Symptoms and treatment of allergic bronchitis in children and adults.
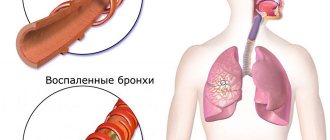
One of the manifestations of the body's hypersensitivity, causing a persistent obsessive cough and other unpleasant symptoms, is allergic bronchitis.
The disease consists of inflammation of the bronchial mucosa under the influence of various irritants.
Allergens entering the body cause a reaction consisting of dilation of blood vessels and contraction of muscles in the respiratory organs.
As a result, a characteristic external manifestation of the disease occurs - cough.
- Allergic bronchitis ICD 10
- Causes of allergic bronchitis
- Features of the course of allergic bronchitis
- Symptoms of allergic bronchitis
- Allergic bronchitis in children
- Diagnosis of allergic bronchitis
- Treatment of allergic bronchitis
- Prevention of allergic bronchitis
- Spa treatment of allergic bronchitis
- Psychological assistance for allergic bronchitis
Allergic bronchitis ICD 10
According to ICD 10, the disease refers to chronic diseases of the lower respiratory tract.
The disease, which at first glance does not seem particularly serious, still requires special attention.
After all, it can develop into quite dangerous forms and lead to disastrous health consequences.
Diagnostics, additional examinations and interpretation of results
Determining the presence of allergic obstructive bronchitis is done using various methods. These include:
- physical examination;
- endoscopic examination;
- lab tests;
- X-ray of the lungs;
- analysis of functional data (EF, peak flowmetry);
- studies to identify the allergen that causes the disease (scarification tests, determination of levels of immunoglobulins to certain allergens).
Physical data indicate the form and stage of the disease. As the disease progresses, the following symptoms become more pronounced:
- vocal tremors become weaker;
- during exhalation, wheezing is heard, accompanied by whistles, changing tone after coughing;
- breathing is harsh, and in the chronic form may be weakened.
If necessary, additionally prescribed:
- bronchoscopy (allows you to examine the mucous membrane and perform a biopsy);
- bronchography (allows us to exclude bronchiectasis, dilation and deformation of the bronchi).
Laboratory tests of urine and blood help to assess the presence of inflammation and its nature, as well as to suggest the allergic nature of the disease.
Radiography makes it possible to:
- detect concomitant respiratory diseases;
- exclude lung damage.
Very often, with allergic obstructive bronchitis lasting more than three years, radiography helps to identify:
- emphysema;
- changes in the roots of the lungs;
- strengthening of the bronchial pattern.
Functional data analysis helps determine:
- bronchial obstruction (presence, degree and reversibility);
- pulmonary ventilation (are there any violations);
- stage of the disease.
Allergy tests are prescribed to identify the irritant that causes a negative reaction in the body. These may be skin tests or blood tests taken from a vein.
To exclude pulmonary tuberculosis, additional studies may be prescribed:
- bacteriological;
- microscopic.
Causes of allergic bronchitis
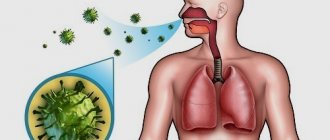
The main provocateurs that cause allergic bronchitis are various irritants that enter the human body along with the air and settle on the mucous membrane of the respiratory system.
The main ones are:
- plant pollen;
- animal hair;
- bird feathers;
- dust;
- household chemicals;
- Food;
- medicines.
Bronchitis does not develop upon contact with an irritant in all people, but only in those who have an increased sensitivity of the body to the provocateur.
Factors contributing to the development of the disease may include:
- living in an area with poor ecology;
- acute bacterial or viral infection entering the airways;
- maternal toxicosis during pregnancy (if the disease occurs in young children);
- cold and damp climate;
- smoking (passive and active);
- work in hazardous industries characterized by increased air pollution;
- previous acute bronchitis;
- heredity.
The first signs of allergic bronchitis are most often noticed in early childhood.
The functioning of a child’s immune system that is not fully formed can be disrupted for various reasons.
And instead of activating protective functions adequately to the danger, the body begins to react to completely harmless substances.
Causes and factors of the disease
Obstructive allergic bronchitis in children and adults develops due to the presence of various provocateurs. The main reasons against which the disease occurs can be divided into three groups.
- Features of the structure of the respiratory system in young children.
- The state of the body before the onset of the disease.
- Environment.
Factors belonging to the first group of reasons include the following features:
- anatomical structure of the diaphragm in children;
- the glandular tissue of the bronchi remains in an enlarged state;
- narrowness of the airways in young children compared to other age groups.
Premorbid background factors causing obstructive bronchitis include:
- increased tendency to allergic reactions;
- rickets and prematurity in infants;
- an increase in the size of the thymus;
- exhaustion;
- intrauterine infections;
- early transfer from breastfeeding to artificial feeding;
- ARVI disease in children under 12 months;
- hereditary predisposition;
- alcoholic fetopathy in children;
- weakening of the protective functions of the immune system.
Environmental factors include:
- active or passive smoking;
- polluted environment;
- contact with harmful substances (especially for representatives of certain professions: builders, miners, employees working in printing shops).
The inflammatory process in the bronchi can occur due to one or several reasons at once. However, a mandatory factor provoking the development of the disease is human contact with the allergen.
Features of the course of allergic bronchitis
A characteristic distinguishing feature of the disease that develops against the background of allergies is:
- cessation of cough after eliminating interaction with the irritant;
- no elevated temperature.
In addition, there are other manifestations of the disease.
Folk remedies against allergies and bronchitis
An infusion of chamomile and coltsfoot helps treat allergic bronchitis. The herbs are brewed in a water bath in equal parts, then settled and filtered. Take 1/2 cup twice. You can add oak bark for greater effect. Store the broth for no more than two days and not in the refrigerator. Take until symptoms become less severe.
You cannot bypass an old remedy that can treat not only coughs, but laryngitis: honey with milk. At night, prepare warm milk, dissolve honey and drink before bed. The warmer the composition, the better the efficiency will be. Treatment with hot milk also helps with concomitant laryngitis.
Inhalation treatment is useful for any disease of the respiratory system, especially for young children who cannot yet be treated with medications. To do this, you need to boil the potatoes, cover yourself and the child with a thick blanket and breathe for 10 minutes. This will not only thin the mucus in the bronchi, but will also warm the nose with concomitant rhinitis.
Inhalations can be done using nebulizers or a hot kettle with a spout. Make boiling water in a simple kettle and dissolve several Validol tablets. Then make a kind of little bag out of cardboard or plastic and put it on the spout of the kettle. Breathe for 15 minutes until a strong expectorant cough appears. The teapot can be replaced with a glass jar.
Symptoms of allergic bronchitis
Signs of allergic bronchitis in adults and children are very pronounced.
The main one is cough. This symptom of the disease is the main one.
It is characterized by the following features:
- attacks consist of persistent and obsessive reflex spasms of the respiratory tract;
- are observed mainly at night, although they can also occur during the day;
- at the beginning of the development of the disease, the cough has a non-productive form (without expectoration of mucus);
- in the later stages of the development of the disease, sharp spastic exhalations may be accompanied by sputum production;
- easily provoked by stress, negative emotions, and physical exertion.
Symptoms of allergic bronchitis are not limited to cough.
Also observed:
- dyspnea;
- labored breathing;
- dry wheezing (very rarely wet).
A characteristic feature of bronchitis that occurs against the background of allergies is that the symptoms begin and stop suddenly.
After coughing attacks that occur several times a day, the patient feels relief, which creates the illusion of recovery.
Classification of allergic obstructive bronchitis
The disease can manifest itself in two forms.
- Spicy.
- Chronic.
- Allergic obstructive bronchitis in the acute stage is most often observed in young children.
- Recurrent disease - in adults.
Allergic bronchitis in children
Allergic bronchitis in adults and children can occur at any age. The disease is characterized by a relapsing course.
Exacerbations occur several times a month. Their duration can be from 1-2 days to several weeks.
Typical symptoms of allergic bronchitis may include a sore throat. Their onset is often preceded by nasal congestion and rhinitis.
In children, the disease can occur against the background of other allergic diseases:
- hay fever;
- skin diathesis;
- neurodermatitis.
In children, typical symptoms of allergic bronchitis are often accompanied by:
- lethargy;
- increased sweating;
- irritability.
Symptoms of the disease
The main symptom of the disease is cough. The more intense it is, the more seriously the disease progresses. The duration and severity of the cough indicate that the lungs are being affected, which can become damaged if allergic bronchitis is left untreated.
The duration of the disease itself can be from several weeks to months. The frequency of its occurrence is up to 2 times a month. Symptoms of allergic bronchitis will help in quickly understanding what is happening to a person in order to help him.
- Wheezing when inhaling, which is heard in the lungs.
- Paroxysmal cough, mainly at night. It is long lasting. At first it is dry, then it turns into wet due to the production of sputum in the bronchi, which comes out with it. The provoking factors of its occurrence are physical activity, outbursts of emotions, and mental activity.
- Difficulty breathing, which is accompanied by shortness of breath.
- No fever, unless there is an infection.
- Nasal discharge. Changes in the paranasal sinuses are possible.
- Alternation of remissions and exacerbations. Relapse is accompanied by dry wheezing.
The appearance of periods of remission, when a person stops coughing and feels good, breathes smoothly and calmly, can be misleading, saying that the disease has passed on its own. Actually this is not true. Perhaps the person stopped contact with the allergen, which is why the symptoms went away. Perhaps there is a transition from the acute form of allergic bronchitis to chronic.
If symptoms of the disease reappear, you should not hesitate to contact an allergist, who will identify the cause and prescribe treatment.
go to top
Diagnosis of allergic bronchitis
Before treating the disease, you must consult a doctor:
- allergist;
- immunologist;
- pulmonologist.
Any of these specialists will be able to determine that bronchitis arose precisely as a result of an allergy, and will determine how to properly treat it.
To do this, the doctor will collect all the anamnestic data:
- examine laboratory tests;
- will conduct an instrumental and physical examination.
With a positive diagnosis of allergic bronchitis, the following indicators are confirmed:
- the chest is not visually deformed, does not change shape or size;
- hard breathing with whistles and wheezing is heard, they can be small and large bubbles;
- when examining the radiograph, you can see changes in the pulmonary pattern: in the medial sections it will be thickened, in the lateral sections it will be sparse, and at the root it will be strengthened;
- according to the results of endoscopic studies, the picture can be different - from the mucous membrane, which has not undergone any changes, to the presence of signs of pus;
- in the patient’s blood, eosinophils and histamine levels increase, a strong concentration of immunoglobulin A and E is observed, the compliment titer is reduced;
- laboratory tests also reveal leukocytosis and increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
First aid for allergic bronchitis
After the onset of an attack of bronchitis that occurs against the background of an allergy, it is necessary to immediately eliminate the patient’s contact with the irritant that provokes a relapse.
Steam inhalations will help relieve the symptoms of allergic bronchitis before visiting a doctor who will diagnose and prescribe adequate treatment.
To carry them out, you need to close the door to the bathroom and turn on the hot water. After the steam fills the room, the patient should be taken there.
After a few minutes of staying in a room with high humidity, the symptoms of allergic bronchitis will subside slightly.
Diagnostic measures
Laboratory methods allow you to accurately determine the diagnosis.
It is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis of a patient based on his complaints.
To accurately determine the nature of the disease, a number of tests are used:
- taking anamnesis;
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- bronchoscopy;
- spirometry;
- determination of immunoglobulins in the blood;
- carrying out allergy tests.
Already during the initial examination, a specialist can make a preliminary diagnosis, but the plan of therapeutic action is determined only after a full examination.
Skin testing is a mandatory diagnostic method.
Treatment of allergic bronchitis
A prerequisite for getting rid of the disease is to stop contact with the irritant that causes attacks of the disease.
Conservative treatment is carried out using:
- medicines;
- folk remedies;
- physiotherapy techniques.
Medications for allergic bronchitis
Treatment of allergic bronchitis with pharmaceuticals has two goals.
- Reduce the intensity of allergies.
- Make breathing easier and reduce coughing.
To achieve the first effect, antihistamines are used. Treatment with bronchodilators and expectorants, as well as glucocorticoids, helps to achieve the second result.
Medicines that reduce the intensity of an allergic reaction
The use of the following medications helps treat the manifestations of the underlying disease and help reduce the unpleasant symptoms caused by it:
- suprastina;
- diazoline;
- Tavegila.
Medicines that help reduce the severity of allergy symptoms
Symptomatic treatment of attacks of allergic bronchitis involves taking expectorant medications:
- broncholithin;
- pertussina;
- mucaltina;
- bromhexine.
Among bronchodilator pharmaceuticals, the disease can be most effectively treated with the help of:
- hexoprenaline;
- atroventa;
- terbutaline;
- cromohexal;
- ketotifen;
- fenoterol;
- neo-theophedrine;
- salbutamol.
The drugs can be either in tablets or in the form of syrups.
If treatment with the above medications does not bring the desired relief, your doctor may prescribe the use of glucocorticoids.
These include the following drugs:
- nazarel;
- ingacort;
- becotide;
- budesonide.
Inhalation of medications helps treat allergic bronchitis in children and adults, as well as its symptoms.
The following solutions are often used:
- lazolvan;
- fluimucil.
They are diluted 1:1 with saline and poured into a nebulizer.
Following certain rules helps to effectively treat the disease:
- inhale the suspension through the mouth and exhale through the nose;
- add soda to stimulate mucus discharge;
- carry out no earlier than 1.5 hours after eating;
- after the procedure, do not go out onto the street or balcony for several hours, and do not eat;
- strictly adhere to the duration of inhalation prescribed by the doctor.
Application diagram
In order to treat the disease correctly, when taking medications, you must follow all the necessary dosages.
| Group of drugs | Name of the medicinal product | Trade names | Treatment regimen for adults | Treatment regimen for children |
| antihistamines | suprastin | chlorpyramine, allergan C, halopyramine, sinopen, chlorneoantergan | 1 tablet 3 times a day; 1-2 ml intramuscularly | ½ tablet 3 times a day |
| diazolin | omeril, mebhydron | 1-2 times a day, 0.05-0.2 g | 0.02-0.05 g up to 3 times a day | |
| bronchodilators | hexoprenaline | ipradol, ginipral | tablets: 0.5-1 mg 3 times a day; aerosol: to relieve an attack of suffocation - 2 breaths (0.2-0.4 mg each) | tablets: from 4 to 6 years, 0.25 mg up to 3 times a day; from 7 to 10 years, 0.5 mg 1-3 times a day; aerosol: only for children over 3 years old (dosage is the same as for adults) |
| fenoterol | Berotec, segamol, aruterol, aerum | for asthma attacks, 1 inhalation (0.2 mg), after 5 minutes, can be repeated if necessary | over 6 years old - the same as for adults | |
| inhaled corticosteroids | budesonide | rhinocort, pulmicort, apulein | 400 - 1600 mcg per day in 2-4 doses at the beginning of treatment, then reduced to 2 times a day, 200-400 mcg | 2 times a day 200-400 mcg |
| flunisolide | ingacort | 2 mg per day (up to 8 inhalations) | 500 mcg/day for 2 procedures | |
| expectorants via nebulizer | ambroxol | lazolvan, ambrolytic, fluixol, secretil, mucovent | 10 ml for the first 2-3 days of the disease in several doses | 1-2 inhalations per day (2 ml) |
| fluimucil | ACC, acestine, exomyuc, acetylcysteine | 5-10 days 1-2 times a day, 300 g | just like adults |
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy helps treat allergic bronchitis in children and adults.
They have the property:
- reduce inflammation;
- prevent the occurrence of obstruction;
- have a positive effect on the general condition of the bronchi.
To combat the disease, doctors often prescribe the following procedures:
- halotherapy (with the help of salt air, ventilation of the respiratory organs is stimulated, their patency improves);
- hypoxic therapy (thin mountain air helps fight the symptoms of the disease and increases the body’s resistance to allergens).
Therapeutic gymnastics has also proven itself to be excellent. When performed regularly, it gives the following effect:
- helps fight asthma attacks;
- stimulates the prevention of shortness of breath;
- strengthens the muscles of the chest, which further contributes to the saturation of tissues with oxygen and normal ventilation of the respiratory system.
Medicines against bronchitis
Treatment of allergic bronchitis begins with identifying the allergen that causes the cough and minimizing the connection with it.
To reduce the strength of the allergic reaction, stop coughing, and restore breathing, drug therapy using expectorants is prescribed.
The severity of allergies decreases after taking Suprastin, Tavegil or Diazolin. Suprastin is prescribed to both adults and children over 14 years of age. Like any medicine, it has side effects: dizziness, weakness, lethargy. Restrictions for taking the drug: asthma, glaucoma, prostate adenoma, stomach ulcer. Suprastin is contraindicated for pregnant women.
Tavegil also has its contraindications. It should not be taken for hypertension, heart failure, pulmonary diseases, expectant mothers or babies under one year old. Side effects of this drug are as follows: headaches, tinnitus, drowsiness, nausea, diarrhea, convulsions. The release form of Tavegil is varied: from tablets to injection solution.
In the treatment of allergic bronchitis, drugs with an expectorant effect are prescribed: breast milk, Mucaltin, Bromhexine, Broncholitin.
Bronchodilators are widely used - medications that relieve spasm of the bronchi, relaxing their muscles and expanding them. These are Ephedrine, Neo-theoferdine, Ventolin, Cromohexal. Neo-theoferdine affects bronchospasm, relieves swelling of the bronchial mucosa, and at the same time lowers temperature and relieves pain. It is contraindicated for use in cases of glaucoma, epilepsy, seizures, and thyroid diseases. Side effects are as follows: nausea, vomiting, heartburn, headaches, insomnia.
Terbutaline, Fenoterol, Volmax, Salbutamol aerosols reduce the number of attacks.
If the above medications do not give a positive effect, then hormonal drugs are prescribed.
drugs: Flunisolide, Budesonide or Fluticasone. The latter (aerosol) gives an anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effect. It is contraindicated for small children, and a side effect may include hoarseness after inhalation. It is not recommended to use these drugs for a long time, as inflammation may intensify. All these medications do not cure the disease, but only relieve symptoms. But there is a modern method of treating allergic diseases. It is called specific immunotherapy (SIT). It removes not the symptoms of the disease, but its cause. An allergist influences the body’s unpleasant reaction to a specific allergen, reducing susceptibility to it. To do this, the patient is given allergy tests, the irritant is determined, and then subcutaneous injections of this allergen are given. But this should be done during a period of remission, and not during an exacerbation of the disease.
Prevention of allergic bronchitis
For children and adults, there are the same recommendations for preventing exacerbations of allergic bronchitis, which consists in avoiding contact with potential irritants.
Effective preventive measures aimed at preventing asthma attacks include the following:
- performing wet cleaning of the premises at least twice a week;
- avoidance of smoking (passive and active);
- constant humidification of the room where the patient is located;
- daily change of bed linen;
- hardening;
- compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- removal from the room where the patient with allergic bronchitis is located of all carpets, plants, upholstered furniture, toys;
- avoiding contact with animals, birds, getting rid of insects and rodents;
- eating only those foods that do not cause allergic reactions;
- use of hypoallergenic household items;
- change of place of work (if attacks occur due to activities in hazardous work);
- taking any medications only after medical consultation;
- immediate treatment of any respiratory ailments.
Prevention
To prevent the development of allergic bronchitis and its exacerbations, it is necessary:
- adhere to a hypoallergenic diet. Foods that provoke the development of allergies (citrus fruits, chocolate, honey, smoked meats, milk, etc.) are excluded from the diet;
- fight house dust, one of the most powerful allergens. To this end, you should: carry out wet cleaning of the room daily, replace feather and down pillows and mattresses with hypoallergenic ones, get rid of carpets, soft toys, heavy curtains and other items on which dust is deposited in large quantities;
- maintain water regime. Drinking plenty of fluids helps thin mucus and facilitates its removal from the bronchi. It is best to drink herbal teas, alkaline mineral waters;
- quit smoking. Tobacco itself is not an allergen, but tobacco smoke has an irritating effect on the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, increasing its sensitivity to the effects of other aggressive agents.
When seasonal allergies worsen, the patient is advised to go outside as little as possible. In the room, you should keep the windows closed and carry out wet cleaning daily. When using an air conditioner, it is necessary to equip it with a special filter that captures and retains dust particles and other allergens.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Spa treatment of allergic bronchitis
The climate has a very strong therapeutic effect on adults and children suffering from allergic bronchitis.
However, when choosing a resort, it is worth considering that for people with a similar disease, treatment in local sanatoriums is more useful than those remote from their permanent area of residence.
Thus, the following are reduced or completely eliminated:
- adaptation terms;
- contrast of climatic zones.
The optimal duration of treatment in sanatoriums is considered to be from 21 days to a month.
Symptoms
The main symptom of allergic bronchitis is a severe dry cough, which manifests itself mainly at night and with new contact with the allergen. In general, the symptoms of the disease are quite extensive. The disease is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Difficulty breathing (later a whistling sound that occurs during inhalation and exhalation will indicate pathology).
- Shortness of breath (even with the slightest physical effort).
- Manifestation of sputum.
- Skin rashes.
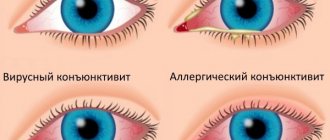
- Conjunctivitis.
- Increased sweating.
- Weakness and malaise.
- Runny nose and nasal congestion.
Typically, the symptoms of bronchitis in the early stages of the disease are subtle or similar to a cold. Therefore, patients almost always turn to a doctor late, when the disease is already quite advanced. The body temperature is normal or slightly elevated, but the person feels overwhelmed and weak.
At the first symptoms of the disease, you should contact your doctor and undergo a full examination. A dangerous pathology can cause serious complications in the patient, so self-medication is unacceptable here.
In an infant under one year old or an older child, the disease manifests itself as whims, irritability and general malaise. With the development of bronchitis, the baby suddenly becomes lethargic. The temperature of a small patient may rise significantly or remain normal. Obstructive bronchitis, when the bronchial lumen narrows to the maximum and causes oxygen starvation, is manifested by a severe cough, mainly at night. Often sputum production increases significantly.
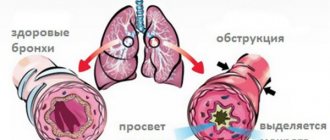
Obstructive and non-obstructive bronchitis: differences
Allergic bronchitis is a chronic disease that is caused by a high concentration of allergens in the inhaled air.
It occurs more often in children than in adults.
He can be:
- obstructive;
- non-obstructive.
Non-obstructive bronchitis
With non-obstructive bronchitis, the mucous membranes of the bronchi become inflamed; this process is accompanied by increased secretion of mucus by the bronchi, hyperplasia of the bronchial glands, and cough with sputum. About 2/3 of those who develop this type of bronchitis are men, and among the main causes of this disease, smoking ranks first.
Bronchitis obstructive
Obstructive bronchitis is characterized by all of the above symptoms, but is supplemented by bronchial obstruction, that is, degenerative-dystrophic changes in the lining of the bronchi.
This type of bronchitis is caused by allergies, bacteria and viral infections.