Breast cancer has been studied for many decades. During this time, leading experts were able to make significant progress in many issues. Rare species were differentiated, which have practically no pronounced clinical picture.
Thanks to the work of oncologists, mammologists, and surgeons, women have a chance to be cured of the disease in the first two stages of its development.
Definition of disease
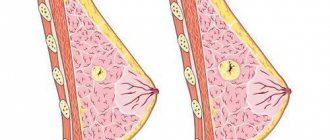
Breast cancer, by all definitions, is a malignant neoplasm, localized specifically in the glandular tissue of the breast. This disease is recognized as very common among women, but the occurrence of the disease in men is not excluded, although only in 1 percent. This type of disease is the second most common among other tumors.
Glandular cancer itself is quite rare, but its subtype, the glandular-squamous form, is very common. This neoplasm consists of 2 components - glandular and squamous epithelial cells. The first is the streaming component, the second is the keratinized component. However, their ratio may be different.
The presence of the second component may explain the lack of a positive reaction to hormones. The need for hormonal treatment can be established by examining the first component of the tumor – the glandular one.
Interesting! This type is not characterized by increased aggressiveness and proceeds calmly. However, in the presence of metaplasia with flat cells, the situation is complicated by the formation of metastases.
By structure
Breast cancer research is carried out by leading experts around the world. This pathology is considered to be the most studied, which makes it possible to successfully combat it, especially in the early stages.
Known types of breast cancer:
- Intraductal - formed in dilated ducts, spreading to branches. Often the pathology is formed from intraductal papilloma. About 30% of patients with this form develop an infiltrating type of malignant process in the mammary gland within 5 years.
- Lobular - the glandular tissue and lobules in which milk should be formed are affected. Occurs in 20% of patients with glandular cancer. The malignant process can spread to the second gland, in which case it is called bilateral cancer.
- Invasive ductal - having formed in the ducts, tumor formation tends to spread beyond their boundaries. It grows into adipose and other tissues, moves with the flow of lymph and blood throughout the body. Malignant particles affect the peripapillary area, deforming it and causing discharge from the nipple. Women over 55 years of age are more often affected.
- Invasive lobular - appears in one lobule of the gland, immediately spreading to other lobules. Occurs in 10-15% of cases of all invasive types of breast cancer. Possible bilateral breast involvement. The pathology is difficult to diagnose because there are no lumps or discharge from the nipples.
- Breast cancer with signs of inflammation – according to clinical manifestations, the malignant process is similar to mastitis. The mammary gland swells, is very painful, there is noticeable redness on it, and the patient’s temperature rises.
The disease is characterized by an acute course. Doctors may confuse tumor formation with mastitis. However, there are a number of differences. This type of cancer occurs in women over 50 years of age; it is not associated with lactation and does not respond to antibiotic treatment. Doctors begin to suspect cancer precisely after an unsuccessful course of antibiotics.
- Tubular carcinoma - malignant particles are formed from the tubules of the epithelial cell layer. The pathology occurs rarely, mainly in women 40-50 years old. The tumor is presented in the form of a star-shaped node, the size of which is 8-40 mm.
- Medullary cancer is extremely rare and is diagnosed only by histological examination. The neoplasm is characterized by rapid growth, but has signs of a benign appearance. It has clear contours and elastic consistency. The formation rarely metastasizes.
- Colloid cancer (mucosal cancer, signet ring cell carcinoma) is a type of mucinous formation characterized by abundant accumulation of mucus inside and outside the cells. The mucous mass has a grayish-blue tint. Malignant particles grow slowly, do not metastasize, and the skin is not affected.
- Papillary cancer - the formation consists of papillary components. The disease is typical for women 64-67 years old. The location of the tumor is the nipple area, which causes discharge. The diameter of the node is usually 20-30 mm; cysts with a bloody substance inside are found in it.
- Metaplastic cancer (squamous cell carcinoma) - tumor formation is rare, more often in women 50-60 years old. It is distinguished by its rather large size and detection in late stages. Malignant particles are very diverse, making the disease difficult to diagnose.
- Cancer with osteoclast-like cells - the neoplasm often develops in the upper outer quadrant of the organ. The node has clear outlines, reddish-brown color, and good density. Diameter about 30 mm.
- Adenoid cystic cancer is extremely rare. The neoplasm is usually 10-30 mm in size and has a grayish-brown tint inside. If the adenoid component is more strongly expressed in the tumor, the prognosis for recovery is higher.
- Secretory carcinoma (juvenile) – tumor-forming particles are distinguished by secretory activity, which is characteristic of pregnancy and lactation. Children and teenagers get sick more often. The prognosis is usually favorable even without radical excision.
- Cystic hypersecretory carcinoma is a neoplasm that was first described about 20 years ago and is a rare form. It is characterized by a size of 10-100 mm, good density, brown color and multiple cysts.
- Apocrine cancer - tumor formation consists of particles with abundant cytoplasm, it is mistakenly confused with sweat gland carcinoma. It has good density, grayish color.
- Cancer with signs of an endocrine neoplasm (primary carcinoid tumor, apudoma) - the neoplasm has clear limitations, its size is 10-50 mm. Sometimes it consists of several nodes.
- Cribose cancer - the tumor node has a developed collagen stroma; under a microscope it resembles a sieve. It is believed that pathology in its pure form has a more favorable prognosis than its mixed form.
What problems are encountered when applying for disability due to breast cancer: cases of refusal. This article lists breast cancer prevention measures.
Here https://stoprak.info/vidy/molochnoj-zhelezy/vazhnye-priznaki-stadii-kotorye-slozhno-zametit.html signs of breast cancer at an early stage are described.
Most types of breast cancer are rare. Some of them have no special features and are differentiated only through histological analysis. It is carried out after complete removal of the tumor formation or as a result of a biopsy.
What is the danger
One of the most important characteristics that can be used to describe this type of breast cancer is its low degree of malignancy. Describing diseases in medical terms, we can say that the tumor is called infiltrating syringomatoid adenoma. It is precisely this type of formation that many scientists do not characterize as oncology. Its formation is attributed to relapses, and the formation of metastases is excluded.
However, there are also cases of the formation of malignant tumors, the appearance of which can be caused by a number of reasons:
- premature start of puberty;
- genetic predisposition;
- late menopause;
- obesity and overeating;
- age over 35 years;
- the impact of poor ecology;
- alcoholism, smoking and other bad habits.
Based on the size of the tumor and the speed of its spread, five stages of the malignant process are distinguished - from stage 0 to stage 4.
Signs that are used in classification
The classification of this disease is based on its specific symptoms and is based on:
- a sign of maturity of cells that have passed the mutation stage;
- a sign of the involvement of mutated cells in tumor growth;
- sign of tumor dislocation;
- a sign of tumor size;
- a sign of predisposition to metastases.
Symptomatic manifestations
For this type of tumor there are also the most characteristic signs and symptoms, which primarily include:
- growth of lymph nodes in the armpit area;
- lumps, thickening, and hardness in the breasts;
- discharge from the nipple, which is bloody and transparent-mucous in nature;
- the appearance of changes in the shape and color of the nipple and areola;
- the appearance of ulcers.
Important! If any of the above signs are detected, immediate consultation with a specialist doctor is necessary, who, if necessary, will refer you to the necessary diagnostics and tests.
Since the early stages of the disease are not characterized by the presence of any symptoms, it is very important to follow a regime of visiting a specialized doctor - a mammologist. And this must be done at least once a year. The regularity of such visits also plays an extremely important role, since each woman’s body is very individual, and it is very difficult to determine from the first time what is normal and what is a disease. It is early detection of the presence of malignant tumors that can save lives.
International classification TNM
The international TNM system was formulated by the French oncologist Pierre Denoit in the 50s of the previous century. Subsequent development was carried out by the Committee on Tumor Nomenclature, based on extensive statistical data on cases of malignant tumors in the breast.
The letters in the abbreviation correspond to the Latin terms “tumor” - tumor, “nodus” - lymph node and “metastasis” - metastasis.
This type of classification is the most reliable and verified. He clearly describes the types of breast cancer, based on the fundamental signs of this disease:
- Localization of the tumor.
- Size of the tumor.
- The volume of regional metastases in case of damage to the lymphatic system.
- The presence of metastases affecting organs and tissues located remotely from the original location of the tumor.
- Stages of tumor development, calculated by the correlation between tumor size and metastasis volumes.
- The type of cells from which the tumor grew.
- Establishing cellular differentiation level of histopathology.
- Cellular expression, which determines the nature of the tumor according to its characteristic receptors, which are localized on mutated cells.
By location
Based on the location of the tumor, they are classified into:
- areolar tumor located in the area of the nipple or its areola;
- upper-outer, affecting other parts of the mammary gland.
Upper external tumors are the most widespread.
According to the initial size of the tumor
The classification of this disease is based on three indicators of breast cancer TN M. The letter T represents the characteristics of the original tumor and its indicators.
Classification based on the parameter of the size of the initial tumor distinguishes the following cases:
- Tx – inability to estimate the size of the initial tumor;
- T0 – lack of primary education;
- Тis – cancer in situ, that is, not spreading to other organs;
- Тis (DCIS) – ductal carcinoma in situ, that is, localized in the ducts and not spreading to other tissues;
- Tis (LCIS) – lobular cancer in situ, that is, located in the lobules of the gland and does not affect other areas;
- Тis (Paget) – Paget's cancer, affecting the nipple;
- T1 – tumor less than 2 cm;
- T1mic – microinvasive cancer, that is, little spreading to neighboring organs;
- T1a – tumor up to 0.5 cm in size;
- T1b – tumor up to 1 cm in size;
- T1c – tumor up to 2 cm;
- T2 – tumor up to 5 cm;
- TZ – tumor more than 5 cm;
- T4 – tumor spreading to the skin or sternum;
- T4a – tumor invades the thoracic septum;
- T4b – tumor includes swelling, as well as metastases spreading to the skin of the breast;
- T4c – characteristics T4a and T4b are present;
- T4d is an erysipelas form of cancer, breast inflammation similar to mastitis.
By degree of metastasis
Types of breast cancer in women, determined by the degree of spread and development of metastases in local lymph nodes, as well as their nature and location, are coded with the letter N.
Degrees of metastasis, according to this classification:
- Nx – the degree of lymph node damage is not determined;
- N0 – no signs of lymph node involvement;
- N1 – metastases are observed in axillary nodes that have not lost mobility;
- N2 – metastases have spread to the axillary lymph nodes, and they have lost mobility;
- N2a - metastases are widespread in the ipsilateral, that is, supraclavicular, lymph nodes;
- N3 – metastases are located in the supraclavicular lymph nodes, distributed in the axillary region;
- N3a – metastases are located in the subclavian lymph nodes;
- N3b – metastases are distributed throughout the lymph nodes of the gland;
- N3c – metastases only in the supraclavicular lymph nodes.
The presence of distant metastases affecting organs and systems is coded by the letter M and is determined by the following parameters:
- Mx - there is no way to determine the distance of metastases;
- MO – no distant metastasis;
- M. – distant metastases are observed in various organs.
The main causes of breast cancer, which can trigger the appearance of this pathology
It is generally accepted that women whose age ranges from 40 years and above are most likely to develop breast cancer. However, according to statistical data, today this disease is beginning to appear in younger women, whose age does not reach 40 years.
What causes breast cancer? The reasons that provoke the appearance and development of breast cancer have not been fully established to date. However, most oncologists believe that the following factors can provoke the appearance of this pathology:
- poor environmental condition;
- frequent and severe stress;
- consumption of low-quality food, as well as alcohol and tobacco;
- the appearance of too early menstruation cycles in a woman (at 9-10 years of age);
- presence of hypertension;
- mastopathy;
- obesity.
In addition, women who gave birth for the first time at the age of 35 years or later are at risk. Women who have never given birth at all and people diagnosed with diabetes are also predisposed to breast cancer.
Various external mechanical influences or damage to the mammary gland can also provoke the appearance of a tumor in the breast area. For example, when playing sports, a woman needs to be careful and protect her breasts from strong impacts or any mechanical damage. After all, even a seemingly insignificant chest injury received in the gym after a few years can become the main cause of oncology.
Depending on the histological structure
Based on the histological structure, the disease is divided into a number of types.
Non-invasive appearance
Non-invasive cancer usually does not spread to other tissues or organs. It, in turn, is divided into subspecies:
- lobular cancer, difficult to diagnose due to the small number of malignant cells;
- ductal cancer, clearly manifesting itself due to discharge from the breast.
Invasive species
This is a species that has the peculiarity of affecting other organs and tissues. When this type of tumor is removed, relapses occur quite often.
Symptoms of breast cancer
- The presence of “lumps” or compaction in the chest area;
- Specific discharge not related to lactation;
- You may find that the nipple has sunk inward;
- Back pain, heaviness;
- Breast asymmetry that you have not noticed before;
- The skin of the breast may wrinkle, crack, or peel;
- When you raise your hand, you will notice depressions in small areas of the mammary glands;
- Swelling of the bust;
- Itching of the nipples or the breast itself;
- Progressive weight loss;
- Increase in local and general temperature;
- Pain when touched.
These 12 cancer symptoms will help you identify breast cancer. If you detect any sign, be sure to contact a mammologist or oncologist.
Classification into subtypes for treatment purposes
To determine the type of therapy needed for each specific case of the disease, a classification into subtypes is used.
There are a number of subtypes of the disease and methods of treating them:
- subtype luminal A , in which endocrine therapy is most often used;
- subtype luminal B , in which endocrine therapy and cytotoxic therapy are used both in combination and separately;
- a subtype of basal-like cancer that is curable with cytotoxic chemotherapy;
- super-progressive subtype, against which cytotoxic therapy is indicated.
Breast cancer, of course, is a very serious and dangerous disease. But modern medicine makes it possible in some cases to cure even its most severe form. In order to maintain health and longevity, it is important not to neglect preventive examinations, and, if necessary, treatment.
Treatment options
If surgery is not permissible, drug treatment, including chemotherapy, is used.
Therapy is carried out immediately after diagnosis: the sooner treatment is carried out, the greater the woman’s chances of survival. The therapeutic regimen depends on the stage, nature and type of disease. In most cases, complex therapy is prescribed using surgery to remove the tumor. But there are also contraindications to the use of surgery. Alternative methods include the use of chemotherapy or conservative treatment based on hormonal drugs.
Medicines
The drug regimen is prescribed after diagnosis, during which the sensitivity of cancer cells is determined. They play the role of antagonists and cause the death of harmful elements. Other groups of drugs do not show any effect. When choosing a drug, they are guided by the patient’s age, so middle-aged women and women after menopause are prescribed different drugs. Tamoxifen, Aminoglutethimide, and Leuprolide are considered universal.
Drug treatment also includes chemotherapy. This is one of the most effective methods of fighting cancer. Therapy involves the administration of drugs intravenously that kill cells. But along with the cancer agents, the living also die, so chemistry is characterized by a large number of side effects. The drugs Alkeran and Methotrexate are used.
Traditional surgery
Depending on the degree of tumor growth, the doctor chooses an intervention method, one of which is mastectomy.
The cardinal method is surgical. It involves removing the tumor from the body. This method is advisable to use in the first stages, when there are no metastases. Radiation therapy is often given before surgery. This method helps to first reduce the cancerous formation, then cut it out. The main surgical techniques for this diagnosis are:
- Lumpectomy - excision of the tumor within its limits.
- Mastectomy - removal of the breast.
ethnoscience
Non-traditional treatment methods are powerless in the fight against cancer. However, they are used in combination with other drugs as supportive or for prevention. To treat the mammary glands, watermelon roots, bedstraw, oregano herb, and swamp grass are used. Such remedies help relieve inflammation and improve the condition of the breast, but will not get rid of cancer.