After reading the article about oligohydramnios, you will learn:
- 1 What is oligohydramnios? Moderate and severe, early and late oligohydramnios.
- 2
Causes of oligohydramnios during pregnancy. - 3
Why is oligohydramnios dangerous during pregnancy and during childbirth? - 4
Symptoms of oligohydramnios during pregnancy. - 5
Diagnosis of oligohydramnios. - 6
Conclusion.
Oligohydramnios is an obstetric pathology characterized by a decrease in the volume of amniotic fluid. According to statistics, oligohydramnios during pregnancy is quite rare, affecting only 4-5% of pregnant women. This pathology can manifest itself at any stage of gestation, but most often the diagnosis is made in the third trimester of pregnancy.
Depending on the gestational age, two types of pathology are distinguished:
- early oligohydramnios, which is detected before 20 weeks, in most cases occurs due to incompetence of the membranes;
- later oligohydramnios is diagnosed in the 2nd - 3rd trimester, as a rule, develops due to the presence of pathology associated with impaired attachment and functioning of the placenta.
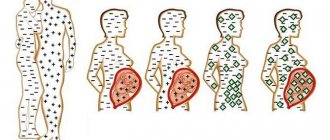
Oligohydramnios in medical terminology is also called oligohydramnios, which means a small amount of amniotic fluid. The maximum volume of amniotic fluid is observed at the 37th - 38th week of pregnancy and averages 1000 - 1500 ml. By the end of pregnancy, the amount of water may decrease to 800 ml as a result of increased fluid excretion from the woman’s body. If the volume of amniotic fluid is below 600 ml, they speak of oligohydramnios. The moderate form of oligohydramnios is characterized by a decrease in the amount of amniotic fluid to 400 - 600 ml. Signs of severe oligohydramnios are a decrease in the amount of water according to the results of ultrasound diagnostics below 400 ml.
What is oligohydramnios?
Oligohydramnios in medical terminology is also called oligohydramnios, which means a small amount of amniotic fluid.
Amniotic fluid in the uterus surrounds the growing baby throughout pregnancy. They perform protective and metabolic functions, help the development of the baby’s lungs and movement in the uterine cavity. At the 10th week of pregnancy, the volume of water is approximately 30 ml, at the 18th week - approximately 400 ml, and by the 38th week it increases to 1-1.5 liters.
If the volume of amniotic fluid is below 600 ml, they speak of oligohydramnios.
Moderate form
Moderate oligohydramnios is characterized by a decrease in the amount of amniotic fluid to 400 ml. The condition requires observation and a special diet, so pregnant women are placed on conservation care.
Severe oligohydramnios
Signs of severe oligohydramnios are a decrease in the amount of water according to the results of ultrasound diagnostics below 400 ml. This can negatively affect the fetus and cause premature birth, so therapeutic measures must be taken.
Low water
Amniotic fluid levels during pregnancy
Determination of the level of amniotic fluid occurs at each stage of ultrasound screening and every pregnant woman encounters this concept.
In the research protocol, this norm is written briefly - IAL.
Often, due to various circumstances, a woman experiences a deviation from the norm to a greater or lesser extent.
This is not a pathology, but requires careful monitoring and correction.
Causes
The causes of oligohydramnios during pregnancy can be divided into several groups:
- chronic diseases of a pregnant woman that provoke a decrease in the amount of amniotic fluid (severe arterial hypertension, heart failure with edema, vascular pathology of the extremities, systemic lesions, rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid disease, obesity, diabetes, alcoholism);
- acute painful conditions of the expectant mother (intoxication with diarrhea and vomiting, poisoning with alcohol, nicotine, toxic products);
- late-term toxicosis (gestosis) is often the cause of oligohydramnios during pregnancy in the 3rd trimester;
- pathology of the placenta, which is associated with developmental defects, circulatory disorders, necrotic lesions, sclerosis, traumatic injuries from the outside;
- rupture of the membranes and leakage of amniotic fluid due to injury, physical stress, infection;
- pregnancy post-term for more than 41 weeks;
- multiple pregnancy;
- Rh conflict when the Rh blood type of mother and baby does not match;
- uncontrolled use of painkillers by the expectant mother (Indomethacin, Diclofenac);
- infections of a pregnant woman that are transmitted to the fetus and affect its membranes (chlamydia, ureaplasma, herpes viruses, cytomegalovirus);
- congenital genetic defects of the fetus associated with the kidneys, urethra, ureter;
- acquired defects due to the impact of adverse factors (toxic, infectious) on the developing organs of the baby.
Is amniotic fluid renewed during pregnancy?
After 5 months of pregnancy, the amniotic fluid begins to renew itself, as the child begins to secrete decay products of its vital activity into it. Amniotic fluid is renewed every three hours. Liquid is released through the walls of the amnion, and the child swallows it approximately every hour, 20-30 ml. The exchange is carried out by exchange in the placental membrane and through special tubules.
When does the update happen?
Amniotic fluid is renewed every 3-4 hours, this is due to the fact that the child can already swallow water, as well as secrete decay products into the uterine space.
What are the consequences for the child?
What threatens a child with oligohydramnios becomes clear by studying the functions of amniotic fluid. Amniotic fluid is needed for:
- fetal nutrition;
- maintaining constant temperature and pressure;
- protection from mechanical and noise environmental influences;
- protection against infectious agents;
- ensuring free smooth movement and lubrication of the skin.
With oligohydramnios, viruses, bacteria and toxins pass through the placental barrier more easily, which can lead to infectious diseases and poisoning of the fetus. If there is a lack of nutrition due to a small amount of water, the growth and development of the baby may be delayed. Signs of hypoxia appear.
Injuries, skeletal distortions, skin damage, and fusion with the amniotic membranes occur due to the fact that the baby does not have enough fluid to move freely in the uterus. The severity of the disorders depends on what pathology contributed to the oligohydramnios.
Severe developmental defects lead to miscarriages. Pathological changes acquired in late gestation can cause premature birth or intrauterine fetal death.
A pregnant woman should know that all the causes and consequences of oligohydramnios, with the exception of severe malformations, can be corrected with well-chosen treatment.
Functions of amniotic fluid
Throughout pregnancy, the baby is in a special bladder, which is filled with amniotic fluid. It is an important protective environment that surrounds the fetus throughout its development inside the mother, which is why it is so important to monitor fluid index readings week by week throughout pregnancy.
Functions of amniotic fluid:
- Protection of the fetus from infectious diseases (it contains a certain amount of immunoglobulin fractions that provide protection from the penetration of viruses and infections);
- Protection from external influences and mechanical damage (amniotic fluid forms the average level of pressure and temperature necessary for the full development of the child);
- Ensuring the functioning of respiratory and digestive functions;
- Nutrition of the child (normally, amniotic fluid contains a large amount of useful substances that are absorbed through the skin and later swallowed by the fetus);
- Protection of the embryo from loud sounds occurring outside; Provides enough space for the child to move freely and learn primary coordination of movement;
- During childbirth, substances contained in the amniotic fluid cause the uterus to dilate.
The development of the fetus is greatly influenced not only by the composition of this fluid, but also by its quantity, therefore, throughout pregnancy, AFI inside the uterus should be measured at each stage. The amniotic fluid is partially replaced within three hours, and then completely changes after two days.
This provides maximum protection for the child.
Composition of amniotic fluid:
- Vitamins;
- Hormones;
- Immunoglobulins;
- Enzymes;
- Useful microelements;
- Antibodies.
A detailed analysis of amniotic fluid week by week makes it possible not only to ensure that the fetus is well supplied with all the necessary substances and to ensure complete protection, but with its help the doctor can determine the sex of the child and even the blood type. Despite the fact that the average AFI during pregnancy represents exclusively the normal volume of amniotic fluid in the uterus in a given week of pregnancy, it is a very important indicator that allows us to identify such disorders during pregnancy as oligohydramnios and polyhydramnios. These pathologies have a very strong impact on the development of the child and can then cause serious illness and even miscarriage, so AFI should be measured every three weeks of pregnancy.
In which trimester is it most often diagnosed?
Based on the time of occurrence, oligohydramnios is divided into 2 types.
- Early oligohydramnios is observed according to the results of ultrasound examination after the 16th week of pregnancy. The condition is unfavorable for the development and growth of the child, so the cause should be identified as soon as possible and treatment should begin.
- Late oligohydramnios is considered after the 26th week of pregnancy (at the end of the second trimester) and most often depends on functional problems in the pregnant woman’s body.
Oligohydramnios during pregnancy in the third trimester should be closely monitored and corrected. At this time there is a risk of premature birth.
A moderate decrease in amniotic fluid is characteristic of the prenatal period, the so-called oligohydramnios at 40 weeks, which is the norm. This is one of the reasons for the negative impact of postterm pregnancy (over 41-42 weeks) on the child’s body.
Study of AFI norms by week
In order to promptly notice negative changes in the course of pregnancy and then prevent the development of complications and diseases of the fetus, women should frequently undergo various examinations. One of them is determining the fluid index, for which in most cases ultrasound is prescribed. Thanks to IAF, you can find out not only the average volume of water within the uterus by week, but also the degree of its homogeneity. This diagnostic method is quite simple and does not take much time. During each examination, the doctor examines the size of the space between the wall of the uterus and the fetus, thanks to which he determines the fullness of the amniotic sac.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms of oligohydramnios during pregnancy in most cases do not have clear specificity.
These signs are:
- decreased activity of the baby pushing in the stomach;
- pain when the child moves and turns over;
- unpleasant pulling sensations in the lower abdomen, as during menstruation;
- increased signs of toxicosis (nausea, thirst, weakness);
- problems with appetite and sleep in a pregnant woman;
- vaginal discharge when water leaks due to rupture of the membranes.
Since these signs can occur with oligohydramnios, and with other pathologies and functional states of a pregnant woman, a clear visual ultrasound diagnosis is necessary.
How to determine oligohydramnios by ultrasound:
- The distance between the anterior abdominal wall and the child’s body is measured in centimeters.
- Four such measurements are made, roughly dividing the uterus into squares.
- All measurements are added and divided by four to give an average value called the amniotic fluid index.
- In the tables, the indices correspond to the week of gestation with a slight difference in the indicators.
Oligohydramnios can be diagnosed after undergoing at least three ultrasound diagnostics, every two weeks.
Diagnostics
A doctor can detect oligohydramnios based on data from an obstetric examination and a survey of the pregnant woman. During a routine examination, attention is drawn to the height of the uterine fundus and abdominal circumference that are inappropriate for the gestational age. To confirm the diagnosis, an ultrasound examination is performed to determine the amniotic fluid index. Indicators of the norm and possible deviations are presented in the table:
| Gestation period | Acceptable Variations | Average normal value |
| 16 weeks | 73–201 mm | 121 mm |
| 17 weeks | 77–211 mm | 127 mm |
| 18 weeks | 80–220 mm | 133 mm |
| 19 weeks | 83–225 mm | 137 mm |
| 20 weeks | 86–230 mm | 141 mm |
| 21 weeks | 88–233 mm | 143 mm |
| 22 weeks | 89–235 mm | 145 mm |
| 23 weeks | 90–237 mm | 146 mm |
| 24 weeks | 90–238 mm | 147 mm |
| 25 weeks | 89–240 mm | 147 mm |
| 26 weeks | 89–242 mm | 147 mm |
| 27 weeks | 85–245 mm | 156 mm |
| 28 weeks | 86–249 mm | 146 mm |
| 29 weeks | 84–254 mm | 145 mm |
| 30 weeks | 82–258 mm | 145 mm |
| 31 weeks | 79–263 mm | 144 mm |
| 32 weeks | 77–269 mm | 144 mm |
| 33 weeks | 74–274 mm | 143 mm |
| 34 weeks | 72–278 mm | 142 mm |
| 35 weeks | 70–279 mm | 140 mm |
| 36 weeks | 68–279 mm | 138 mm |
| 37 weeks | 66–275 mm | 135 mm |
| 38 weeks | 65–269 mm | 132 mm |
| 39 weeks | 64–255 mm | 127 mm |
| 40 weeks | 63–240 mm | 123 mm |
| 41 weeks | 63–216 mm | 116 mm |
| 42 week | 63–192 mm | 110 mm |
To confirm the diagnosis of oligohydramnios, the ultrasound assessment of the amniotic fluid index should be repeated 2-3 times, since due to the peculiarities of the child’s position, a one-time assessment may be unreliable.
When performing an ultrasound, the doctor also carefully examines the structural features and attachment of the placenta, determines the degree of its maturity, and identifies possible abnormalities in fetal development that could cause insufficient amniotic fluid.
A carefully collected anamnesis allows us to identify the probable cause of oligohydroamnion, which plays a huge role in determining subsequent examination and treatment tactics.
If an infectious factor is suspected in the occurrence of oligohydroamnion, the examination plan includes a number of laboratory research methods:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- Nechiporenko test;
- microscopy and bacteriological examination of discharge from the vagina, urethra and cervix.
According to indications, the following is also carried out:
- electrocardiography (ECG);
- echocardiography (Echo-CG);
- determination of glucose level in blood serum;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys.
If there is a somatic pathology, the obstetrician-gynecologist refers the pregnant woman for consultation to the appropriate specialists (cardiologist, endocrinologist).
All pregnant women with oligohydramnios should regularly undergo cardiotocography (CTG) - a modern method of diagnosing the condition of the fetus, based on recording its heart rate, as well as its changes under the influence of fetal movements, external stimuli and contractile activity of the myometrium.
Is treatment required?
Medical measures aimed at eliminating varying degrees of oligohydramnios begin after the first detection of a decrease in the amount of amniotic fluid. In order not to miss time and prevent negative consequences for the unborn baby and mother. The specialist decides how to treat oligohydramnios individually, depending on the causes and severity of the pathology.
What should a woman do?
When a reduced volume of amniotic fluid is initially detected, the expectant mother is prescribed vitamins and a drug to improve microcirculation “Curantil” for a month. The doctor supervising the pregnancy will tell you what a pregnant woman should do if she has oligohydramnios, how to eat, and what lifestyle to lead.
What is the treatment and in what cases?
Treatment of oligohydramnios in a hospital is carried out when a decrease in amniotic fluid is established during three dynamic ultrasound examinations. If there is pathology of the placenta, which can be seen on the initial examination, as well as noticeable malformations, the woman should be hospitalized.
In a pregnancy pathology hospital, treatment is prescribed depending on the cause:
- vitamin preparations (ascorbic acid and group B);
- diet with a high content of protein, mineral and plant components;
- bed rest if there is a threat of miscarriage or leakage of water;
- means for improving blood supply to the placenta (Actovegin, Curantil);
- symptomatic treatment of the underlying disease of the pregnant woman, which has caused a condition with a reduced amount of amniotic fluid (hypertension, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, heart disease, thyroid disease and vascular pathology);
- antibiotics for infectious pathologies;
- termination of pregnancy in case of fetal pathologies incompatible with life;
- opening the membranes to induce labor in post-term pregnancy;
- Caesarean section with severe oligohydramnios and signs of increasing fetal hypoxia.
Signs of oligohydramnios during pregnancy
This pregnancy pathology differs from other possible pathologies in the absence of symptoms. For a long time, oligohydramnios does not manifest itself in any way, so the pathology is detected during a routine ultrasound. Only with a pronounced decrease in the volume of amniotic fluid do characteristic symptoms appear, indicating a possible complication. Among the main symptoms, the following are signs of oligohydramnios:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- dizziness;
- dry mucous membranes and skin;
- painful sensations during fetal movements;
- aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- discrepancy between the size of the uterus and the duration of pregnancy.
Degrees of oligohydramnios during pregnancy
Before treating oligohydramnios during pregnancy, doctors determine the severity of the abnormalities. When diagnosing oligohydramnios, doctors pay attention to such important indicators as amniotic fluid index (AFI) and SVR (single vertical pouch). So, when the AFI is less than 5 cm, doctors diagnose oligohydramnios during pregnancy. The maximum depth of the OVK does not exceed 2 cm. Depending on the value of the IAF, the following are distinguished:
- mild degree of oligohydramnios – 5–4 cm;
- moderate oligohydramnios - during pregnancy the indicator fluctuates between 3.9–2.1 cm;
- severe degree - less than 2 cm.
Review Reviews
Medical reviews of oligohydramnios during pregnancy indicate that 95% of all detected pathologies of this type disappear within a month after correcting nutrition, lifestyle, vitamin therapy and taking vascular-strengthening drugs.
By studying reviews from pregnant women, the predictions described above can be confirmed. The diagnosis is suspected in half of pregnant women, but it is confirmed only in 4-5% of women after repeated studies. Sometimes advice on forums can have negative consequences, so before exploring the Internet, you should ask all your questions to the gynecologist who is supervising the pregnant woman.
Forecast
In most cases (95%), oligohydramnios is either not confirmed by repeated studies, or goes away within a short time with corrective treatment.
An unfavorable prognosis depends on the duration and manifestation of the pathology:
- In the first trimester of pregnancy, severe oligohydramnios leads to the death of the unborn child, which is largely associated with developmental defects that served as the causative mechanism of oligohydramnios.
- When oligohydramnios continues for a long time, if no treatment attempts are made, the nutrition of the fetus is disrupted, which leads to a delay in its growth and formation of organs and systems, including deformities.
- The lack of oxygen with a reduced supply due to pathology of the placenta is called hypoxia, which is negative for the baby’s brain.
- Oligohydramnios during late pregnancy can result in premature birth associated with rupture of the membranes.
- Late intrauterine death with a pronounced decrease in amniotic fluid is possible with defects and severe acquired pathologies of the fetus.
Polyhydramnios
Polyhydramnios, or polyhydramnios, is the exact opposite of the condition described above. This obstetric pathology is characterized by an increase in the amount of amniotic fluid over one and a half liters by the end of the third trimester. On average, this problem affects about one percent of pregnant women worldwide.
The causes of polyhydramnios are infections (herpes viruses, chlamydia, syphilis), the presence of diabetes mellitus in a pregnant woman, Rh conflict, multiple pregnancy, placental insufficiency.
Pathology with an increased amount of amniotic fluid can occur acutely or chronically. Depending on the volume, polyhydramnios comes in three degrees. The more excess fluid in the uterus, the more dangerous the condition for the child and mother. With acute early polyhydramnios, the risk of miscarriage and intrauterine bleeding, as well as uterine rupture increases, so urgent hospitalization in a specialized hospital is required. Chronic polyhydramnios in the third trimester can lead to gestosis and premature birth, uterine atony, which complicates labor.
Excessive accumulation of amniotic fluid
Possible risks when a problem is detected
A discrepancy between the norms of the amniotic fluid index by week of pregnancy indicates the occurrence of polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios in a woman. The manifestation of such conditions is quite dangerous, even threatening serious complications.
Dangers of polyhydramnios:
- possible placental abruption;
- development of infection of the birth canal;
- fetal development disorder;
- miscarriage is possible.
Most often, oligohydramnios is detected after 26-30 weeks or after post-term pregnancy at 41 weeks. In addition, oligohydramnios threatens serious fetal diseases.
If the amniotic fluid index at 31 weeks is 66, with an average value at 31 weeks of 14 cm, then you need urgent specialist intervention.
Dangers of oligohydramnios:
- disorders of the respiratory and genitourinary systems;
- hypodynamics and pressure on the fetus, which can cause various anomalies: changes in fetal weight, dislocations, deformations of bones and spine;
- the occurrence of hypoxia;
- possibility of premature miscarriage;
- risk of bleeding after childbirth.
Excess amniotic fluid (polyhydramnios) is detected in 1 to 3% of women in labor. For example, at week 34 your AFI is more than 278 units, this indicates a critical level of amniotic fluid. The causes of polyhydramnios are influenced by the presence of certain factors.
From the mother's side:
- Rh factor, blood group;
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- the presence of infections or inflammatory processes in the body.
According to placenta analysis:
- when a benign tumor of the fetal membrane occurs;
- with swelling of the placenta.
- multiple pregnancy;
- hereditary pathologies or diseases.
Causes of oligohydramnios:
- abnormalities of the fetus inside the womb;
- various pathologies: infections, chromosomal abnormalities, poor fetal development, etc.;
- the presence of diseases in a woman: problems with the heart, blood vessels, inflammatory and infectious symptoms, kidney disease;
- placental insufficiency, defects, heart attack;
- post-maturity of the fetus;
- placental abruption;
- premature death of a child inside the womb.
People in white coats
Polyhydramnios can be of different types.
- In moderate condition, the size of the inner pocket ranges from 7 cm to 18.
- With severe polyhydramnios, the value appears in the range from 18 to 24 cm.
- In chronic cases, the indicator is slightly higher, but stable.
- In borderline and acute conditions, the index value varies between the average and the highest. In this case, inpatient treatment is recommended.
- In case of acute excess fluid, specialists will prescribe an amniotomy; in case of chronic excess, complex therapeutic treatment.
Self-treatment is not recommended at all. Only observation by specialists and compliance with all doctor’s instructions guarantee the safety of the mother and fetus.
These recommendations also apply to oligohydramnios; in case of acute symptoms, the pregnant woman will be offered hospital treatment. For example, your amniotic fluid index is 5 5, this indicates critical oligohydramnios, which can become a threat to the life of the fetus.
Recommendations for moderate polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios:
- everyone without exception is prescribed Curantil, Actovegin;
- minimum physical activity;
- healthy diet, diet in combination with a vitamin complex;
- preventive treatment to protect against the formation of infectious and inflammatory processes;
- in case of postmaturity – stimulation of labor.
As the baby grows
In traditional treatment, antibiotics are usually used to restore hypodynamic functions. For various infections, immunomodulators are prescribed. Diuretics are required.