Viral pharyngitis is an infectious form of the disease. Symptoms of the disease appear clearly and can affect the general condition, despite the absence of elevated body temperature. There is no specific therapy, the use of antibiotics is not required. In uncomplicated cases, symptomatic treatment is usually prescribed.
Symptoms of viral pharyngitis usually develop abruptly and manifest themselves in the initial stages as a sore throat
Viral pharyngitis is an inflammation that develops in the mucous membrane and lymphoid tissue of the pharynx as a result of a viral infection entering the body, which can be seen in the photo. How to distinguish it from bacterial pharyngitis? It is quite difficult to do this during inspection, since visually most of the signs are almost the same. The bacterial form of the disease is characterized by an increase in body temperature. It should also be taken into account that viral infection is often the first phase of the disease, and in the future it acts as the main initiating factor in the addition of a bacterial pathogen.
Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa
Acute pharyngitis is rarely an independent disease; in most cases it is combined with an inflammatory process in the upper respiratory tract - acute respiratory viral infection (ARVI), influenza, etc.
Isolated damage to the pharynx occurs only when this area is directly exposed to certain irritants (cold food or drinks, alcohol, smoking). In some cases, the disease can be triggered by inhaling cold air or prolonged conversation in the cold.
Reasons for the development of pharyngitis of viral etiology
Damage to the pharyngeal mucosa caused by viruses is observed among patients more often than bacterial inflammation. Doctors agree that about 70% of cases of pharyngitis are associated with a viral infection. There are many microorganisms that can provoke symptoms of the disease. Most of them are respiratory viral agents that cause ARVI. In such a situation, there is a similarity in the signs of pathology.
Medicine also knows cases of the development of viral pharyngitis with manifestations atypical for ARVI. This phenomenon is observed when a patient is infected with a pathogen of the herpesvirus group.
Damage to the pharyngeal mucosa is caused by the following microorganisms:
- rhinoviruses;
- adenoviruses;
- viral influenza and parainfluenza infection;
- coronaviruses.
A number of rare viruses can cause pharyngitis, these include:
- cytomegalovirus;
- herpes simplex virus;
- respiratory syncytial virus;
- Coxsackie virus.
The pathogen enters the body through airborne droplets when a person inhales air containing particles of infected saliva from a carrier of a viral infection. Infection often occurs through close contact, sharing utensils and other household items.
The inflammatory process can occur in the form of isolated pharyngitis, but more often spreads to nearby anatomical areas. Therefore, along with the pharynx, the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity, mouth, lips, bronchi, and tonsils is affected.
What it is
In acute pharyngitis, the back wall of the pharynx becomes inflamed . The diagnosis is made based on examination of the child's larynx. As a rule, children complain of pain, soreness and/or itching in the throat.
According to the nature of the flow, they are distinguished :
- Acute pharyngitis (up to 2 weeks).
- Chronic pharyngitis (more than 2 weeks).
- Catarrhal pharyngitis is characterized by damage only to the mucous structure of the pharynx.
- In the granulosa form, the mucous layer and lymphoid tissue are involved.
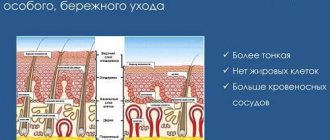
- The atrophic form is observed in a chronic process. Thinning of the mucous membrane is characteristic.
Photo:
Causes
The causes of pharyngitis are classified on different grounds. Depending on the cause, the disease is treated. So, the reasons could be:
- Viruses : corona viruses, rhinoviruses, adenoviruses, influenza/parainfluenza virus, herpes virus, Epstein-Barr virus, etc.
- Bacteria : more often group A streptococcus, less often group C, diphtheria bacillus, meningococcus, anaerobes, mycoplasma.
- Fungi of the genus Candida.
- Allergic reaction.
- Traumatic injury (foreign body, burn of the oropharynx).
, the following contributing factors may also influence the development of the disease :
- child age from 4 to 14 years (get sick more often),
- contact with a carrier of infection,
- decreased immunity,
- prolonged nasal congestion,
- inhalation of dust particles from the air,
- damage to the mucous membrane by hot or hard food,
- spread of infection from another organ,
- crowd of people (schools, kindergartens, sports clubs).
Clinical symptoms
Quite often, viral pharyngitis, which occurs in an acute form, is confused with tonsillitis. The difference lies in the spread of the inflammatory process during angina not only to the mucous membrane of the pharynx, but also to the tonsils. In this case, obvious signs of intoxication are observed.
The incubation period is 2–3 days. Pharyngitis of viral origin is characterized by a sudden onset. The severity of symptoms increases in the first hours or days. First, the patient feels slight discomfort in the throat, and then he experiences a detailed clinical picture:
- the appearance of painful sensations when making swallowing movements;
- dry cough caused by the accumulation of mucus in the throat;
- irradiation of pain to the hearing organs, in some cases, ear congestion is noted;
- general signs of intoxication: state of weakness, increased fatigue, lack of appetite, decreased performance;
- increase in body temperature up to 38 °C;
- when palpating the upper part of the neck, enlarged lymph nodes are detected.
The clinical picture of pharyngitis is often complemented by swelling, congestion, disruption of the respiratory function of the nose, and the presence of discharge from the nasal cavity. There is redness and swelling of the pharyngeal mucosa. Sometimes a purulent plaque forms on the walls of a characteristic organ.
The lack of proper therapy contributes to the development of viral and then bacterial tonsillitis. Another negative consequence of ignoring pharyngitis is its transition to a chronic form.
Possible complications
If acute pharyngitis is not detected in a timely manner, its symptoms are ignored, or its symptoms are not treated correctly, serious complications may develop:
- purulent throat abscesses (inflammatory process localized in the area of the lymph nodes);
- autoimmune reactions (destruction of tissues and organs by one’s own immune system);
- damage to the brain, kidneys and heart.
In addition, the transition of pharyngitis from the acute to the chronic stage is not excluded. Additionally, read the publication “Purulent pharyngitis.”
Diagnostic measures for pharyngitis
To make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a visual examination of the throat and review the test results. The doctor must determine the nature of the pathogen, since different forms of the disease require different treatments. Taking the wrong medications only makes the problem worse. To determine the etiology of the disease, the treating specialist examines a smear taken from the throat.
The following methods allow you to diagnose viral pharyngitis:
- a clinical blood test indicates a decrease in the concentration of leukocytes, lymphocytosis, and an increase in ESR;
- collecting mucus to determine the origin of pharyngitis;
- biochemical blood test, which determines the type of microorganism by the presence of antibodies;
- performing pharyngoscopy using an endoscope to exclude other ENT pathologies.
This infectious disease often develops into laryngitis; a specialist may additionally prescribe laryngoscopy.
After determining the nature of pharyngitis, the doctor prescribes complex therapy individual for each patient. The presence of chronic diseases, predisposition to an allergic reaction to medications, and indicators of immune defense are taken into account. The optimal treatment for the patient is then prescribed.
Diagnostics
The doctor makes a diagnosis by collecting anamnesis and performing a pharyngoscopy (examination of the pharynx). In most cases, this is enough to determine the cause of the disease. If the disease is viral in nature, the specialist will determine swelling and redness of the pharynx, lymphoid granules on the mucous membrane.
If pharyngitis was caused by bacteria, specific sputum will be released when you cough. Due to the pus content, its color is greenish, dark yellow, brownish. In difficult cases, it will be necessary to conduct additional research on throat swab materials to determine the type of pathogen.
Treatment regimen
Modern therapy for viral pharyngitis involves not only taking medications, but also following a special regimen that reduces the risk of complications:
- providing the patient with healthy sleep and rest in comfortable conditions;
- carrying out wet cleaning and ventilation of the patient’s room;
- adherence to a diet that excludes cold and hot foods that irritate a sore throat;
- maintaining the recommended drinking regime – 2–3 liters of warm liquid per day;
- giving up bad habits, in particular smoking;
- limiting contact with a sick person to prevent further infection with the virus.
Antibiotics are ineffective to fight viruses; they do not affect these microorganisms. There are special antiviral drugs that affect certain types of pathogens.
Medicines aimed at intracellular elimination of the viral agent are used:
| A drug | Photo | Price |
| Arbidol | From 246 rub. | |
| Tsitovir | From 338 rub. | |
| Tamiflu | From 1254 rub. |
For mild forms of pharyngitis, it is recommended to use restorative and symptomatic medications.
Such medications are prescribed exclusively by the attending physician. Self-administration of these medications is prohibited.
To relieve the symptoms of pharyngitis, the following medications are prescribed:
- antipyretic, normalizing body temperature;
- disinfectants and saline solutions for gargling;
- irrigation of the oropharynx with anti-inflammatory drugs;
- sucking lozenges, tablets and lozenges to soften inflamed mucous membranes.
After the symptoms of pharyngitis disappear, it is recommended to avoid hypothermia; the functioning of the immune system should be enhanced with the help of immunomodulators and a complex of vitamins.
Folk remedies
Pharyngitis can also be treated using traditional methods, and some traditional medicine can have an even more beneficial effect than conservative therapy.
The following recipes for combating pharyngitis are popularly known:
- Baking soda (2 tsp) is diluted in 400 ml of boiling water. Inhalations are made with this solution - every day throughout the course of the disease.
- Coltsfoot leaves (2 tsp), peppermint oil (1 drop), string (1 tsp) pour 200 ml of boiling water, wait about an hour and add this mixture to the inhalation solution or gargle with it every 3 hours.
- Linden flowers (1 tbsp), sage (2 tbsp), calendula (1 tbsp), pour a glass of boiling water, infuse and gargle.
Despite the almost complete absence of contraindications, before using any folk remedy you should definitely consult a doctor.
Features of the treatment of pharyngitis in children
Therapy for pharyngitis of viral origin in children is carried out using local agents, disinfectants and anti-inflammatory lozenges. It is necessary to provide the child with a drinking regime. During treatment of pharyngitis, some precautions should be taken so as not to harm the child’s body:
- reduce the likelihood of an allergic reaction to medications, including folk remedies;
- avoid long-term use of relatively toxic medications (iodine-based);
- Do not give your baby large lozenges; you should give preference to drops or syrups;
- It is prohibited to use throat aerosols in children under 5 years of age, as the risk of laryngospasm increases.
Before using any drug, you should carefully read the instructions for use, in particular, consider the age restrictions for use.
Prevention measures
Since viral pharyngitis is an infectious disease, its prevention is aimed, in addition to general measures to strengthen and improve the health of the body, at blocking the spread of viruses. Following several rules will help protect against inflammation of the respiratory tract:
- after visiting the street, public places, or large crowds of people, you need to thoroughly wash your hands with soap;
- during viral epidemics, it is recommended to gargle with warm boiled water, especially for children;
- take courses of multivitamin complexes several times a day;
- be active;
- Carrying out wet cleaning and airing the room has a beneficial effect on health.
You also need to teach your child to use his own cutlery, cups, and towels; viruses often enter the body through saliva when using other people’s things.
To avoid exacerbations of the chronic course of a viral disease, it is necessary to completely stop smoking. In addition, complete and timely treatment of acute respiratory infections should be carried out, do not tolerate the disease on your feet, and self-medication should be avoided. When the first symptoms of pharyngitis caused by viruses appear, you should immediately seek medical help to avoid negative consequences and complications. Only a qualified specialist is able to prescribe adequate therapy that does not harm the patient’s health.