Author's rating
Author of the article
Green Elena Stanislavovna
Otolaryngologist of the second category
Articles written
665
about the author
Tonsillitis is one of the most common diseases. It is characterized by an inflammatory process in the palatine tonsils. It occurs mainly in children, due to a poorly developed immune system and the peculiar structure of the tonsils. If pathology in the early stages is not given due attention, acute purulent tonsillitis develops or the disease becomes chronic.
Causes
The following main causes of acute tonsillitis can be identified:
- bacteria;
- viruses;
- fungus.
The most common pathogen among bacteria is streptococcus, much less commonly staphylococci, pneumococci, and atypical bacteria.
Any viral infection of the respiratory tract can lead to the development of tonsillitis.
The following factors contribute to the occurrence of the disease:
- inhalation of polluted air in production, or while living in large cities;
- hypothermia of the body;
- the presence of foci of chronic infections (pharyngitis, sinusitis, adenoids, otitis media, caries);
- long-term uncontrolled use of antibacterial drugs;
- poor nutrition;
- excessive smoking.
The spread of pathogens among the adult population occurs through airborne droplets (during coughing or sneezing), and very rarely through household contact.
During contact-household transmission, spread occurs through the use of shared utensils, household items, and failure to comply with personal hygiene rules.
Prevention
To minimize the likelihood of developing tonsillitis in adults, it is necessary to begin strengthening the body’s defenses and immunity as early as possible.
Preventive measures:
- to harden;
- eat properly and balanced;
- ensure proper sleep;
- walk in the fresh air more often;
- carefully monitor oral hygiene;
- promptly sanitize foci of infection and treat teeth.
Tonsillitis in adults is a serious disease that needs to be treated as early as possible . If you take action in the early stages of the disease, you can recover quickly and prevent relapses and complications.
Tonsillitis is caused by various pathogens. Therefore, careful diagnosis in order to correctly prescribe treatment. Self-medication for this disease is unacceptable and can lead to undesirable consequences.
Tonsillitis is one of the infectious diseases of the throat, provoked by pathogenic pathogens. What kind of disease is this? Is it possible to fight it at home? What medications will be needed? Below are some rules of patient behavior for angina and the main methods of treatment.
Symptoms of acute tonsillitis
After infection and until clinical signs of tonsillitis appear (incubation period), it can take from several hours to three days.
Clinical symptoms of acute tonsillitis depend on the type of tonsillitis.
Signs of catarrhal acute tonsillitis
Thus, with the catarrhal form of acute tonsillitis, shallow damage to the mucous membranes of the tonsils develops.
Initially, the patient shows signs of intoxication, but the intoxication syndrome is mild. The following symptoms are typical for intoxication:
- the temperature rises within 37-38 degrees;
- moderate general weakness;
- slight headache.
Catarrhal tonsillitis also occurs without fever.
Local symptoms appear a little later:
- sore and dry throat;
- moderate pain in the throat when swallowing;
- swollen tonsils;
- hyperemia (redness) of the tonsils.
There are no plaques on the tonsils due to catarrhal inflammation. Catarrhal tonsillitis is most often caused by viruses; sometimes it can be an early manifestation of other forms.
This type of acute tonsillitis has a favorable and milder course. In addition to the signs of the disease itself, with catarrhal tonsillitis there may be signs of viral damage to neighboring organs:
- rhinitis;
- pharyngitis;
- laryngitis.
After three days, the process begins to decline, or it turns into another, more serious, form of tonsillitis.
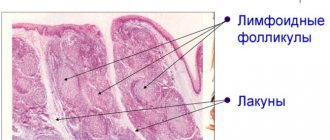
Signs of lacunar and follicular tonsillitis (purulent tonsillitis)
Lacunar and follicular tonsillitis are purulent types of tonsillitis that develop due to bacterial infections.
Both types begin with a pronounced intoxication syndrome:
- Body temperature with follicular tonsillitis rises to 39 degrees;
- with lacunar tonsillitis, the temperature rises to 40 degrees or more;
- aches throughout the body;
- muscle pain;
- intense headaches;
- severe general weakness;
- chills;
- increased salivation.
Local changes are included:
- intense sore throat;
- when swallowing, pain may radiate to the ear;
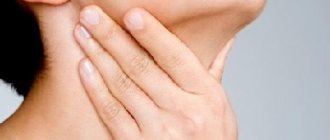
- submandibular and cervical lymph nodes enlarge;
- pain on palpation of regional lymph nodes;
- swelling of the tonsils;
- hyperemia of the tonsils;
- with the follicular form, there are purulent follicles on the tonsils - round formations up to 5 mm in diameter, white-yellow in color;
- with the lacunar form on the tonsils there are accumulations of pus in the lacunae of the tonsils, also white-yellow in color;
- purulent discharge can cover the entire surface of the tonsils (purulent plaque).
The duration of clinical manifestations of these two forms is usually up to 7-10 days.
Ulcerative membranous form of tonsillitis
Ulcerative membranous tonsillitis does not cause disturbances in the general condition of the body. A distinctive feature is the presence of grayish deposits, which, when removed, result in ulcerative lesions of the tonsil mucosa.
Features of sore throat
What is the difference between acute tonsillitis and tonsillitis? There is no difference, since sore throat is tonsillitis, which occurs in an acute form. The disease is infectious in nature and is accompanied by inflammation of the tonsils, the formation of purulent plaque and plugs.
You can get a sore throat either from a sick person or as a result of infection from other sources. For example, this could be a chronic infection, the focus of which is caries, chronic diseases of the nose and paranasal sinuses. If a sore throat is not treated in a timely manner or is treated incorrectly, it can lead to serious complications in the form of exacerbations of various systems and organs.
Sore throat can occur in various forms. Based on the nature of the damage to the tonsils, catarrhal, follicular, necrotic, herpetic, lacunar, phlegmonous and fibrinous tonsillitis are distinguished.
Diagnostics
If signs of acute tonsillitis appear, you must consult your local doctor or otolaryngologist.
There is no need to self-medicate; this can lead to the development of complications or the transition of tonsillitis to a chronic form.
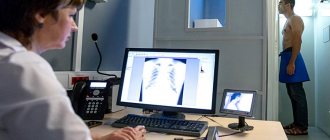
The diagnosis is established on the basis of characteristic complaints, medical history, and of course examination data.
The doctor performs pharyngoscopy - an examination of the oral cavity and pharynx, during which local changes are detected.
A smear is taken from the mucous membranes of the tonsils to determine the causative agent of the disease, and to select drugs for the treatment of the inflammatory process. It is determined which drugs the pathogen is sensitive to.
In case of acute tonsillitis, it is necessary to take a smear from the tonsils to exclude diphtheria.
In a general blood test, there may be inflammatory changes - accelerated ESR, leukocytosis.
Treatment of acute tonsillitis
Important! This section is written in accordance with the Federal Standard of Primary Health Care for Acute Tonsillitis
Treatment of acute tonsillitis should be carried out strictly under the supervision of a physician.
There are general recommendations during treatment:
- isolation of the patient in a separate room;
- regular ventilation of the room;
- wet cleaning of the room daily;
- providing separate dishes for the patient;
- drinking plenty of water;
- avoiding foods that are too hot;
- food should be warm and pureed;
- Do not eat spicy, sour foods (this additionally irritates the throat mucosa).
Antipyretic drugs should be taken at a temperature of 38.5 degrees or more. The following drugs are prescribed:
- Aspirin;
- Ibuprofen;
- Nurofen;
- Paracetamol.
Etiotropic therapy (directed at the causative agent of the disease) is mandatory.
Antiviral drugs
For the viral etiology of acute tonsillitis, antiviral drugs are used, however, there is still intense debate in the scientific community about the effectiveness of such drugs. Opponents of antiviral therapy rightly argue that its effect is insignificant. Currently, the most popular antiviral drugs are:
- Kagocel;
- Ingavirin;
- Arbidol;
- Ergoferon.
Antibiotics for acute tonsillitis
Antibacterial drugs must be taken for purulent (bacterial) forms of tonsillitis. Antibiotics are prescribed with a wide spectrum of antibacterial action:
- Penicillins (Amoxiclav, Flemoclav, Augmentin);
- Macrolides (Hemomycin, Azithromycin, Klacid);
- Cephalosporins (Cefixime, Zinnat, Ceftriaxone).
The dosage, frequency and duration of administration are determined only by the attending physician.
Typically, the course of antibacterial treatment is about ten days, but not less than seven.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines are used to relieve swelling of the tonsils:
- Diazolin;
- Cetrin;
- Suprastin.
Local therapy
Local therapy for acute tonsillitis is mandatory.
- gargling;
- irrigation of tonsils with sprays;
- sucking lollipops, tablets.
For gargling use:
- furatsilin;
- hydrogen peroxide;
- soda solution;
- sea salt;
- miramistin;
- chlorhexidine;
- herbal infusions
Rinsing can be done every 1.5-2 hours, alternating several products.
After the procedure, do not drink for 30 minutes.
Irrigation of the mucous membranes of the tonsils is carried out:
- ingaliptom;
- stopangin;
- cameton;
- hexoral;
- Lugol.
Lozenges and lozenges have not only an anti-inflammatory effect, but also an analgesic effect:
- Falimint;
- Doctor Mom;
- Septolete;
- Antiangin;
- Faringosept.
Therapy for acute tonsillitis should be comprehensive, then recovery occurs much faster.
Compliance with the course of treatment is mandatory.
Tonsil removal is not performed for acute tonsillitis. It can only happen if the patient has a complication of acute tonsillitis - peritonsillar edema or difficulty breathing due to the significant size of the tonsils.
But there are also contraindications for surgical treatment:
- severe concomitant diseases;
- pregnancy;
- blood diseases with bleeding disorders;
- active tuberculosis.
Traditional medicine
As an auxiliary to the main drug therapy, with the permission of the doctor, traditional medicine can be used. They cannot replace medications prescribed by the doctor, and especially antibiotics, as this will worsen the condition.
Rinsing is a good help to alleviate the patient's condition. For this purpose, decoctions of medicinal herbs such as chamomile, St. John's wort, eucalyptus, and oak bark are used. These plants have anti-inflammatory effects.
In addition to decoctions, a soda-salt solution is used for rinsing. To prepare the product, add a teaspoon of soda and salt and a few drops of iodine to a glass of boiled, cooled water. Treat the throat 3-4 times a day. Salt removes swelling, soda relieves irritation, iodine disinfects.
For purulent tonsillitis, thermal procedures such as steam inhalations and compresses should not be used. Under the influence of heat, bacterial microorganisms increase their growth and reproduction. The process will move into a more complex form.
Traditional medicine.
Complications
Complications of acute tonsillitis are divided into local and general.
Local complications include:
- peritonsillar abscess;
- phlegmon of the neck;
- laryngitis;
- bronchitis;
- otitis.
Common complications include:
- rheumatic damage to the heart, joints;
- glomerulonephritis (kidney inflammation);
- meningitis (inflammation of the membranes of the brain);
- infectious-toxic shock (intoxication with waste products of microorganisms);
- sepsis (bacteria entering the bloodstream and spreading throughout the body).
To prevent the development of complications, timely treatment of acute tonsillitis is necessary.