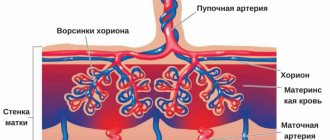
What is the placenta and its functions
The placenta is an organ that connects the inner lining of the uterus and the fetus . It is formed in the second week (4th obstetric week) of pregnancy, when the fertilized egg is fixed in the uterus. The placenta reaches maturity only by the 12th week, and until this moment it grows and forms.
The placenta has a complex structure, which is a plexus of the circulatory systems of the mother and fetus, between which there is a protective barrier. This kind of membrane protects the baby from harmful substances that can enter the mother’s body and ensures the removal of waste products from the fetus.
Functions of the placenta:
- Nourishing, excretory. Through the placenta, all substances necessary for development are supplied to the baby and waste products are removed.
- Respiratory. The placenta allows oxygen to enter the baby's blood and then removes the resulting carbon dioxide from it.
- Immune. The placenta allows antibodies from the mother's body to pass through to the fetus, which provides it with immunological protection.
- Hormonal. The placenta produces hormones responsible for the development of a woman’s mammary glands and preparing them for milk production, the growth of the mucous membranes of the uterus, preventing the release of new eggs and a number of other functions.
What is premature placental abruption
Placental abruption is the process of separating it from the lining of the uterus. Can be partial or complete. During abruption, blood collects between the fetus and the walls of the uterus, pushing the placenta away from the walls.
This process is completely natural and occurs during the third stage of pregnancy. But it happens that under the influence of various unfavorable factors, placental abruption occurs ahead of time. We will talk about what the consequences of such a pathology may be below.
Placental abruption in different trimesters of pregnancy
Depending on the stage of pregnancy, the process of separation of the placenta proceeds differently and leads to different consequences.
- First trimester. At this stage, it is important to quickly diagnose the pathology. Surgical treatment will help to completely avoid the consequences, and the subsequent growth of the placenta will compensate for the insufficient area of contact with the walls of the uterus. In this case, the complication will not have any harmful effects on the development of the child or the course of pregnancy.
- Second trimester. During this period, the actions of doctors will depend on the specific stage of pregnancy. This is due to the fact that the placenta grows until the middle of the second trimester, and an increase in the area of the organ itself compensates for the abruption. If the pathology began to develop at the end of this period, then the only way to save the child is a caesarean section.
- Third trimester. Separation of the placenta in late pregnancy is considered the most dangerous, and with serious consequences, since the placenta loses its ability to grow and can be serious. Therefore, emergency delivery is usually performed. However, in some cases, with a small detachment, doctors can place the pregnant woman in a hospital, where, under constant supervision, she will be able to carry the child to term.
Treatment
Treatment is prescribed by the doctor according to the situation, depending on the condition of the fetus and the patient. Placental abruption has its own stages and characteristics. With a small detachment in the early stages and timely assistance, the prognosis is very favorable. The patient is prescribed medications that relieve uterine tone, vitamins, iron supplements, and hemostatic agents. With proper treatment and the absence of serious pathologies, the placenta grows to the wall of the uterus due to its increase in area as pregnancy progresses. In the future, pregnancy can proceed without complications if you follow all the doctor’s recommendations. Such a detachment is called partial and non-progressive.
If the placental abruption is partial but progresses, the patient’s condition is considered more dangerous. It is necessary to stop the growing hematoma and restore fetal nutrition. To do this, a pregnant woman is admitted to a hospital, carefully observed, prescribed bed rest, and various medications to reduce the tone of the uterus and to alleviate blood loss. If no means can help, the hematoma grows, and the question of urgent delivery arises. In the first trimester, the child, as a rule, dies, but with timely help the mother can be saved.
Complete placental abruption is rare.
In this case, the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the fetus completely stops, and it dies. The only possible treatment in this case is emergency delivery. Doctors may refuse to induce labor and try to continue the pregnancy if the pregnancy is short and the baby has little chance of surviving after birth, and also if there are no signs that the abruption is progressing, there is little blood loss, and there are no obvious signs of oxygen starvation in the fetus.
Useful video - Placenta during pregnancy.
Read: What is dangerous and how is varicose veins on the legs treated?
To improve the condition, the woman is prescribed antispasmodic drugs (No-shpa, Drotaverine, Papaverine in the form of suppositories, Magnesia), hemostatic drugs (Vikasol in the form of tablets or Decinon injections), as well as iron supplements to prevent the development of anemia. Under no circumstances should you try to treat a detachment at home without consulting a doctor. Without professional medical help, this condition can lead to the death of mother and child.
Causes of placental abruption during pregnancy
The reasons that cause abruption of a normally located placenta include:
- gestosis and toxicosis;
- hypertension (high blood pressure);
- increased capillary fragility;
- chronic diseases of the genitourinary system;
- abnormalities in the structure of the uterus itself;
- post-term pregnancy;
- previous multiple births;
- placental abruption may be an allergic reaction to medications;
- age of the woman in labor - the older the woman, the higher the likelihood of pathology;
- abdominal injuries (fall, blow);
- chronic, hereditary and infectious diseases (for example, diabetes, pyelonephritis).
There are also a number of factors that can (but not always) cause pathology. Among them:
- bad habits (drug addiction, smoking, alcoholism);
- damage to the uterus due to past physical trauma;
- formation of fibroids (benign tumor) in the area where the placenta is attached;
- the presence of postoperative scars in the space of contact between the uterus and placenta.
Causes
The following groups of factors and causes can be noted that influence premature placental abruption:
- predisposing;
- etiological.
Etiological reasons:
- abnormal structure of the uterus (these anomalies include saddle-shaped and bicornuate uterus);
- increased fragility and fragility of capillaries and vessels, caused by the loss of their plasticity, can cause poor blood flow through them;
- pressure fluctuations, this can be caused by the stress of a pregnant woman;
- hypertension (high blood pressure in a pregnant woman);
- various diseases of the pregnant woman’s systems (kidney diseases, endocrine glands, diabetes mellitus, diseases of the cardiovascular system);
- gestosis and toxicosis in the early stages of pregnancy (during gestosis, blood pressure rises, protein in the urine increases, blood vessels and capillaries become fragile, and swelling appears);
- chronic diseases of the genitourinary organs;
- One of the important causes of detachment is considered to be insufficiency of the placenta itself, a violation of its basic function (abnormal development or location);
- a large number of births can also contribute to the development of this pathology (frequent childbirth can disrupt the uterine mucosa, this can provoke placental abruption);
- a high probability of developing premature placental abruption during post-term pregnancy;
- allergies, including to medications;
- autoimmune reactions (formation of antibodies to one’s own tissues, this leads to their rejection).
Risk factors that provoke the appearance of premature placental abruption:
- the age of the pregnant woman (the older the woman, the greater the risk of detachment; as a rule, the risk increases after 35 years);
- the presence of this pathology in previous pregnancies (determined in the anamnesis, this makes it possible to monitor the condition of the placenta at the beginning of pregnancy);
- long-term treatment for infertility can also cause detachment;
- when a pregnant woman gives birth via cesarean section (and a scar forms on the placental site), the risk of pathology increases significantly;
- abdominal trauma in a pregnant woman, thereby beginning to provoke trauma to the uterus (this may be one of the factors of detachment);
- Presence of bad habits in a pregnant woman (cigarettes, drug use, alcoholic drinks).
All these reasons, indirectly or directly, cause the pathology of placental abruption in the early stages of pregnancy. In order to respond in a timely manner, you need to know the symptoms of this disease and immediately contact a specialist.
Symptoms and diagnosis of placental abruption
Signs of placental abruption:
- Uterine bleeding. This is usually the first symptom of pathology. The discharge may be copious or not very abundant, has a rich color, usually without clots. In rare cases, detachment may begin without bleeding.
- Dull pain in the lumbar region and lower abdomen. May have a paroxysmal form. When feeling the uterus, the woman feels pain.
- Contractions that don't stop.
- The activity of the fetus decreases, its heartbeat is disturbed.
- Convulsions may occur.
- A pregnant woman experiences severe weakness and may faint. Her skin turns pale and her sweating increases.
Primary diagnosis is carried out by the presence of the symptoms described above. Ultrasound is used to confirm the diagnosis or insufficient symptoms (no bleeding or pain). The images clearly show the area of detachment and the size of the resulting hematoma.
In any case, even if not all the symptoms of the pathology appear, it is necessary to urgently seek medical help . The sooner placental abruption is diagnosed, the higher the chance of saving the child.
Symptoms
Most often, placental abruption begins to be accompanied by bleeding that occurs due to damage to capillaries and blood vessels. If the placenta separates from the uterus, blood begins to accumulate in the resulting space, causing a hematoma.
As already described above, placental abruption can occur in several types. In its simplest form, there are almost no symptoms. And this pathology can only be determined by performing an ultrasound. In other cases, symptoms are more severe and include fetal immobility, lower back pain and bleeding.
The following groups of symptoms are noted: abdominal pain, uterine bleeding, cardiac dysfunction in the fetus, uterine tension. We need to look at each group in more detail.
Uterine bleeding
Bleeding is considered the most common symptom of placental abruption. In approximately 4 out of 5 cases, bloody discharge is observed from the vagina. Taking into account the general state of blood coagulation and the size of the detachment in a pregnant woman, bleeding from the uterus can be heavy or insignificant.
But there may be no visible bleeding. Blood can accumulate in the place where the placenta has separated from the walls of the uterus, most often this is common when the placenta is separated in the middle part of the placenta. This is considered the most dangerous manifestation of the disease, since bleeding from the capillaries and vessels does not stop, but it is characterized by an internal manifestation. The medical term for this occurrence of placental abruption is retroplacental hematoma.
During central placental abruption, blood accumulates more and more in the resulting space, this begins to lead to an increase in the size of the abruption. As a result, the walls of the uterus become saturated with blood. In this case, we will already be talking about saving the woman’s life, since the fetus is threatened with death in 100% of cases.
Marginal bleeding is not so dangerous because blood does not accumulate in the uterus, but is expelled, causing visible bleeding. When the blood is scarlet in color, then the exfoliation has just occurred; when the shade of the blood discharge is darker in color, then a certain time has passed between the bloody discharge and the exfoliation.
Mixed bleeding is sometimes observed. In this situation, the exact volume of blood loss cannot be assessed by determining only external secretions. In this case, it is already necessary to take into account the general condition of the woman.
Therefore, you need to be attentive to your feelings, since the absence of discharge does not mean at all that pathology does not exist.
Uterine tension and abdominal pain
A symptom of placental abruption in the absence of visible bleeding may be pain. As a rule, this pain is characterized as dull and manifests itself in peculiar attacks. There is also no clear localization of this pain. Most often it radiates to the thigh, perineum or lower back.
When palpating the uterus, pain is noted, both without a clear location and local. When pressing on the uterus, more acute pain occurs during internal bleeding. You can also determine the tension of the uterus and its density.
Heart failure in the fetus
The higher the level of blood loss and the larger the area of placental abruption, the greater the likelihood of cardiac dysfunction in the fetus. The presence of this symptom indicates hypoxia in the baby. This symptom appears at stages 2 and 3 of detachment (more than a quarter of the total area). Fetal death is inevitable when detachment occurs from half of the total area.
One way or another, when any of these symptoms appear, you need to contact a specialist as quickly as possible.
Treatment of placental abruption in pregnant women
Treatment for placental abruption is not prescribed by a doctor in all cases. The duration of pregnancy, the amount of bleeding and the health indicators of the woman and her baby are of great importance. If time permits and the mother’s condition worsens, doctors prefer to perform a quick delivery. If placental abruption occurs in early pregnancy, drug treatment is performed.
But in cases where the area of the detachment is small and the woman’s health is not in danger, treatment is prescribed, which includes:
- mandatory bed rest;
- medications that relax the uterus;
- hemostatic drugs;
- agents that have an antispasmodic effect;
- drugs for anemia.
In addition, patients are constantly monitored for their condition, ultrasound examinations, CTG (monitoring the fetal heartbeat and monitoring the tone of the uterus), and Doppler measurements (measuring the speed of blood flow in the vessels of the uterus) are performed.
If treatment does not help and the condition of the expectant mother worsens, doctors usually perform an emergency caesarean section.
Causes of placental abruption in the early stages
Many factors can cause placental abruption in the early stages
Placental abruption can occur at any stage of pregnancy and even during childbirth. At any stage and in any situation, placental abruption can be dangerous, so medical care and observation are necessary.
Early pregnancy is considered to be up to 20 weeks. In this case, detachment can occur both at the 8th and at the 19th week. It is sometimes impossible to reliably determine the cause of the incident, since the causes of detachment have not been sufficiently studied.
However, there are certain most common causes of placental abruption:
- Numerous births. If this is not the first birth, the condition of the uterus worsens, which also affects the placenta. It can age prematurely, which causes detachment.
- Bad habits. Alcohol, smoking, fatty foods, and taking medications without consulting a doctor can provoke circulatory problems and placental abruption.
- Preeclampsia. In this condition, blood flow is disrupted and blood pressure increases. The blood vessels of the placenta become more fragile and weak, which provokes abruption.
- Autoimmune diseases. In such diseases, the human immune system reacts inadequately to stimuli, recognizing the cells of one’s own body as foreign. The placenta and fetus can be damaged in the same way.
- Intrauterine infection. Infection provokes many problems: from abnormalities in fetal development to placental abruption and intrauterine death. Any infection that enters the body of a pregnant woman requires the attention of doctors and immediate treatment.
- Pathology of the uterus. In some cases, placental abruption can only be explained by pathological processes in the uterus. They are dangerous because it is quite difficult to identify and prevent them.
- Abdominal injuries. Injuries can occur from a fall, accident, or blow to the abdomen. This can be dangerous for the baby and cause bleeding, placental abruption and premature birth.
- Chronic diseases. Some cardiovascular diseases, as well as diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney diseases, can lead to detachment.
Signs and diagnosis
Pain in the lower abdomen and spotting are signs of placental abruption
In the initial stages, placental abruption may be asymptomatic. It can only be detected by ultrasound. The doctor determines the presence of a hematoma in the area where the placenta is attached.
If the placenta has moved slightly, then blood will accumulate between it and the uterus, and there will be no external bleeding. However, more often this phenomenon is accompanied by pain in the abdominal area and uterine tone (tension, hard stomach).
The main symptoms of placental abruption in the early stages:
- Bloody vaginal discharge. Blood at any stage of pregnancy frightens expectant mothers; they strive to see a doctor as quickly as possible, and rightly so. If placental abruption occurs on one side, blood will come out; this is an alarming symptom that in no case should be ignored. With timely help, you can stop blood loss and maintain pregnancy. The most dangerous are internal bleeding, which can lead to the death of mother and child.
- Stomach ache. They can occur with or without bleeding. Placental abruption almost never occurs without pain. The pain can be of varying intensity, strong and constraining or pulling and aching. In any case, the appearance of pain requires consulting a doctor. Severe pain may indicate dangerous internal bleeding.
- Heart rhythm disturbances and oxygen starvation of the fetus. In later stages, expectant mothers notice the baby’s active movement or lack of movement, but in the early stages such symptoms are impossible. Typically, fetal heart rate is reported during a routine ultrasound. If abnormalities are noted and there are signs of detachment on ultrasound, the pregnant woman is admitted to the hospital for preservation.
Detachment is often indicated by symptoms, after which the doctor prescribes an additional ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis. It is very important to inform the doctor in a timely manner about what is bothering the pregnant woman and not avoid hospital treatment. Also, if abruption is suspected, the doctor will examine the patient in a chair to determine whether the cervix has opened.
Prevention of placental abruption
Many women, knowing about the possibility of premature placental abruption, think about how to avoid this. This issue is especially troubling for those who have already suffered this pathology in previous pregnancies.
Unfortunately, the recurrence of the disease in subsequent pregnancies is very high. After the first pregnancy with placental abruption, 17% of women experience a recurrence of the complication. And after two similar pregnancies – in 25%.
At the moment, there is no therapy that could completely protect a woman from this pathology. However, there are a number of preventive measures that will help reduce the risk of the disease. Among them:
- systematic visits to a gynecologist;
- blood pressure tracking;
- absence of mechanical injuries (falls, blows);
- regular ultrasound examinations;
- rejection of bad habits;
- absence of allergic reactions;
- timely treatment of diseases that arise during pregnancy;
- absence of stressful situations.
Recommendations for a pregnant woman
What should a woman do if she has placental abruption? If the term is already long and there is not much time left before the birth, it is better to agree to a quick delivery. The fact is that the detachment may begin to progress, and this will threaten the child’s death.
If the end of the term is still far away, the condition of the mother and child does not cause serious concern, and the process of detachment is static, then it is better to postpone delivery. Here we need to proceed from the ratio of the degrees of risk of premature birth and possible progression of abruption. In this case, you can consult a doctor so that he can determine the degree of danger for the child and mother when choosing one or another solution.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosing this disease, as a rule, does not cause difficulties. Detachment can be determined already during the collection of the pregnant woman’s medical history and initial examination. Doctors perform all the required laboratory examinations, study the medical record and complaints of the pregnant woman. The presence of pain, increased tone of the uterus and the presence of bloody discharge are determined. The condition of detachment is also characterized by oxygen starvation of the unborn baby.
Diagnosis using ultrasound provides full confirmation of the disease. Using an ultrasound examination, it is possible to determine the volume of the retroplacental hematoma, the area of placental abruption, and the presence of internal bleeding.
When a woman experiences bleeding, this is not always the cause of detachment. The doctor examines the vagina and cervix to identify its opening, benign neoplasms, and infectious diseases.
Video about placental abruption in a pregnant woman
In the video presented, you can learn more about what the placenta is , what it consists of, what it looks like, and what functions it performs. And also what changes occur in the placenta throughout the entire period of gestation.
You can talk a lot about the danger of placental abruption, the symptoms and ways to avoid this pathology, but these are just words. The most valuable thing in such situations is experience. Therefore, if among those reading this article there are women who have just encountered this situation or have already experienced it, please share with us !