A constant companion of colds is a runny nose, or, scientifically speaking, rhinitis. It is also a mandatory manifestation of allergies and the body’s reaction to the presence of harmful and irritating factors in the atmosphere. We are accustomed to not paying much attention to this annoying and not very comfortable symptom, often not treating it and letting the process take its course. But in vain! An untreated runny nose can eventually develop into a chronic form and “delight” the patient throughout the rest of his life. Moreover, it can lead to serious complications. One of the extremely unpleasant forms of such advanced rhinitis will be discussed below.
Treatment methods
It is unacceptable to treat the disease at home without seeking medical help.
It will not bring the desired result, and time will be lost. Conservative treatment of the disease is applicable only if it has just begun to develop. Next, surgical methods are used to eliminate the growths. Traditional therapy can be used only at the very beginning of the development of pathology. Physiotherapy is also prescribed as an auxiliary treatment for conservative therapy. Hospitalization is usually not required even with surgical therapy.
Igor Branovan tells what to do if your nose is pouring like a bucket.
Medication
It is prescribed only at the onset of the disease. The main drugs used for treatment are:
- anti-edema agents;
- administration of hydrocortisone - if the pathology affects exclusively the mucous membrane;
- rinsing the nose with antiseptic drugs;
- antibiotic drugs if bacterial infection of tissues is added.
The necessary medications and the regimen for taking them are determined by the attending physician.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is used for mild cases of the disease. With this treatment, irradiation of the nasal cavity with ultraviolet radiation, as well as UHF therapy, is indicated. These are the main methods of treating the disease, with physiotherapeutic effects.
Surgical
Surgical therapy is the main treatment for advanced forms of hypertrophic rhinitis. To eliminate the disease, cauterization is carried out (using a laser) or freezing of the overgrowth areas. If this is not possible, a radical intervention is performed, in which the hypertrophied area is excised and further plastic surgery is performed to restore normal patency of the nasal passages.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are used as an additional treatment and can relieve most of the unpleasant symptoms of the disease.
- Peppermint tincture with water. Rinse your nose with the composition (1 large spoon per 500 ml of water) 3 times a day, and also drink ½ glass of it orally three times a day.
- Rinse with sea salt solution (1 tsp per 500 ml of water). Rinse with warm water in the morning and evening.
- Inhalation. Passive inhalation of tea tree oil, which is poured into an aroma lamp, is useful. Carry out the procedure before going to bed for at least 10 minutes.
- Agave juice. Instill 4 drops in pure form into each nostril after 4 hours. Treatment is carried out until the conservative treatment of rhinitis is completely completed.
Regarding the use of traditional treatment, you should consult your doctor.
Causes
Many factors can provoke pathology. Doctors identify the following as the main causes of the disease:
- advanced chronic rhinitis, which causes serious exacerbations more than 3 times a year and is not subject to quality treatment;
- defects in the structure of the nasal septum, leading to a significant narrowing of the nasal passages, which causes insufficient outflow of mucous secretions;
- injuries leading to deformation of the facial bones, against the background of which a violation of the outflow of mucus from the sinuses develops;
- incorrect, excessively long or excessively intense use of nasal medications to narrow the vessels of the nasal mucosa (drops and sprays);
- prolonged inhalation of dust;
- work in hazardous production;
- too dry and hot air;
- prolonged exposure to very cold air;
- heart and vascular diseases;
- insufficient saturation of the tissues of the nasal cavity with oxygen;
- nasal polyps;
- adenoids.
For any reasons that cause hypertrophic rhinitis, it is necessary to carry out high-quality treatment of the disease.
Etiology
The following predisposing factors can provoke the appearance of a hypertrophic runny nose:
- curvature of the nasal septum - divided into congenital and acquired;
- indiscriminate use of certain medications aimed at narrowing blood vessels;
- addiction to addictions, in particular, smoking or inhaling drugs through the nose;
- chronic ailments of the nasal cavity;
- adenoid vegetations;
- the formation of polyps and cystic tumors in the nose;
- complete lack of therapy or improper treatment of rhinitis of another etiology;
- disorder of the neuro-reflex function of the nose;
- unfavorable environmental influences, namely living in conditions with constantly low temperature and dry air;
- low humidity or, conversely, increased humidity in the room;
- frequent exposure to an allergen;
- pathological influence of pathogenic microorganisms;
- disruption of the blood supply to the nose;
- decreased immune system;
- burdened heredity;
- chronic runny nose.
Treatment
Such a disease is practically not amenable to drug therapy, especially for the chronic form of the disease. At an early stage, treatment of hypertrophic rhinitis is carried out using:
- irradiation of the nasal cavity with ultraviolet radiation;
- exposure to high frequency radiation;
- administration of medicinal suspensions;
- the use of decongestants, which are aimed at reducing swelling.
The implementation of such procedures is effective only for mild cases of the disease and is due to the fact that they eliminate only minor clinical manifestations of the disease and prevent further development of the disease process.
In cases where the tissues of the mucous layer have grown significantly, the only method of therapy is surgery. Treatment of chronic hypertrophic rhinitis involves one of the following operations:
- conchotomy – involves excision of the mucous membrane in the area of the lower and middle nasal concha;
- laser submucosal vasotomy – involves removal of vessels under the membrane;
- galvanocautics or electrocoagulation. This method of surgery for hypertrophic rhinitis is based on cauterization of mucous tissues with electric current;
- cryodestruction - using the influence of a cryoapplicator cooled with liquid nitrogen on hypertrophied areas;
- ultrasonic disintegration of nasal turbinates;
- osteoconchotomy – involves removing the bone edge.
Surgeries are also advisable if conservative therapy is ineffective.
Another part of complex therapy is alternative medicine, which involves the use of the following components for rinsing the nasal cavity:
- mint and chamomile;
- St. John's wort and sage;
- plantain and honey;
- table or sea salt.
Before using such therapy methods, you should consult your doctor. When trying to treat the disease on your own with alternative medicine recipes, there is a risk of aggravating the inflammatory process and its spread.
Sources
- https://nos-zdorov.com/rinit/gipertroficheskij-nasmork
- https://www.krasotaimedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_lor/hypertrophic-rhinitis
- https://lorcabinet.ru/rinit/vidy/hronicheskij-gipertroficheskij-nasmork.html
- https://StopOtit.ru/kak-i-chem-lechit-hronicheskij-rinit.html
- https://SimptoMer.ru/bolezni/organy-dykhaniya/2304-gipertroficheskiy-rinit-simptomy
How to cure chronic runny nose at home
Many people wonder whether chronic rhinitis can be cured at home. There are various folk remedies for chronic runny nose, which you should definitely familiarize yourself with.
Inhalations
In some cases, treatment of chronic rhinitis in adults is carried out using so-called dry inhalations. To carry out such procedures, you can use garlic, horseradish, or onions. These products have a lot of phytoncides, with which you can quickly get rid of inflammation.
The recipe for creating this product is quite simple. To prepare, you need to chop 150 grams of the above vegetables and place in a small saucepan. Then the whole thing is filled with water and boiled for about 10 minutes. When the product is ready, you need to breathe in its vapor for 20-30 minutes. You will have to fight the disease with inhalations for a week.
Laundry soap
Sometimes chronic rhinitis is treated at home using products made from laundry soap. The recipe for this remedy has been used by many for many years.
Almost always, treatment of chronic runny nose with folk remedies begins with their preparation. In this case, you will need to moisten a cotton swab with water and rub it on a small piece of laundry soap. Then, using this stick, you need to lubricate the nasal cavity. After the procedure, nasal discharge may increase and severe sneezing may occur.
It is during sneezing that the nose is cleared of all purulent secretions and bacteria. Rhinitis is treated with this method for 2-3 weeks.
Beet juice
Quite often, when treating chronic runny nose with folk remedies, beet juice is used. It will quickly get rid of this disease and cleanse the nasal cavity. Even some medications that can be purchased in pharmacies are created using beet juice.
To create medicinal drops at home, you can use the following recipe for their preparation. To do this you will need the following ingredients:
- 200 ml beet juice;
- 50 g honey;
- 100 ml water.
Sometimes 100-200 ml of tincture made from propolis is added to the recipe.
All ingredients are placed in a small container, mixed, left for 20 minutes, after which they fight rhinitis. The prepared drops are applied twice a day. Treatment lasts about two weeks. If the first improvements appear during treatment, you do not need to immediately stop taking the drops.
Treatment of chronic hypertrophic rhinitis
As already mentioned, drug treatment of hypertrophic rhinitis is not able to cope with uncontrolled changes in the tissues of the nose, but there is no need to rush to resort to surgical intervention.
There are several more conservative methods to relieve acute symptoms of changes in the mucous membrane of the nasal passages. If therapy is followed, nasal hyperplasia can be stopped and uncontrolled growth of bone tissue will slow down.
Mild symptoms will be relieved by one of the following methods:
- Irradiation of the nasal passages and nasal turbinates with ultraviolet light;
- UHF EP procedures;
- Massage the nasal mucosa using penin ointment;
- Introduction of Hydrocortisone into the mucous membranes of the nasal passages;
- Vasoconstrictor drugs - to improve the outflow of abundantly secreted mucus.
But if the symptoms appeared a long time ago and treatment did not start for a long time, such conservative methods will no longer help. After all, the longer the treatment was delayed, the more the hyperplasia progressed. Changes in the mucous and bone tissue of the nose have become too profound, which, alas, has become irreversible, and in this case standard ones will not help.
In addition, physiotherapy, such as massage, will help more in the treatment of chronic rhinitis than in eliminating rhinopathology, but advanced hypertrophic rhinitis can only be treated surgically. These include:
- Cauterization with chemicals;
- Disintegration of lower shells with ultrasound;
- Laser destruction;
- Vasotomy.
Of these, cauterization is considered the least effective and is rarely used in eliminating nasal hyperplasia. But, if the doctor is confident that such a gentle intervention will help, then cauterization can be successfully used.
When changes in the mucous and bone tissue are already quite significant, accompanied by difficulty breathing and complete dysfunction of the nasal passages, more serious types of surgical intervention are prescribed:
- Partial resection of the nasal concha;
- Removal of the nasal mucosa (conchotomy);
- Removal of the edge of the turbinate bone (osteoconchotomy).
Surgical treatment is the most effective and fastest way in which hyperplasia of the mucous and bone tissue and hypertrophic rhinitis can be cured. If the patient does not have allergies, the operation is performed under local or general anesthesia. For this purpose, anticholinergic and antihistamine drugs, narcotic analgesics are used.
With the help of modern equipment, hyperplasia is eliminated in ten or twenty minutes, and it is absolutely painless.
Classification of form and stage
There are two main forms of the disease - diffuse (when all areas of the nasal passages and mucous tissue are involved in the inflammation process) and limited. If a patient is diagnosed with a limited form of pathology, hypertrophic changes can be observed in the following areas:
- hyperplasia of the posterior side of the inferior turbinate;
- hyperplasia of the anterior portion of the inferior turbinate;
- hyperplasia of the middle turbinate.
There is also a classification of the hypertrophic form of the runny nose, depending on what type and character the altered tissues acquire:
- Cavernous (vascular) form. It occurs as a result of a violation of the independent regulation of vascular tone, for example, with drug-induced rhinitis. Symptoms are aggravated by lying on your side. When the patient turns his head to the other side, breathing problems occur on the corresponding side.
- Fibrous. With prolonged inflammation of the nasal passages, the mucous epithelium turns on the function of protection from external and internal factors, trying to seal the damaged tissue. In this case, thickening of the mucosa occurs in the posterior parts of the inferior nasal concha.
- Polycystic. Connective tissue growths are localized in the area of the middle turbinate, but in its anterior section.
- Papillary. Pathological growths are formed in the posterior sections, resembling a raspberry fruit in appearance - they provoke constant nasal congestion and abundant production of mucous secretion.
- Bone. With this form of pathology, there is a thickening of the osteochondral tissue that makes up the nasal turbinates.
Often, an ENT doctor diagnoses several of the listed forms of hypertrophic rhinitis in the same patient. In this situation, treatment should be comprehensive, aimed not only at eliminating severe symptoms, but also at the cause of its development.
The development of pathology begins with the occurrence of a prolonged runny nose, which cannot be treated with conventional methods. Initially, except for the layer of ciliated epithelium, other structures of the nasal passages are not damaged - this is called mild hypertrophy of the membranes.
Then the involvement of glandular tissue in the process joins the damage to the ciliary tissue. The muscle fibers and capillary walls become inflamed, which leads to compression of the lymphatic vessels.
This is followed by an edematous phase, when all tissues and structures of the nasal passages are affected, the symptoms are pronounced. As a result of diffuse infiltration of the epithelium, its walls thicken, externally it becomes smooth or lumpy, and polypous growths often form on the surface.
The mechanism can be briefly described as follows: as a result of chronic inflammation, blood circulation through small branches of blood vessels is disrupted, hypoxia (lack of oxygen) develops in the tissues, which leads to pathological disturbances in metabolic processes. Local immunity is significantly reduced, and this already causes the addition of secondary bacterial infections.
If there is a significant change in bone structures, the patient is indicated for urgent surgical intervention. The degree of the inflammatory process can be different and depends on the structure of the nasal turbinates, the area of the lesion and concomitant pathologies.
What does this disease mean?
Chronic hypertrophic rhinitis (ICD-10 code J31.0.) is an inflammation of the mucous membranes of the nasal cavity, during which their proliferation is observed. This process has several stages:
- First stage. The ciliated epithelium is slightly affected. The mucous membranes are inflamed. Nearby tissues are not damaged.
- Second phase. Glandular tissues and ciliated epithelium are affected. The inflammatory process spreads to the walls of blood vessels and muscle fibers. Because of this, the lymphatic and blood vessels begin to be compressed.
- Third stage. The swelling increases. The symptoms are pronounced. The ciliated epithelium, as well as glandular and mucous tissues, are affected. Vessels are damaged. The inflammatory process can also affect bone tissue. At this stage, surgery cannot be avoided.
Symptoms and diagnosis of hypertrophic rhinitis
Symptoms of hypertrophic rhinitis are as follows:
- Difficulty or impossibility of nasal breathing. This occurs due to swelling of the mucous membranes and proliferation of tissues of the nasal cavity. In the first and second phases of hypertrophic rhinitis, breathing becomes more difficult. In the third phase – absent. The use of vasoconstrictor drugs does not produce a positive effect due to the fact that hypertrophy of the tissues of the nasal cavity occurs.
- A person feels dry mouth. As a result of difficult nasal breathing, a patient with this pathology has to breathe through the mouth.
- The voice changes, the patient speaks “in the nose”, “nasally”.
- Snoring during sleep.
- There is mucous discharge from the nasal cavity (most often transparent, but purulent impurities in shades of yellow and green are possible).
- Decreased performance, increased irritability, fatigue, weakness, headaches. This is a consequence of improper breathing and squeezing of the nasal passages, impaired circulation in the blood and lymphatic vessels.
- Deterioration of sleep (due to the inability to breathe through the nose and snoring).
- In some cases, excessive lacrimation is observed, the eyelids swell and turn red, and conjunctivitis develops.
- Feeling of discomfort and pain in the nasal cavity (“something is in the way”).
- In cases of advanced hypertrophic rhinitis, the sense of smell may disappear and hearing impairment may develop.
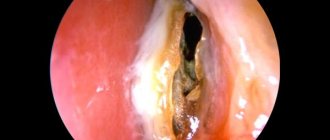
Experts diagnose hypertrophic rhinitis using rhinoscopy. The examination reveals overgrown tissues of the nasal cavity, narrowing of the nasal passages, hyperemia of the mucous membranes and their thickening.
For a more detailed clarification of the extent of spread and localization of the disease, additional diagnostic methods are used: rhinomanometry, endoscopic examination of the nasal cavity, as well as rhinopneumometry.
Symptoms
Like any other disease, hypertrophic rhinitis has its own special clinical signs, but despite this, it is easy to confuse it with other types of runny nose. So, the main symptoms of the disease are:
systematic nasal congestion;- complete or partial inability to implement the respiratory process;
- voice nasality;
- severe nasal discharge with or without pus;
- complete or partial loss of smell;
- periodic occurrence of pain in the head area;
- insomnia;
- nosebleeds;
- fatigue;
- systematic sneezing.
Treatment of chronic rhinitis
There is no single method for treating chronic rhinitis. Each type of rhinitis has its own treatment protocol.
1. Catarrhal chronic rhinitis. How to treat: patients are prescribed nasal drips with protargol or collargol (these are medications that have an antibacterial effect and also reduce mucus production). In case of exacerbation of catarrhal rhinitis, apply antibacterial ointments locally, for example, 2% salicylic or 2% sulfanilamide ointment. Instead of ointment, you can use an antibacterial nasal spray, for example, Polydex or Isofra. An otolaryngologist should prescribe treatment after bacteriological culture of nasal mucus.
2. Atrophic chronic rhinitis. Treatment is usually symptomatic
It is very important to regularly moisturize the nasal mucosa with a saline solution; a sea salt solution is suitable for this. The solution can be instilled into the nose with a pipette or irrigated into the nasal passage using sprays or irrigators
Instilling drops into the nose with the addition of various oils (olive, peach) or lubricating the nasal mucosa with a 5% solution of iodine-glycerin also alleviates the patient’s condition. If, as a result of bacteriological culture of mucus from the nose, pathogenic microflora is isolated, then antibacterial treatment is prescribed.
3. Hypertrophic chronic rhinitis. How to cure: only surgery will help the patient. During the operation, overgrown tissue of the nasal mucosa is removed. If the hyperplasia is small, then gentle treatment methods are used: cauterization (with chromic or trichloroacetic acid), radio wave surgery, electrocoagulation, laser, ultrasound, cryofreezing.
4. Vasomotor chronic rhinitis. How to treat: patients are prescribed topical hormonal drugs (corticosteroids). Medicines are used in the form of injections under the nasal mucosa or sprays. Corticosteroids only eliminate the symptoms of the disease and remove swelling of the mucous membrane. In severe cases, radio wave and electrocoagulation, laser radiation are used for treatment to destroy blood vessels in the submucous membrane of the nose.
5. Allergic chronic rhinitis. How to treat: Patients are prescribed systemic antihistamines. If the course of the disease is not severe, then nasal sprays are prescribed, for example, Cromoglin or Cromohexal (active ingredient sodium cromoglycate), Nazaval (based on plant cellulose). These medications are used for prophylactic purposes and can be used for a long time: from several months to a year. In severe cases, patients are prescribed intranasal corticosteroids in the form of a spray. The correct dosage of the medicine will allow you to take it for a long time. If the above medications do not give the expected effect, then you should consult an allergist. The patient may need allergen-specific immunotherapy.
The use of vasoconstrictor drugs in this case is ineffective, since it does not eliminate the symptoms of allergic rhinitis. And their long-term use can lead to vasomotor chronic rhinitis.
Diagnosis and treatment
In order to diagnose the disease, you need to contact an otolaryngologist. Based on symptoms, medical history, rhinoscopy and rhinopneumometry, a preliminary diagnosis will be made. Additionally, the patient is prescribed to take a blood test, check the levels of eosinophils and immunoglobulin E in the blood, and also have a CT scan and x-ray of the nasal sinuses.
Based on laboratory data and diagnostic manipulations, the previously made diagnosis of “hypertrophic rhinitis” is confirmed or excluded.
The treatment format depends on the duration and phase of the disease. At the early stage of this disease, rinsing with saline solution, administration of medicinal suspensions and decongestants, irradiation with a UV lamp, and exposure to high-frequency radiation are used.
If the hypertrophic process could not be stopped, the bone structure was damaged, then this problem cannot be solved without surgical intervention.
Depending on the form of the pathology, cryodestruction, electrocoagulation, laser submucosal vasotomy, ultrasonic disintegration, partial, total or microlaser conchotomy are used.
Treatment of hypertrophic rhinitis
The patient is advised to exclude spicy, hot foods from the diet, and limit easily digestible carbohydrates (sugar, confectionery, white bread, candies and other sweets). Breathing exercises are very useful, improving the function of the glands of the nasal mucosa.
Drug therapy
At the initial stages of development of hypertrophic rhinitis, rinsing the nasal cavity with saline solutions is used. Also, for mild hypertrophy, sclerotherapy is used: glucocorticoid hormones are injected into the inferior nasal concha (under its mucous membrane), the course consists of eight to ten procedures.
In cases of severe hypertrophy of the nasal mucosa, cauterization with trichloroacetic acid (chromic) and also with Lapis is used. Before the cauterization procedure, local anesthesia must be administered.
Symptoms of severe inflammation of the nasal mucosa are an indication for the prescription of hormonal ointments.
Physiotherapy of hypertrophic rhinitis
Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed in the presence of severe hypertrophy of the nasal mucosa. The most used of them are: UHF, internal massage of the mucous membranes using ointments, ultraviolet irradiation of the nasal turbinates. If complex treatment in the form of a combination of drug therapy and physical treatment is ineffective, they proceed to surgical treatment of hypertrophic rhinitis.
Surgical treatment of hypertrophic rhinitis.
The indication for surgical intervention for hypertrophic rhinitis is the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment. The type of surgical intervention is determined by the doctor, taking into account the clinical picture and severity of the disease. The result of successful treatment is the restoration of free nasal breathing, the disappearance of other complaints, and an improvement in the patient’s quality of life. There are several types of operations:
1. Submucosal disintegration (destruction) of the inferior turbinates using ultrasound.2. Lateroconchopexy - displacement of the conchal area to widen the nasal passages.3. Submucosal vasotomy - destruction of areas of the choroid plexus feeding the inferior turbinates.4. Lower conchotomy (removal of the posterior section) using a gentle technique, accompanied by preservation of the anterior turbinates.5. Endoscopic osteoconchotomy under microscopic control.6. The shape of the nasal septum is also corrected if it is deviated.
Consequences and complications
With rhinitis with overgrowth of tissue in the nasal cavity, the following consequences are possible:
- Development of eustachitis and otitis. When they become inflamed, the auditory tube and ear cavities become inflamed.
- Hearing impairment.
- Loss of smell.
- Sinusitis (inflammation of the maxillary, frontal, ethmoid or sphenoid sinuses).
- Eye damage such as dacryocystitis and conjunctivitis. Inflammation of the superior and inferior turbinates often leads to damage to the lacrimal sacs. This is manifested by narrowing of the palpebral fissure, swelling and lacrimation. Conjunctivitis is characterized by watery eyes, redness of the eyes, burning, itching and swelling.
- Pharyngitis (inflammation of the pharynx). The reason is constant breathing through the mouth.
- Tracheobronchitis (combined inflammation of the mucous membrane of the trachea and bronchi).
- Formation of polyps (growths).
Complications can be avoided by timely consultation with a doctor and comprehensive treatment.
How to treat hypertrophic rhinitis: surgery and conservative methods
When answering the question of how to treat hypertrophic rhinitis, we can say that in relation to the disease in question, one should mainly assume surgical intervention, because the described pathology, first of all, leads to irreversible structural changes.
At the same time, with moderate hypertrophy, doctors try to use minimally invasive techniques. For example, these are cauterization with chemicals, laser destruction, disintegration of the lower shells using ultrasound, etc. However, such a gentle intervention is carried out only when the doctor is one hundred percent confident in its effectiveness.
In case of pronounced changes characterizing hypertrophic rhinitis, a deeper and more serious operation is required. As such, partial resection of the nasal concha, or removal of the bony edge of the inferior concha, or removal of the mucous membranes of the concha, can be used.
In addition to surgery for such a disease as chronic hypertrophic rhinitis, treatment can also be carried out using conservative methods. In particular, to relieve acute symptoms of the disease, tactics are used aimed at stopping the thickening and uncontrolled growth of epithelial tissues.
This treatment tactic includes ultraviolet irradiation of the olfactory organ shells and the introduction of a hydrocortisone suspension into the nasal passages. To improve the outflow of secretions, anticongestants are used. A good effect is possible after a massage of the mucous membranes, which is usually carried out using penin ointment.
However, such conservative treatment aimed at hypertrophic rhinitis may be ineffective. This happens when the symptoms of the disease are protracted, and structural changes affect deeper parts. Moreover, physiotherapy methods are more suitable for combating the vasomotor variant of the runny nose than for getting rid of hypertrophic pathology.
This article has been read 2,671 times.
Preventive measures
It is necessary to carry out therapy for a disease such as hypertrophic chronic rhinitis strictly under the supervision of a doctor. We discussed the symptoms and treatment earlier, but you also need to know what preventive measures exist.
We list a few recommendations that can be considered preventive measures:
- Timely and effective treatment of all nasal diseases.
- In hazardous, dusty and gas-filled production, it is necessary to use personal protective equipment - masks or respirators.
- Avoid very dusty and gas-filled areas.
- If you are allergic to any drugs or substances, you should avoid contact with them and take antihistamines in a timely manner.
- Try to exclude allergens in your diet and contact with them in everyday life.
- Treat inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs in a timely manner.
- Hardening procedures are recommended.
- Walks in the open air.
- Sunbathing.
- Strengthen immunity.
- Get rid of bad habits.
- Don't get too cold.
Young people often ask the question: “Is chronic hypertrophic rhinitis and the army compatible?” It is worth noting that with such a diagnosis, the young man is fit for military service. He may not be drafted into the armed forces if he has a foul runny nose, purulent or polypous sinusitis with frequent exacerbations and persistent impairment of nasal breathing.
Treatment
The correctness of treatment depends 100% on the correct diagnosis. You should not self-medicate - at least until the true cause of rhinitis has been established. To make a diagnosis, your doctor may order a number of the following tests:
- Rhinoscopy;
- X-ray or computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses;
- Blood chemistry;
- General urine analysis;
- Allergy tests;
- Culture of nasal discharge;
- Histological examination of the nasal mucosa.
Depending on the results of the studies, the doctor draws up a treatment regimen and prescribes medications. If necessary, surgical treatment methods are used (for hypertrophic rhinitis).
Drug therapy
Treatment of chronic runny nose is a long and complex process, and conservative treatment depends entirely on the clinical picture compiled on the basis of diagnosis. Even if some deterioration occurs at the beginning of treatment, this is not a reason to refuse treatment. In this case, it is necessary to obtain additional consultation from a doctor and adjust the treatment regimen.
During drug therapy, drugs from the following groups of drugs may be prescribed:
- Vasoconstrictors: Naphthyzin, Galazolin, Nazivin, Tizin, Nazol. When using these remedies, do not forget that their use is limited to 3-5 days and is symptomatic in nature, i.e., can only be used to temporarily eliminate swelling;
- Moisturizing: Aquamaris, Salin, Aqualor, Marimer. The preparations keep the mucous membrane in working condition, preventing it from drying out and providing the necessary microelements and salts of potassium, manganese, iron, potassium, etc. Their use is justified in case of slight swelling and abundant mucus;
- Antihistamines: Vibrocil, Sanorin-Analergin, Rinofluimucil, Koldakt, Orinol. They are used when the allergic nature of the runny nose has been identified and most of them have a combined effect (vasoconstrictor, mucus-liquefying, sedative);
- Antibacterial: Framacetin, Fusafungin, Mupirocin. Prescribed when the bacteriological nature of the runny nose has been identified and for the prevention of sinusitis and tonsillitis. If the runny nose is viral in nature, they are not used;
- Hormonal: Beconase, Nasonex, Flixonase, Nasobek. They can be used in the treatment of allergic rhinitis, but are contraindicated for bacterial or fungal rhinitis. The use of these drugs should only be as prescribed by a doctor;
- Herbal: Pinosol, Eucabol, Thuja Oil, Sinupret. As a rule, they are made on the basis of essential oils and are prescribed for the treatment of atrophic rhinitis. If rhinitis is of an allergic nature, the use of these drugs is possible only after receiving the results of allergy tests.
In addition to the main groups of drugs, homeopathic drugs (Edas-131, Euphorbium Compositum), silver-based drops (Protargol, Collargol), and combination products (Dr. Theiss Nazolin, Pinosol, Bactroban, Polydex with Phenylephrine) can be used in the treatment of chronic rhinitis.
To consolidate the effect of complex treatment, physiotherapeutic procedures can be prescribed: ultraviolet and UHF heating, endonasal electrophoresis, therapeutic inhalations, magnetic therapy and mud therapy.
ethnoscience
- A tablespoon of dry mint is brewed with 2 tbsp. boiling water, leave for 1 hour, filter and use for nasal rinsing;
- 2 tbsp. l. eucalyptus leaves are poured into 100 g of vegetable oil (preferably olive), infused in a dark place for 7 days and used to lubricate the nose for atrophic rhinitis;
- Pour 1 tbsp. l. calendula flowers with a glass of boiling water, infuse for 0.5 hours, filter and use for rinsing the nasal passages;
- 1 tsp. sea salt is diluted in 200 ml of warm boiled water and used for rinsing the nose 2 r. per day for a month. The procedures are carried out every other day, after washing, 1 drop of eucalyptus oil is instilled into each nostril;
- Inhalations with chamomile infusion are carried out for 15 minutes. twice a day, inhaling the vapors alternately through each nostril. To prepare the infusion, take 1 tbsp. l. raw materials for 1 tbsp. boiling water
Diagnostics
First of all, the otorhinolaryngologist must assess the existing symptoms and take into account the patient’s complaints
Also, special attention is paid to the ailments that the patient had or has, how they were treated, whether traditional methods of treatment were used, etc. After the medical specialist familiarizes himself with the medical history and complaints, diagnostic procedures begin:
- anterior rhinoscopy – examination of the nasal cavity is carried out using a rhinoscope (special tweezers). The main purpose of the procedure is to determine the thickness of the mucous membrane, the condition of the nasal passages, that is, whether they are narrowed, as well as the presence of curvatures in the septum area;
- test with adrenaline - carried out during anterior rhinoscopy. The nasal shells are treated with a 0.1% solution of adrenaline, which causes local vasoconstriction. Hypertrophic rhinitis is characterized by the presence of mucous membrane in limited hyperplasia areas, while in a healthy person the nasal passages are completely free, and the mucous membrane is completely reduced;
- An endoscopic examination makes it possible to completely examine the nose from all angles. After its implementation, the doctor can determine the subsequent tactics of immediate treatment;
- CT and radiography of the paranasal sinuses are performed to minimize the possibility of the disease spreading to the paranasal sinuses.
In addition, biochemical and general analysis of blood and urine can be performed. The data obtained will allow you to find out whether the disease was caused by other ailments.