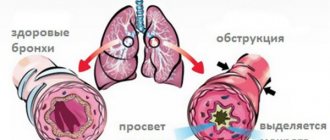
Bronchitis in Latin means “inflammation”. Viral bronchitis is a very dangerous and insidious infection, the causative agents of which are various viruses (rhinovirus, influenza virus, respiratory interstitial virus, adenoviruses, etc.). Influenza and parainfluenza viruses can also become a factor in the development of viral bronchitis. Infection usually occurs through contact with a patient through inhalation of contaminated air. Penetrating into the human body, these biological microparticles cause inflammation of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract.
Viral bronchitis is a very dangerous and insidious infection, the causative agents of which are various viruses.
The child's body is most susceptible to infection with viral bronchitis due to the lack of developed immunity and is highly likely to catch the infection in kindergarten. Most often, the causative agents of the disease are viruses, but with a weakened immune system, when the body does not have enough strength to fight rapidly multiplying bacteria against the background of inflammation, viral bronchitis develops into another form - bacterial. It doesn’t matter whether you suspect viral or bacterial bronchitis, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Causes
The cause of viral bronchitis is the entry of pathogenic viruses into the body of an adult or child.
There are risk factors that significantly increase the likelihood of the occurrence and development of this disease. These include:
- weakened immunity (in the case of adults);
- unformed immunity (in the case of children);
- frequent colds;
- severe hypothermia of the body;
- wet and cold weather;
- advanced viral rhinitis (runny nose).
We would like to pay special attention to a runny nose. Often it is not even considered a full-fledged disease. This attitude is more common in adults and is accompanied by a complete lack of treatment. Meanwhile, infectious rhinitis can cause the development of many diseases, including viral bronchitis.
In addition, cigarette smoking can significantly contribute to the occurrence of this disease. You can get more detailed information in the article “Smoker's Bronchitis”.
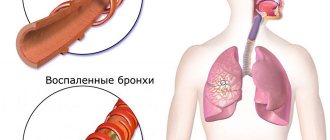
Features of bacterial bronchitis
Features of bacterial bronchitis
Bronchitis of bacterial origin is a disease of the lower respiratory tract. Its appearance is caused by pathogenic bacteria. Most often, this disease occurs as a complication after its viral form. This happens due to the fact that the body, which has already suffered from the disease, has reduced resistance, and against this background, pathogenic microflora begins to intensively reproduce in the tissues of the bronchi.
If bacterial bronchitis began as an independent disease, this indicates that an exacerbation of a chronic illness has occurred. The primary disease, bronchitis of a bacterial nature, occurs when the body’s defenses have been undermined even without the influence of viruses. This can happen due to allergic reactions, stress, hypothermia. People with an unfavorable environment are at increased risk of developing bacterial bronchitis.
This disease can be caused by the following pathogenic microorganisms:
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- chlamydia;
- hemophilus influenzae;
- Moraxella;
- pneumococci;
- mycoplasma.
The peculiarity of the signs of bacterial bronchitis is its sharp manifestations. The symptoms of this disease are:
- Intoxication. It is expressed in a feeling of weakness and lethargy, the presence of a headache, and a constant sleepy state.
- Painful sensations. The patient feels discomfort or burning in the chest area, which is very debilitating.
- Cough. Appears some time after the onset of the disease.
The nature of the cough also changes as the disease progresses. At first it is dry, because of it the patient cannot sleep fully at night. This usually lasts from 3 to 4 days, and then the cough becomes wet. The sputum can be mucous, but sometimes it is mucopurulent and also has a greenish color.
Further, if the disease proceeds normally, then after a few days other symptoms are noted:
- increased temperature (up to 37.5 degrees);
- hardness of breathing is felt;
- wheezing occurs.
The disease of moderate severity has the same symptoms as the mild form, but the duration and severity increase. In this case, the person is bothered by severe coughing attacks accompanied by shortness of breath. After clearing his throat, he feels relief.
A severe form of the disease is accompanied by the following additional symptoms:
- increased breathing and shortness of breath;
- tachycardia;
- wheezing, dry or wet;
- redness of the walls of the pharynx;
- blood parameters change - ESR and the number of leukocytes increase.
With timely initiation of therapy, the unadvanced disease quickly recedes, but coughing can last up to a month.
Is it possible to get infected with it?
Viral bronchitis is contagious. The disease is transmitted by airborne droplets. For infection, it is enough for an adult or a child - a carrier of the corresponding viral infection - to sneeze a few meters away from you.
With close personal contact, the likelihood of infection with viral bronchitis increases many times. In such a situation, even ordinary conversation is dangerous.
Of course, you may not get sick. Much depends on the strength of your immune system. In a strong and healthy body (especially in an adult), the virus can die without being able to provoke the onset of the disease.
Many adult patients try to cope with the disease on their feet, making do with self-treatment. The first available pills and often rather dubious folk remedies from the standpoint of official medicine are used.
This approach is completely wrong. Firstly, you can develop chronic bronchitis and other serious complications. Secondly, by not taking care of your own health and proper, comprehensive treatment, you create a real threat to the children and adults around you.
In this regard, it is very important to contact a qualified doctor when you notice the first signs and symptoms of bronchitis so that he can select appropriate treatment methods.
The incubation period of viral bronchitis is individual for each child and adult patient. Depending on the specific viral infection and the state of the immune system of the sick person, it can last from 2 to 7 days.
Prevention
The main point of preventing bronchitis is strengthening the immune system. In addition, to minimize the risk of developing the disease, you should:
- balance the diet;
- walk daily, ventilate the room, do wet cleaning;
- avoid hypothermia and overwork;
- exercise;
- When treating any disease, complete the course of therapy to the end. An untreated infectious focus causes weakened immunity and increases the risk of secondary infection;
- give up smoking and alcohol;
- maintain personal hygiene;
- to harden;
- prevent the development of chronic diseases;
- When in contact with a sick person, wear a disposable protective mask.
Main symptoms
The main symptoms of viral bronchitis are:
- discomfort and sore throat;
- a sharp increase in body temperature (up to 39 degrees);
- aches in joints and muscles;
- paroxysmal cough;
- shortness of breath and difficulty breathing;
- weakness and dizziness;
- noises and wheezing in the chest;
- chills and fever.
I would like to dwell in more detail on such a symptom as cough. During the illness itself, patients suffer from a dry cough. As the disease progresses, it is replaced by a wet (wet) cough, accompanied by copious discharge of dirty yellow sputum.
Causes and provoking factors
The bacteria that cause bronchitis develop against the background of the primary source of infection, which can be rhinitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, laryngitis.
Often, diseases of the nasopharynx reduce the body's resistance, which accelerates the growth of pathogenic microflora. For this reason, children and the elderly are more likely to suffer from bronchitis.
In addition, patients at risk include:
- smoking and alcohol abusers;
- with hereditary lung pathologies;
- those who have suffered chest injuries;
- working in hazardous conditions;
- having a tendency to allergies;
- suffering from diseases of the cardiovascular system that cause swelling of the lung tissue. These include carditis, stenosis of the atrioventricular valve on the left;
- untreated respiratory disease. Some patients quit therapy when they feel better, while the infection still remains in the body in a weakened form;
- with immunodeficiency;
- with a foreign object in the bronchi. This is possible if a person inhales a foreign body, or during aspiration with food, in children - with breast milk;
- those who have had whooping cough or have cystic fibrosis;
- neglecting personal hygiene.
Haemophilus influenzae and Klebsiella can only be introduced in a certain way, for example, in a hospital during tracheostomy or intubation.
Therefore, operations on the respiratory apparatus can also be considered a predisposing factor.
In children, bacterial bronchitis may be associated with:
- adults smoking near children;
- chronic diseases of the nasopharynx;
- untreated colds, acute respiratory viral infections;
- congenital predisposition to allergies;
- hypothermia.
How is diagnosis carried out?
There are two main methods for diagnosing viral bronchitis. These include:
- auscultation;
- blood analysis.
Auscultation is a diagnostic method characterized by listening to sounds produced during the functioning of certain organs. When determining bronchitis, the doctor uses a stethoscope to try to detect wheezing and noise in the chest that appears when the patient breathes.
A general laboratory blood test is the most accurate method for diagnosing viral bronchitis. It allows you to reliably determine the presence of a viral infection in the human body.
You can get more information by reading the article “Diagnostics of bronchitis”.
Factors that increase the risk of viral bronchitis
A favorable environment for the life and reproduction of infectious agents is cool and damp weather, attending events with a large number of people during a dangerous period for infection, when the human immune system is susceptible to disease.
Viral bronchitis can occur as a result of complications of influenza and ARVI.
People suffering from viral infections such as sinusitis, rhinitis, viral laryngitis, pharyngitis are most susceptible to viral bronchitis.
People suffering from rhinitis are most susceptible to infection with viral bronchitis.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment of viral bronchitis is always complex. This is due to the fact that there is no universal pill that, by drinking it, the patient would certainly be cured of this disease.
The choice of methods and means of treating viral bronchitis is the prerogative of the attending physician.
Why is this so?
Many people mistakenly believe that the main medical treatment for viral bronchitis is taking antibiotic drugs.
Antibiotics are powerless against viruses. They are prescribed if pathogenic bacteria have joined the viral infection and the disease has acquired a viral-bacterial character. In addition, antibiotics are prescribed to minimize the possibility of any complications.
The main methods of treating the viral form of bronchitis are:
- use of immunomodulatory drugs;
- use of antipyretic drugs;
- use of mucolytic (expectorant) drugs;
- carrying out inhalations.
Immunomodulatory drugs are designed to help strengthen the patient's immune system. This is done to help the body fight the virus. After all, after the body produces the appropriate antibodies, the patient will rapidly recover. Doctors often prescribe Broncho-munal to their patients.
Antipyretics are designed to lower high body temperature. They are drugs for symptomatic therapy.
A high body temperature is an indicator that the patient’s body is actively fighting an existing infection. But if the temperature becomes too high (38-39 degrees).
Mucolytic drugs are used for dry cough. Taking them thins mucus and promotes its removal.
The prescription of specific drugs is carried out exclusively by the attending physician.
Complications and prognosis
The prognosis for viral bronchitis is favorable. Most often it goes away within a week, leaving no trace behind. However, in some cases complications may occur, the most common of which are:
- addition of a bacterial infection;
- transition to a recurrent or chronic form;
- development of an allergic reaction;
- pneumonia;
- sepsis;
- adverse reactions to the medications used.
It must be remembered that even such a harmless disease as acute viral bronchitis can cause serious complications. But you can significantly reduce the risk of their development by consulting a doctor in time and following all his recommendations.
Therapy methods
Only a doctor should decide how to treat bronchitis in children and adults, otherwise, due to improper therapy, the patient’s general condition may worsen, and other, more severe diseases may be added to the main disease.
General recommendations
If you have symptoms of viral bronchitis and need to start treatment as quickly as possible, then start it by following the following tips.
- Maintain bed rest. Otherwise, the effect of the drugs on the body will be weak. It will take much longer to completely get rid of the disease.
Bed rest
- Don't walk outside, especially in the cold season.
- Every day for 10-15 minutes, ventilate the room in which you are constantly located. Do this 2-3 times a day.
- Monitor the air humidity in the room. It should be 50-70%. This can be achieved using:
- humidifier;
- laying wet towels on radiators;
- hanging wet sheets or diapers in the house;
- evaporation of mineral water. To do this, you need to pour it into a saucepan and put it to cook over low heat;
Treatment will be ineffective if this condition is not met.
- Drink plenty of fluids. The total amount drunk per day should be at least 3 liters. During treatment, drink not only water, but also black tea with lemon, milk with honey, tea with raspberries, compote. Their use will help remove waste products of pathogenic viruses from the body.
- Do breathing exercises. Blow up the balloon several times throughout the day. Do this exercise daily for 2-3 weeks. Thanks to this action, phlegm will be removed from the lungs faster. Restoration of respiratory tract function will also begin.