Fever, cough, severe chest pain - all these signs may indicate the onset of a disease such as bronchitis. Many do not consider this disease to be insidious and are in no hurry to consult a doctor, trying to recover at home. But in vain!
Patients are often interested in the question of whether bronchitis is contagious. It is not possible to give an unambiguous answer right away - it is necessary to establish the cause of the disease.
Causes of bronchitis: risk group
Some people are more susceptible to bronchitis than others. For an unknown reason, men suffer from bronchitis 10 times more often than women. Chronic bronchitis affects smokers 50 times more often than non-smokers.
Recent research data indicate that 4.6 million of our citizens suffer from chronic bronchitis and the disease that often accompanies it - pulmonary emphysema.
This disease causes 50,000 deaths annually, ranking at the top of the list of diseases that cause death. About 90% of all deaths are caused by cigarette smoking. The risk of death for people who smoke more than 25 cigarettes per day is 30% higher than for non-smokers.
Smokers and people with severe obstructive pulmonary disease (caused by obstruction of air flow into the lungs) suffer from constant shortness of breath, even at rest. It is difficult for them to make any effort to tense the neck and shoulder muscles when inhaling.
For smokers, the likelihood of developing chronic bronchitis increases with age and thus with the number of cigarettes smoked. More than half of mature men who smoke a pack or more of cigarettes a day suffer from a constant cough with phlegm. In those who quit this bad habit, their susceptibility to chronic bronchitis gradually decreases over time.
Causes of bronchitis
Bronchitis usually occurs in winter, more often in areas with high humidity, significant levels of environmental pollution and high population density. Colds and fatigue are additional risk factors.
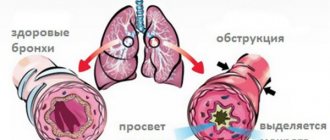
The most common cause of acute bronchitis is a bacterial infection that affects the airways. Chronic bronchitis causes irritation of the respiratory tract and coughing. The lungs lose elasticity and oxygen metabolism is disrupted. Persistent inflammation of the bronchi develops, resulting in increased secretion of mucus by the goblet cells of the bronchial walls. The mucus produced is called sputum.
Since direct examination of the bronchi is impossible, infectious disease doctors rely on the main symptoms - cough and sputum production - to make an accurate diagnosis. The color of sputum indicates the severity of chronic bronchitis.
Answers to some questions
Is it true that bronchitis can lead to cancer?
No. But smoking, which is the cause of chronic bronchitis, is often the cause of cancer. If you smoke more than 20 cigarettes a day, your chances of getting lung cancer increase by 20 times, and chronic bronchitis by 50 times.
I have never smoked, but I was recently diagnosed with chronic bronchitis. Can this condition lead to the development of emphysema?
Highly unlikely. Although chronic bronchitis can be caused and aggravated by smoking, it can also be caused by other factors, such as industrial pollution. Emphysema affects smokers, and susceptibility to it increases with the number of cigarettes smoked. Long-term consequences of this disease are observed in 12% of people who smoke a pack of cigarettes a day, and with a larger volume of smoking the figure is 20%.
In our other publications
Breathing exercises by Strelnikova
Breathing exercises using the Strelnikova method are one of the most effective for bronchitis. The gymnastic complex is designed in such a way as to involve the muscles of the abdomen, arms, and legs, which increases its effectiveness.
Rules for doing the exercises:
- all movements must be performed while inhaling;
- the inhalation should be short, and you should not inhale a lot of air, the inhalation should be natural;
- exhalation should be natural, you should exhale silently through your mouth, you should not hold your breath or stimulate exhalation;
- You should alternate inhalations through your mouth and through your nose.
Exercise to relieve a coughing attack: during an attack, take a deep breath and immediately exhale the air, then hold your breath for a while. Repeat 3-5 times.
Exercise for bronchial obstruction: pour water into a suitable container (bowl, pan, etc.), and lower a cocktail tube into it. The patient takes a deep breath and exhales through the tube into the water. It is recommended to do the exercise for 5–15 minutes several times a day.
Also, for obstructive bronchitis, an exercise is recommended that improves the removal of accumulated mucus: in the morning, without getting out of bed, turn on your back, after removing the pillow and blanket, take a deep breath, exhale sharply, drawing in your stomach as much as possible, and cough. Repeat several times.
It is recommended to practice inhalation and exhalation by inflating balloons.
Gymnastics according to the Strelnikova method should be performed 2 times a day for 2-3 weeks. A set of exercises takes from 8 minutes to 10-15. It is recommended to do exercises in the fresh air, or at least by ensuring a flow of fresh air into the room. If during their performance the patient experiences shortness of breath and/or dizziness, a short break should be taken, after which the gymnastics should be continued.
Classes should begin under the supervision of a specialist in physical therapy (physical therapy), and after mastering the technique, they can be continued independently.
Depending on the patient’s condition, the number of repetitions and the total duration of gymnastics can be adjusted. The complex is contraindicated for spinal injuries, traumatic brain injuries, osteochondrosis of the cervical or thoracic spine.
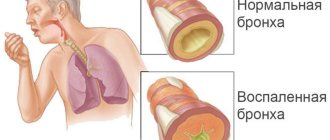
What is bronchitis?
The inflammatory process, which is localized in the bronchi, is called bronchitis. If we approach the issue from the anatomical point of view, it is useful to know that the lower respiratory tract begins with the trachea, which is divided into the right and left bronchi. The bronchi, in turn, have numerous branches - bronchioles, which end in alveoli.
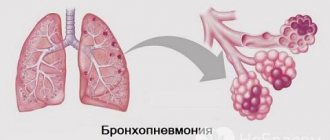
When the latter are involved in the inflammatory process, then we are talking about pneumonia, and not bronchitis. A competent, experienced doctor can distinguish one process from the other by listening to the chest, and X-ray examination will confirm the accuracy of the diagnosis.
A person who does not have a medical education, but often suffers from colds, is already able to determine an approximate diagnosis based on existing symptoms. Acute bronchitis is characterized by a dry, irritating cough that provokes chest pain. Body temperature may be slightly increased.
How can you get infected?
You can get sick after suffering acute respiratory diseases, in which during the incubation period the infection gradually descends lower and affects the bronchi. After some time, the cough becomes more wet, as the sputum begins to liquefy, health improves, and the person quickly recovers.
The chronic form of bronchitis is sluggish and does not give such an acute picture; its symptoms are more blurred (the usual prolonged cough, absence of fever). For this reason, many people do not even suspect that they have long been classified as suffering from chronic bronchitis. Especially those who are fond of smoking and whose professions involve constant contact of the respiratory tract with harmful irritants.
Frequent recurrences of acute bronchitis (more than twice a year) indicate the presence of a chronic course of the disease.
The causes that contribute to the occurrence of the disease can be grouped into the following groups:
- past viral infections (acute respiratory infections, influenza, etc.);
- bacterial infections (staphylococcus, pneumococcus, streptococcus, chlamydia);
- harmful working conditions (chemicals, dust, etc.);
- unfavorable environment;
- the presence of allergies can also cause allergic bronchitis;
- smoking, both passive and active.
Often the disease is mixed in nature (begins with a viral infection, and is subsequently complicated by the addition of a bacterial one).
Symptoms
The first sign of acute bronchitis is a cough. As a rule, the occurrence of this symptom occurs simultaneously with other manifestations of a respiratory infection. At first the cough is dry, but with proper treatment on the second or third day it becomes moist and a large amount of sputum is coughed up. Also in the clinic of the acute form of the disease the following symptoms are present:
The course of acute bronchitis is accompanied by an increase in body temperature
- general malaise;
- difficulty in nasal breathing due to congestion, runny nose;
- temperature rise;
- shortness of breath (with complications, obstructive lesions);
- clearly visible wheezing in the lungs;
- pain and heaviness in the chest area.
After a few days of therapy, the main symptoms disappear, but the cough may persist. If the temperature lasts more than three or four days, this indicates the addition of a bacterial infection or complication.
The chronic form of the pathology is manifested by a cough, the duration of which is more than two months. Typically, this is a productive cough that occurs in the morning. In the autumn-winter period, this symptom manifests itself more intensely, and subsides in the warm season.
Slow inflammation leads to changes in the structure and function of the bronchi, and the pathology worsens over time. Attacks of severe debilitating cough appear, purulent impurities are found in the sputum. Patients complain of fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
What can be done to prevent the disease?
- With the beginning of the season, when the likelihood of catching an infection increases significantly, start taking antiviral drugs in advance for the purpose of prevention.
- Avoid hypothermia to prevent the appearance of a runny nose and sore throat, which can contribute to bronchitis. Personal protective equipment (masks), which it is advisable to use when in crowded places, will help you avoid getting sick during epidemics of influenza and acute respiratory infections.
- Leading a correct and healthy lifestyle is also within our power. Giving up bad habits, proper nutrition and exercise will complement each other, increasing the protective properties of the body.
- If the cause of frequent bronchitis is unfavorable working conditions, then you should think about changing jobs in order to avoid the disease becoming chronic.
- Immunization (vaccination). There are vaccinations against influenza and pneumococcal infection, which can also cause bronchitis. It is recommended to do them in combination and at the same time, as this can create more powerful protection. Of course, a vaccinated person can subsequently get sick, but at the same time he will experience cold symptoms in a milder form than a non-vaccinated person.
Implementation of all of the above preventive measures is aimed at preventing colds, reducing the risk of their occurrence, creating an additional barrier to the penetration of pathogens and strengthening the body as a whole.
Read expert advice and stay informed on how to properly treat bronchitis.
We are all susceptible to the negative effects of viruses on our body. A surge in morbidity is recorded in the autumn-spring period, the time of restructuring of the body from the usual temperature regime to a new regime, to which one still needs to adapt. As a rule, a strong immune system is able to defeat a viral attack with adequate treatment, but bronchitis is often a complication of ARVI. This is a rather difficult disease to treat, so the logical question is whether bronchitis is contagious to others.
Therapy methods
Treatment of various forms of bronchitis in adults and children is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease, restoring the patency of the airways and eliminating the negative factors that provoked the disease. In difficult cases, the patient must be hospitalized, but more often treatment is carried out at home under the supervision of a doctor.
Patients are advised to drink plenty of warm fluids
The choice of treatment regimen depends on the form and type of bronchitis. In the acute period, it is necessary to select such means to quickly and effectively relieve the patient from the manifestations and causes of the pathology.
The patient is advised to rest completely and drink plenty of warm fluids. Smoking should be avoided during the onset of acute symptoms. It is also recommended to adhere to a diet with a predominance of dairy and plant products. In the room where the patient lies, you should install a special air humidifier and place several vessels with water or wet towels.
Drug therapy for acute bronchitis includes:
The drug Remantadine
- antiviral drugs (Remantadine, Amiksin, Arbidol, Zanamivir - orally or by injection, Interferon drugs - nasally) are prescribed if the viral etiology of the disease is established;
- antibiotics are used for a purulent form of the disease accompanied by a bacterial infection;
- in case of febrile symptoms and high temperature, antipyretic drugs are prescribed (Ibuprofen, Paracetamol);
- medications with an expectorant effect and mucolytics (ACC, Lazolvan, Fluimucil, breast preparations) to transform a dry cough into a productive one and better transport of sputum;
- for a non-productive cough, antitussives are used that affect the brain centers (Libexin, butamirate preparations - Omnitus, Sinekod);
- Codeine preparations can be prescribed for severe, debilitating cough that is not controlled by other medications.
In case of obstructive damage to the bronchi, inhalations are done with saline solutions, Berodual, and phytoncides. Dry warm compresses (for example, a bag of heated salt) or mustard plasters on the respiratory tract are considered an effective treatment method.
Among the physiotherapeutic methods for the treatment of acute forms of bronchitis, UHF, medicinal electrophoresis, vibration massage, and microwave therapy are indicated. You can also get rid of bronchitis by using folk recipes to relieve symptoms (black radish juice with honey, warm milk with butter and honey).
Chronic forms of the disease require therapeutic measures both during relapses and during remission. Outside of exacerbations, regular breathing exercises and the use of restorative procedures are recommended. To improve respiratory function, long walks in a forested area are suitable. To prevent exacerbations, it is necessary to increase the immune status by eating properly and taking vitamin complexes.
Breathing exercises have a positive effect on lung function
During the period of exacerbation, antibiotic therapy is carried out (in the presence of purulent sputum or severe inflammation). The type of drug is determined by the attending physician after conducting bacteriological examinations of sputum and identifying the pathogen. To eliminate cough, mucolytics and expectorants are used. Bed rest and drinking plenty of fluids are recommended. Physiotherapy is recommended.
The mechanism of development of bronchial inflammation
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bronchial tree that lines it from the inside. This occurs due to the penetration of pathogenic viruses and bacteria into the body. They are able to destroy cells, penetrating deeper into the mucosa. As a result, the amount of bronchial secretion increases and their lumen narrows due to thickening of the walls. Sometimes you can get bronchitis not from pathogenic microorganisms, but from irritating factors: allergens, chemicals.
It is not always possible to become infected with this disease; it all depends on the factor that caused it and the form of the disease.
Methods of transmission
Many people think that bronchitis is a non-contagious disease. It is impossible to become infected from a patient only if the disease is caused by allergies, polluted air or chemicals. If the inflammation is caused by viruses, bacteria or fungi, the patient becomes infectious to others during the acute period of the disease or until antibiotics are included in the treatment regimen.
You can become infected in shops and transport. Children attending preschool institutions often suffer from bronchitis in large numbers.
Forms of bronchitis
This disease occurs in acute and chronic forms.
- Acute bronchitis is characterized by a sharp and intense inflammation of the bronchial mucosa, sometimes the inflammation spreads to the trachea and vocal cords (you can even lose your voice for a certain time). A person often coughs, sputum is released along with the cough, swelling of the mucous membrane is diagnosed, even obstruction of the bronchi, their blockage is possible, and symptoms of obstructive bronchitis appear.
- In the chronic form of the disease, such exacerbations occur frequently and alternate with periods of remission. This is a complication of the acute form, not a complete cure. With chronic bronchitis, structural changes in the bronchi and secretion systems occur; the bronchi are rarely in normal condition. The bronchial tree gradually loses its functions of protecting the bronchi and cleansing them.
So, are acute and chronic bronchitis contagious or not? Acute inflammation of the bronchial tree can be contagious if it is caused by viruses. Chronic bronchitis is not always contagious. During the period of remission, the inflammatory process develops inside the person, but does not manifest itself externally. But here the reason that caused the inflammation of the bronchi is also important. The viral nature of exacerbation of chronic bronchitis can become dangerous for others due to the easy route of transmission - airborne droplets.
Effective exercises
You need at least two weeks of training in the morning and evening. Exercises called “pump”, “hug your shoulders” and “large pendulum”, which perfectly ventilate the lungs, are very helpful. They need to be repeated, alternating 16 breaths through the nose and 16 breaths through the mouth without stopping. There are three complexes in total. “Head turns” are also good along with this. These exercises can be performed both sitting and standing.
Breathing exercises for bronchitis prevent complications of bronchitis and cope with both chronic and acute conditions. An important fact is that gymnastics prevents obstructive conditions from developing into asthma.
The main rule is that you must perform the exercise consciously and correctly, otherwise the effect will be greatly reduced. The fact of constancy is also important. Reducing symptoms is not a reason to quit the exercise routine.
Causes of bronchitis
The causes of the development of the disease are certain microorganisms, internal processes in the body - an allergic reaction of the body to a certain irritant. Let's take a closer look at these reasons. Is bronchitis contagious in all cases of its occurrence?
- Penetration of viruses - there are more than 200 varieties of viruses that can cause the development of acute bronchitis. But often inflammation of the bronchi causes ARVI.
- Bacteria – if bacteria constantly multiply in a person’s nasopharynx, then staphylococci, streptococci and other bacteria can lead to various forms of bronchitis. In this case, antiviral drugs will be ineffective, and antibiotics are used. As you know, bronchitis caused by bacteria is not transmitted by airborne droplets.
- Non-infectious causes - inflammation of the bronchial tree can develop not only from microorganisms. Sometimes the cause may be particles of substances that irritate the bronchi. This disease develops in miners and mining industry workers as a result of coal dust entering the bronchi. Also, workers in the chemical industry suffer from illness as a result of inhaling particles of washing powder and toxic substances. Professional welders suffer from chronic bronchitis due to inhalation of small particles of metal and other substances while welding. Upon contact with allergic substances, allergic bronchitis develops.
Infection with bronchitis
We cannot see all the causative agents of bronchitis in people who are close to us. Therefore, an exciting question arises about how one can become infected with this disease, whether short-term communication with a patient will bring long-term inflammation of the bronchi.
In the autumn-spring period and after various stresses, the body’s defenses cease to intensively perform their functions, which increases the likelihood of diseases of viral etiology. When viruses and bacteria penetrate and multiply in the body, other human defense mechanisms are activated - the unconditioned protective reflexes of sneezing and coughing. When sneezing and coughing, pathological microorganisms are released from the human body and released into the environment. They, together with small drops of saliva, scatter around sick people, settling on the clothes, organs of the interlocutors, and other surrounding objects. If you inhale at this time, tiny droplets of viruses can enter the respiratory tract of a healthy person. The airborne route of infection with bronchitis of viral etiology is the most common.
In contact with a patient with bronchitis of bacterial etiology, infection is also possible; bacteria can be transmitted by contact, through saliva.
A disease provoked by allergic and other irritating factors is not contagious to others unless it is accompanied by viral or bacterial components.
Bronchitis can be contracted from others, but bacteria and viruses that enter a healthy body can cause inflammation of the upper respiratory tract rather than inflammation of the bronchi. It could be laryngitis, tonsillitis, sore throat, pharyngitis. Whether this will be a bronchial inflammatory process depends on the protective forces of each organism individually.
Prevention of bronchitis infection
The external cause of infection is poor ventilation of the room in which healthy and sick people are located. In such a confined space, droplets from a sneeze or cough have nowhere to land except on the organs and clothes of other people. To avoid contracting this disease, you need to take care to implement methods to prevent inflammation of the respiratory tract:
- It is necessary to ventilate the room where a large number of people constantly accumulate.
- Use a handkerchief when sneezing or coughing for sick people, and healthy people can cover their nose with it when breathing if there is a sick person nearby.
- After being in a place where there are many people, you need to wash your hands with soap. This will help prevent contact transmission of infection.
- Take care to increase your own immunity through natural means, if necessary, seasonally use vitamin complexes or drugs that stimulate the functioning of the body’s immune system.
- At the first symptoms of an acute respiratory viral infection, appropriate effective treatment should be started immediately so that a complication of the disease does not develop in the form of inflammation of the bronchial tree.