the fetus, there is pain in the lumbar and perineal area.
The main functions and tasks of amniotic fluid
Where does amniotic fluid come from? The process of their formation is quite complex. Once fertilization occurs, the egg moves into the uterine cavity. There it meets the endometrium (special tissue). It is this place that will be chosen for the attachment of the future fetus. To ensure that the embryo is protected from various damages, infections and other negative factors, nature has created a special dense “bag” that is filled with amniotic fluid.
It is worth noting that the amount of fluid increases as the embryo matures and grows larger. The composition is quite simple: 97% is water, in which the necessary nutrients and minerals are already dissolved in sufficient quantities.
What functions do amniotic fluid perform? Let's look at them below:
- Fetal nutrition. In the first weeks, amniotic fluid reaches the baby through its skin. At this time it is quite thin. After 14 weeks, the fetus begins to swallow liquid. Useful elements remain in his esophagus, and all unnecessary elements are excreted in the urine.
- Ensuring the required temperature conditions. The structure of the embryo is designed in such a way that it cannot independently regulate its body temperature. Thanks to the amniotic fluid, it is always maintained around 37 degrees;
- They exercise and regulate the pressure inside the fetal bladder in which the baby is located;
- Do not allow the umbilical cord to tighten;
- Protects from mechanical damage and injury. A pregnant woman can move freely and exercise without fear that the baby will be harmed;
- Protect from external noise;
- The walls of the amniotic sac are quite thick, so the likelihood of infection is negligible. In addition, the amniotic fluid itself contains special antibodies that protect the fetus from infection;
- Thanks to amniotic fluid, the baby can move safely in the uterus until the third trimester. After this, the fruit is so large that it is quite difficult for it to move freely.
As you can see, amniotic fluid plays a special role in the process of pregnancy. It is important to monitor their quantity; an excess can lead to the formation of serious pathologies in the baby.
How is it diagnosed?
The doctor may suspect the presence of polyhydramnios during a routine examination of the patient; the following factors visually indicate the presence of pathology:
- abdominal dimensions that do not correspond to the duration of pregnancy;
- abnormal position of the fetus;
- the presence of a dull heartbeat.
To confirm the diagnosis, an ultrasound examination is required, through which the amniotic fluid index is calculated.
In parallel with the ultrasound, a number of other studies are performed:
- blood for sugar - to detect or refute the presence of diabetes;
- vaginal smear;
- PCR;
- general blood and urine tests;
- blood for antibodies - donated only if the woman is Rh negative;
- Dopplerometry - performed to analyze the condition of the fetus.
Consequences
Polyhydramnios negatively affects the health of the mother and the development of the fetus. If the problem is not corrected in time, an increase in the amount of amniotic fluid can lead to the following consequences:
- the uterus, enlarged due to an excess of fluid, compresses large and small blood vessels for a long period, which provokes an increase in blood pressure and edema in the mother;
- With polyhydramnios, the uterus is greatly stretched, which can provoke massive bleeding and placental abruption;
- childbirth against the background of polyhydramnios occurs earlier than expected in 30% of cases, because due to the large accumulation of fluid, the uterus increases to the size of a full-term pregnancy;
- leaving the uterus prematurely, amniotic fluid can take out an arm, leg or umbilical cord;
- early release of amniotic fluid weakens labor, sometimes to the point of complete cessation.
For a child
In addition to the complications listed above, polyhydramnios also negatively affects the unborn baby in the womb. The development of fetoplacental insufficiency at an early stage leads to poor development of the embryo, and at a later stage – to retarded fetal growth. Doctors call the following negative consequences for the child:
- intrauterine infectious process;
- malformations of the gastrointestinal tract;
- insufficient formation of the nervous system;
- chronic fetal hypoxia;
- decreased immunity;
- premature birth.
These pathologies can be hidden and appear only some time after birth. For example, polyhydramnios in the last stages of pregnancy in an infant can cause mental and mental retardation, which pediatricians determine after 1-1.5 years. The birth of a baby prematurely threatens a low level of the body's defenses and is fraught with the development of respiratory diseases and infection with infectious diseases.
Is it possible to treat with folk remedies?
If a woman has been diagnosed with polyhydramnios, then from that moment she must be constantly under the supervision of the attending physician. Accordingly, during this period, medications are taken, but folk remedies can also be used as an auxiliary treatment, the main thing is to first consult with a doctor.
Treatment of polyhydramnios with folk remedies is not aimed at getting rid of the cause of the pathology, but at alleviating negative symptoms.
To remove excess fluid from the body, you should consume as many lingonberry and strawberry fruit drinks as possible; if in their pure form these drinks are highly acidic, then you can dilute them with water. You can drink either store-bought fruit juice or prepare it yourself; to do this, perform the following manipulations:
- 200 ml of lingonberries or cranberries are poured with a liter of water;
- the mixture is placed on the stove and cooked over low heat for 2 hours;
- It is recommended to consume chilled.
Parsley can be a quite useful remedy for edema:
- the plant is crushed in a blender and then filled with water in a ratio of 2:1;
- leave in a warm place for 7 hours, after which it is filtered and the juice from one lemon is added;
- taken 3 times a day before meals, 100 ml, course 3-5 days.
A decoction with parsley and lemon will also help with swelling:
- take 800 grams of parsley, wash it thoroughly, and then pour boiling water over it;
- the plant is finely chopped, placed in a pan and poured with milk, all leaves must be completely covered;
- the mixture is placed in the oven, the milk should boil, but not completely evaporate;
- the resulting decoction is filtered and consumed in a volume of 1-2 tablespoons every hour.
Another product that has a diuretic effect and can get rid of swelling in the shortest possible time is dill. To prepare a medicine from it, the following manipulations are performed:
- a tablespoon of seeds is poured into 100 ml of boiling water;
- the product is infused for an hour;
- consumed 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals.
If there is a thermos in the house, then the dill medicine can be prepared according to the following recipe:
- a spoonful of seeds is poured with 300 ml of boiling water and infused for several hours;
- The product is used in a volume of 200 ml in the morning and evening, the course of administration is 21 days.
This infusion is strictly forbidden to be taken without a break for more than 3 weeks. The minimum break is 3 days.
Another effective remedy for eliminating swelling during polyhydramnios during pregnancy is dried apricots. It is poured with boiling water, after which the resulting infusion is taken every morning before meals.
Symptoms
Signs of polyhydramnios during pregnancy are as follows:
- abdominal circumference exceeds 1 m in girth;
- fluctuation;
- a large number of stretch marks on the abdomen that appear in a very short period of time;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach;
- pain in the abdomen and back;
- pain in the perineum;
- swelling of the legs;
- the pregnant woman has tachycardia, the fetus has a weak pulse;
- due to overstretching of the uterus, there is more space in it, and the fetus may take an incorrect position - gluteal or transverse, and in addition, there is also a risk of entanglement of the umbilical cord.
What does medicine say?
What medications will be used to treat polyhydramnios directly depends on the cause that triggered the development of the pathology.
If there is a moderate or severe degree of the disease, women are immediately hospitalized in the clinic.
If the cause of polyhydramnios is gestational diabetes mellitus, then treatment for the disease consists of regulating blood glucose levels. When the problem is incompatibility of Rh factors, treatment is carried out aimed at preventing the child from developing a hemolytic disease.
But most often, the cause of polyhydramnios is not identified, then treatment consists of normalizing uteroplacental blood flow, and the following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- antispasmodics – Nosh-pa;
- antiplatelet agents – Trental;
- tocolytics – Partusisten;
- vitamin complexes – group B, E, C.
A drug such as Indomethacin tablets is very effective. Regardless of whether an infection is detected, the pregnant woman is prescribed antibacterial drugs that are part of the macrolide group.
In some cases, with severe polyhydramnios, amniocentesis is performed, the peculiarity of which is to pierce the abdominal wall, insert a needle into the uterine cavity and remove excess fluid.
Treatment of polyhydramnios in pregnant women
Mostly, the diagnosis of polyhydramnios is made based on the results of an ultrasound examination. From the moment the pathology is detected, the expectant mother should be under constant medical supervision. If there is no significant circulatory and respiratory disorder (mild to moderate polyhydramnios), doctors strive to maintain the pregnancy until its physiological completion. Otherwise, there is a need for early delivery, as the situation may pose a threat to the woman’s life.
If the pregnancy is maintained, the cause of polyhydramnios should be established, since it threatens the development of chronic oxygen starvation of the fetus. Depending on the identified cause of the disease, appropriate treatment is carried out.
Treatment of polyhydramnios includes antibiotic therapy for viral etiology, immunomodulatory therapy, prescription of diuretics and vitamins, and abdominal amniocentesis. As a rule, hypothiazide, B vitamins are prescribed, and in some cases, broad-spectrum antibiotics (except tetracycline), bijoquinol. If labor is weak, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Especially for beremennost.net – Elena Kichak
Prevention
It is much easier to prevent the development of polyhydramnios than to get rid of the disease later.
Therefore, preventive manipulations must be carried out, which consist of following a daily routine, proper nutrition and leading a healthy lifestyle. It is worth protecting your body as much as possible from various types of inflammation and infections.
It is mandatory to regularly visit a gynecologist; this will allow timely detection of pathology, even before it reaches a severe stage.
If you do not take any measures aimed at protecting the body, then there is a high probability of developing polyhydramnios, which will entail the following complications:
- in 28% of cases a miscarriage occurs;
- 36% of pregnant women suffer from regular vomiting;
- 6.5% are diagnosed with fetal malposition;
- high probability of developing fetoplacental insufficiency, which causes the occurrence of a chronic form of hypoxia and, as a consequence, fetal death;
- disturbances develop in the formation of the baby’s central nervous system and his gastrointestinal tract;
- if the cause of the disease is an infection, then infection of the fetus is possible;
- in 38% of cases bleeding occurs;
- 5-20% of pregnant women develop late gestosis;
- premature labor;
- during labor, the arms or legs of the fetus and the umbilical cord may fall out;
- as a result of overstretching of the uterus, difficult labor is observed.
Pregnant women should understand that polyhydramnios is a serious pathology that requires immediate treatment. If the disease is not detected in a timely manner, the prognosis is disappointing and there is a high probability of termination of pregnancy. Therefore, you should not delay going to the doctor.
Polyhydramnios during pregnancy: consequences for the child and mother
Due to the increase in free space, the baby feels more free in the stomach, even in recent weeks. The fetus may be malpresented or entangled in the umbilical cord, which is dangerous for the baby, especially at the time of birth. During childbirth, the baby's limbs may fall out into the birth canal (before the head appears).
Due to polyhydramnios, a woman may experience a lot of unpleasant sensations: toxicosis develops with frequent vomiting, and metabolism is disrupted.
In some pregnant women, an increase in the amount of amniotic fluid is accompanied by the development of gestosis. Deviations in a woman’s body provoke disturbances in the functioning of the placenta, which is why the fetus also suffers from a lack of nutrients and oxygen.
In some cases, polyhydramnios can cause miscarriage.
Due to polyhydramnios, a woman may not develop labor, so in the last weeks she should be under the supervision of doctors, and if necessary, she is given a caesarean section.