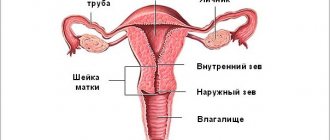
Ultrasound of the cervix is an ultrasound scanning procedure that is performed to detect a wide range of diseases, disorders and pathological abnormalities in the reproductive system. Thanks to modern equipment and special regimes, the doctor can identify any negative changes at preclinical stages and select appropriate treatment. The procedure is usually performed in combination with a pelvic ultrasound.
Ultrasound examination of the uterine cervix has no restrictions and can be prescribed to patients of any age, during pregnancy and on any day of the menstrual cycle.
What does an ultrasound scan of the cervix show?
During the study, the doctor examines the location, shape, size and structure of the uterine cervix. Thanks to the information received, he identifies a wide range of pathological disorders and diseases:
- Cysts are a pathology that occurs due to hormonal imbalance or inflammation;
- Polyposis is a benign tumor that forms in the cervical canal. May develop into a malignant neoplasm;
- Erosion is a violation of integrity, a malformation of epithelial tissue. As such, cervical erosion is not visible on ultrasound. Only indirect signs indicate its presence. The most effective method for diagnosing erosion is colposcopy;
- Endometriosis is a hormone-dependent benign disease that is characterized by the proliferation of the mucous membranes of the uterus into other parts of the body;
- Myoma is a benign tumor that is formed from connective fibers and the outer layer of smooth muscle tissue;
- Adenocarcinoma, carcinoma - malignant tumors that develop from glandular epithelial tissue;
- Cervical pregnancy is a pathology in which a fertilized egg attaches and develops in the uterine cervix;
- Cancer is an oncopathology that is quite difficult to diagnose using echography in the early stages. In this case, the specialist visualizes pathological disorders of the organ, but the diagnosis can be confirmed only after additional research.
Ultrasound of the cervix is a non-invasive research technique that allows you to study the structure and condition of the mucous membranes of the uterine cervix, evaluate the characteristics of blood flow and diagnose various diseases in the early stages.
In addition, ultrasound examination of the cervix is good at identifying scar changes formed after surgery, abortion and difficult childbirth. Cervical dysplasia is not detected by ultrasound. This disease can be diagnosed by cytological examination.
Research options
Depending on the intended diagnosis and the purpose of the study, ultrasound scanning of the uterine cervix is performed in several ways:
- Through the abdominal wall (transabdominal). This technique is used when it is impossible to insert a sensor intravaginally - in virgins, during pregnancy, in some pathologies of vaginal development;
- Through the vagina (transvaginally). In this case, the sensor is inserted into the vaginal cavity. Using this method, gynecological ultrasound is performed on all patients who are sexually active. The procedure can also be prescribed in the early stages of pregnancy and at 38-40 weeks of gestation to assess the maturity of the uterine cervix;
- Through the anus (transrectal). Examination of the cervix in this way is used for the purpose of more detailed visualization of the structure of the organ in virgins;
- Through the skin of the perineum. This technique is used in virgins, patients with vaginal atresia and children with suspected pathology of the uterine cervix.
Each technique has its own characteristics and contraindications. The most optimal method for performing echography is determined by the attending physician after a preliminary consultation.
How do they do it?
The algorithm for performing ultrasound diagnostics depends on the examination method. Transabdominal method - diagnosis through the abdominal wall. Transvaginal is carried out according to the indications of the gynecologist for all women.
Reference! For pregnant women, this method is used in the first trimester and after 37 weeks, when it becomes necessary to assess the degree of readiness of the cervix for labor.
A thorough assessment of the structure of the cervical walls is provided by the transrectal diagnostic method. It is used for virgins. Examination through the perineum is carried out in the same cases, as well as for children and in the absence of a vagina (atresia) in women, if cervical disease is suspected.
Indications and contraindications for ultrasound of the cervix
Since the examination of the uterine cervix is performed together with the uterus and appendages, indications for diagnosis relate to a general ultrasound scan of the pelvic organs:
- Pain in the lower abdomen of any intensity;
- The appearance of pathological vaginal leucorrhoea with an unpleasant odor;
- Disorders of the menstrual cycle;
- Pathologies of the endocrine system;
- The occurrence of uterine bleeding after intimacy or outside of menstruation;
- Suspicions of tumor neoplasms and inflammatory processes;
- Urinary disorders;
- Preventive annual examination;
- Suspicions of infertility;
- Preoperative preparation;
- Monitoring the condition of the organ after surgical interventions.
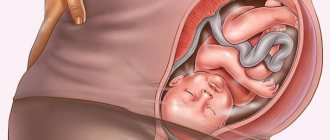
During pregnancy, an ultrasound is performed to assess the closure and length of the uterine cervix.
Contraindications to echography of the cervix are individual and depend on the technique of performing the manipulation. Transvaginal ultrasound is not prescribed for virgin women, girls and patients with structural defects of the vagina. It is also not recommended to conduct an examination several days after surgical manipulation of the vagina.
Transabdominal ultrasound has no restrictions. However, if for certain reasons the patient cannot hold urine in the bladder or fill it, the study will be difficult. The transrectal ultrasound procedure is not used for inflammation or after recent rectal surgery.
Specifics of preparation for ultrasound examination
Preparatory measures for examining the cervix with ultrasound depend on the diagnostic technique. Examination of the cervix through the skin of the perineum and the transvaginal examination procedure do not require prior preparation.
If an ultrasound is performed through the abdominal wall, you should adhere to a slag-free diet for 1-2 days before the examination. You need to exclude sweet fruits, carbonated drinks, dairy products, legumes, cabbage, and brown bread from your diet. Also, 1-1.5 hours before the procedure, you need to drink a liter of liquid to fill the bladder.
Examination through the rectum is performed after bowel cleansing. To do this, 6-8 hours before the upcoming procedure, you can give a cleansing enema or use a laxative.
During pregnancy, there is no need to prepare for an ultrasound scan of the cervix.
Preparation
The scope of preparatory measures depends on the type of procedure. A minimum of preparation is required for diagnostics using the intrauterine method - it is enough to come to the examination with an empty bladder.
Preparation for an ultrasound of the uterus, which is performed through the abdominal wall, requires dietary restrictions. 24 hours before the test, it is recommended to exclude all gas-forming foods from your menu, from carbonated drinks to legumes and black bread. If a woman suffers from flatulence, carminatives (Semiticon, Espumisan) are recommended.
You need to go to the test with a full bladder. To do this you should:
- Drink 1 liter of clean water without gas and refrain from visiting the toilet.
- Or does not urinate for 3 hours before the procedure.
It is recommended to carry out the procedure on an empty stomach. Diet restrictions will also be necessary for other types of ultrasound diagnostics. They are needed to prevent gas bubbles from accumulating in the intestines. Air (gas) may interfere with imaging.
When conducting a TVU study, if a woman suffers from flatulence, she should also take carminatives. Before the examination, the bladder must be emptied.
When learning how to prepare for an ultrasound of the uterus during TRU, a woman needs to take into account that the sensor will be inserted into the rectum. That is, the intestinal ampoule should be as clean as possible. To do this, 8 hours before the procedure you need to take a microenema (Norgalax) or drink a laxative (Sanade).
Ultrasound technique
The specifics of the procedure depend on the research technique used. To perform transvaginal diagnostics, the patient must remove her underwear, lie on her back and bend her legs. Before insertion, a condom is placed on the sensor and lubricated with sound-conducting gel. The procedure does not cause pain. During an additional examination of the fallopian tubes, a sterile liquid is injected into them, which makes it possible to assess the dynamics of movement.
For transabdominal diagnosis, the woman undresses to the waist and lies on her back. A gel is applied to the skin of the abdomen, which ensures better passage of ultrasound waves.
During a transrectal examination, the woman lies on her right side and bends her legs. Before insertion, a condom is placed on the sensor. During the procedure, the patient may experience some discomfort.
Indications and contraindications for ultrasound of the cervix
An ultrasound shows the cervix, which allows you to study its condition in detail. But when is it necessary to diagnose the cervix with ultrasound? Where can I get an ultrasound? At any ultrasound diagnostic center.
- Acute pain in the lower abdomen. This may indicate such female diseases as torsion of the cyst leg, ovarian apoplexy, necrosis of the myomatous node, rupture of the fallopian tube in the case when an ectopic pregnancy occurs;
- Vaginal discharge, which is called leucorrhoea. Such discharge may indicate inflammation occurring in the uterine cervix, as well as an inflammatory process inside the uterus itself and appendages;
- Increase in the size of the uterus. This may indicate fibroids;
- Bloody vaginal discharge. This pathology is a sign of a large number of female diseases, such as cervical erosion, ectopic pregnancy, cervical canal polyp and endometriosis;
- Suspicion of the appearance of malignant neoplasms in the uterus;
- When pregnancy occurs, to clarify the location of the fertilized egg.
Ultrasound of the cervix: how is it done?
This ultrasound is usually performed in one of two ways: transvaginal or transabdominal. You can find out where you can get an ultrasound from your doctor, he will tell you the cost. The cost varies depending on the region.
In the first case, a condom is put on the sensor, which is placed in the vagina for diagnostics, to prevent infection. Such a study allows you to examine in detail the uterine structures, appendages and body of the uterus, as well as the fallopian tubes. Does an ultrasound show the cervix? Undoubtedly. The image is displayed on the screen and based on it the doctor makes conclusions about women’s reproductive health. Another advantage of the technique is the ability to visualize the ectopic space.
Transabdominal ultrasound is performed through the anterior wall of the peritoneum. Most often performed on pregnant women. Such an ultrasound allows us to draw a conclusion about the state of the amniotic fluid, the position of the fetus and its size. In the second trimester of pregnancy, such a study is very convenient to carry out, because ultrasound waves pass perfectly through the already hardened uterus.
Ultrasound cost
An ultrasound is performed in a antenatal clinic on the direction of a gynecologist. The procedure is free if you have a medical insurance policy.
You can get tested for a fee in private clinics and reproductive health centers.
| City | Cost, rubles |
| Moscow | 500-1200 |
| Saint Petersburg | 450-1100 |
| Ekaterinburg | 500-1000 |
| Novosibirsk | 400-1000 |
| average cost | 462-1075 |
Ultrasound of the cervix allows you to determine a woman’s readiness for childbirth and indications for cesarean section. During pregnancy, the procedure helps to promptly identify the threat of miscarriage.
Leave comments on the article and share your own experience. Share useful information with your friends on social networks.
Is the cervix visible on ultrasound during pregnancy?
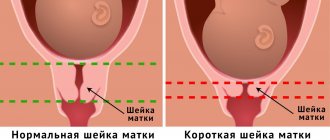
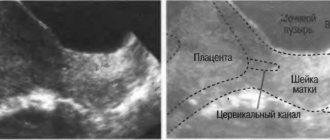
A study such as cervicometry, that is, an examination of the cervix, is carried out in the second trimester of pregnancy. Is the cervix visible on ultrasound at this time? The answer is yes. The purpose of this study is considered to be to determine the size of the uterine cervix.
- The normal length of the cervix on ultrasound in this case should be 35 - 45 mm, and the size of the os should not exceed 5 mm;
- Until the thirtieth week of gestation, the length of the uterine cervix should be at least 35 mm;
- At the thirty-fourth to thirty-sixth week, the cervix will begin to decrease in length as it begins to prepare for childbirth. A length of about 30 mm is considered within normal limits.
It should also be remembered that this procedure is especially necessary for those women who experienced isthmic-cervical insufficiency during a previous pregnancy.
Photo of ultrasound of the cervix during pregnancy: how is such an image made? Everything is very simple. The doctor takes a shot of what was displayed on the screen during the diagnostic test. After completion, the photograph is given to the patient. Of course, this is done at will.
Get a free doctor's consultation
Treatment of a short cervix
With a short cervix, a woman needs to put on and wear a support bandage every day. With its help, it is possible not only to prevent premature labor, but also to relieve the spine from unnecessary stress. In addition, you should maintain bed rest and avoid active physical activity.
More information about isthmic-cervical insufficiency can be found in the video:
The doctor sent me for an ultrasound of the cervix (somewhere closer to the 28th week of pregnancy) when the baby was in a very low position. I went with joy, as this was another opportunity to look at the child and check his condition. Fortunately, I was lucky and my neck size was normal.
Tatyana says
Each time during the next examination, the gynecologist said that the cervix was a little short, but did not prescribe an additional ultrasound. There were cervical ruptures during childbirth. How long after giving birth can I go for an ultrasound of the cervix?
Pathological conditions of the uterine cervix identified through diagnostics
There are a considerable number of such pathologies, and almost all of them are detected using ultrasound diagnostics. It is very important that during a routine examination of the patient, the doctor suspects the presence of a particular pathology in order to promptly refer the patient for the necessary examination. There are no indications or contraindications for cervical ultrasound as such.
Listed below are the main pathologies of the uterine cervix that can be diagnosed using ultrasound.
- Cervical cancer (ultrasound). This is the most dangerous type of pathology and it is desirable that it be detected as soon as possible. Ultrasound diagnostics shows where exactly the pathology is localized, how affected nearby organs are and what condition the lymph nodes are in. All data obtained allows us to make a diagnosis indicating the stage of the disease, which will allow us to choose the correct therapy in the future;
- Cervical cyst (ultrasound). This pathology is diagnosed quite rarely. It is a benign type neoplasm with homogeneous contents and rather thin walls. On ultrasound, such a cyst looks like a round formation. Transvaginal ultrasound if a cervical cyst is suspected should be performed as carefully as possible to avoid injury to the cyst;
- Cervical polyp on ultrasound. This disorder occurs due to infection and replication of the human papillomavirus in the cells of the uterine cervix. The virus multiplies and the normal structure of the epithelial tissue is disrupted, which is why a polyp appears. They differ from malignant neoplasms in that their structure is homogeneous and the boundaries are quite clear. That is, in appearance they are an elongated neoplasm with well-visualized boundaries;
- Cervical erosion on ultrasound. This pathology is observed in approximately thirty percent of women at any age. The negative point is that this disease can transform into cancer in the future. That is why timely diagnosis and treatment are very important. There are pseudo-erosion and true erosion. The first case is often diagnosed in girls under twenty-five years of age and is a defect in the uterine mucosa. This condition needs to be monitored. True erosion occurs due to injury and penetration of microorganisms. This pathology needs to be observed and treated.
All iLive content is reviewed by medical experts to ensure it is as accurate and factual as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable sites, academic research institutions and, where possible, proven medical studies. Please note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to such studies.
If you believe that any of our content is inaccurate, out of date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Indications and technique for performing ultrasound of the cervix
Ultrasound examination of the cervix is an additional diagnostic method that is used only as prescribed by a doctor in order to clarify the diagnosis or conduct a differential diagnosis. Therefore, it is important to take into account each individual case and decide on this research method, especially since its information content is very high, along with low harm. Before prescribing, the doctor must explain the technique and main points of this examination.
Preparation for an ultrasound of the cervix has no distinctive features, except for the difference in the technique. On the eve of the study, it is necessary to carry out basic hygiene procedures, which are no different from the daily toilet. As a rule, for better visualization, with different examination techniques it is necessary to empty the gallbladder - this facilitates the free passage of waves. This must be done immediately before the examination. These are the basic elements of preparation, which are very simple; if this examination is accompanied by additional manipulations, then there may be other methods of preparation, which the doctor will advise individually.
Indications for an ultrasound scan of the cervix are conditions that require additional examination to clarify the diagnosis. As for ultrasound of the cervix, the indications are as follows:
These are the main indications for which an ultrasound scan of the cervix and uterus is necessary, and depending on the goal, the technique is determined. There are two main ultrasound techniques: transvaginal and transabdominal. Transabdominal ultrasound is performed on pregnant women to assess the condition of the fetus, measure its size, measure the amount of amniotic fluid, as well as for functional diagnostics of its main systems. This method is convenient for pregnant women in the second half, since there is good conductivity of ultrasound waves through a dense, enlarged uterus.
Transvaginal ultrasound is performed for all other conditions that require examination. In this case, in order to prevent infection, a condom is put on the transvaginal sensor and inserted into the vagina, which allows visualization of all uterine structures, as well as the ovaries and tubes. With this technique it is possible to see the ectopic space.
Such diagnostics allows us to identify all structural changes in both the uterus and ovaries, the periuterine space and neighboring organs.
Indications for the procedure
A woman's cervical size is monitored throughout her pregnancy.
One of the most common causes of early miscarriage is isthmic-cervical insufficiency. Medical practice shows that this pathology in women most often ends in termination of pregnancy. With this pathological condition, painless dilatation of the cervix of the reproductive organ is observed, which mainly occurs in the middle of the term or the beginning of the third trimester.
The reason for termination of pregnancy is that the fertilized egg lacks support in the lower segment and this is due to the poor condition of the muscle ring. In addition, the neck of the reproductive organ is greatly softened and shortened, and this condition is complicated by the gaping of the cervical canal and internal pharynx. While expecting a baby, the pressure inside the uterus gradually increases and the consequence of this is the displacement of the fertile membranes into the cervical canal. In addition, the risk of infection is high.
This pathology can occur without the appearance of characteristic symptoms, which significantly complicates the timely identification of the problem. In such a situation, the only way out is regular screening examinations by a gynecologist, with the help of which it is possible to identify deviations from the norm.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency can cause the following symptoms:
- stabbing pain in the vaginal area, feeling of fullness pressure
- severe discomfort in the lumbar area and lower abdomen
- the appearance of slight vaginal discharge
- discharge of mucus from the genitals, which may contain streaks of mucus
Ultrasound makes it possible to diagnose the smoothness of the cervical canals, the degree of opening of the pharynx, the increase in the length and dilation of the cervical canal and its dilation.
In addition, during the procedure it is possible to identify changes in the structure of the canal walls and the condition of the internal os during palpation of the uterine fundus.
Ultrasound of the cervix of the reproductive organ during pregnancy can be prescribed if the appearance of neoplasms is suspected, as well as during long-term therapy to monitor its results. In such situations, the study is screening and is carried out regularly.
Time frame for performing ultrasound
In the 1st trimester, ultrasound is performed transvaginally
A study such as an ultrasound of the cervix is carried out at the same time as an anatomical ultrasound examination of the unborn child.
This usually occurs at 18-22 weeks, but the procedure can be performed much earlier in the following cases:
- the woman had a history of premature birth
- The patient had a late miscarriage
- a woman carries several fetuses
If such events have occurred in the patient’s history, then an ultrasound scan can be performed much earlier at 11-16 weeks. Those women who have had sutures placed on the cervix, as well as those with suspected isthmic-cervical insufficiency, are also at risk. In addition, an ultrasound can be prescribed much earlier if the expectant mother has a history of surgery on the reproductive organ.
Ultrasound and possible results
There are two ways to conduct the study (transvaginal and transabdominal):
- With the transabdominal method of examination, for better visualization it is necessary that the bladder is full. Such an ultrasound is considered less accurate, since with a full bladder, it is possible to create the effect of lengthening the neck of the reproductive organ by several millimeters.
- Transvaginal examination provides a more accurate image due to proximity to the object and high-frequency data. Medical practice shows that it is not possible to determine changes in the internal pharynx with all types of ultrasound. This pathological condition is detected during a transvaginal examination, but during a transabdominal examination it may go unnoticed.
To perform a transvaginal ultrasound, the patient must empty her bladder. After this, the woman should lie comfortably on the couch and bend her knees. The specialist applies a sound-conducting gel to the sensor and the cover covering it. After this, the device is placed in the vagina so that the lower segment of the uterus and its midsection are clearly visible on the monitor. This arrangement of the sensor allows you to view the cervix, its opening and the mucous membrane of the walls of the cervical canal.
Normally, the cervix should not be shortened
During pregnancy, no special preparation is required for an ultrasound of the cervix. As a rule, a transvaginal examination is performed in the early stages of pregnancy, and a transabdominal examination in later stages. Both types of ultrasound are considered completely safe for women's health.
By assessing the condition of the cervix of the reproductive organ, one can judge the possible risk for the unborn child and mother. In the early stages of pregnancy, the normal length of the cervix should be 4-4.5 cm, and at a period of 32-36 weeks it decreases to 3-3.5 cm. If the indicators of the cervix of the reproductive organ do not correspond to the norm, then the woman is selected treatment necessary for a healthy pregnancy.
Ultrasound of the cervix during pregnancy
Ultrasound diagnostics during pregnancy is a mandatory research method and is carried out at least three times in each trimester. The first ultrasound is performed between 9 and 11 weeks and allows you to determine the number of fertilized eggs in the uterus, their location, the level of placentation, and the condition of the uterus. At this time, it is possible to see the pathology of fetal development - chromosomal mutations, and if the development of congenital anomalies is suspected, a referral for invasive examination methods may be possible. The technique is transvaginal.
The next ultrasound is performed in the second trimester and an important element here is a special examination - cervicometry. This method consists of an ultrasound examination of the cervix and measuring its size.
Interpretation of the results of ultrasound of the cervix during pregnancy is that the standard indicators for the length of the cervix are 35-45 millimeters, and the size of the uterine pharynx is no more than 5 millimeters. Until the thirtieth week of pregnancy, the length of the cervix should be at least 35 millimeters. Further, at the next ultrasound in the third trimester at 34-36 weeks, the length of the cervix decreases as it prepares for childbirth. Moreover, its length is approximately 34-36 millimeters, but it can be 30. This is considered a normative indicator. If the length of the cervix is less than 35 millimeters, then a diagnosis of isthmic-cervical insufficiency is made. This condition is characterized by possible complications in the form of premature pregnancy, premature rupture of amniotic fluid, and entanglement of the umbilical cord. If this diagnosis is made in a timely manner, surgical treatment is carried out in the form of applying an obstetric pessary - this is a suture on the cervix, which reduces the uterine pharynx and lengthens the cervix. This suture is removed before childbirth. Therefore, it is very important to conduct an ultrasound of the cervix during pregnancy, especially over time, as this allows you to monitor not only the condition of the fetus, but also the readiness of the birth canal and its condition. It should also be noted that in women who previously had isthmic-cervical insufficiency during their first pregnancy, the ultrasound cervicometry method is mandatory to monitor the condition of the cervix.
Preparing for diagnosis
Preparation for the study depends on the diagnostic method. Before ultrasound analysis, you must perform the following steps:
- Before the transvaginal examination, you need to empty your bladder. Otherwise, this organ will close the uterus and appendages. If a woman is allergic to latex, you need to warn the diagnostician about this, since during an ultrasound, a condom is placed on the sensor.
- The transabdominal diagnostic method requires full filling of the bladder. 1 hour before the test you need to drink 0.5 liters of water and not visit the toilet. If the bladder is poorly filled, the doctor will not be able to see the pelvic organs, and the study will be uninformative. In this case, the intestines must be emptied. If a woman suffers from constipation or flatulence, she should not eat foods that cause gas formation 2 days before the ultrasound.
- If a transabdominal ultrasound is performed on a pregnant woman starting from the 2nd trimester, then filling the bladder is not of great importance. But this is only if the patient has not given birth before or has given birth naturally. If the pregnant woman has a history of cesarean section, the study is performed with a full bladder.
- In some cases, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound of the cervix during pregnancy (cervicometry). This examination is most often performed using the transvaginal method and requires the same preparation as conventional ultrasound diagnostics.
- If ultrasound is performed transrectally, then you need to have a bowel movement 6 hours before the procedure. It is useful to do an enema or drink a laxative.
- Intrauterine ultrasound does not require special preparation. You just need to empty your bladder before the procedure.
- If a study of the patency of the fallopian tubes is being carried out, then before the procedure you need to wash the external genitalia. 40-45 minutes before hysterosalpingoscopy, the patient may be given an antispasmodic. Further preparation will depend on which method of examination is performed - transabdominal or transvaginal.
Pathological changes in the cervix according to ultrasound results
There are many pathologies of the cervix, the diagnosis of which can be established only by ultrasound. Therefore, ultrasound is the “gold standard” for diagnosing pathology of the female reproductive system. It is important to suspect some pathology during a routine examination, in order to further conduct additional research methods and exclude or confirm the suspected diagnosis.
- Cervical erosion is a fairly common pathology that occurs in every third woman of any age. This pathology is a background disease and is associated with a possible risk of developing cancer in the future. Therefore, it is important to make a timely diagnosis and carry out treatment. First of all, one should distinguish between pseudo-erosion and true erosion of the cervix. Pseudo-erosion is a defect in the mucous membrane of the cervix, which most often occurs in girls under 25 years of age and is physiological. It occurs due to the action of hormones and does not require treatment, but only observation. Erosion is a true defect of the mucous membrane, which can occur as a result of trauma, the action of microorganisms, and therefore requires treatment. This pathology can be detected during a routine examination of a woman in the mirror or during colposcopy. Then the woman is sent for an ultrasound to exclude a malignant nature - then there will be no spread deep into the tissue. With ultrasound of the cervix, erosion has a characteristic appearance - a shallow superficial defect of the cervix without spreading deep into the tissue. Sometimes, erosion may not be visualized, which depends on the separation ability of the device and the size of the defect.
- Cervical cancer is a very dangerous pathology and requires the earliest possible diagnosis. Ultrasound allows you to accurately determine the localization of the pathological process, the degree of damage to neighboring organs, and the condition of regional lymph nodes. This allows not only to establish a diagnosis, but also to classify the disease according to stage, which is important for choosing treatment tactics.
Cervical cancer on ultrasound looks like “plus tissue” and has a vague structure in the form of a heterogeneous echogenic formation with unclear contours, which fills the cavity of the cervical canal or is located on the cervix itself. This picture is observed with exophytic tumor growth. With endophytic growth of cervical cancer, ultrasound shows heterogeneity in the structure of the cervix or cervical canal in the form of a node with unclear boundaries and a blurred structure.
- Cervical dysplasia is also a precancerous condition and requires timely diagnosis. This is a pathology in which epithelial metaplasia occurs, that is, stratified squamous epithelium, which is normally located in the exocervix, appears in the transition zone or in the cervical canal. This structural disorder is a superficial defect and, unfortunately, has no manifestations on ultrasound. This pathology is identified and confirmed by cytological examination.
- Cervical polyp is a very common pathology, which is caused by infection and replication of the human papillomavirus in the cells of the cervix. This virus multiplies and contributes to disruption of the normal structure of the epithelial cover, as a result of which benign formations are formed that have the appearance of cauliflower - polyps. These polyps look like “plus tissue” on ultrasound, but unlike malignant tumors, they have clear boundaries and uniform density, do not spread or grow in depth, and grow only exophytically. Thus, they have the appearance of an additional elongated formation with clear boundaries.
- Cervical cysts are not a common occurrence, but they also happen and require diagnosis. A cyst is a non-proliferative benign formation that has thin walls and a homogeneous composition. On an ultrasound, a cervical cyst looks like a clear, rounded formation, which has a homogeneous composition inside in the form of a liquid - which is clearly visible on the screen. It is necessary to carefully conduct a transvaginal examination if a cervical cyst is suspected, since a complication in the form of injury to the cyst is possible.
- Carcinoma and adenocarcinoma are malignant tumors of the cervix that develop from epithelial glandular tissue. Often has exophytic growth and heterogeneous structure. On ultrasound it looks like a fuzzy formation with a significant depth of penetration into the thickness of the cervix, the sizes are different, the boundaries are heterogeneous. On ultrasound it is difficult to distinguish between cancer and adenocarcinoma, since they have similar characteristics; one can only suspect a malignant nature, and an accurate diagnosis is established by the histological picture.
Ultrasound of the cervix is an informative diagnostic method that allows you to diagnose a normal pregnancy, monitor the dynamics of the fetus’s condition, and also determine possible pathological processes not only on the cervix, but also on the pelvic organs. Timely diagnosis of benign, background, and malignant formations on the cervix allows one to avoid complications and prescribe treatment in a timely manner.
Pathologies
What does the diagnosis show?
In gynecology, pathological changes in the cervix are distinguished:
- Background. These include erosions, polyps, ectopia and cysts.
- Precancerous (dysplasia).
- Oncological.
What pathologies are detected using ultrasound? There are a number of unhealthy conditions when an ultrasound scan is necessary.
Cyst
The cause lies in inflammatory diseases and hormonal imbalance. On ultrasound, it is determined by an anechoic inclusion due to the inability to reflect ultrasound waves. It is a formation with smooth edges of regular shape, clear outlines.
Video 1. Cervical cyst on ultrasound.
Polyps
Formations in the area of the cervical canal in the form of growths of connective tissue, covered with epithelium. On the monitor they are displayed as oval formations. Polyps can expand the canal. Small polyps are diagnosed.
Dysplasia
Some women are interested in whether dysplasia is visible on ultrasound, and is it advisable to undergo ultrasound with such pathology? This abnormal condition of the uterus can be diagnosed without much difficulty.
The cause of pathological changes in cervical tissue can be sexually transmitted and infectious diseases. With dysplasia, organ cells are destroyed.
Erosion
It is a defect of the epithelium. Forms of erosion - false (pseudo-erosion) and true. More details here.
Other changes
Uneven walls of the cervix, barrel-shaped shape and changes in echogenic character raise the question of the presence of oncological formations.
Other conditions that may suggest pathological processes include fluid in the cervix.
Important! The diagnosis is made in conjunction with clinical tests and a number of other examinations.
To clarify the diagnosis, an additional Doppler study is prescribed, which helps to assess the condition of the vessels, their tortuosity, the appearance of pockets and changes in the direction of enlarged lymph nodes.