The concept of atrophic rhinitis implies the presence of an inflammatory process of the nasal mucosa, which is accompanied by atrophy and destruction of the membrane itself, which leads to the loss of its functional ability. Particularly severe cases end in the destruction of bone tissue.
The disease is always chronic, long-term and sluggish; the development occurs unnoticed by patients, which contributes to the fact that people simply do not pay attention to its symptoms. On the other hand, pathology causes significant inconvenience to patients and even those around them.
Treatment of the disease does not always give a good effect due to its high chronicity and low attention to it from patients in the early stages of its development.
It is important to understand that the success of therapy depends on how soon it begins after diagnosis. Moreover, almost any runny nose can acquire a chronic form and transform into atrophic rhinitis.
Types of atrophic rhinitis
Atrophy of the nasal mucosa has several types:
- Simple . It is characterized by scanty secretions; their structure is viscous. Violations of the integrity of the blood vessels of the nasal cavity are possible, which contributes to the appearance of bleeding. This type of pathology is characterized by dry nose, decreased appetite and sense of smell, sleep disturbance, mouth breathing, and the appearance of crusts.
- Subatrophic and chronic atrophic rhinitis. They are caused by a malnutrition of the mucous membrane, which leads to its roughness and the appearance of crusts in the nasal passages. In this case, no other pronounced signs of the disease are noted.
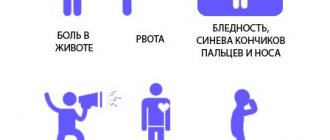
- Infectious . Occurs with inflammation of the mucous membrane. It has certain symptoms - hyperthermia (fever), anxiety, decreased appetite, sleep disturbance. Over time, asymmetry of the jaws develops, swelling of the face (more so in the eyes), the nasal septum becomes bent - all this is accompanied by a characteristic infectious and atrophic runny nose.
- Ozena . This pathology appears due to the formation of foul-smelling mucus, which, when dried, turns into green-yellow crusts. When the atrophic process spreads to the larynx and trachea, symptoms such as hoarseness and dry cough appear. One of the main manifestations is the lack of sense of smell, mouth breathing due to congestion of the nasal passages.
Causes of development and what provokes
Atrophy of the nasal mucosa develops under the influence of several environmental factors, as well as due to the presence of other diseases of the body that have a tendency to atrophy. The most striking example is atrophic gastritis, which quite often leads to atrophy of the nasal mucosa. It is characterized by the death of its elements, which leads to the appearance of a typical clinical picture. Etiological and trigger factors:
- poor quality of inhaled air;
- inflammation of the respiratory tract;
- genetic predisposition;
- lack of vitamins;
- stress;
- uncontrolled use of drops that have a vasoconstrictor effect;
- contact with chemicals;
- hormonal imbalances due to diseases of the endocrine system or taking hormonal drugs, including contraceptives;
- traumatic injuries;
- sudden climate changes;
- complication after ENT operations.
Symptoms of the disease and diagnosis
Dry atrophic rhinitis is a chronic disease, the course of which is typical. The disease occurs with severe dryness of the nasal cavity due to thinning of the mucous membrane. Other important signs are:
- The formation of dry crusts, causing unpleasant sensations such as tickling or the presence of foreign bodies.
- Breathing through the nose is significantly impaired.
- Sometimes mucous discharge from the nose appears.
- The sense of smell first deteriorates, then disappears completely.
When removing crusts with your fingers, nosebleeds occur due to injuries to the mucous membrane. At the site of these injuries, ulcers periodically form, which can be complicated by a violation of the integrity of the septum.
Simple atrophic rhinitis occurs with the same symptoms, but dilation of the nasal passages is added. Sometimes they enlarge to such an extent that the nasopharynx and eustachian tubes can be seen through them.
With this pathology, the process rarely spreads throughout the body. Hyperthermia also does not occur, patients do not complain of a significant deterioration in well-being.
Subatrophic rhinitis is characterized by a more sluggish course, the mucous membrane is not so severely affected. However, with it, the volume of nasal discharge increases and, as a result, the size and number of crusts increases. Taking into account the cause that provoked the onset of the disease, the speed of its development may be different.
The diffuse form of atrophic rhinitis is characterized by the spread of the pathological process throughout the entire nasal cavity, which leads to severe impairment of olfactory function.
Etiology
Before studying the nature of the pathology, it is advisable to analyze information regarding the disease. Atrophic rhinitis - what is it? This is a serious disease, the successful elimination of which requires knowledge of the causes of its occurrence and the distinctive features of its course. The characteristic of the pathology lies in the gradual negative change in the tissues and cells of the inner part of the nasal cavity (atrophy).
Traditional atrophic rhinitis is a disease with mixed symptomatic manifestations. The cause of the disease is environmental conditions that do not meet the standards, long-term use of medications against the common cold and insufficient amounts of vitamins present in the body. The development of the disease is influenced by certain concomitant abnormalities: lupus, disruption of the functionality of the endocrine system and skin disease caused by thickening of the epidermis and narrowing of small vessels.
Rhinitis is actively developing as a result of the use of radiation therapy, the onset of menopause in women and a lack of mineral components. Additional factors that provoke the onset of the disease include:
- fracture of the bone tissue of the skull;
- getting injured;
- making mistakes during medical procedures;
- violation of the rules for carrying out cosmetic surgery.
The development of atrophic rhinitis is associated with a weakening of the activity of the human immune system. When the respiratory system is affected in children in childhood, the cause of active spread of the disease is infections, autoimmune processes and predisposition at the genetic level. The development of the inflammatory process is provoked by the transition of a runny nose to a chronic form, which prevents nutrients from reaching the mucous membrane and intensifies the inflammatory process.
//youtu.be/heUUcpTy91I
How to treat atrophic rhinitis
To cure the disease, conservative therapy or surgery is used. Conservative methods, in addition to the use of pills and other medications, include:
- Cleansing the nasal cavity using moisturizers based on sea salt - Aquamaris, Aqualor. Sometimes it is advisable to use special aspirators - devices for pumping mucus from the nose. Local antiseptics are also widely used - Miramistin, Dioxidin, especially in the presence of purulent discharge.
- Pathogenetic therapy includes antibacterial agents - Amikacin, Rifampicin. This is necessary to eliminate the infectious component. In children, it is possible to use Lugol's solution.
- Symptomatic therapy involves instillation of alkaline solutions to soften the contents of the nasal passages and nasal cavity. To relieve swelling, it is advisable to use vasoconstrictor drops.
- If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, stimulating therapy will also be prescribed, which includes vitamins, autohemotherapy - intramuscular injection of your own blood. Physiotherapy techniques cannot be excluded that will be especially useful for the child in order to limit the use of pharmaceuticals.
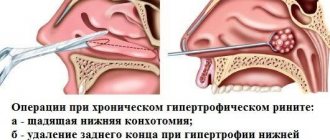
The surgical approach is used when conservative therapy is ineffective. It is also indicated for severe atrophic processes, to alleviate the patient’s condition as a palliative operation, for tissue transplantation when it is impossible to use other techniques.
The greatest effectiveness is shown by mobilization of the lateral wall of the nasal cavity with subsequent localization at the nasal septum. This operation is carried out from the age of 10.
Surgical treatment
Surgical intervention is used quite rarely, and mainly when the bone frame is damaged to form a free nasal passage. Surgical treatment involves implantation of various alloplastic materials into the area of the bottom of the nasal cavity and septum. For this purpose, mesh lavsan, embryonic bones, auto-homochondrium, placenta, chemically pure paraffin, alloplastic antimicrobial biopolymer “Biolan”, umbilical cord, amniotic membranes, acrylic plastic, Teflon or nylon are used. Such manipulations are carried out with the aim of narrowing the nasal passages, but, unfortunately, it is not always possible to achieve the maximum therapeutic effect.
The effectiveness of the measures taken can be assessed by the results of rhinoscopy and the response of clinical symptoms. Side effects of therapy include nephrotoxic and ototoxic effects of aminoglycoside antibiotics, and surgery carries a risk of implant rejection. Recently, operations on the Vidian nerve with the intersection of its sympathetic part, as well as blockade and alcoholization of the superior stellate sympathetic ganglion, have become increasingly used.
In adults
In adults, chronic atrophic rhinitis involves treatment with the maximum number of techniques available today. At the same time, doctors always try to first use conservative therapy to restore the nasal mucosa without surgical intervention. The pathology is treated by an ENT doctor.
If the patient follows the doctor’s instructions well, he can carry out therapy at home. Most often, for this it is recommended to use various saline solutions, oils and decoctions of medicinal plants, which you can prepare yourself or purchase from a pharmacy chain.
For the treatment of atrophic rhinitis in children and adults, doctors do not recommend the use of adenotomy and tonsillectomy.
Basic principles of treatment
If you have atrophic rhinitis, treatment should be carried out under the supervision of a qualified otolaryngologist, since inadequate therapy can lead to serious consequences. Today, there are a huge number of different recipes that allow you to get rid of atrophic rhinitis, but you must clearly understand that folk remedies can only be an addition to drug treatment. And again, before using traditional medicine, you need to consult your doctor. A logical question arises about how to treat atrophic rhinitis. The effectiveness of treatment increases if the specific cause that triggered the development of the disease is established.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods of treating pathology have also found wide application, as they show high efficiency. For example, rosehip oil well moisturizes the nasal passages and its mucous membrane, eliminating one of the most unpleasant symptoms of pathology. Instilling a few drops of iodine works well against infectious agents or the development of ozena.
To stimulate local immunity, eliminate inflammation, and soften crusts, a decoction of chamomile and oak bark is used.
Successful treatment at home is achieved by constantly moisturizing the nasal mucosa, limiting contact with chemicals or their evaporation, taking vitamins, and lubricating the crusts in the nose with various oils.
Diagnostic procedures
The form of rhinitis, in which the performance of the mucous membrane decreases, requires careful diagnosis. Depending on the results of the examinations, the doctor will develop an effective treatment program.
Typical studies:
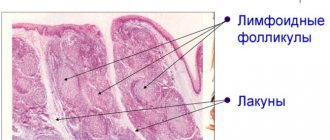
- rhinoscopy (examination of the nasal cavity) anterior and posterior;
- general blood analysis
- sinus endoscopy
Additional procedures:
- nasal cavity cytology
- rhinopneumometry
- bacterial culture (examination of secreted mucus and determination of sensitivity to antibiotics)
- X-ray of the nasal cavity
- CT or MRI
- Blood chemistry
Prevention of atrophy
Preventive measures include:
- Active leisure, which is impossible without the principles of a healthy lifestyle.
- Daily rinsing of the nasal passages.
- Prevention of traumatic injuries to the face.
- Maintaining hygiene, including housing, including humidifying the air in the room.
- Proper nutrition.
- Knowledge of basic methods of treating the common cold.
Possible complications
Most often, atrophic rhinitis is complicated by:
- reduction or complete disappearance of the sense of smell;
- infectious diseases, such as ozena;
- endocrine dysfunction;
- inflammatory processes of the upper respiratory tract;
- dyspeptic symptoms, implying various digestive disorders, as well as gastritis, pancreatitis, colitis;
- neurological dysfunction – apathy, decreased mood, decreased performance.
Particular attention should be paid to ozena, which develops quite often with atrophic rhinitis.